The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)
What's that sail for? Generally, I don't know. So I've come up with a system. I'll explain you everything there is to know about sails and rigs in this article.
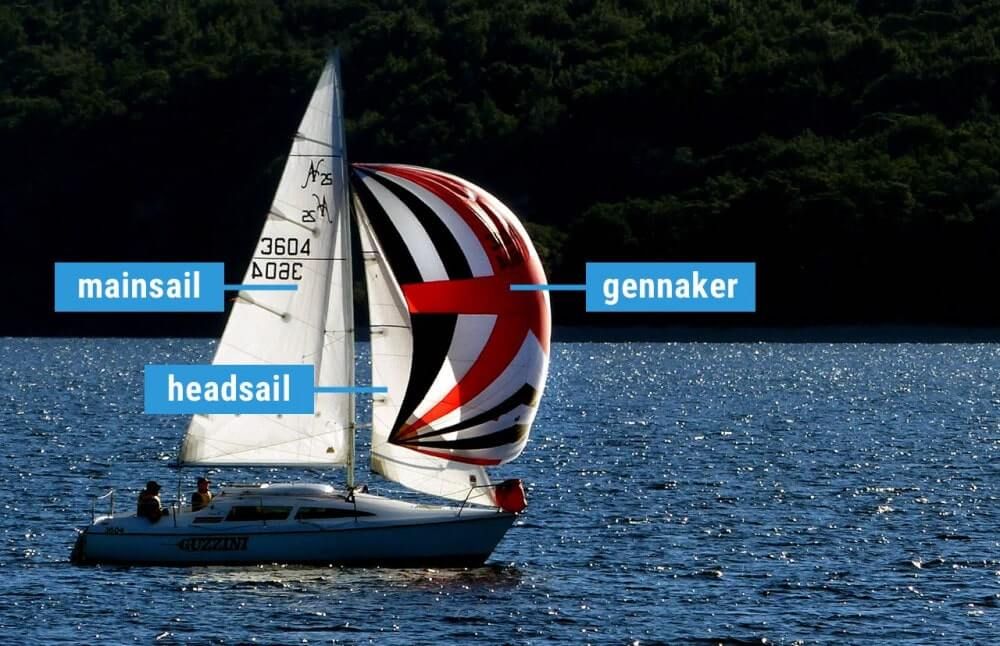
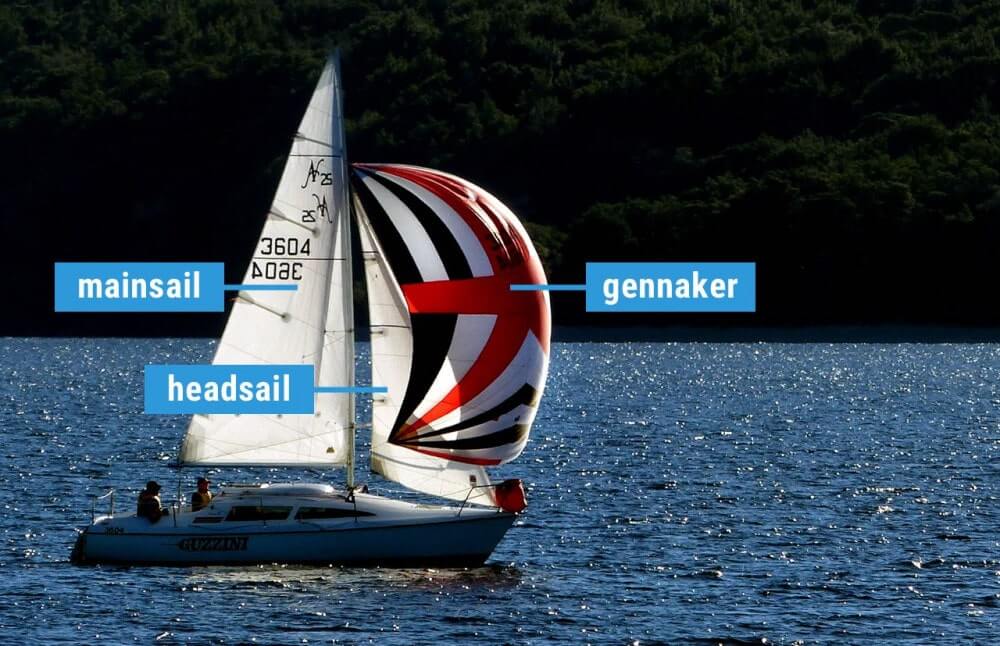
What are the different types of sails? Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. Typically, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft bermuda rig (triangular shaped). A jib or genoa is used for the headsail. Most sailors use additional sails for different conditions: the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), gennaker, code zero (for upwind use), and stormsail.
Each sail has its own use. Want to go downwind fast? Use a spinnaker. But you can't just raise any sail and go for it. It's important to understand when (and how) to use each sail. Your rigging also impacts what sails you can use.


On this page:
Different sail types, the sail plan of a bermuda sloop, mainsail designs, headsail options, specialty sails, complete overview of sail uses, mast configurations and rig types.
This article is part 1 of my series on sails and rig types. Part 2 is all about the different types of rigging. If you want to learn to identify every boat you see quickly, make sure to read it. It really explains the different sail plans and types of rigging clearly.

Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types (with Pictures)
First I'll give you a quick and dirty overview of sails in this list below. Then, I'll walk you through the details of each sail type, and the sail plan, which is the godfather of sail type selection so to speak.
Click here if you just want to scroll through a bunch of pictures .
Here's a list of different models of sails: (Don't worry if you don't yet understand some of the words, I'll explain all of them in a bit)
- Jib - triangular staysail
- Genoa - large jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Spinnaker - large balloon-shaped downwind sail for light airs
- Gennaker - crossover between a Genoa and Spinnaker
- Code Zero or Screecher - upwind spinnaker
- Drifter or reacher - a large, powerful, hanked on genoa, but made from lightweight fabric
- Windseeker - tall, narrow, high-clewed, and lightweight jib
- Trysail - smaller front-and-aft mainsail for heavy weather
- Storm jib - small jib for heavy weather
I have a big table below that explains the sail types and uses in detail .
I know, I know ... this list is kind of messy, so to understand each sail, let's place them in a system.
The first important distinction between sail types is the placement . The mainsail is placed aft of the mast, which simply means behind. The headsail is in front of the mast.
Generally, we have three sorts of sails on our boat:
- Mainsail: The large sail behind the mast which is attached to the mast and boom
- Headsail: The small sail in front of the mast, attached to the mast and forestay (ie. jib or genoa)
- Specialty sails: Any special utility sails, like spinnakers - large, balloon-shaped sails for downwind use
The second important distinction we need to make is the functionality . Specialty sails (just a name I came up with) each have different functionalities and are used for very specific conditions. So they're not always up, but most sailors carry one or more of these sails.
They are mostly attached in front of the headsail, or used as a headsail replacement.
The specialty sails can be divided into three different categories:
- downwind sails - like a spinnaker
- light air or reacher sails - like a code zero
- storm sails

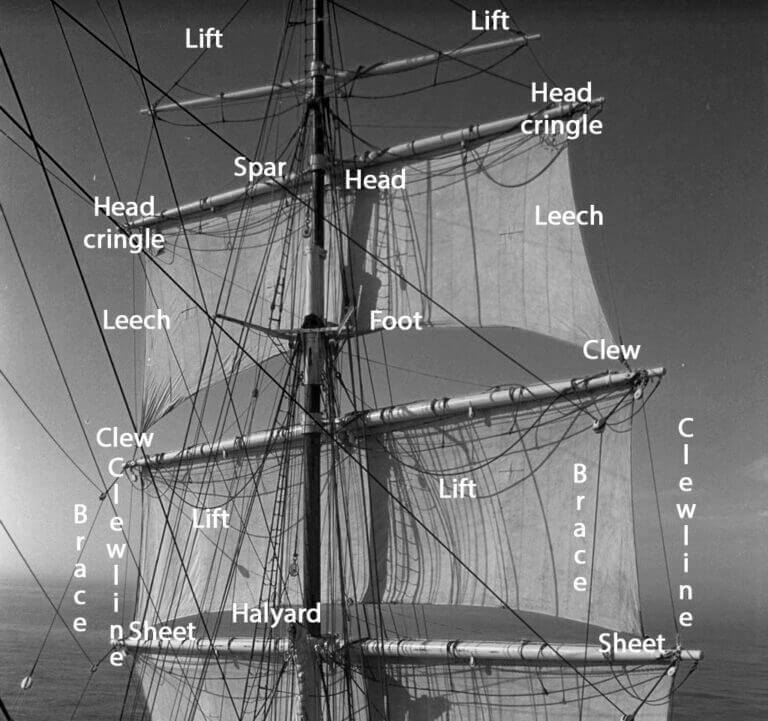
The parts of any sail
Whether large or small, each sail consists roughly of the same elements. For clarity's sake I've took an image of a sail from the world wide webs and added the different part names to it:

- Head: Top of the sail
- Tack: Lower front corner of the sail
- Foot: Bottom of the sail
- Luff: Forward edge of the sail
- Leech: Back edge of the sail
- Clew: Bottom back corner of the sail
So now we speak the same language, let's dive into the real nitty gritty.
Basic sail shapes
Roughly speaking, there are actually just two sail shapes, so that's easy enough. You get to choose from:
- square rigged sails
- fore-and-aft rigged sails
I would definitely recommend fore-and-aft rigged sails. Square shaped sails are pretty outdated. The fore-and-aft rig offers unbeatable maneuverability, so that's what most sailing yachts use nowadays.

Square sails were used on Viking longships and are good at sailing downwind. They run from side to side. However, they're pretty useless upwind.
A fore-and-aft sail runs from the front of the mast to the stern. Fore-and-aft literally means 'in front and behind'. Boats with fore-and-aft rigged sails are better at sailing upwind and maneuvering in general. This type of sail was first used on Arabic boats.
As a beginner sailor I confuse the type of sail with rigging all the time. But I should cut myself some slack, because the rigging and sails on a boat are very closely related. They are all part of the sail plan .
A sail plan is made up of:
- Mast configuration - refers to the number of masts and where they are placed
- Sail type - refers to the sail shape and functionality
- Rig type - refers to the way these sails are set up on your boat
There are dozens of sails and hundreds of possible configurations (or sail plans).
For example, depending on your mast configuration, you can have extra headsails (which then are called staysails).
The shape of the sails depends on the rigging, so they overlap a bit. To keep it simple I'll first go over the different sail types based on the most common rig. I'll go over the other rig types later in the article.
Bermuda Sloop: the most common rig
Most modern small and mid-sized sailboats have a Bermuda sloop configuration . The sloop is one-masted and has two sails, which are front-and-aft rigged. This type of rig is also called a Marconi Rig. The Bermuda rig uses a triangular sail, with just one side of the sail attached to the mast.
The mainsail is in use most of the time. It can be reefed down, making it smaller depending on the wind conditions. It can be reefed down completely, which is more common in heavy weather. (If you didn't know already: reefing is skipper terms for rolling or folding down a sail.)
In very strong winds (above 30 knots), most sailors only use the headsail or switch to a trysail.

The headsail powers your bow, the mainsail powers your stern (rear). By having two sails, you can steer by using only your sails (in theory - it requires experience). In any case, two sails gives you better handling than one, but is still easy to operate.
Let's get to the actual sails. The mainsail is attached behind the mast and to the boom, running to the stern. There are multiple designs, but they actually don't differ that much. So the following list is a bit boring. Feel free to skip it or quickly glance over it.
- Square Top racing mainsail - has a high performance profile thanks to the square top, optional reef points
- Racing mainsail - made for speed, optional reef points
- Cruising mainsail - low-maintenance, easy to use, made to last. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- Full-Batten Cruising mainsail - cruising mainsail with better shape control. Eliminates flogging. Full-length battens means the sail is reinforced over the entire length. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- High Roach mainsail - crossover between square top racing and cruising mainsail, used mostly on cats and multihulls. Generally have one or multiple reef points.
- Mast Furling mainsail - sails specially made to roll up inside the mast - very convenient but less control; of sail shape. Have no reef points
- Boom Furling mainsail - sails specially made to roll up inside the boom. Have no reef points.
The headsail is the front sail in a front-and-aft rig. The sail is fixed on a stay (rope, wire or rod) which runs forward to the deck or bowsprit. It's almost always triangular (Dutch fishermen are known to use rectangular headsail). A triangular headsail is also called a jib .
Headsails can be attached in two ways:
- using roller furlings - the sail rolls around the headstay
- hank on - fixed attachment
Types of jibs:
Typically a sloop carries a regular jib as its headsail. It can also use a genoa.
- A jib is a triangular staysail set in front of the mast. It's the same size as the fore-triangle.
- A genoa is a large jib that overlaps the mainsail.
What's the purpose of a jib sail? A jib is used to improve handling and to increase sail area on a sailboat. This helps to increase speed. The jib gives control over the bow (front) of the ship, making it easier to maneuver the ship. The mainsail gives control over the stern of the ship. The jib is the headsail (frontsail) on a front-and-aft rig.
The size of the jib is generally indicated by a number - J1, 2, 3, and so on. The number tells us the attachment point. The order of attachment points may differ per sailmaker, so sometimes J1 is the largest jib (on the longest stay) and sometimes it's the smallest (on the shortest stay). Typically the J1 jib is the largest - and the J3 jib the smallest.
Most jibs are roller furling jibs: this means they are attached to a stay and can be reefed down single-handedly. If you have a roller furling you can reef down the jib to all three positions and don't need to carry different sizes.

Originally called the 'overlapping jib', the leech of the genoa extends aft of the mast. This increases speed in light and moderate winds. A genoa is larger than the total size of the fore-triangle. How large exactly is indicated by a percentage.
- A number 1 genoa is typically 155% (it used to be 180%)
- A number 2 genoa is typically 125-140%
Genoas are typically made from 1.5US/oz polyester spinnaker cloth, or very light laminate.

This is where it gets pretty interesting. You can use all kinds of sails to increase speed, handling, and performance for different weather conditions.
Some rules of thumb:
- Large sails are typically good for downwind use, small sails are good for upwind use.
- Large sails are good for weak winds (light air), small sails are good for strong winds (storms).
Downwind sails
Thanks to the front-and-aft rig sailboats are easier to maneuver, but they catch less wind as well. Downwind sails are used to offset this by using a large sail surface, pulling a sailboat downwind. They can be hanked on when needed and are typically balloon shaped.
Here are the most common downwind sails:
- Big gennaker
- Small gennaker
A free-flying sail that fills up with air, giving it a balloon shape. Spinnakers are generally colorful, which is why they look like kites. This downwind sail has the largest sail area, and it's capable of moving a boat with very light wind. They are amazing to use on trade wind routes, where they can help you make quick progress.
Spinnakers require special rigging. You need a special pole and track on your mast. You attach the sail at three points: in the mast head using a halyard, on a pole, and on a sheet.
The spinnaker is symmetrical, meaning the luff is as long as its leech. It's designed for broad reaching.

Gennaker or cruising spinnaker
The Gennaker is a cross between the genoa and the spinnaker. It has less downwind performance than the spinnaker. It is a bit smaller, making it slower, but also easier to handle - while it remains very capable. The cruising spinnaker is designed for broad reaching.
The gennaker is a smaller, asymmetric spinnaker that's doesn't require a pole or track on the mast. Like the spinnaker, and unlike the genoa, the gennaker is set flying. Asymmetric means its luff is longer than its leech.
You can get big and small gennakers (roughly 75% and 50% the size of a true spinnaker).
Also called ...
- the cruising spinnaker
- cruising chute
- pole-less spinnaker
- SpinDrifter
... it's all the same sail.

Light air sails
There's a bit of overlap between the downwind sails and light air sails. Downwind sails can be used as light air sails, but not all light air sails can be used downwind.
Here are the most common light air sails:
- Spinnaker and gennaker
Drifter reacher
Code zero reacher.
A drifter (also called a reacher) is a lightweight, larger genoa for use in light winds. It's roughly 150-170% the size of a genoa. It's made from very lightweight laminated spinnaker fabric (1.5US/oz).
Thanks to the extra sail area the sail offers better downwind performance than a genoa. It's generally made from lightweight nylon. Thanks to it's genoa characteristics the sail is easier to use than a cruising spinnaker.
The code zero reacher is officially a type of spinnaker, but it looks a lot like a large genoa. And that's exactly what it is: a hybrid cross between the genoa and the asymmetrical spinnaker (gennaker). The code zero however is designed for close reaching, making it much flatter than the spinnaker. It's about twice the size of a non-overlapping jib.

A windseeker is a small, free-flying staysail for super light air. It's tall and thin. It's freestanding, so it's not attached to the headstay. The tack attaches to a deck pad-eye. Use your spinnakers' halyard to raise it and tension the luff.
It's made from nylon or polyester spinnaker cloth (0.75 to 1.5US/oz).
It's designed to guide light air onto the lee side of the main sail, ensuring a more even, smooth flow of air.
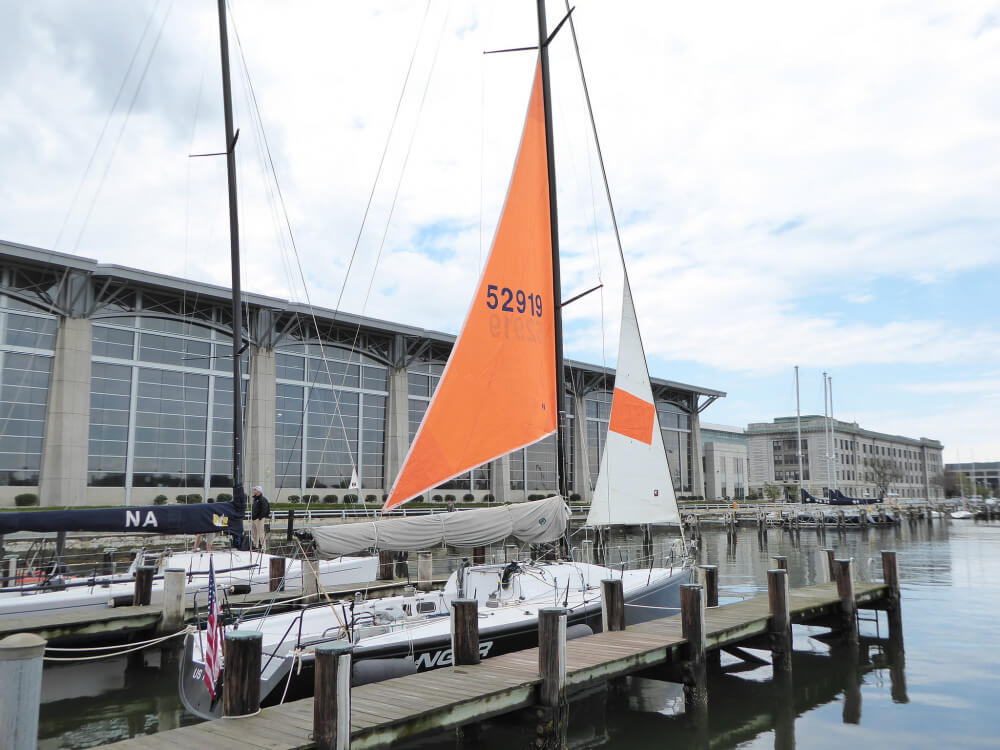
Stormsails are stronger than regular sails, and are designed to handle winds of over 45 knots. You carry them to spare the mainsail. Sails
A storm jib is a small triangular staysail for use in heavy weather. If you participate in offshore racing you need a mandatory orange storm jib. It's part of ISAF's requirements.
A trysail is a storm replacement for the mainsail. It's small, triangular, and it uses a permanently attached pennant. This allows it to be set above the gooseneck. It's recommended to have a separate track on your mast for it - you don't want to fiddle around when you actually really need it to be raised ... now.

Why Use Different Sails At All?
You could just get the largest furling genoa and use it on all positions. So why would you actually use different types of sails?
The main answer to that is efficiency . Some situations require other characteristics.
Having a deeply reefed genoa isn't as efficient as having a small J3. The reef creates too much draft in the sail, which increases heeling. A reefed down mainsail in strong winds also increases heeling. So having dedicated (storm) sails is probably a good thing, especially if you're planning more demanding passages or crossings.
But it's not just strong winds, but also light winds that can cause problems. Heavy sails will just flap around like laundry in very light air. So you need more lightweight fabrics to get you moving.
What Are Sails Made Of?
The most used materials for sails nowadays are:
- Dacron - woven polyester
- woven nylon
- laminated fabrics - increasingly popular
Sails used to be made of linen. As you can imagine, this is terrible material on open seas. Sails were rotting due to UV and saltwater. In the 19th century linen was replaced by cotton.
It was only in the 20th century that sails were made from synthetic fibers, which were much stronger and durable. Up until the 1980s most sails were made from Dacron. Nowadays, laminates using yellow aramids, Black Technora, carbon fiber and Spectra yarns are more and more used.
Laminates are as strong as Dacron, but a lot lighter - which matters with sails weighing up to 100 kg (220 pounds).
By the way: we think that Viking sails were made from wool and leather, which is quite impressive if you ask me.
In this section of the article I give you a quick and dirty summary of different sail plans or rig types which will help you to identify boats quickly. But if you want to really understand it clearly, I really recommend you read part 2 of this series, which is all about different rig types.
You can't simply count the number of masts to identify rig type But you can identify any rig type if you know what to look for. We've created an entire system for recognizing rig types. Let us walk you through it. Read all about sail rig types
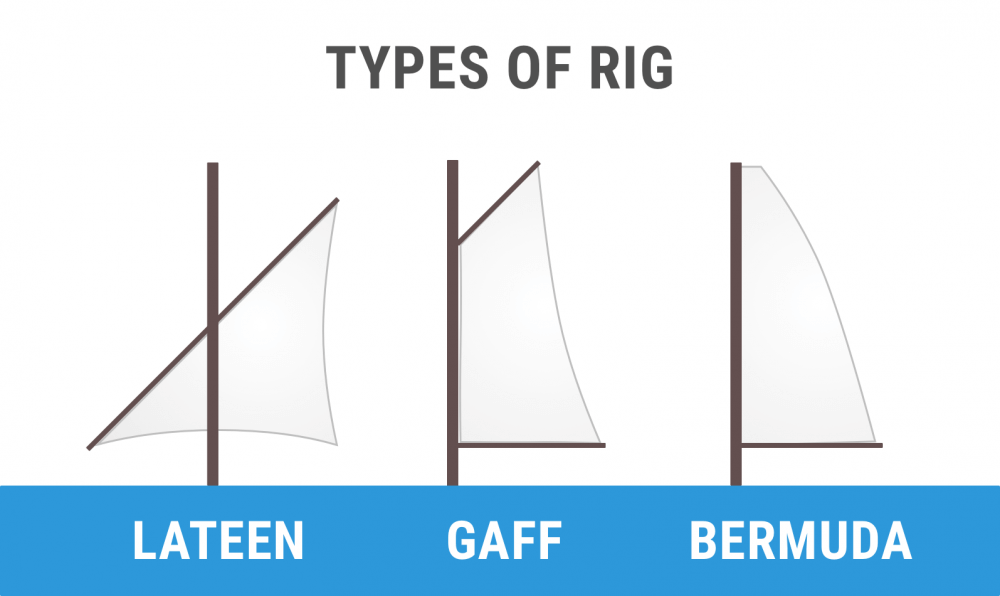
As I've said earlier, there are two major rig types: square rigged and fore-and-aft. We can divide the fore-and-aft rigs into three groups:
- Bermuda rig (we have talked about this one the whole time) - has a three-sided mainsail
- Gaff rig - has a four-sided mainsail, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff
- Lateen rig - has a three-sided mainsail on a long yard
There are roughly four types of boats:
- one masted boats - sloop, cutter
- two masted boats - ketch, schooner, brig
- three masted - barque
- fully rigged or ship rigged - tall ship
Everything with four masts is called a (tall) ship. I think it's outside the scope of this article, but I have written a comprehensive guide to rigging. I'll leave the three and four-masted rigs for now. If you want to know more, I encourage you to read part 2 of this series.
One-masted rigs
Boats with one mast can have either one sail, two sails, or three or more sails.
The 3 most common one-masted rigs are:
- Cat - one mast, one sail
- Sloop - one mast, two sails
- Cutter - one mast, three or more sails
1. Gaff Cat
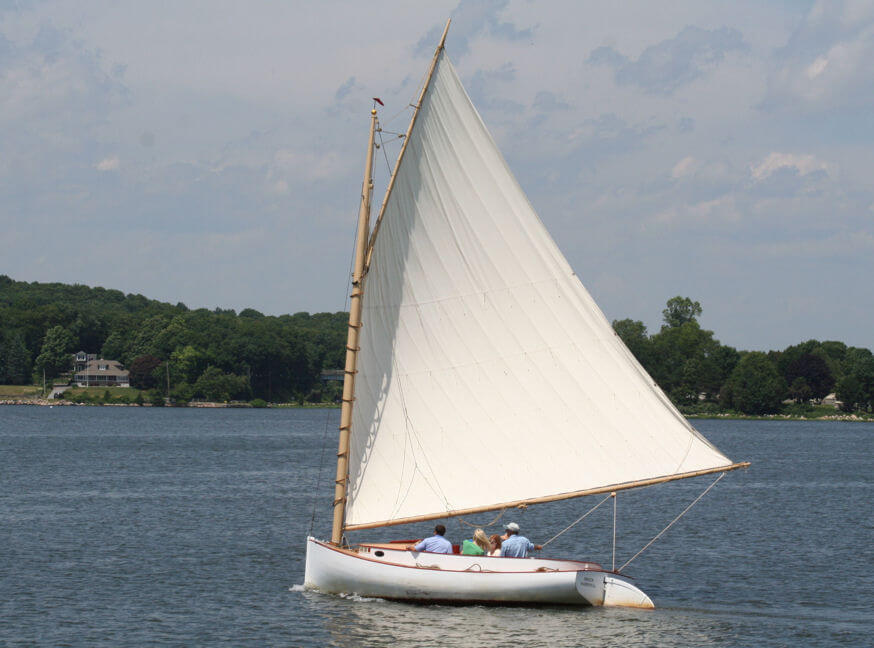

2. Gaff Sloop
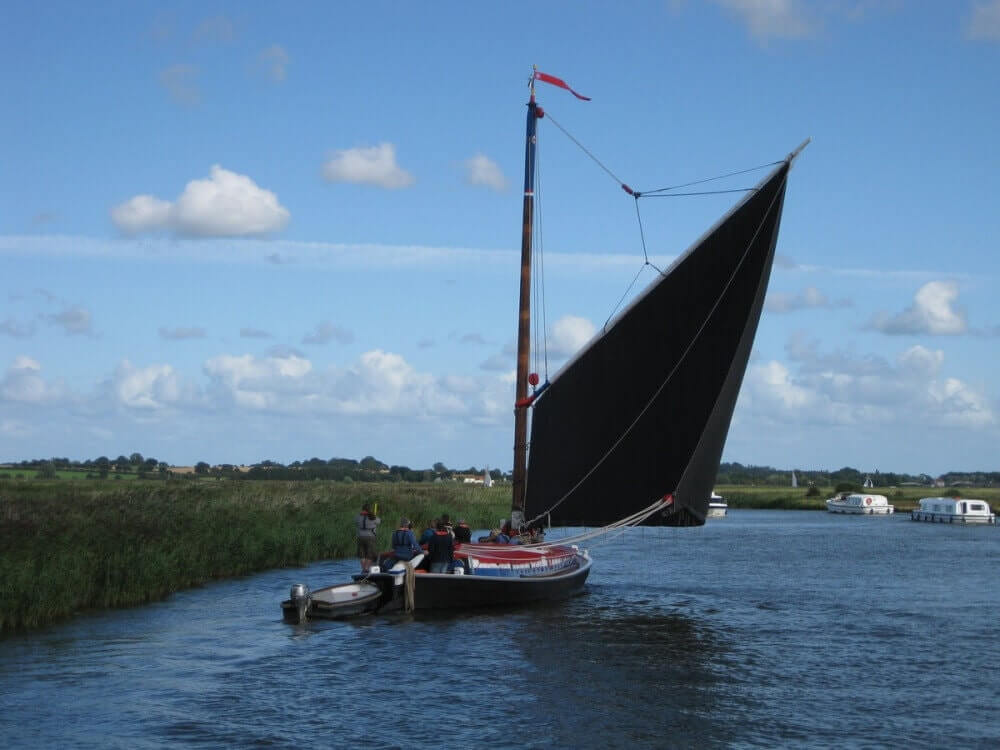

Two-masted rigs
Two-masted boats can have an extra mast in front or behind the main mast. Behind (aft of) the main mast is called a mizzen mast . In front of the main mast is called a foremast .
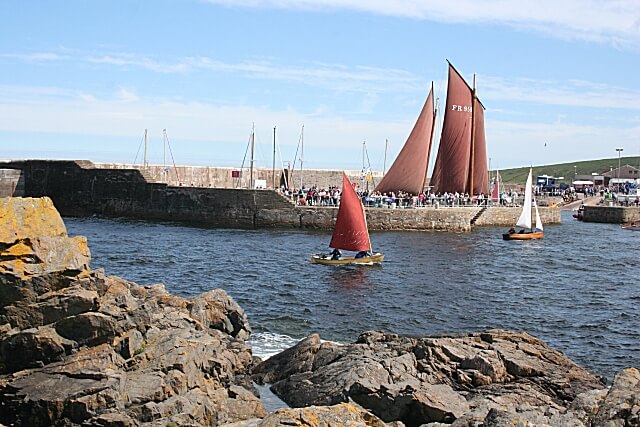
The 5 most common two-masted rigs are:
- Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts
- Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without mainsail.
- Ketch - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller mizzen. Mizzen has mainsail.
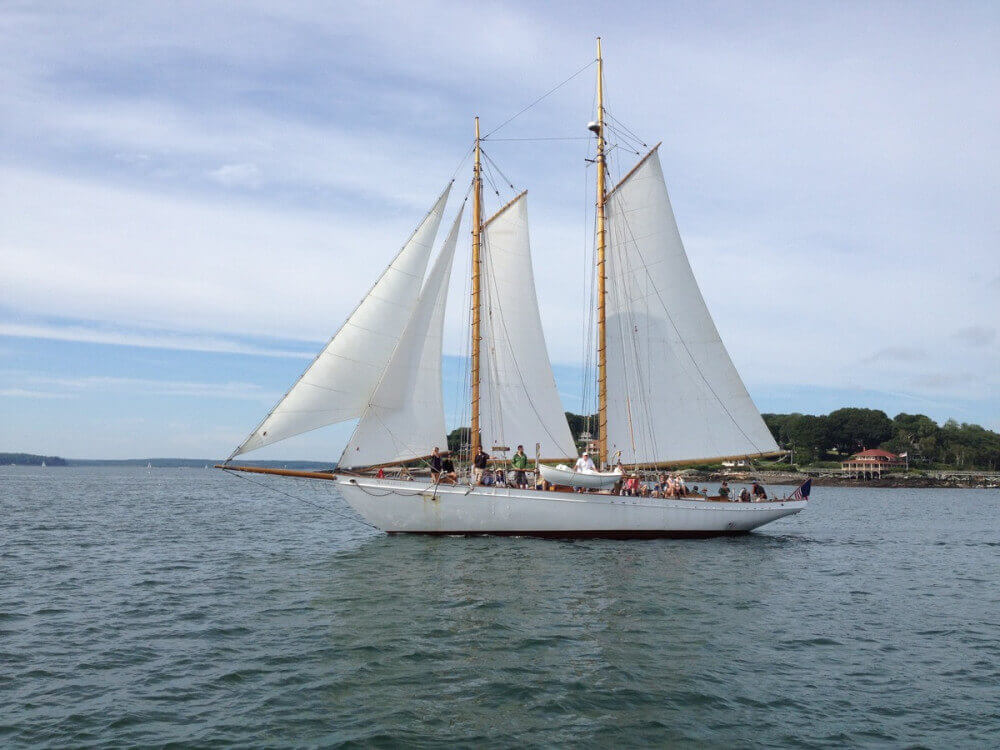
- Schooner - two masts (foremast), generally gaff rig on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller foremast. Sometimes build with three masts, up to seven in the age of sail.
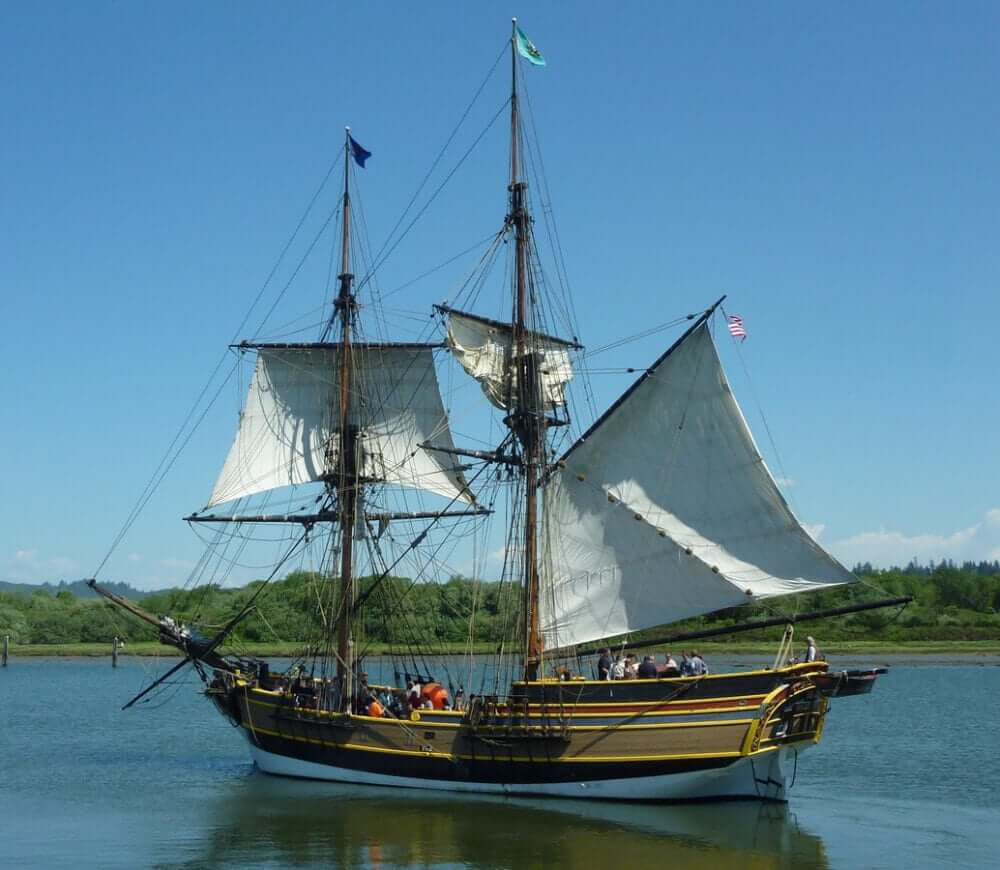
- Brig - two masts (foremast), partially square-rigged. Main mast carries small lateen rigged sail.

4. Schooner

5. Brigantine

This article is part 1 of a series about sails and rig types If you want to read on and learn to identify any sail plans and rig type, we've found a series of questions that will help you do that quickly. Read all about recognizing rig types
Related Questions
What is the difference between a gennaker & spinnaker? Typically, a gennaker is smaller than a spinnaker. Unlike a spinnaker, a gennaker isn't symmetric. It's asymmetric like a genoa. It is however rigged like a spinnaker; it's not attached to the forestay (like a jib or a genoa). It's a downwind sail, and a cross between the genoa and the spinnaker (hence the name).
What is a Yankee sail? A Yankee sail is a jib with a high-cut clew of about 3' above the boom. A higher-clewed jib is good for reaching and is better in high waves, preventing the waves crash into the jibs foot. Yankee jibs are mostly used on traditional sailboats.
How much does a sail weigh? Sails weigh anywhere between 4.5-155 lbs (2-70 kg). The reason is that weight goes up exponentially with size. Small boats carry smaller sails (100 sq. ft.) made from thinner cloth (3.5 oz). Large racing yachts can carry sails of up to 400 sq. ft., made from heavy fabric (14 oz), totaling at 155 lbs (70 kg).
What's the difference between a headsail and a staysail? The headsail is the most forward of the staysails. A boat can only have one headsail, but it can have multiple staysails. Every staysail is attached to a forward running stay. However, not every staysail is located at the bow. A stay can run from the mizzen mast to the main mast as well.
What is a mizzenmast? A mizzenmast is the mast aft of the main mast (behind; at the stern) in a two or three-masted sailing rig. The mizzenmast is shorter than the main mast. It may carry a mainsail, for example with a ketch or lugger. It sometimes doesn't carry a mainsail, for example with a yawl, allowing it to be much shorter.
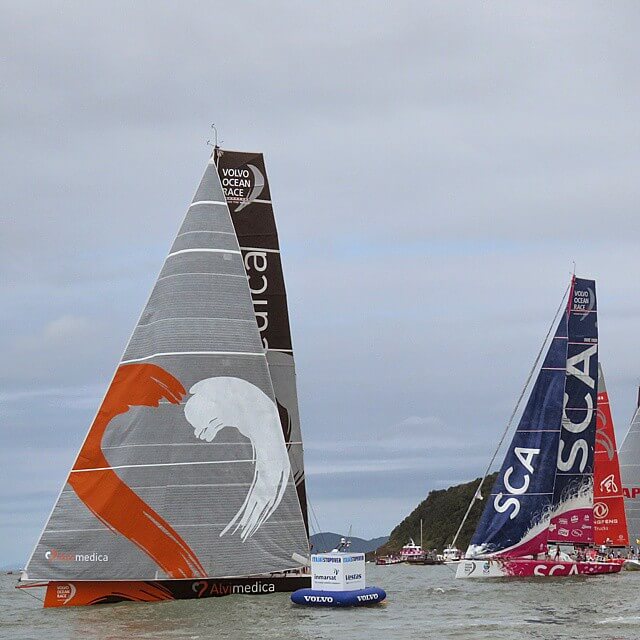
Special thanks to the following people for letting me use their quality photos: Bill Abbott - True Spinnaker with pole - CC BY-SA 2.0 lotsemann - Volvo Ocean Race Alvimedica and the Code Zero versus SCA and the J1 - CC BY-SA 2.0 Lisa Bat - US Naval Academy Trysail and Storm Jib dry fit - CC BY-SA 2.0 Mike Powell - White gaff cat - CC BY-SA 2.0 Anne Burgess - Lugger The Reaper at Scottish Traditional Boat Festival
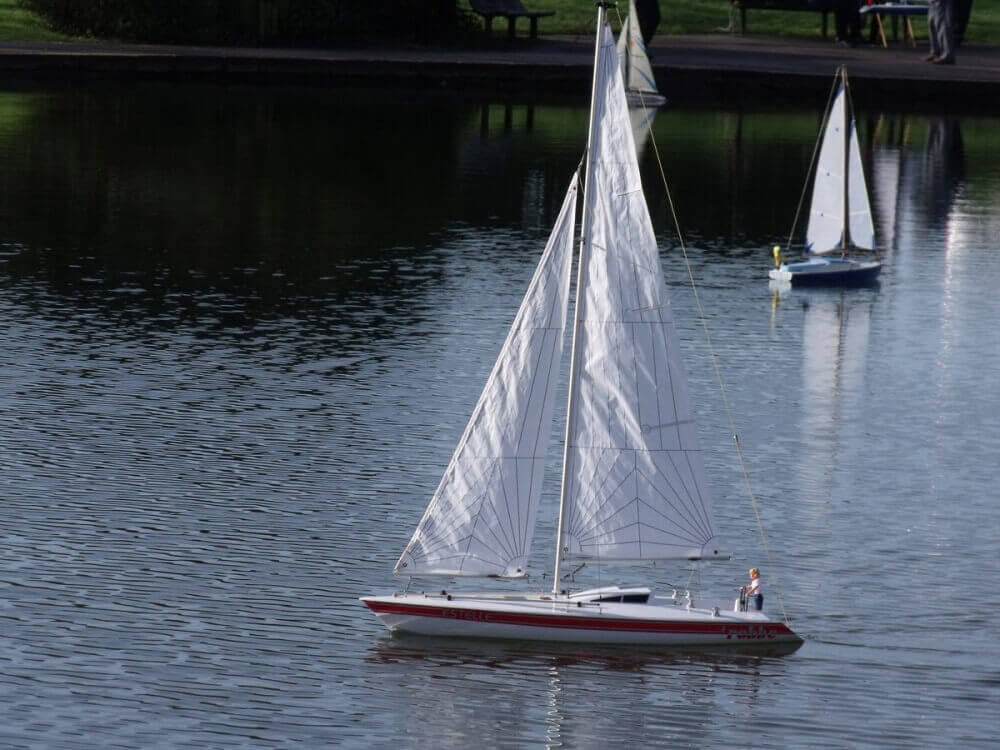
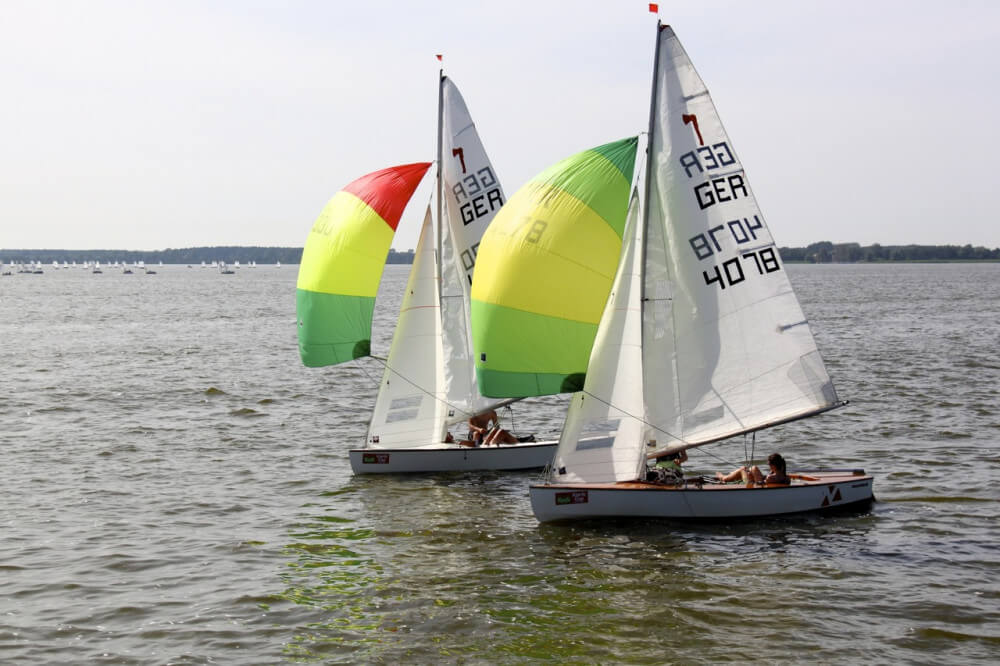
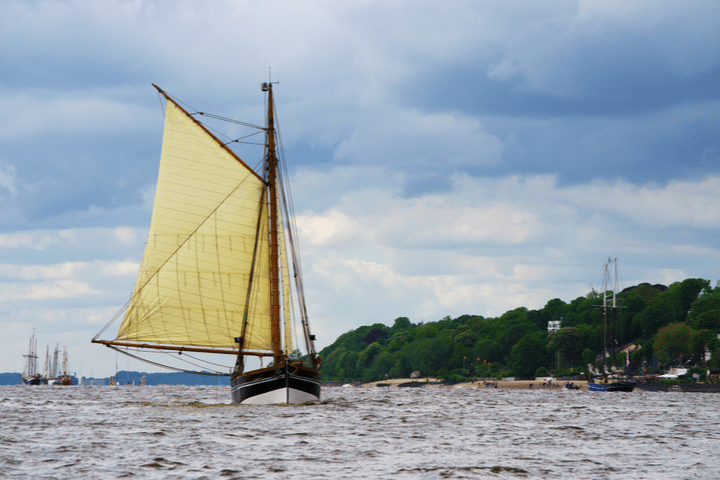
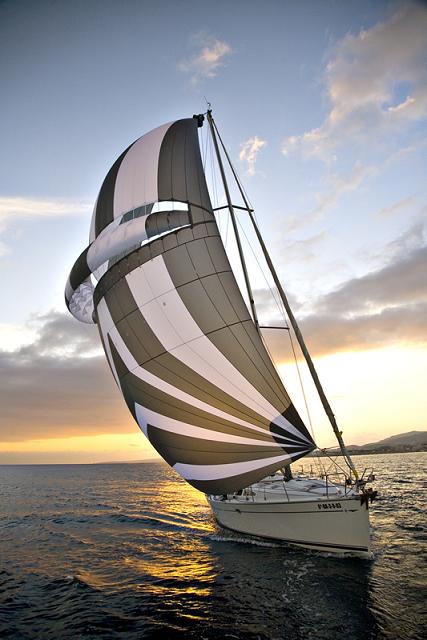
Hi, I stumbled upon your page and couldn’t help but notice some mistakes in your description of spinnakers and gennakers. First of all, in the main photo on top of this page the small yacht is sailing a spinnaker, not a gennaker. If you look closely you can see the spinnaker pole standing on the mast, visible between the main and headsail. Further down, the discription of the picture with the two German dinghies is incorrect. They are sailing spinnakers, on a spinnaker pole. In the farthest boat, you can see a small piece of the pole. If needed I can give you the details on the difference between gennakers and spinnakers correctly?
Hi Shawn, I am living in Utrecht I have an old gulf 32 and I am sailing in merkmeer I find your articles very helpful Thanks
Thank you for helping me under stand all the sails there names and what there functions were and how to use them. I am planning to build a trimaran 30’ what would be the best sails to have I plan to be coastal sailing with it. Thank you
Hey Comrade!
Well done with your master piece blogging. Just a small feedback. “The jib gives control over the bow of the ship, making it easier to maneuver the ship. The mainsail gives control over the stern of the ship.” Can you please first tell the different part of a sail boat earlier and then talk about bow and stern later in the paragraph. A reader has no clue on the newly introduced terms. It helps to keep laser focused and not forget main concepts.
Shawn, I am currently reading How to sail around the World” by Hal Roth. Yes, I want to sail around the world. His book is truly grounded in real world experience but like a lot of very knowledgable people discussing their area of expertise, Hal uses a lot of terms that I probably should have known but didn’t, until now. I am now off to read your second article. Thank You for this very enlightening article on Sail types and their uses.
Shawn Buckles
HI CVB, that’s a cool plan. Thanks, I really love to hear that. I’m happy that it was helpful to you and I hope you are of to a great start for your new adventure!
Hi GOWTHAM, thanks for the tip, I sometimes forget I haven’t specified the new term. I’ve added it to the article.
Nice article and video; however, you’re mixing up the spinnaker and the gennaker.
A started out with a question. What distinguishes a brig from a schooner? Which in turn led to follow-up questions: I know there are Bermuda rigs and Latin rig, are there more? Which in turn led to further questions, and further, and further… This site answers them all. Wonderful work. Thank you.
Great post and video! One thing was I was surprised how little you mentioned the Ketch here and not at all in the video or chart, and your sample image is a large ship with many sails. Some may think Ketch’s are uncommon, old fashioned or only for large boats. Actually Ketch’s are quite common for cruisers and live-aboards, especially since they often result in a center cockpit layout which makes for a very nice aft stateroom inside. These are almost exclusively the boats we are looking at, so I was surprised you glossed over them.
Love the article and am finding it quite informative.
While I know it may seem obvious to 99% of your readers, I wish you had defined the terms “upwind” and “downwind.” I’m in the 1% that isn’t sure which one means “with the wind” (or in the direction the wind is blowing) and which one means “against the wind” (or opposite to the way the wind is blowing.)
paul adriaan kleimeer
like in all fields of syntax and terminology the terms are colouual meaning local and then spead as the technology spread so an history lesson gives a floral bouque its colour and in the case of notical terms span culture and history adds an detail that bring reverence to the study simply more memorable.
Hi, I have a small yacht sail which was left in my lock-up over 30 years ago I basically know nothing about sails and wondered if you could spread any light as to the make and use of said sail. Someone said it was probably originally from a Wayfayer wooden yacht but wasn’t sure. Any info would be must appreciated and indeed if would be of any use to your followers? I can provide pics but don’t see how to include them at present
kind regards
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:

Type Of Sails: A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
If you are approaching sailing and sailboats from a very beginner’s perspective , then the concept of different kinds of sails can be a strange one. We often believe we see one kind of sailboat with one kind of sail, and our simple minds lead us to believe you are only meant to move them around, and you will get to where you need to go.
However, you would not have landed on this article if you did not suspect that there was more to sails and sailboats. So here, you can have a kind of in-depth, kind of summarized review of the different kinds of sails and the most popular sail and mast configurations out there.
It is also important to understand why there are so many different kinds of sails. When you are out on the water, different weather conditions can occur. Your sail acts as a motor of some sort, moving your sailboat forwards, but your sail is also highly dependent on the wind conditions around it. This is why having different kinds of sails can help you navigate your weather conditions and turn them to your own advantage while sailing.
Different sails also come with different danger levels in case of strong wind, so knowing what kinds you might need to watch out for is also extremely important. So, without further ado, let us get into it.
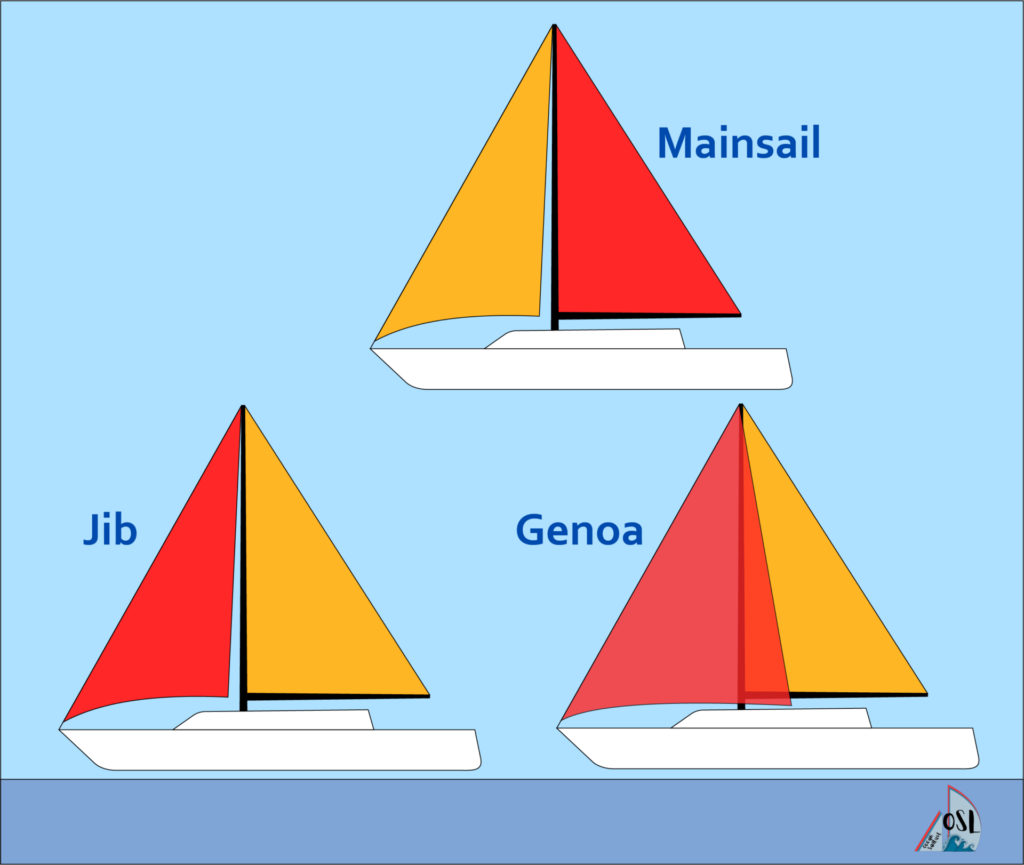
You may have heard of this one before or seen it portrayed in movies and TV shows. As the name suggests, the mainsail is the most popular kind of sail on any sailboat, and they are found behind the mast. They are also attached to the boom. Because they take up so much space on your sailboat, they are also one of the most important sails to take care of and keep an eye on.
Since the mainsail is such a large sail, it does not require too strong a wind to propel it forward , as its large surface area will easily catch a breeze. At the same time, the fact that it can be moved around by moving the boom makes it, so it is easy to steer. This makes it so that the mainsail is the most important sail on your sailboat.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail, or the jib, is likely the second most popular kind of sail found on sailboats. This is because it often accompanies the mainsail, the most popular kind. On all sailboats , the headsail is put at the front of the mast over the sailboat’s bow . It is always a smaller sail than the mainsail.
The fact that the headsail is smaller can be especially useful if you are caught in strong winds. In this situation, you likely do not want to use your mainsail (or trim it as much as possible) to move slower and not be thrown around by the winds. Smaller sails catch less wind, meaning they do not propel your boat as strongly as larger sails.
Having a good headsail can be an incredible safety measure, especially if the seas you are trying to sail are known to be wild and unpredictable.
You may have seen a genoa sail before if you have been around boats or have ever lived in a coastal town. This kind of sail is a large sail that you can attach to the front of the forestay (similarly to the headsail). This is a larger sail than the headsail and can even cover the mainsail either partially or completely. For this reason, the genoa also used to be called an “overlapping jib.”
You should use a genoa if you are sailing through either light or medium winds and if your sailboat is at a dead run point of sail (this means that the wind is coming directly from the rear. If you attempt to use a genoa sail in stronger winds , you might start going too fast and put yourself and your boat at risk since it is such a large sail. So, it is important to be careful .
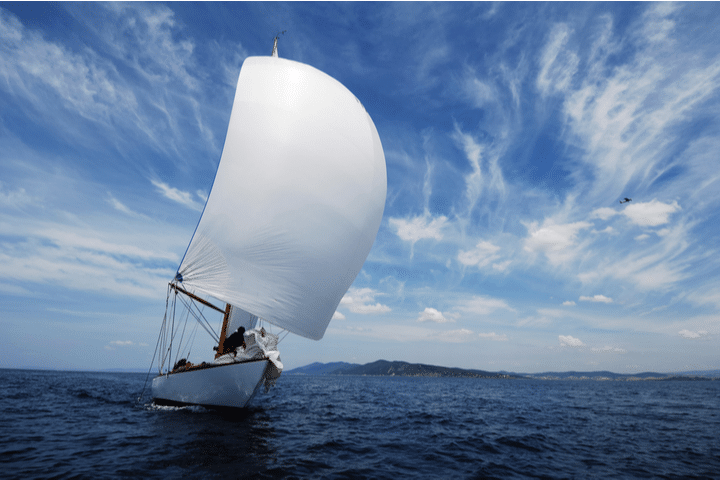

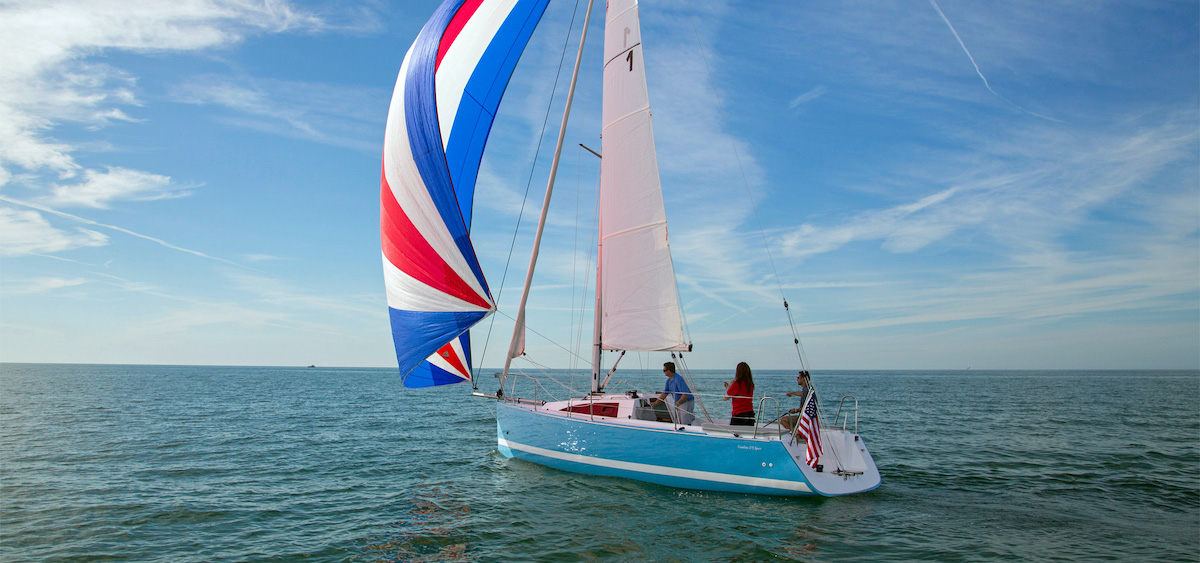
The spinnaker is the most whimsical kind of sail since it is a large and colorful kind. They are also often symmetrical, which means they are more appropriate for reaching different points of sail, such as the running point of sail. They are lighter sails, and they do not cover the mast as the genoa sail does. You do not attach a spinnaker to the forestay and instead let it stretch out past the boat’s bow.
The large surface area of the spinnaker means that you have to be even more careful than with others on the kind of conditions you choose to use this sail in. If the winds are too strong, you could be putting yourself and your passengers at serious risk using this sail, so you should choose to use it only at times when the wind is low or in seas that are known for their low winds and tranquility.
As the name suggests, the gennaker sail mixes the genoa sail and the spinnaker sail. These kinds of sails are more recent inventions. They are as large as the spinnaker sail, but they are not symmetrical. Unlike the genoa or the headsail, they are also not meant to be attached to the forestay, like the spinnaker sail.
The usefulness of this sail is that if the winds change from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, then sailors do not have to resort to using a spinnaker from a genoa, instead of being able to take advantage of different winds while still using the same sail as they were before. This kind of sail is still only meant for lighter and milder winds , but there is more flexibility with the gennaker than the genoa and the spinnaker sails.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
There are many different ways to place the sails we have learned about in the above section. We have compiled a list of some of the most popular ones so you can understand how these sails can be used to make a sailboat move through the oceans.
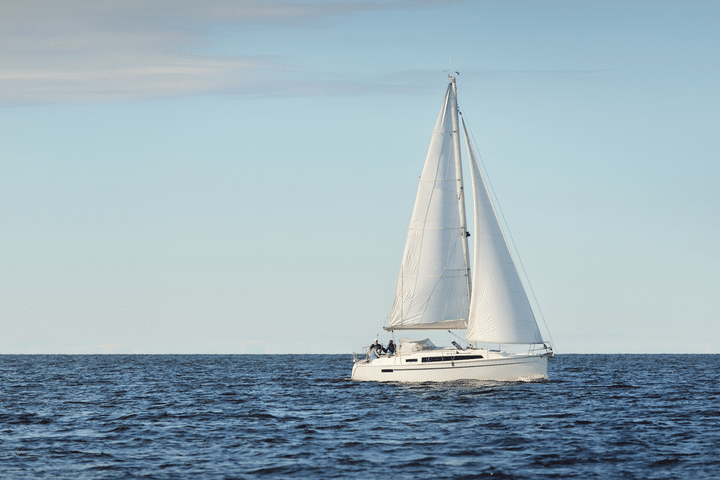

A sloop is by far the most popular configuration. It features a single mast, double sail (the mainsail and the headsail), and mast configuration. The headsail is located from the forestay on the mast to the top of it. The type of headsail used can also vary from a genoa, a spinnaker, or a gennaker sail.
Fractional Rig Sloop
A fractional rig sloop also features a single mast with a double sail setup similar to a sloop. However, what makes the fractional rig sloop different is that the forestay does not reach the top of the mast. This means the headsail is constricted to a smaller amount of surface than on a regular sloop, making it so that your sailboat captures less wind and moves slower .

Cutters are interesting because they’re like a sloop but with a second forestay. This can be useful because it allows them to carry two headsails (a mainsail and one of the jibs). Cutters are good for cruising because they offer a range of wind options, giving you more time to get from place to place.
This is a less common mast configuration than previous others on this list. This is because a ketch features two masts. There is a larger mast fit for the mainsail and the headsail and a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern (the rear) of the boat. This kind of mast configuration is more commonly found among Northern European freighters or fishing boats. This mast configuration is also called the mizzen mast.

A schooner mast configuration features two or more masts. This is similar to the previous configuration, the ketch. It also features multiple sails. While a ketch’s aft mast (also known as the rear mast) is higher than the forward mast, a schooner’s aft mast is shorter than the forward mast. A schooner can also have up to six masts (although two are the most common). These are the main differences between the two.
This one is quite similar to a ketch mast configuration (mentioned above). The only real difference between them is that the mizzen mast is put directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post in a yawl.
A cat sail will have one mast and one sail. The mast is put at the bow of the sailboat. This kind of mast configuration is often found on smaller boats, more specifically on dingy boats. Boats with the cat mast configuration are also often called catboats.
Final Verdict
Having the appropriate kind of sail on your sailboat is incredibly important. At the same time, being aware of the kinds of sails that there are and the kind of sail and mast configuration can make you into a more well-rounded and informed sailor. With that in mind, we hope that you leave this article feeling more confident in your skills when you are out at sea.

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Fishing in Sacramento & San Joaquin Valley Guide

Rent the boat. Own the moment.

Puget Soundkeeper Creating Safe & Sound Seattle Waters | #MindYourWake Series

Key West Water Activities You Must Experience
Sail Types: A Comprehensive Guide to 8 Types of Sails
Sailboats come in all shapes and sizes. And that means there are many types of sails on the market! For those who might not know, sails are made of canvas and use wind power to propel sailboats through the water.
Understandably, different sails are required for different types of sailboats . And sailboats are categorized by the number of hulls they have. Monohulls have a single-hull design, catamarans have two hulls, and trimarans have three. Generally, sailors use catamarans for upwind sailing (but they can be used to sail downwind in certain conditions).
The type of sail you'll need for your sailboat depends on the kind of sailboat you have. Additionally, sails are highly dependent on the wind and weather conditions. Therefore, it's always a good idea to have different types of sails on board to navigate the ever-changing weather conditions.

8 Types of Sails for Sailboats
As mentioned, you should carry multiple sails when sailing to prepare for various weather conditions. Here's a brief overview of the types of sails for sailboats:
1. Mainsails
The mainsail is the largest and most important sail. Therefore, it's probably the first sail to come to mind when you think of camping. Typically, it's situated directly behind the mast — connected to the boom — and uses wind energy to move the vessel. The mainsail plays a significant role in tacking and gybing, making it essential for any voyage.
Since the mainsail is a larger sail, it doesn't require wind to propel it forward. And the fact that it can be moved by moving the boom makes it uber-easy to operate.
Learn More About Sailing
2. Headsail
The headsail often accompanies the mainsail, though it is smaller in size. Regardless of your sailboat type, the headsail is positioned at the front of the mast – over the sailboat's bow.
Because headsails are small, they are helpful when navigating through windy conditions. Smaller sails catch less wind, preventing them from propelling your boat as strongly as larger sails. Additionally, headsails help lift, balance, and protect the vessel from inclement weather conditions.
While the term 'headsail' refers to any sail in front of the mast, the jib is the most common type of headsail. (And when a jib is so large that it overlaps the mast, it's called a genoa.)
Learn More About Sailboats
3. Genoa
The genoa is a large sail that attaches to the front of the forestay. (In this instance, it's similar to a headsail.) However, the genoa is larger than the headsail and overlaps the mainsail partially or completely to help the boat go faster.
Genoa sails are useful when sailing through light or medium wind. You can also use it when the wind comes directly from the rear. If you use a Genoa sail during high winds, you'll probably start sailing too quickly and put yourself and your boat at risk.
4. Spinnaker
The spinnaker is a large and whimsical (often colorful) sail. Spinnaker sails are usually symmetrical, allowing them to reach different points of sail. Generally, these are lighter sails and don't cover the mast like the genoa.
Because spinnaker sails are on the larger side, you have to be incredibly careful with them. Don't use them in rough conditions. Instead, save them for sailing in low winds and calm seas.
5. Gennaker
As the name suggests, the Gennaker sail combines a spinnaker and a Genoa sail. They are as large as the spinnaker, although they're not symmetrical.
They come in handy whenever the wind changes from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, as sailors can navigate various wind types with the same sail. It's still only meant for lighter and milder winds, but it's more versatile than the spinnaker and genoa.
6. Light Air Sails
Light air sails are useful in calmer conditions when the headsail and mainsail alone aren't cutting it. They include:
- Code Zero : A code zero sail is a gennaker sail ideal for sailing in light to mild winds. It's designed to create lift and boost boat speed whenever regular sails don't generate enough power. For that reason, many racers and cruisers use code zero sails to improve performance and gain control in various situations.
- Windseeker : This small, special sail is reserved for no wind or light wind. Essentially, it helps boats remain maneuverable in extremely calm conditions. And for that reason, it's valuable to long-distance sailors.
7. Storm Jib
Storm jibs can be used as a headsail whenever the weather is particularly rough and windy. Because it functions as a safety seal, it prevents boats from capsizing by reducing the sail area exposed to the wind. Therefore, it's a necessary sail for every sailor.
Read Next: Boating in Inclement Weather
During strong winds and storms, sailors can raise a trysail — a small, triangular sail near the boat's stern — for better control and stability. Generally, sailors do this whenever the mainsail becomes too large and challenging to maneuver.

Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.

The Different Types Of Sails And When To Use Them – Complete Guide

Sail forms an integral part of a sailboat. When you sail on the open water and observe other boats (in various sizes), you’d have noticed how each boat type has a specific model of sail. If you’re a beginner in boating, you must know that there are a ton of different sails and they each have their own purpose.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker.
While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily differentiate between them and choose the ideal model based on your purpose. This article guides you on this aspect. Let’s begin!
Different Types of Sails & When To Use Them
1. mainsail.
Mainsail is by far the most widely spotted sail model, and it’s usually fixed to the boom and fitted behind the mast. This offers the highest mileage to your sailboat, thereby maximizing speed and performance.
You can use a mainsail if:
- You’re concerned about the performance
- You need to go faster and utilize all wind power
- You need to steer your boat irrespective of the wind’s status
- You’ve a large boat and can offer adequate space to this sail.
This mainsail displays a wide surface area to make the most out of the available wind condition. As a result, you can steer your boat quite easily. However, the downside is its size. It is very large and hard to store if you need to take it down for some reason.
Check out my other article all about maintaing sails!
2. Headsail
Similar to a mainsail, it’s very easy to spot a head sail. Just look at the bow of the boat and see if there is a sail. If you see one then yes that’s a headsail. Also called a jib or genoa, a headsail is smaller in size compared to a mainsail and attaches in front of the mast to the forestay. The Foresail will not have a boom for the clew of the sail to attach to. The clew will be attached to the foresails sheet. It can be used without the mainsail in certain conditions but for the most part the two sails are used together. The foresail is always forward of the main.
The headsail comes in many different forms such as a jib, genoa, spinnaker or storm jib. The most common headsail is a jib or genoa.
You can use a headsail if:
- Your sailboat is set up for it.
- You don’t want to use the mainsail at this time.
- Your mainsail is not usable.
The biggest advantage of a headsail is the option to protect yourself even if the wind turns unpredictable or wild. This all depends on the type of headsail you are using.
So, what are the different types of headsails? Let’s take a look!
As more boaters chose to use a headsail for their boats, the jib was introduced as one of its forms. The Jib is a form of headsail that is attached to a shackle present on the deck’s front region.
The Jib is a sail that does not go past the mast when it is raised and in use. If it goes past the mast then you probably have a genoa.
You can use a jib if:
- You are out for a normal day of sailing in moderate wind speeds
- You have a roller furling. Which is a sail that wraps up around itself.
Some weather conditions can make maneuvering harder or tighter than usual. As a result, it’s essential to use a jib in such cases. It functions well with boats containing a roller furling as the jib handles different positions and tackles the movement of the boat at ease.
2.2 Genoa
Just when you’ve got acquainted with the jib, genoa comes into the picture as a larger version of the jib. If you’re boating along a coastal region, the genoa sail is the one widely used and is attached to the front area of the deck as well.
Here’s a quick trick to find out if a boat has a genoa sail. This genoa is usually larger than a Jib. This means that the genoa effortlessly overlaps and extends itself beyond the mast, thereby covering the mainsail as well.
You should use a genoa sail if:
- You’re planning to sail in minimum wind conditions. Less wind means you need more sail.
- You find the wind to originate from the rear area.
- You own a large boat. Remember that genoa can partially or completely cover the mainsail too. Larger sails for larger boats!
While it’s great for sailing in regular conditions, there are downsides associated with it. A genoa can put you in a dangerous situation if you are sailing in high wind conditions and don’t have the ability to furl in the sail. Furling in the sail will reduce the area of the sail and catch less wind.
Genoas do come in many sizes as well such as 110% or 120%.
The next section of the sail list are ones that aren’t necessary but can be helpful in certain situations. Let’s look at specialty sails!
3. Specialty Sail
While headsails and mainsails are quite commonly used, there are also specialty sails in the market to address specific requirements. Some of the widely seen specialty sails are spinnakers, storm jibs, and code zeros.
3.1 Spinnakers
Spinnaker is a sail dedicated to downwind and is quite large. Think of a beautifully covered parachute.
It’s easy to spot spinnakers as they resemble kites or parachutes. However, it crosses the bow of the boat and isn’t attached to the forestay.
Unlike the genoa sail that covers the mast, a spinnaker fails to do so. The advantage of a spinnaker is the surface area. When the wind is light, the spinnaker can catch a lot more wind giving you more speed. The Spinnaker is usually fixed to three points – pole, halyard, and sheet.
You should use a spinnaker if:
- You have minimal wind on a run.
- You are trying to harness as much wind power as you can.
While it has a wide surface area, the downside is its inability to steer the boat during strong wind conditions. It can even put the passengers at risk when the wind is at high speeds.
Make sure you have experience before trying out the spinnaker.
3.2 Storm Jibs
Storm jib is another type of specialty sail meant exclusively for rough weather. It’s a tiny, triangular structure that helps during offshore racing or cruising. Just think of it as a smaller jib.
You should use a storm jib if:
- You’re going to sail in heavy weather conditions.
- You anticipate high wind speeds.
- You’re going to be in an offshore race and they are an approved sail type.
Note: In the case of an offshore racing requirement, it’s critical to take prior permission from the regulatory authority for using a storm jib.
3.3 Code Zeros
Code zero is another updated version of a spinnaker that’s meant to be a combination of genoa and gennaker sails. It resembles the look of a genoa but is a lot bigger.
You should use a code zero if:
- You’re looking for an overlapping flying headsail.
- You’re sailing only in light air conditions.
- You’re looking for an alternative to a Genoa.
Having said that, a code zero or a screecher does the job of a genoa with better efficiencies.
3.4 Trysail
Trysail is another type of specialty sail that’s tiny, triangular, and can be fixed right above a gooseneck on the sailboat.
The Trysail is less known in the market as most boaters go ahead with common mainsails and headsails. It’s essential to acknowledge trysail as a front-and-aft mainsail model. It offers excellent performance and contains a permanent pennant in it.
You should use a trysail if:
- You’re sailing in heavy weather conditions.
- You’re looking for a storm replacement.
- You are experienced with using them.
The quadrilateral sail in a trysail is usually turned and bent to a mast, and this helps in heading the vessel during windy conditions.
3.5 Gennakers
If you’ve been able to spot genoa and spinnaker in the past, identifying a gennaker is incredibly easy. A gennaker is a hybrid sail form that is small, slow, and requires no pole attached to the mast.
You should use a gennaker if:
- You’re looking for a smaller version of a spinnaker.
- You’ve no space to fix a pole to the mast.
- You require the sail to be easily manageable.
- You’re sailing in a region requiring minimum downwind levels.
Choosing a hybrid sail has a lot of benefits as it combines the usefulness of 2 sail models. However, being aware of their cons is critical to planning a safe sail.
As you begin using these sails, you can also look for better customizations. There are drifters, wind seekers, and other jib types that are meant to handle different wind conditions.
How Many Sails On A Sailboat ?
In general, a sailboat contains two sails. Two sails is the typical setup for the best performance of the boat during different wind conditions. It’s essential to pick your two sails based on your sailing plan.
Why Are There Two Sails On A Sailboat?
A sailboat uses two sails because the wind left over by the first sail is easily caught by the second sail. This helps in steering the sailboat to a better extent and gives the sailboat more power.
Final Thoughts
Sails are one of the major assets of a sailboat. From managing wind to maximizing the performance and longevity of a sailboat, the type of sails you use, plays a huge role. From the various sail types listed in this article, you can choose the best model that fits your sailing routine. Just make sure to remember to check and make sure they are the correct size for your vessel.
Make sure to plan ahead and have the right sails for your sailing weekend. Cheers!
Boatlifehq owner and author/editor of this article.
Recent Posts
Sailboat Racing - Rules & Regulations Explained
Sailboat racing, a blend of skill, strategy, and adherence to intricate rules and regulations, offers a thrilling and intellectually stimulating experience on the water. Navigating through the...
What is the best sailboat to live on? Complete Guide
Embarking on the journey of living aboard a sailboat requires careful consideration of your budget, desired amenities, and storage options. This guide offers a concise, step-by-step approach to...

Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
In the enchanting world of sailboat dynamics, where the dance between wind and water takes center stage, the significance of sails cannot be overstated. Like the wings of a bird, these meticulously crafted sails unfurl to catch the slightest whisper of breeze, converting it into a powerful forward thrust that carries us through the vast expanse of the ocean. They are the very essence of a sailboat, the conduits through which dreams and aspirations set sail.
Join us on a captivating voyage as we unfurl the secrets of the myriad types of sails adorning the mastheads of sailboats across the globe. From the grandeur of the mainsail, proudly dominating the skyline, to the nimble headsails that steer with precision, and the enigmatic mizzensails that add an extra touch of finesse, we shall embark on a comprehensive exploration of the diverse array of sail types.
Different Types of Sails on a Sailboat: Why Use Different Sails at All?
Different sail types for different wind conditions.
Triangular sails, such as the mainsail and jib, are commonly used on modern sailboats to optimize performance when sailing upwind. The shape of these sails helps to create lift, which propels the boat forward even against the wind’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the mast at the front edge and a boom at the bottom. Jibs, on the other hand, are headsails that are attached to a stay near the bow of the boat.
Balloon sails, like spinnaker sails, are designed for downwind sailing and catching more wind to increase boat speed when sailing with the wind behind it. These types of sails have a large surface area that allows them to catch more wind than triangular sails. Spinnaker sails can come in different shapes depending on their intended use and can be flown from a spinnaker pole or directly from the bow.
Sail Plans: Different Combinations for Different Boats
Sail plans refer to how different types of sails are arranged and combined on a sailing craft. Sail plans can vary depending on specific design features and intended use of boats. For example, some boats may have multiple masts with several triangular-shaped sails attached while others may only have one mast with one triangular sail (mainsail) and one square sail (spinnaker). The combination of different types of sails can also affect how easy it is to handle a boat under certain conditions.
Understanding Sail Anatomy
Head, tack, foot, luff, leech, and clew. These are the different parts that make up a sail’s anatomy. But what exactly are they and why are they important? In this section, we’ll take a closer look at each part and how it contributes to the performance of a sailboat.

The Head: The Top of the Sail
Starting from the top, we have the head of the sail. This is where the halyard (the rope or wire used to hoist the sail) is attached. The head determines how high or low the sail sits on its mast. A higher head means more power but less control over the sail’s shape. Conversely, a lower head provides better control but less power.
The Tack: The Lower Front Corner of the Sail
Next is the tack which is found at the lower front corner of most sails. It’s where one end of a line called a “sheet” attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet will affect your boat’s speed and direction.
The Foot: The Bottom of the Sail
At the bottom edge of any sail lies its foot which helps determine its overall shape and size. Generally speaking, longer feet result in larger sails that provide more power while shorter feet result in smaller sails with better maneuverability.
The Luff: The Forward Edge of the Sail
The forward edge of any sail is called its luff which runs along its mast track or forestay depending on what type of rigging you have set up on your boat. It helps maintain proper airflow over your sails by keeping them from flapping around too much in high winds.
The Leech: The Back Edge of Your Sail
Opposite from your luff is your leech – or back edge – which helps create lift by allowing air to flow smoothly over your sail. A longer leech will result in a more powerful sail, while a shorter one will provide better control and maneuverability.
The Clew: The Bottom Back Corner of Your Sail
Lastly, we have the clew which is found at the bottom back corner of most sails. It’s where the other end of your sheet attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet here can affect how well you’re able to steer your boat.
Primary Sail Types
The main sail is attached to the main mast and boom and can be adjusted to match the wind conditions. Its main purpose is to keep the boat steady and under control by providing stability to the stern (back) of the vessel.
There are several variations of mainsails that sailors can choose from depending on their needs. One popular type of mainsail is an in-mast furling mainsail. This type of sail can be easily furled and unfurled by pulling a line, making it ideal for short-handed sailing or cruising. Another variation is a slab reefing mainsail, which has horizontal strips called battens that help maintain its shape. Finally, there is also a boom furling mainsail, which uses a roller system inside the boom to make it easier to handle.
A headsail is any sail located forward of the mast on a sailing vessel. These sails are designed to work in conjunction with the main sail to provide optimal performance under varying wind conditions. There are several types of headsails available, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes.
One popular type of headsail is known as a genoa. This large foresail extends beyond the mast and overlaps with the main sail, providing additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Genoas come in various sizes ranging from 110% up to 150%, depending on how much overlap you want.
Another common type of headsail is called a jib. This smaller foresail does not overlap with the main sail but instead works in conjunction with it. The jib is typically used in higher wind conditions when a smaller sail area is needed to maintain control of the boat.
A staysail is a smaller sail located between the mast and the forestay. This type of headsail is typically used on larger boats to provide additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Staysails are often used in conjunction with other sails, such as a genoa or main sail.
Finally, there is also a mizzensail, which is located aft of the main mast on ketches and yawls. This sail provides additional power when sailing downwind or reaching across wind angles. Mizzensails come in various sizes and can be either fully battened or free-flying.
Lightwind Sails
Spinnaker sails are a type of downwind sail that can be used to increase boat speed when sailing in light winds. They are typically used in wind conditions below 10 knots, which are considered light air sails. Spinnakers come in two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical.

Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Spinnaker
The symmetrical spinnaker is designed to sail directly downwind or with the wind coming from behind the boat. It is shaped like a balloon, with equal amounts of material on both sides of the sail. The sail is attached to a spinnaker pole, which extends out from the mast and holds the sail away from the boat.
Asymmetrical spinnakers, on the other hand, are designed for sailing at angles off the wind. They have an uneven shape, with more material on one side than the other. This design allows them to be flown without a spinnaker pole, making them easier to handle for smaller crews.
Another type of downwind sail is called a gennaker. Gennakers are similar to asymmetrical spinnakers but have a hybrid characteristic between a spinnaker and a genua. They are designed for reaching or running downwind at higher speeds than traditional cruising chutes or asymmetric spinnakers.
For those who prefer an even more user-friendly option than asymmetrical spinnakers or gennakers, parasailors might be what you’re looking for! A parasailor combines aspects of both a traditional spinnaker and a parachute into one easy-to-use package. The unique design of this sail makes it ideal for use in light winds when other sails may not perform well enough.

Finally, there’s another type of upwind/downwind sail called the code zero. Code zeros are designed to be used in light winds when sailing upwind, but they can also be used for reaching and running downwind. These sails have a flat shape that allows them to generate lift even in very light wind conditions.
Heavy Weather Sails
Heavy weather sailing is a challenging and potentially dangerous activity. The use of heavy weather sails, such as trysails, is crucial to ensure the safety of sailors and their vessels.
A trysail is a small triangular sail made of heavy-duty material, typically spinnaker cloth or other lightweight fabric. It is designed to be used in stormy weather conditions when winds are high and the seas are rough.
The role of a trysail is to provide an alternative source of propulsion when the main sail or jib cannot be used. In addition, it helps reduce the heeling effect on the vessel caused by strong winds. Trysails are rigged using a separate halyard and can be set up quickly when needed.
A trysail should be used in severe weather conditions when winds exceed 40 knots or more. It is recommended that sailors practice setting up their trysail before they need it so that they can do it quickly and efficiently in an emergency situation.

Another type of heavy weather sail that every sailor should have on board is a storm jib. This sail is typically much smaller than a regular jib and made from heavier materials such as Dacron or nylon. Its purpose is to provide additional stability during high wind speeds and rough seas.
The features of a storm jib include its size, shape, and weight distribution. It has a large luff (the leading edge) which allows it to be hoisted higher up on the rigging than other sails. This helps keep the boat stable during high-speed sailing in strong winds.
A storm jib should be used in extreme weather conditions where wind speeds exceed 50 knots or more. When using this sail, it is important to ensure that the halyard is properly tensioned and that the sail is sheeted in tightly. This will help prevent any unnecessary movement or fluttering of the sail.
Overview Common Sail Types
100% of mainsail
Light – High
100% of foretriangle
Moderate – High
triangular, overlapping
110% – 150% of foretriangle
Light – Moderate
60% – 80% of foretriangle
Close Reach – Broad Reach
Lightwind, Downwind
balloon shape, free flying
200% of mainsail (or even more)
Broad Reach, Running
parachute shape
100% of spinnaker
80% – 85% of spinnaker
Lightwind, Upwind
75% of spinnaker
30% – 60% of mainsail
Mainsail, heavy weather
17.5% of mainsail (or less)
Headsail, heavy weather
max. 65% of the hight of the foretriangle
Unconventional Sails
Wing sails are a type of sail design that is not commonly used in traditional sailboat designs. They are essentially vertical airfoils that generate lift and propulsion by directing the wind over the surface of the sail. Wing sails have become increasingly popular in modern sailing craft, particularly in high-performance racing boats.
One of the main advantages of wing sails is their ability to produce a significant amount of power with very little heeling force. This means that they can be used effectively in high-wind conditions without causing the boat to tip over. Additionally, wing sails are highly efficient at sailing upwind, which allows sailors to point higher into the wind than with other types of sails.
While wing sails may seem like a relatively new concept, they have actually been around for quite some time. The first recorded use of a wing sail was by German engineer Wolfgang Zimmermann in 1959. Since then, many different variations on the design have been developed and tested.

Kite sails are another unconventional type of sail that has gained popularity in recent years. Unlike traditional downwind sails such as spinnaker or parasailors, kite sails are flown from a line attached to the bow of the boat and do not require a mast or boom.
Sail Materials and Technology
Traditional sail materials.
Sails have been used for thousands of years to harness the power of the wind and propel boats across water. Traditional sail materials were flax, hemp, or cotton. These natural fibers were woven together to create a strong, yet flexible material that could withstand the harsh conditions at sea. However, as technology advanced and sailors began to demand more from their sails, new materials were developed.
Modern Sail Materials
Modern sailboats use synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, or laminated fabrics for their sails. These materials are lightweight and incredibly strong, allowing sailors to achieve greater speeds with less effort. They are also more durable than traditional sail materials and can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and saltwater.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations

The sloop rig is one of the most popular sail plans for modern sailboats. It features a single mast and one headsail, like a jib or genoa. The mainsail is typically triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast using a backstay to support it. The jib or genoa is attached to the forestay that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat.
Another popular sail plan is the cutter rig, which also features a single mast but has two headsails – an overlapping jib and a smaller staysail. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support.
Moving onto two-masted rigs, we have ketch rig, which features a main mast and a shorter mizzen mast located in front of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Lastly, we have the yawl rig which is similar to the ketch rig but has its shorter mizzenmast located aft of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Conclusion: Understanding the Different Types of Sails
Understanding the Different Types of Sails is crucial for any sailor who wants to optimize their performance and safety on the water. Whether you’re racing, cruising or simply enjoying a day out on your sailboat, having the right sails for the conditions can make all the difference.
Ultimately, understanding the different types of sails is essential for any sailor looking to improve their skills on the water. By selecting the right sail for your boat and conditions, you can optimize your performance while staying safe and comfortable during your time at sea.
So whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, take some time to explore the various types of sails available and find the ones that work best for you. With a little knowledge and experience under your belt, you’ll be well on your way to mastering this exciting sport!
Similar Posts

Mainsail Furling Systems – Which one is right for you?
With the variety of options of mainsail furling systems available, including slab, in-boom, and in-mast systems, it can be challenging to determine which one best suits your needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the pros and cons of each system, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your sailing requirements….

How Much Does Biofouling Slows Down your Boat?
Are you wondering how much biofouling can impact the performance of your sailboat? The amount of how much biofouling slows down a sailboat depends on various factors, such as the type of boat, its size, and the severity of the biofouling. On average, a sailboat with a heavily fouled hull can experience a reduction in…

Basic Sailing Terminology: Sailboat Parts Explained
Sailing is a timeless activity that has captivated the hearts of adventurous souls for centuries. But, let’s face it, for beginners, sailing can be as intimidating as trying to navigate through a dark, labyrinthine maze with a blindfold on. The vast array of sailing terminology, sailboat parts and jargon can seem like a foreign language…

What is a Keel?: The Backbone of a Ship
As ships sail through tumultuous seas, their stability and maneuverability are tested to the fullest extent. The intricate design and engineering that go into a ship’s construction ensure that it can withstand the forces of nature and navigate through any challenging conditions. One of the most critical components of a ship’s design is the keel,…

What is a Sloop? Definition, Types and History
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig. Sloops are a type of sailboat that has been around for centuries. They are known for their versatility and ease of handling, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. Sloops have a single mast and a fore-and-aft…

Whats the Difference between Standing Rigging and Running Rigging?
Running rigging refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the position and shape of the sails on a sailboat. Standing rigging, on the other hand, refers to the fixed wires and cables that support the mast and keep it upright. As the sun rises on another day, we find ourselves immersed in…
No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Most Popular Types Of Sails On A Sailboat
A sloop-rigged sailboat typically features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker. The mainsail is rigged aft of the mast, while the headsail is attached to the forestay. The two most commonly used headsails are the Genoa and Jib.
The sails are vital parts of a sailboat since you obviously couldn’t sail without them! There are many different sails depending on the type of sailboat and its rig configuration, and we’ll walk through them together in this article.
The different types of sails on a sailboat
We can divide the selection of sails on a sailboat into three categories:
- Standard sails
Light-wind sails
- Storm sails
Each category serves different purposes depending on the vessel’s rig configuration and the sail’s functionality.
The standard sails
The standard sails usually form a sailboat’s basic sail plan and include :
- The Mainsail
- The Staysail
- The Mizzen sail
These sails are the ones that are used most frequently on sloop, ketch, and cutter-rigged sailboats and are usually set up to be ready to use quickly.
Headsails are often rolled up on a furler, while the main and mizzen sail are stored on the boom or furled into the mast.
The halyards and sheets are kept within easy reach, making these sails the primary choice in most situations. Let’s dive further into each of them.
The mainsail is a triangular sail that flies behind the mast on top of the boom . Although it may not always be the largest sail on the vessel, we commonly refer to it as “the main.”
It is a vital sail, and keeping the sail shape trimmed properly on every point of sail is crucial for the stability and performance of the boat.
A Jib sail is a headsail that does not overlap the mainsail. It is typically between 100% and 115% of the foretriangle but can also be smaller. The foretriangle is the triangular area formed by the mast, deck, and forestay. The Jib is often used with a self-tacking system involving a sheet traveler in front of the mast.
This sail is often seen on newer boats with fractional rigs, which typically have a larger mainsail area than the headsail area. However, the Jib is versatile and also used in other configurations.
People often mix the terms Genoa and Jib. Many refer to any headsail as a Jib, which is incorrect. I personally prefer to use the correct terms to avoid confusion .
A Genoa sail resembles a large Jib but extends past the mast and overlaps the mainsail. Genoas are usually larger than 115% of the foretriangle , with sizes ranging from 120% to 150%. They are often used on vessels with masthead rigs and smaller mainsails but are also common on fractional rigs.
The Staysail is typically found on cutter rigs and is set on the inner forestay or cutter stay. It can be combined with other sails, such as a Jib, Genoa, or Yankee, or on its own in stronger winds.
The Staysail is also useful when sailing downwind, as it can be paired with a headsail and extended to opposite sides of the boat using a pole.
The Yankee sail resembles a Genoa and Jib but has a high-cut clew. This shape allows for improved airflow when used with another headsail. The Yankee is often used on cutter-rigged boats in combination with a staysail and is known for its versatility in different wind conditions.
Mizzen Sail
A mizzen sail is similar to the mainsail, only smaller . It is set on the aft mast of a boat with multiple masts, such as a ketch rig. The mizzen sail is usually used to provide balance and stability to the vessel and provides additional power when sailing downwind.
Another handy usage is to fly the mizzen at anchor to keep the bow up against waves and swell.
The light-wind sails are large, made of thin nylon, and typically shaped like a half-balloon. They are a type of headsails that are great when the winds are too light to fill the standard headsail and are often used when sailing downwind.
The four most commonly used light-wind sails are:
- The Spinnaker
- The Gennaker
- The Code Zero
- The Parasailor
They all provide excellent forward propulsion on a sailboat but usually require some extra rigging to be set.
Experienced cruisers love to use light-wind sails in nice weather, but they have a critical weakness to be aware of. These sails easily get overpowered when the wind increases, and I strongly advise being careful and observant of the wind conditions when flying them.
(Yes, I have managed to rip mine on one occasion due to getting overpowered, but that’s a different story…)
Let’s continue and take a closer look at each of the light wind sails.
A Spinnaker sail is a large, lightweight downwind sail used at deep angles between 120 and 180 degrees. It is symmetrical in shape with two clews and is often brightly colored.
The Spinnaker is set by using a pole to extend the sail’s clew to the vessel’s side. Then, a sheet is attached to the other clew and led back to the stern of the boat.
A Gennaker sail combines the characteristics of the Genoa and Spinnaker. It is made of nylon like the Spinnaker but is asymmetrical like a Genoa and rigged slightly differently. The tack is attached to the bow, and the clew has a sheet led aft to the cockpit. The Gennaker can be equipped with a snuffer to make it even easier to set up and take down.
It is popular among cruisers because it is simpler to use than a spinnaker and it doesn’t require a pole. The sail is effective at angles between 90 degrees and almost all the way down to 180 degrees, making it versatile for various light-wind conditions.
A Parasailor is similar to the Spinnaker in many aspects but has some distinct differences. It has a double-layer wing that inflates as the sail is filled with air, creating a batten-like effect pushing the leech out while providing lift to the bow.
The wing also helps to prevent the rolling movements you get with a Spinnaker and the collapsing of the leech that can occur with a Gennaker at deep angles.
This makes the parasailor effective at sailing angles between 70 and 180 degrees dead downwind. Parasailors can be set like a Gennaker when reaching or with a pole like the Spinnaker for running downwind.
A Code Zero sail combines some elements of the Genoa and Gennaker. Unlike the Gennaker, the Code Zero has a different shape, allowing it to be used while sailing upwind.
Another benefit is that it can be used with a furler which makes it easy to roll in and out. However, it can’t replace the Gennaker or Spinnaker entirely, as it is not effective at sailing angles deeper than 120 degrees.
If you see a big yacht with three forestay’s, the forward one probably holds a code zero sail. A bow spirit allows the ability to fly additional light wind sails as well!
Storm Sails
The storm sails consist of a small Mainsail and Jib in heavy-duty materials designed for rough conditions. These sails enable us to maintain speed and stability in the boat in severe weather too strong for the standard sails.
Storm sails are often brightly colored , such as red, orange, or yellow, to make them more visible at sea.
Storm Mainsail
A storm mainsail is used when the reefing setup doesn’t allow the standard mainsail area to be reduced enough to prevent overpowering. The sail can handle rough conditions and is excellent for maintaining stability.
A storm Jib is used when the headsail has been furled to the point where it is no longer effective. It is especially useful for sailboats rigged with a Genoa, as the Genoa gets inefficient when heavily reefed. As the storm Jib is smaller than the standard headsail, it also lowers the center of gravity, making the vessel heel less and become more stable.
Explaining the terms for the parts of a sail
Let us talk some more about sails. The goal is to go sailing, right?
Identifying the different parts of the sails is crucial to understanding which lines go where.
Let’s zoom in on a sail and break down the terms :
The head is the top corner of the sail . Most mainsails have a headboard or plate where the halyard is connected, while headsails use a metal ring. A halyard is a line we use to raise and lower sails with.
The leech is the aft part of a sail , located between the clew and head. We use a combination of the outhaul, main sheet, and traveler to trim and adjust the leech on the mainsail.
The headsail’s leech is trimmed by adjusting sheet tension and angle according to the wind speed and direction. A traveler is a track with a movable car or pulley system for adjusting the position and angle of a sheet, and most sailboats have one main traveler for the mainsail and car tracks along the side decks for the headsail.
The luff of a sail is the front part of the sail between the tack and head. On a mainsail, the luff runs vertically along the mast and along or close to the forestay on a headsail. Headsails are often equipped with luff foam to help maintain their shape when partially reefed on a furler.
Battens are slats or tubes inserted into pockets on the mainsail to help the sail maintain its shape and increase its lifespan . A traditional sail hoisted and lowered on the boom typically has horizontal battens. Vessels with in-mast furling can use vertical battens instead of horizontal ones.
- A fully battened Mainsail has the battens run through the entire sail length from the luff to the leech.
- A standard battened main sail has the battens along the sail’s leech.
Telltales are small ropes, bands, or flags attached to a sail to give an indication of the airflow around the sail. They help us understand how the wind affects the sail and allow us to fine-tune the trim for optimal performance. Telltales are usually found on the mainsail’s leech and in the front of the headsail’s leech.
The clew of a sail is the lower aft corner and where the outhaul is connected on a mainsail. Headsails have sheets attached to their clew for controlling and trimming the shape and tension.
The tack is the lower, forward corner of a sail. On a traditional Mainsail, the tack is attached to the Gooseneck, a hinge in front of the boom attached to the mast.
With in-mast furling, the tack is connected to the furling mechanism. This mechanism is used to roll the sail into the mast.
The headsails tack is connected to a furler drum on the forestay on most sailboats. Vessels using traditional hank-on headsails connect the tack to a fixed point on the bow.
The foot of the mainsail is the bottom portion of the sail between the clew and the tack. It is trimmed using the outhaul, a line attached to the clew, and used to adjust the tension on the foot of the sail. Some mainsail are configured loose-footed, and others are attach-footed.
The foot of the headsail is trimmed by adjusting the tension and angle of the sheets, which are the lines used to control the headsail’s clew. We use cars, or pulleys, to adjust the angle of the sheets and thus the trim of the headsail.
Traditional and less commonly seen sails
We’ve now looked at the most commonly used sails and walked through the different parts of them. But what about the less common ones? The art of sailing has a rich history, with some unique sail designs that we rarely see today.
Read on if you want to peek into some traditional sails, or skip straight to popular sail and mast configurations here.
Square sails
Square sails are rectangular and usually set across a ship’s mast, mostly seen on traditional square-rigged sailing ships and Viking ships. These sails are efficient for downwind sailing and are hung from horizontal spars called yards. Though not as agile as modern fore-and-aft sails when sailing upwind, they were central to naval exploration for centuries. Today, they’re mainly seen on traditional vessels and tall ships, symbolizing maritime heritage.
If you’ve been to Martinique in the summer, you may also have noticed the round skiff sailboats the local fishermen traditionally used for fishing in the Atlantic Ocean with their distinctive big squared sails. Tour de Martinique des Yoles Rondes is a popular yearly event where the locals race and show off these beautiful old boats with colorful sails!
A gaff sail is a traditional four-sided sail held up by a horizontal spar called the “gaff.” They are used on classic gaff-rigged sailboats and allow for a larger sail area with a shorter mast. Gaff-rigged boats were traditionally popular and usually carried 25% more sail area than the equivalent Bermudan rig, making them fast on a downwind run. The Gaff rig could also carry a topsail between the gaff and the mast.
However, they don’t sail well to windward, and modern designs have shifted towards triangular sails for better upwind performance.
Jib-headed topsail
The Jib-headed topsail is a small triangular sail used on gaff rigs and is set between the gaff and the top of the mast.
A lug sail is an angled, four-sided sail that attaches at a point on its top side, making it hang tilted. The sail is simple to use and often found on smaller or older boats. There are different types, like standing, dipping, and balance lugs, each hanging differently around the mast.
The lug sail evolved from the square sail to improve how close the vessels could sail into the wind. Because of their upwind performance, fishermen used them widely in Europe from the seventeenth through the nineteenth centuries.
Sprit sails
The spritsail, with its unique four-sided design, stands out thanks to a diagonal support called the “sprit.” It was traditionally popular in Thames sailing barges due to its ability to accommodate high-deck cargo. These days, it’s primarily found in smaller boats like the Optimist dinghy in a variant called “leg of mutton spritsail.”
The spritsail was also used in traditional wooden boats like the fearing version of the Oselvar wooden boat traditionally used in western Norway.
It is also commonly used by the indigenous Guna Yala tribes in Panama in their dugout Ulu’s up to this day. We saw plenty of them when we cruised along the coast, and some of them approached us to sell us their delicious catch of the day!
Lateen sails
A lateen sail is a triangular sail set on a long spar angled on the mast. It was originally popular in the Mediterranean and on Arab shows, and its design enhanced maneuverability and played a crucial role in historic sea exploration.
The lateen sail was used on lateen rigs, the predecessor to the Bermuda rig – one of today’s most commonly used rigs!
Which brings us to the following topic:
Popular sail and mast configurations
There are many different rigs and sail configurations between sailing vessels. From the old-school square rigs to schooners, gaff rigs, and more. However, this article will focus on the three most popular rigs seen on modern sailboats:
- The Bermuda Sloop Rig
- The Cutter Rig
- The Ketch Rig
The three rigs have similarities and differences between their sail and mast configurations. We’ll walk through each of them to understand how they utilize their different types of sail.
If you want to learn more about other rigs, take a look here .
Bermuda Sloop Rig
The Bermuda sloop rig is the most common rig on modern vessels. It is characterized by a single mast, a triangular mainsail, and a headsail. This rig is named after the Bermuda Islands, where it was developed in the 17th century.
Some of the key features of the Bermuda sloop rig:
- The mast is typically tall and raked, which allows for a large sail area and excellent stabilit y.
- The mainsail is attached to the mast and boom. It is usually combined with a single headsail at the front of the boat, making it powerful and easy to sail.
- The Sloop is usually equipped with a masthead or fractional rig and flies a Jib or Genoa as its primary headsail.
The Bermuda Sloop rig is known for its simplicity, is often used for racing and cruising, and is popular among sailors worldwide.
The cutter rig is very similar to the sloop rig. The significant difference is that it has a single mast and two headsails – a Staysail and a Yankee. The cutter rig is known for its versatility due to the multiple options in sail plans and the double headsail setup.
Some key aspects that separate the Cutter from the Sloop:
- The rig is often more robust than its Sloop sister because of the additional cutter stay and running backstays.
- The mast is located closer to the center of the boat.
- The Cutter has a staysail on the inner forestay and a Yankee sail on the outer. The sails can be used in combination with each other or independently.
- Tacking the headsail between the forestay and cutter stay is more involved than on a sloop.
- The Cutter rig has two similar variations: the Slutter rig and the Solent rig.
Like the Sloop, the Cutter rig is relatively easy to operate. Still, the additional headsail and rigging make it costlier to maintain. It is also less suitable for racing than the Sloop, but the added versatility helps in different weather conditions and makes it an excellent choice for cruisers.
The ketch rig is also similar to the Sloop but has an additional mizzen mast placed further aft of the main mast. Another mast gives it the advantage of even higher versatility in sail plans. The ketch typically uses three sails. The mizzen sail, a mainsail, and a headsail. The mizzen mast also allows it to fly a second light-wind sail.
Here are a few more distinctions of the ketch rig:
- The ketch typically carries a smaller mainsail than a similarly sized sloop and a smaller mizzen sail.
- A small mizzen and a medium mainsail are easier to handle than one large mainsail.
- The additional mizzen sail makes the vessel easy to balance and gives extra stability downwind.
- The ketch usually doesn’t point as close to the wind as the Sloop and Cutter.
The headsail setup on a ketch is generally the same as for the Sloop. But the ketch can also be rigged as a cutter ketch, which gives it the benefits of the cutter rig! The tradeoff with a cutter-rigged ketch is the higher complexity and additional rigging, hardware, and sails required.
Final words
Well done, you now have a good grasp of the most common sails and their strengths. We have discussed a few rigs and how they utilize different kinds of sails in various sail plans. Remember that more sail types, other rigs, and even more variations are available. It is a complex topic, but this guide covers the basics and gives you a great starting point.
If you still have questions, look below at the FAQ, or leave me a comment. I’m more than happy to help you out!
A sailboat is only as good as its sails, and sails need wind to work. The next logical step is learning how the wind works when we sail and practicing some wind awareness! Head to the following guide to continue your research: Learn The Difference Between True And Apparent Wind Speed.
FAQ: The Different Types of Sails On A Sailboat
What is the foretriangle on a sailboat.
The foretriangle on a sailboat refers to the triangular area formed between the mast, forestay, and deck. If you want to order a new headsail, for example, you’ll have to measure and supply the sailmaker with these details.
What is the difference between a loose-footed and attached-footed mainsail?
A loose-footed mainsail is attached to the boom only at its corners, leaving the rest of the sail’s bottom edge free. An attached-footed mainsail, on the other hand, is secured to the boom along its entire length. The main difference lies in how the bottom of the sail connects to the boom, with the loose-footed design offering more adjustability in the sail shape.
What is a high-cut clew on a sail?
A high-cut clew refers to the design of a foresail, such as a jib or genoa, where the back lower corner (the clew) is raised or “cut” higher above the deck compared to standard designs. This design allows for better visibility beneath the sail and makes it easier to sail over waves without the sail touching the water, which is especially beneficial for offshore or blue-water cruising. Very high-cut clews are commonly seen on yankee sails on cutter-rigged sailboats.
What is luff foam on a sail?
Luff foam is a padded strip sewn into the forward edge of roller furling sails. It ensures the sail is appropriately shaped when partially rolled up, especially in strong winds. This foam not only helps with sail performance but also protects the sail when it’s furled.
What are the most common sails?
The sloop rig sailboat is the most common and usually features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker.
What are the different types of sails?
There are several different types of sails, and we can divide the most common into three categories:
The standard sails:
- Mizzen sail
The light-wind sails
The storm sails:
- Storm mainsail
- Storm jib
What is a spinnaker sail?
A Spinnaker sail is a large, lightweight downwind sail used at deep angles between 120 and 180 degrees.
What is a Jib sail?
A Jib sail is a headsail that does not overlap the mainsail and is set on the forestay. The Jib can also be set up with a self-tacking system, making it very effective when sailing into the wind.
Is Genoa sail the same as a jib?
People often mix the terms Genoa and Jib. The Genoa is different from a Jib sail as it is larger and overlaps the mainsail, whereas the Jib is smaller and does not overlap the mainsail.
What is a Genoa sail?
A Genoa is a headsail larger than the Jib extending past the mast and overlapping the mainsail. The advantage over the Jib is the larger sail area, making it more effective when sailing off the wind.
How many types of sail plans are there?
Sail plans refer to the configuration and arrangement of sails on a boat or ship. While there are countless customizations and variations, the three most common sail plans are:
Sloop: Characterized by a single mast, a triangular mainsail, and a headsail.
Cutter: Similar to a sloop but has a single mast and carries two or more headsails.
Ketch: Features two masts, with the aft mast (called the mizzen) shorter than the main mast.
What is a Mainsail?
The mainsail is a triangular sail that flies behind the mast on top of the boom.
What is a Gennaker?
A gennaker is basically an asymmetrical spinnaker. A hybrid sail that combines the characteristics of a Genoa and a Spinnaker, designed for sailing off the wind and often used in light to moderate wind conditions.
What is a Storm Jib?
A storm jib is a small, heavy-duty sail used in strong winds or stormy conditions. It is commonly used when the headsail has been furled to the point where it is no longer effective.
What factors determine the type of sail to be used?
The type of sail to be used depends on various factors such as wind conditions, points of sail, sailboat size , and sailing experience. It’s smart to choose the appropriate sail for optimal performance. A Jib, for example, will be more effective than a Genoa while sailing to windward, and vice versa.
How do sails affect the performance of a sailboat?
Sails are the engine of a sailboat. Their design, size, and trim influence the boat’s speed, direction, and stability. Properly adjusted sails capture wind efficiently, allowing the boat to move faster and in the desired direction.
The balance and condition of the sails also impact comfort and safety, with well-maintained sails ensuring optimal performance. The sails are essential in determining how a sailboat performs in various wind conditions.
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
What specifically do you want my point of view on?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Boat Sailor
Type of sails: a comprehensive guide to sails.

As an avid sailing enthusiast and advisor, I am excited to share a complete guide to different types of sails for sailboats. Choosing the right sail is crucial for optimizing sailing performance and ensuring safety in various weather conditions. In this article, we will explore the main type of sails, their advantages, and when to use them effectively. So let’s set sail and delve into the world of sails!
The Main Types of Sails
Mainsail: The Backbone of Sailing
The mainsail, being the largest and most essential sail on a sailboat, plays a central role in driving the vessel forward. It is a fore-and-aft rigged sail attached to the mast and the boom. Mainsails are incredibly versatile and suitable for various wind conditions, making them the go-to sail for most situations. They are easy to steer, even in light winds, making them ideal for relaxed cruising.
Headsail/Jib: Your Go-To Sail for Safety
The headsail, also known as a jib , is a smaller sail located forward of the mast. Its primary purpose is to maintain stability and balance the boat in strong winds. When the wind picks up, the mainsail can become overpowering, and that’s when the headsail steps in to ensure safe and controlled sailing. It’s like having a safety net during rough weather conditions.
Genoa: Power and Versatility Combined
The genoa is a type of headsail that offers more sail area and power compared to a standard jib. It’s perfect for boosting speed and maneuverability, especially in light winds. Genoas are incredibly versatile, making them an excellent choice for sailors who want to get the most out of their sailboat in various conditions.
Sailing Ship Rigs: A Historical Perspective
In the era of the “golden age of sail,” different sail plans were used on sailing vessels to optimize their performance and accommodate smaller crews.
Fore and Aft Rig
The fore-and-aft rig, consisting of sails aligned along the length of the boat, includes popular designs like schooners and sloops. These rigs required smaller crews and were well-suited for coastal and fishing trades.
Square topsail schooners with athwart sails were also prevalent during that time. They were used for cargo ships and long voyages, but their complex rigging required larger crews to handle the sails effectively.
The Golden Age of Sail
This period marked the peak of sailing ship technology and saw remarkable advancements in shipbuilding and sail design. It’s a fascinating chapter in the history of sailing that continues to inspire sailors to this day.
Type of Sails Names: Decoding the Terminology
Mainsail and Foresail
The mainsail, as mentioned earlier, is the principal sail that catches the wind to move the boat forward. Foresail is a general term that includes various sails positioned near the bow of the sailboat, such as the jib and genoa.
Genoa and Jib
The genoa and jib are both types of foresails. The genoa is larger and overlaps the mainsail, providing additional power and efficiency. The jib, on the other hand, is smaller and is used when the wind is stronger.
Staysail and Spinnaker
Staysails are triangular sails set between masts and stays, used to improve stability and balance. Spinnakers are large, balloon-shaped sails used for downwind sailing, providing an extra boost of speed.
Choosing the Right Sail for Different Conditions
Sailing in Light Winds
In light winds, the mainsail is your best friend. It’s highly efficient and capable of catching even the slightest breeze, propelling the boat forward smoothly.
Sailing in Strong Winds
When the wind picks up, it’s time to rely on the headsail or jib. These sails provide a reduced surface area, preventing the boat from becoming overpowered and ensuring a controlled sail.
Navigating Challenging Weather
Different weather conditions call for different sails. Understanding the intricacies of each sail and when to use them will help you navigate through challenging weather with ease.
Type of Sails Materials: Quality Matters
Traditional Canvas Sails
Traditional canvas sails, made of materials like cotton or linen, were commonly used in the past. While they offer a classic charm, their performance and durability have limitations compared to modern sail materials.
Modern Sail Materials
Today, sail manufacturers utilize advanced materials like Dacron, Mylar, and Kevlar. These materials offer superior strength, low stretch, and better shape retention, contributing to improved sailing performance.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Understanding the pros and cons of different sail materials will help you make an informed decision when purchasing or maintaining your sails.
Understanding Sail Shapes and Configurations
The Science of Sail Shape
Sail shape is crucial for maximizing performance and efficiency. Properly trimmed sails allow you to sail efficiently, whether you’re sailing upwind or downwind.
Balancing Performance and Stability
Finding the right balance between performance and stability is essential. Adjusting sail shape and trim can significantly impact your sailing experience.
Fine-Tuning Sail Trim
Sail trim is an art form. Mastering the art of fine-tuning sail trim will make you a more skilled sailor and enhance your overall sailing experience.
The Evolution of Sail Designs
From Classic to Cutting-Edge
Sail design has come a long way. From classic traditional sails to modern, innovative designs, sailmaking has witnessed significant evolution.
How Technology Impacted Sail Design
Technological advancements have revolutionized sailmaking, resulting in more efficient, aerodynamic, and performance-oriented sails.
Innovation in Sailmaking
Sailmakers are continually exploring new materials and construction techniques to create sails that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient than ever before.
Sailing Techniques: Getting the Most Out of Your Sails
Tacking and Gybing
Tacking and gybing are essential sailing maneuvers used to change the direction of the boat and optimize the use of wind.
Maximizing Speed
To get the most out of your sails, understanding how to trim them properly and sail at optimal angles is crucial for achieving higher speeds.
Safety Precautions
Sailing is exhilarating, but safety should always be a top priority. Understanding safety procedures and precautions will ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
Maintaining and Storing Sails
Sail Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance are essential to prolong the life of your sails and keep them in top condition.
Storing Sails Properly
When not in use, storing sails correctly can prevent damage and maintain their performance over time.
Extending the Lifespan of Sails
With proper care and attention, you can extend the lifespan of your sails, making them a worthy investment.
Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Sail Materials
The Impact of Traditional Sails on the Environment
Traditional sail materials, while charming, may have a more significant environmental impact compared to modern, eco-friendly alternatives.
Eco-Friendly Sail Options
Eco-conscious sailors can explore sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental harm without compromising performance.
Embracing Sustainable Practices
As sailors, we have a responsibility to protect the oceans and environment. Embracing sustainable practices in sailing is essential for the well-being of our planet.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to different type of sails, I hope you now have a deeper understanding of the critical role sails play in sailing. Choosing the right sail and mastering sail techniques will elevate your sailing experience to new heights. Remember, sailing is an ever-evolving journey of learning and adventure.
Which sail is best for light winds?
The mainsail is the most suitable sail for light winds as it can efficiently catch even the slightest breeze and keep the boat moving smoothly.
What is the purpose of a genoa?
The genoa is a type of sails that provides additional power and versatility, making it an excellent choice for boosting speed and maneuverability in various wind conditions.
What sail material is most durable?
Modern sail materials like Dacron and Kevlar offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional canvas sails made of cotton or linen.
How do I maintain my sails?
Proper care and maintenance, including regular cleaning and inspection, will help prolong the life of your sails and ensure they perform optimally.
Are there eco-friendly sail options?
Yes, eco-conscious sailors can opt for sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental impact, contributing to a greener and more sustainable sailing experience.

Michael Thompson
Embarking on a lifelong love affair with the sea, I found solace and exhilaration in the art of sailing. From navigating treacherous waters to harnessing the wind's untamed power, my passion has evolved into a mission to inspire others. Join me on a voyage of discovery as we explore the vast horizons of sailing's timeless allure.
More to Explore

Sailing Apparel: Essential Gear for Smooth Sailing

Sail Boat Trailers: Your Guide to Safe and Convenient Transportation

Sail Boat Decor: Enhancing Your Nautical Oasis

Types of Sails on Sailboats: A Comprehensive Guide
Sailboats come in many shapes and sizes, but all have one thing in common: sails. The type of sail used on a boat can make a big difference in how it performs on the water. Understanding the different types of sails and their advantages and disadvantages can help sailors choose the right sail for their boat and the conditions they will be sailing in.
One of the most common types of sails is the mainsail. This sail is attached to the mast and boom and is used to catch the wind and propel the boat forward. Mainsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including full-batten, partial-batten, and no-batten designs. Each design has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the type of sailing the boat will be doing.
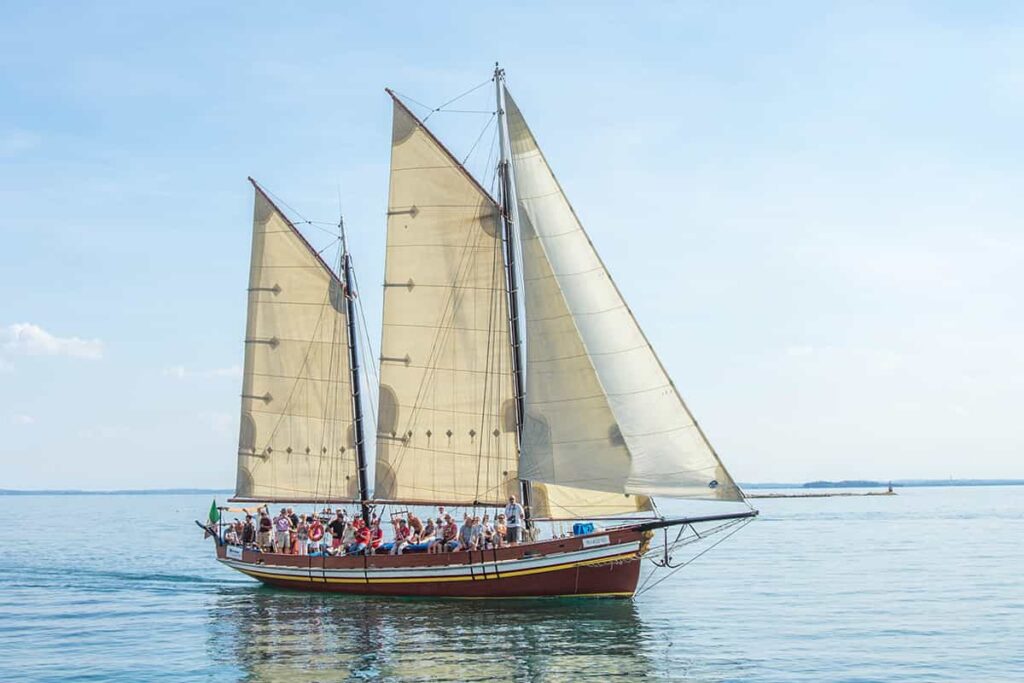

Another important sail on a sailboat is the headsail. This sail is located at the front of the boat and is used to catch the wind from the side. Headsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including genoas, jibs, and spinnakers. Choosing the right headsail can make a big difference in how the boat performs , especially in heavy wind conditions.
Basic Types of Sails
Sails are an essential part of any sailboat. They are used to harness the wind to propel the boat forward. There are several types of sails available for sailboats , and each serves a different purpose. Here are the three basic types of sails:
The mainsail is the most critical sail on a sailboat. It is a large, triangular sail that is hoisted up the mast. The mainsail is the primary source of propulsion for the boat and is used to control the boat’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the boom, which is a horizontal spar that runs along the bottom of the sail. The boom helps to control the mainsail’s shape and angle to the wind.
The mainsail can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the mainsheet, the traveler, and the boom vang. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The jib is a smaller sail that is located at the front of the boat. It is a triangular sail that is attached to the forestay, which is a wire that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat. The jib is used to balance the boat and to help control its direction. It is often used in conjunction with the mainsail to provide additional power and control.
The jib can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the jib sheet and the jib halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker is a large, colorful sail that is used for downwind sailing. It is a symmetrical sail that is attached to the boat’s mast and bow. The spinnaker is used to catch the wind and provide additional power to the boat. It is often used in racing and can help to increase the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the spinnaker sheet and the spinnaker halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
Specialty Sails
While many sailors may be familiar with the standard mainsail and jib combination, there are a variety of specialty sails that can be used for specific purposes. These sails can be particularly useful for racing, cruising, or for handling difficult weather conditions.
The genoa is a type of jib that is larger than the standard jib and overlaps the mainsail. This sail is particularly useful for upwind sailing as it provides more power and lift than a standard jib. The genoa is also useful for light wind conditions where a larger sail area is needed to catch the breeze.
A storm sail is a heavy-duty sail that is designed for use in strong winds and heavy seas. These sails are typically smaller than the standard mainsail and jib, and are made from heavy-duty materials such as Dacron or Kevlar. The storm sail is used to reduce sail area and provide better control in difficult conditions.
The gennaker is a hybrid between a spinnaker and a genoa. This sail is designed for downwind sailing and is particularly useful in light wind conditions. The gennaker is typically made from a lightweight nylon material and is larger than a spinnaker, but smaller than a genoa. This sail is particularly popular with cruising sailors as it provides a comfortable and stable ride in light wind conditions.
Sail Materials
Sailboats are equipped with sails made from a variety of materials. The type of sail material used depends on the intended use of the sailboat, as well as the budget of the sailor. The following are some of the most common sail materials used on sailboats today:
Dacron is a synthetic material that is commonly used in sails. It is durable, easy to handle, and relatively inexpensive. Dacron sails are ideal for cruising and recreational sailing, as they are not designed for racing or high-performance sailing.
Dacron sails are available in a variety of weights, with heavier sails being more durable and lighter sails providing better performance. Dacron sails are also available in a variety of colors, allowing sailors to customize the look of their sailboat.
Kevlar is a high-performance synthetic material that is commonly used in racing sails . Kevlar sails are lightweight, strong, and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, Kevlar sails are more expensive than Dacron sails and require more maintenance.
Kevlar sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material that is commonly used in racing sails. Carbon fiber sails are extremely lightweight and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, carbon fiber sails are the most expensive option and require the most maintenance.
Carbon fiber sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
In conclusion, the type of sail material used on a sailboat depends on the intended use of the sailboat and the budget of the sailor. Dacron is the most common sail material used for cruising and recreational sailing, while Kevlar and carbon fiber are used for racing and high-performance sailing.
Sail Shapes
Sail shape is an important factor in determining the performance of a sailboat. Different sail shapes are designed for different wind conditions, and the choice of sail shape can greatly affect a boat’s speed and maneuverability. Here are three common sail shapes:
Bermuda Rig
The Bermuda rig is the most common sail shape on modern sailboats. It consists of a triangular mainsail and a smaller jib or foresail. The triangular shape of the mainsail allows for efficient wind capture, while the jib helps to balance the boat and control the sail’s shape. The Bermuda rig is versatile and can be used in a wide range of wind conditions, making it a popular choice for cruising and racing sailboats .
The gaff rig is an older sail shape that was commonly used on sailing vessels in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It features a four-sided mainsail with a gaff spar at the top, which provides additional sail area. The gaff rig is less efficient than the Bermuda rig, but it has a distinctive appearance and can be used in light to moderate wind conditions. Gaff-rigged sailboats are often seen in traditional and classic boat regattas.
The lateen rig is a triangular sail shape that is commonly used on small boats and traditional sailing vessels in the Mediterranean and Middle East. It consists of a single, triangular sail that is mounted on a long, diagonal spar called a yard. The lateen rig is efficient in light to moderate winds and is particularly well-suited to sailing downwind. It is often used on small sailing dinghies and traditional wooden boats.
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

Lifeboats: Regulations and Requirements
In an emergency, portable vessels called lifeboats will get a ship’s occupants to relative safety. So how do lifeboats work?

What Are the Most Common Shipbuilding Woods?
While shipbuilders have switched to other practices, wood still has a place in the maritime industry. The numerous types available mean manufacturers have myriad options, so here’s a guide on shipbuilding woods.


Fiberglass vs. Steel: Which Is More Reliable?
Shipping professionals should get the most from their investment, so which is more reliable: steel vs. fiberglass? Here’s how to determine the better option.
How to choose the right sails for your sailboat
Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is crucial to ensure optimal performance, safety, and enjoyment while out on the water. This guide will help you navigate the world of sails and make an informed decision based on your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
How to Choose the Right Sails for Your Sailboat
Welcome to our unique and adventurous website, dedicated to those who are leaving the rat race behind, purchasing a boat, and setting sail to explore the world with their families. In this article, we will discuss one of the most important aspects of sailing: choosing the right sails for your sailboat. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about sails, from the different types and materials to the factors you should consider when making your decision.
Table of Contents
Introduction, storm sails, carbon fiber, sailing style, maintenance.
Sails are the heart and soul of any sailboat, providing the power needed to propel the boat through the water. Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is crucial to ensure optimal performance, safety, and enjoyment while out on the water. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to decide which sails are best suited for your needs. This guide will help you navigate the world of sails and make an informed decision based on your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Types of Sails
There are four main types of sails that you will encounter when outfitting your sailboat: mainsails, headsails, spinnakers, and storm sails. Each type of sail serves a specific purpose and is designed for different sailing conditions.
The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailboat and is attached to the mast and boom. It is responsible for generating the majority of the boat’s forward motion and is used in nearly all sailing conditions. Mainsails come in various shapes and sizes, with the most common being the standard triangular shape. Some other popular mainsail designs include the square-top, roach, and full-batten mainsails.
Headsails, also known as jibs or genoas, are the secondary sails on a sailboat and are attached to the forestay, a cable that runs from the mast to the bow of the boat. Headsails are used in conjunction with the mainsail to increase the boat’s speed and maneuverability. They come in various sizes, with larger headsails (genoas) providing more power in light wind conditions and smaller headsails (jibs) offering better control in stronger winds.
Spinnakers are large, lightweight sails designed for sailing downwind, with the wind coming from behind the boat. They are typically used in racing or when cruising in light wind conditions to maximize speed and performance. Spinnakers come in two main types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Symmetrical spinnakers are used for sailing directly downwind, while asymmetrical spinnakers are designed for sailing at an angle to the wind, known as reaching.
Storm sails are small, heavy-duty sails designed for use in extreme weather conditions when the wind is too strong for the mainsail and headsail. They are typically made from a durable material like heavy-duty Dacron or Kevlar and are designed to withstand high winds and rough seas. Storm sails include the storm jib, which replaces the headsail, and the trysail, which replaces the mainsail.
Sail Materials
Sails are made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and benefits. The most common sail materials include Dacron, laminate, Mylar, Kevlar, and carbon fiber.
Dacron is a type of polyester fabric that is widely used for sail construction due to its durability, affordability, and ease of maintenance. It is a popular choice for cruising sails, as it can withstand the wear and tear of long-term use and requires minimal maintenance. Dacron sails are typically heavier than other sail materials, which can result in reduced performance in light wind conditions.
Laminate sails are made from multiple layers of material, including a film of Mylar or other plastic, sandwiched between layers of woven fabric. This construction provides a lightweight, strong, and low-stretch sail that is ideal for racing or performance-oriented cruising. Laminate sails are more expensive than Dacron sails and require more maintenance, as the layers can delaminate over time, especially in high UV exposure areas.
Mylar is a type of polyester film that is used in the construction of laminate sails. It provides excellent strength and low stretch properties, making it ideal for high-performance sails. However, Mylar is susceptible to UV damage and can become brittle over time, requiring more frequent replacement than other sail materials.
Kevlar is an aramid fiber that is known for its incredible strength and lightweight properties. It is often used in the construction of high-performance racing sails, as it provides minimal stretch and excellent shape retention. Kevlar sails are more expensive than other sail materials and can be more difficult to maintain, as the fibers are prone to chafe and UV damage.
Carbon fiber is a high-tech material that is used in the construction of some of the most advanced racing sails on the market. It offers exceptional strength, lightweight properties, and minimal stretch, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Carbon fiber sails are the most expensive option and require specialized care and maintenance to ensure their longevity.
Factors to Consider
When choosing the right sails for your sailboat, there are several factors to consider, including your sailing style, boat size, budget, and maintenance preferences.
Your sailing style will play a significant role in determining the type of sails that are best suited for your needs. If you primarily sail for leisure and enjoy cruising with your family, you may prioritize durability and ease of maintenance over performance. In this case, Dacron sails may be the best choice for you. On the other hand, if you are an avid racer or performance-oriented cruiser, you may prefer the lightweight and low-stretch properties of laminate, Kevlar, or carbon fiber sails.
The size of your boat will also influence your sail selection, as larger boats require more powerful sails to propel them through the water. If you have a small to medium-sized boat, you may find that Dacron or laminate sails provide sufficient power and performance for your needs. However, if you have a larger boat, you may need to consider high-performance materials like Kevlar or carbon fiber to achieve the desired performance.
Your budget will undoubtedly play a role in your sail selection, as sail prices can vary significantly depending on the material and construction. Dacron sails are typically the most affordable option, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious sailors. Laminate sails are moderately priced, while Kevlar and carbon fiber sails are the most expensive options. It’s essential to weigh the benefits of each material against the cost to determine the best choice for your needs and budget.
Finally, consider the maintenance requirements of each sail material when making your decision. Dacron sails are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements, making them an excellent choice for sailors who prefer a low-maintenance option. Laminate, Kevlar, and carbon fiber sails require more specialized care and maintenance, including regular inspections for chafe, UV damage, and delamination. If you are willing to invest the time and effort into maintaining these high-performance sails, they can provide exceptional performance and longevity.
Choosing the right sails for your sailboat is a critical decision that will impact your sailing experience, performance, and enjoyment. By understanding the different types of sails, materials, and factors to consider, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs and preferences. Whether you prioritize durability, performance, or a balance of both, there is a sail option out there that will help you achieve your sailing goals and enjoy your time on the water.

Most Popular Types of Sails on a Sailboat

Learning about how there were different types of sails on sailboats for me was a bit strange at first. I thought something along the lines of “Don’t you just need to put some fabric on some polls and grab the wind?” Obviously, there’s far more to it than that.
So what are the most popular types of sails on sailboats? The mainsail, headsail (or jib), genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker are the most popular types of sails on sailboats. There are also a number of different configurations when considering the type of sail and mast in use including a sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat.
Simply put, different sailboat sails serve different purposes when out on the water.
The sail is kind of like the “engine” of your sailboat (of course, sailboats can have actual engines) in that it’s the main source of forward propulsion.
So, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why including the many different names of sails on a ship.
Types of Sails
There are a number of reasons why you’d want to use one sail over another, but the most important points to consider have to do with the point of sail you’re sailing in and the wind strength.
Maybe you need downwind sails, square sails, or a triangular sail. Maybe a unique sail shape, sail cloth, or sail area. With that in mind, let’s check out the different sail types!

The mainsail is by far the most popular type of sail on sailboats and is often the first image that comes to mind when thinking about a sailboat.
Mainsails are found behind the mast and attached to the boom, which makes it a common part of the sailboat to keep an eye on as it takes up a lot of real estate on a boat with sails especially during a sail tack.
Mainsails are able to cover a lot of surface area with respect to incoming winds, especially since they’re attached to the boom.
The fact that they have a large surface area means they don’t require very strong winds to provide good forward propulsion on a sailboat.
Also, since the position of the mainsail can be easily configured thanks to the boom, all points of sail are achievable.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail (or jib) is probably the second most popular type of sail on sailboats since it usually accompanies the mainsail.
The headsail is always placed at the front of the mast and can cover a good amount of the bow of the sailboat. It’s also smaller than a mainsail, making it more portable and easy to work with.
Headsails aren’t as big as mainsails, therefore they have a smaller surface area which results in the fact that they’re not capable of catching as much wind as a mainsail.
This is an important point though since if the current wind is exceptionally strong and your mainsail has been trimmed as much as possible, being able to put away your mainsail and depend on your headsail alone is an excellent strategy to reduce speed.
When the wind is just too strong to keep your mainsail out, putting it away and using only your headsail is a great option.
You won’t be grabbing as much wind as with the mainsail and you’ll be able to have a much more enjoyable (and safer!) sailing experience.
One of the most picturesque sailing images one can conjure up is the one with a sailboat using a genoa sail (see the image above on the right).
A genoa is a type of large jib that’s attached to the front of the forestay just like a headsail.
One of the main differences with the genoa sail is that it’s bigger than the normal headsail and oftentimes extends behind the mast partially or completely covering the mainsail. It actually used to be called an “overlapping jib”.
Using a genoa sail means you have light to medium winds and your sailboat is more or less in a dead run point of sail (wind coming directly from the rear or sailing downwind).
Since the surface area of a genoa sail is so large, it’s important only to use it when winds are relatively low. Otherwise, you’ll be moving exceptionally fast resulting in a potentially risky situation.
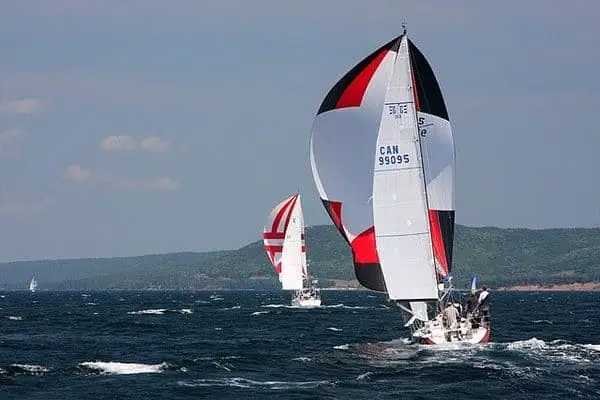

A spinnaker sail is a fun sail to use since it’s quite large, colorful, and can pick up a lot of wind.
Unlike a genoa sail, they’re often symmetrical making them more sensitive to the reaching points of sail and thus more appropriate for the running point of sail. They’re also lighter and have a “kite” kind of feel to them.
The reason they resemble a “kite” is not only that they’re generally lighter and more colorful than other types of jibs, but also they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail.
Instead, they don’t attach to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat. Since they’re bigger than genoa sails, you want to be even more careful to only use them in relatively low and non-volatile wind environments.

A gennaker sail is a more recent type of sail on sailboats since they were developed around 1990.
Gennakers are a cross between genoa and spinnaker sails (as the name might suggest), which are big like a spinnaker, aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker, and aren’t attached to the forestay like a genoa sail or headsail.
The reason for the invention of the gennaker is that sailors wanted to take advantage of lighter winds without having to resort to using a spinnaker if the winds change from a pure dead run to more of a reaching point of sail.
All in all, the gennaker sail is able to bridge the performance gap between a genoa and spinnaker sail in terms of being able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of relatively softer winds.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you’re familiar with the most popular types of sails on a sailboat, it’s good to get an idea of how these sail types relate to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast.
There are a huge number of combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, so I thought I’d lay out the most popular ones you’ll likely run into out on the water.

A sloop is the most common type of sail and mast configuration for sailboats. The sloop is the classic single mast, double sail setup.
The sails on a sloop consist of a mainsail and a headsail. The headsail can be different types of jibs, including the genoa, spinnaker, or gennaker sails. The headsail is connected to the forestay on the mast and runs all the way to the top of the mast.
Fractional Rig Sloop
Similar to a sloop, a fractional rig sloop has a single mast, double sail setup. The only difference, however, is that the forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast, resulting in the headsail being restricted to a fractional amount of space a normal sloop would allow for.
This reduction of surface area for the headsail means that less wind can be captured and, thus, reduced sailboat speed.
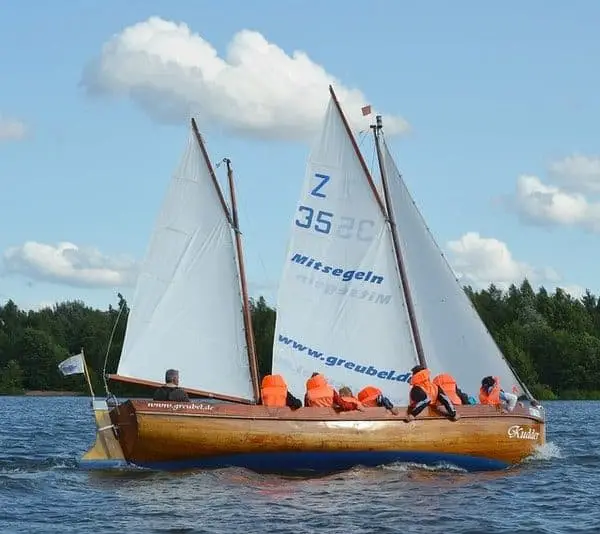

A cutter is an interesting setup since it’s just like the sloop and fractional rig sloop setup, but instead of one forestay it has two. With two forestays on the mast, cutters are able to house two headsails.
This can be a preferred setup because it allows for easy cruising due to it offering a diverse combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.

A ketch is a less common setup when compared to the previous setups since it has two masts.
Just like a sloop, it has a mast that allows for a mainsail and headsail with a full range forestay, but it also has a smaller sized mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
This mast configuration was commonly used in Northern European freighter and fishing boats and is called the mizzen mast.

If you’ve ever seen Pirates of the Carribean, you’ll have seen almost nothing but schooners. A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts, similar to a ketch, while having a number of sails to manage.
The main differences between a ketch and a schooner are that a schooner’s aft mast (the rear mast) is taller than the forward mast and a schooner can have up to six masts some including a square sail or two. This makes names of sails on a schooner the fore and aft sail (or fore and aft rig).
A yawl is almost identical to a ketch with the only difference being that the mizzen mast is located directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post. In terms of a ketch vs yawl, the mizzen sail is also much smaller than the mizzen sail on a ketch due to its position on the sailboat.

A cat has one mast and one sail with the mast being positioned at the bow of the sailboat. This mast configuration is most commonly found on smaller sailboats, especially dingy sailboats. These types of sailboats are colloquially called “catboats”.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Types of Sails on a Boat – Complete GUIDE for Cruiserlife
There are dozens, if not hundreds, of names for the many varied types of sails found on sailboats. Sailboats have been plying the waters and oceans of the world throughout history. When sailors had dozens of sails on board, they would need to quickly and concisely identify each sail, and each sail had a specific name.
Today, most modern cruising sailboats have just a few sails. The most common sails are the mainsail and the jib.
Table of Contents
Common sailboat terms and sail types, points of sail and wind speed, types of rigs, sailboat sail names, types of sails, gaff rig square sails, lateen rig sails, types of sails on a ship, types of sails on a sailboat, faqs – sails on a boat.
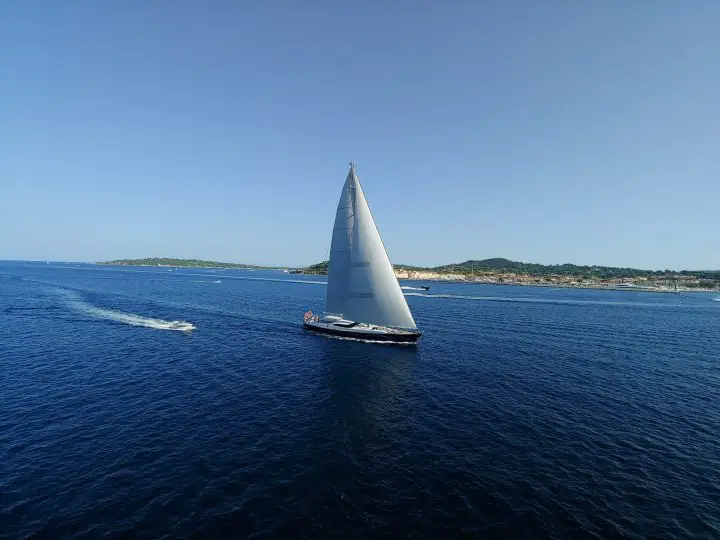

A sail’s job is to harness the power of the wind to get the boat moving. Selecting the right sail combination will get your sailboat moving fast and efficiently.
The sails each do different jobs in different wind conditions. The mainsail is aptly named. It’s the main sail and can be used in most wind conditions.
Sailboats may have just one or two sails onboard, or they may have a large assortment. Boats that race usually have many sails so that they can use the best sail combination to win.
A mast is a strong wood or metal pole that stands vertically on a sailboat. Its job is to provide a stable way of raising the mainsail and keeping the mainsail steady.
Mizzen Mast
On a two-masted sailboat, the aftmost and smaller mast is known as the mizzenmast. The mizzen sail is hoisted on it.
A boom provides structure and attachment points to the foot, or bottom, of a sail.
A special line that pulls a sail up to hoist it. When sailors are ready to put away the sail, they can release the halyard, and the sail will drop.
Roller Furler
A device that rolls a sail around a stay or inside a mast. A stay is a sturdy piece of rigging that helps keep the mast in place. A sail that is rolled on a furler can be easier to store and manage.
A hanked-on sail is a sail that doesn’t use a roller furling. Hanked-on sails are more traditional. This sail is stored in a bag instead of on a roller furler. To raise a hanked-on sail, the sailor must walk to the sail’s location and raise the sail using a halyard.
Apparent Wind Angle (AWA)
The apparent wind angle describes where the wind is coming from in relation to the sailboat. Let’s think of the sailboat as its own compass. The bow of the boat is 0 degrees. The side of the boat is 90 degrees. The stern (back) of the boat is 180 degrees. If the Apparanant Wind Angle is 160 degrees, the boat is headed almost downwind. Different sails are used in different AWA scenarios.
Close-Hauled
Close-hauled means the boat is sailing upwind. You can’t sail directly into the wind, but you can sail “close” to it. A boat sailing an AWA of 45 degrees is closed-hauled.
Reaching is often a preferred point of sail because it’s easy to manage. When a boat is reaching, the wind is coming from the side. A boat sailing an AWA of 90 degrees is reaching on a broad reach. At an AWA of 135 degrees, the boat is on a broad reach.
Sailing Downwind
A boat that is sailing downwind has the wind behind it. So, for example, if your AWA is 180 degrees, you are sailing dead downwind. Spinnaker sails are examples of a downwind sail.
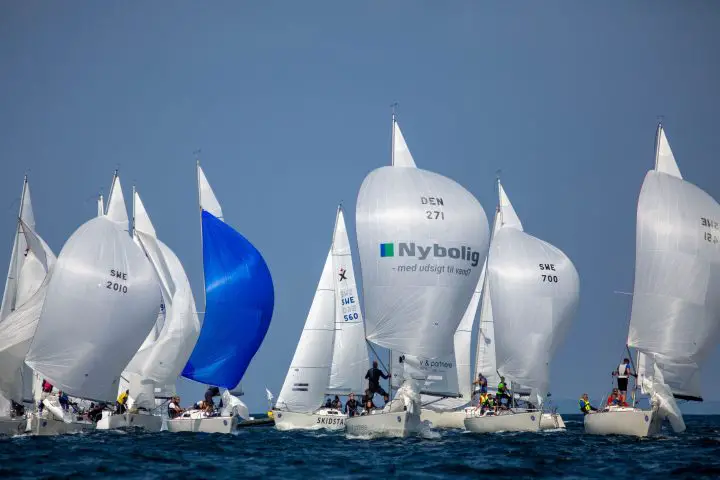

Light air refers to low-speed speeds. Anything less than about 12 knots is considered light air. Sailors will want to use light air sails to get the most out of light air.
Heavy Air refers to stronger winds. Any wind over 20-25 knots is considered heavy air. Sailors will want to reduce sail and use heavier sails to prevent damage to the sails.
What type of sails are on a boat depends on the sail’s rig. A sailboat’s rig design describes how many masts it has, where the masts are, and what type of sails it uses. There are different names for each mast configuration. The most common, single mast sailboat is called a sloop.
For example, a Bermuda rigged sloop has one mast, a mainsail, and a jib on the boat’s bow. A catboat has one large sail on a mast that is forward of the boat’s bow.
Bermuda or Marconi Rigged Sloop
The Bermuda rig is what is found on most sailing yachts today. The rig type was originally built in Bermuda in the 17th century. The term “Marconi Rig” comes from Guglielmo Marconi, who invented the radio in the 20th century. The standing rigging reminds people of radio masts.
The Bermuda sloop rig features a single mast with a mainsail attached to a boom. In addition, Bermuda rig sailboats have a jib mounted on the bow. On a fractional rig sloop, the arrangement is the same but the jib is much smaller. Instead of being mounted at the masthead, it is attached lower down the mast.
A lateen or Latin rig is one of the most traditional sail-rigs. This sail type was revolutionary in early history as it allowed sailors to sail into the wind. Before the lateen rig, square sail sailing vessels could only travel downwind. Romans used the lateen rig to navigate Europe. The lateen rig features a triangular sail set at an angle. It has a yard, or spar, at the top of the sail to provide structure. This rig isn’t common on sailing yachts, but it is common in the Mediterranean and the Indian Ocean.

The ketch features two masts. The main mast is similar to the main mast on a Bermuda rig. The second mast, called a mizzenmast, is smaller and set forward of the rudder. Ketches also have a jib mounted on the bow. Ketches are popular as they allow sailors to carry a large sail area that is manageable.
A yawl has two masts and is similar to a ketch. However, the smaller mast, or mizzenmast, is set aft of the rudder. A yawl’s mizzen boom overhangs the stern of the boat.
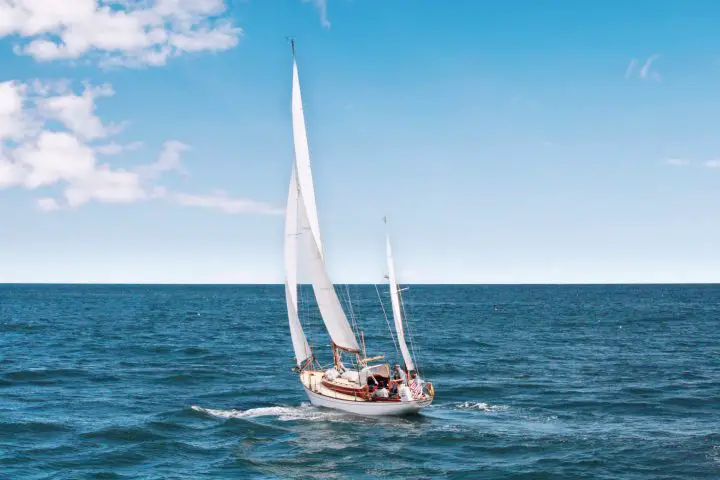

A schooner has two or more masts. On most masts, the mainmast is usually taller than the foremast. However, some schooners have masts that are all the same height. Schooners might have two, three, or four masts. They often feature gaff-rigged sails. These beautiful, traditional boats were popular from the 17th to the early 20th centuries.
Gaff-rigged boats can be sloops, schooners, ketches, or yawls. A gaff-rigged boat has a large mainsail attached to the mast. The gaff sail’s foot (the bottom of the sail) is usually attached to a boom. On a sloop, there will be just one gaff mainsail. On a schooner, there will be two gaff-rigged mainsails. The gaff-rigged boat always has more than one sail. For example, gaff-rigged boats may have several headsails. Gaff-rigged boats were popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and won many America’s Cup races.

A catboat has a mast that is forward on the bow. It usually has one big gaff-rigged sail. It’s different from a gaff rig because it has just one sail. Most catboats are under 26 feet in length. A few catboat designs have Marconi-style sails, which are triangular instead of square.
Let’s focus on the types of sails carried by most modern cruising boats. Most of today’s cruising and liveaboard boats are Bermuda rigs, followed by ketches and yawls. For the sake of simplicity, we’ll assume that our standard boat with standard sails has a Bermuda rig.
- Spinnaker Sail
The mainsail is the most important and most used sail on a sailboat. The mainsail is attached to the main mast and the boom. On a Bermuda rig, the mainsail is usually triangular.
The mainsail is raised up the mast using slides that fit inside a sail track. The mainsail, once raised, provides most of the lift needed to move a sailboat. When wind pushes on the sail, air particles rush over both sides of the sail. The particles on the outside, curvier side of the sail have a longer distance to travel. As a result, they speed up and travel faster and form a low-pressure area. The particles on the inside of the sail are moving slower and create a high-pressure area. The difference produces lift and moves the sail forward.
Most cruising mainsails have reef points. Reef points give sailors the ability to reduce the size of a sail. When it gets too windy, sailors can reef the sail and not overpower the boat or damage it. Sailors need to reef sails to provide a more comfortable ride, keep the boat controllable, and lessen the risk of damage or capsize. A reef point allows the sailor to take down the lowest part of the sail and tie the mainsail at a new, smaller size.
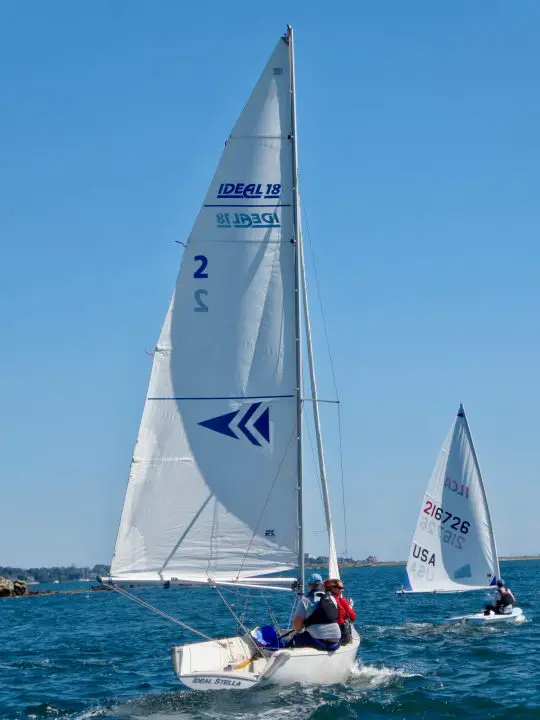

Mainsails with Battens
Some mainsails are full-batten. A batten is a flexible insert, often made with plastic, that fits in an insert on the mainsail. The battens are in line with the boom and are inserted fore-and-aft. These battens help the mainsail keep its shape and prevent the sail from flapping loosely.
Mainsails with Partial Battens
A partial batten mainsail features battens that don’t run the whole width of the sail. Because the sail is more flexible without full battens, sailors can more easily adjust the sail’s shape. Battens are heavy, and the added weight might decrease performance, so many sailors choose to have a partial batten sail.
Mainsails with Square Tops
Some boats have mainsails that, instead of completing the triangle, are squared off. A square top mainsail has more sail area and therefore should improve the boat’s performance. Square top mainsails are popular with boaters that race or want to get the most out of their sails performance.
Furling Mainsails
Most mainsails are attached to the mast with slides. When not in use, the mainsail sits on the boom in a sail cover. However, there are newer ways of storing and managing mainsails. Furled mainsails are becoming more popular. An in-mast-furled mainsail is similar to a jib on a roller furler. The sail is stored inside the mast and rolled out and rolled back in.
Some modern sailors opt for boom-furled mainsails. This type of mainsail is stored inside a specially-built boom. The sail is raised by unrolling the sail. Sailors can reef or reduce the sail size by rolling some of the sail back up.
Headsails are mounted at the head of the boat, usually attached on a the forestay from the bow to the top of the mast. A jib is one of the most common types of headsail.
A jib’s purpose is to generate lift and reduce the mainsail’s leeward side turbulence. A jib can be used in most sailing conditions and apparent wind angles. For example, if the boat is headed downwind, the jib might be flown by itself. Or, the jib might be poled out to port while the mainsail is sailed to starboard. This type of configuration is called wing-on-wing.

Roller Furled Jibs
Many modern cruising boats have roller furled jibs. The jib can be easily unfurled when the sailor is ready to use it and furled back up for onboard storage. Sailors can reef, or reduce, the sail area by rolling the jib in a small amount. Sailors can control a roller-furled jib with sheets (lines) that lead to the cockpit.
Hank-On Jib
Hank-on jibs are stored in a bag and raised with a halyard. This requires a sailor to physically move forward to the bow to raise the jib. However, a roller furler requires maintenance and can get stuck, so a hank-on jib might be considered more reliable.
Headsail Percentage
You might have heard sailors refer to a percentage along with a jib. For instance, a boat might have a 110% jib or a 135% genoa. This percentage refers to how much area the sail uses within the forward triangle. For example, a 100% jib takes up 100% of the fore-triangle. A 115% jib starts to overlap the mast. Most standard jibs are between 100%-115%.
If a boat sails in an area of heavier winds, it is likely to have a jib as a headsail instead of the larger genoa.
A genoa is a headsail. This sail is similar to a jib, but it is larger. Genoas overlap the mast. Most genoas overlap the mast by 120%-150%. So if someone says they have a 130% headsail, they have a genoa. Genoas work better than jibs in areas of lighter winds. This is because their larger size allows them to capture more wind. Since many boats have roller furlers on their headsails, a large genoa can be rolled up slightly and flown as if it were a smaller jib when the wind pipes up.
A staysail is smaller than a jib and located just behind the jib sail. When a Bermuda rigged boat has a staysail, it is called a cutter. The staysail offers the sailor an additional sail area. If the boat is headed upwind in good sailing conditions, the staysail will provide lift. The staysail is often used along with a reefed mainsail and provides stability to the boat.
Downwind Sails
Most sailors dream of downwind sailing. It’s easier on the boat and crew to fly along with the wind at your back. Downwind sailing can also mean light-wind sailing. A downwind sail is often made of lighter sail cloth and provides the most sail area possible.
Symmetrical Spinnaker
A spinnaker is a very large and often colorful sail mounted at the bow of the boat. A spinnaker almost looks like a parachute and is built to offer as much sail area as possible. A symmetrical spinnaker has the same shape on either side of its centerline.
A spinnaker can be used when the AWA is between 90 degrees and 180 degrees. In addition, they can be flown when the wind is between three knots and up to 20 knots.
Most boats use a spinnaker pole to give the spinnaker a proper shape. A spinnaker is often considered hard to manage because sailors must spend time to set it up correctly. In addition, it can be challenging to take down if the wind speed increases. This large sail is also challenging to store on a boat.
Asymmetrical Spinnaker
An asymmetrical spinnaker has a more triangular shape than a symmetrical spinnaker. Asymmetrical spinnakers are known to be easier to set and manage than symmetrical spinnakers. Racers usually prefer symmetrical spinnakers, and cruisers usually prefer asymmetrical spinnakers.
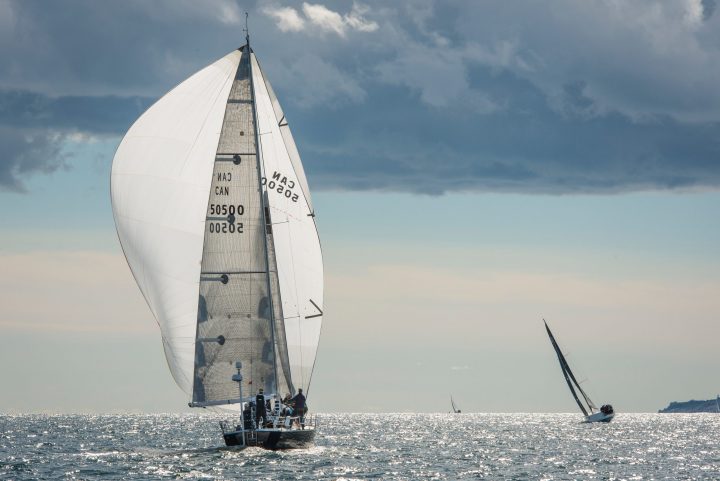

A gennaker is a combination of the best parts of a genoa and a spinnaker. A gennaker can be mounted on a furler, making it easier to store and manage. A gennaker is attached like a genoa but has more girth like a spinnaker. It is popular among cruisers who want the performance of a spinnaker but the easy handling of a genoa.
A code zero sail was originally created for racing boats but has become extremely popular on cruising boats. It’s lightweight and can be used in more wind conditions than a spinnaker. It is used to sail in light air and can be used when the sailboat is reaching.
The code zero sail can also be used when the boat is close-reaching or going closer to the wind. Depending on the exact sail plan, code zeros can be used when the apparent wind angle is between 45 degrees to 180 degrees.
Code zero sails can be flown when the wind speed is between about five knots and 25 knots. Because it is heavier than a spinnaker, it can be used in higher winds.
Code zeros are much bigger than other furled headsails and can be twice the size of a regular jib. A code zero sail can be stored on a roller furler, making it easy to store and use.
A drifter is a large sail that’s used in very light winds, usually less than 10 knots. It can be used when the AWA is between 45 degrees and 180 degrees. Because a drifter is large, hard to store, and only usable in the lightest of winds, it is not commonly used on cruising boats.
Most cruising boats sail in decent weather conditions and can reef their mainsail and jib and keep sailing. However, in storm conditions, a storm sail could be flown. A storm sail is small and made of heavy sailcloth. Its purpose is to keep the boat steady in storm conditions.
Storm sails can be attached to the forestay or to the mainmast. A storm jib is attached to the forestay, either in place of or over the rolled jib. A trysail is attached to the mainmast.
A gaff-rigged sail has a spar or pole on the top of the sail. It is also attached to the mast and boom. Gaff-rigged sails look almost square. Because a square has more area than a triangle, these sails have more sail area. The mast on a gaff-rigged sailboat is often shorter than a comparable Bermuda-rigged boat. A gaff rigged mainsail can be shorter because it has increased area.
The lateen sail is triangular and has a spar that runs from the boat’s bow to the top of the sail.
The lateen was the world’s earliest fore and aft rig sail. This type of sail revolutionized transportation during medieval times. The Romans were the first to start using a lateen rig in the Mediterranean. This new style of rig meant that sailors could sail more into the wind. Previously, sailboats were rigged with square sails that could only sail downwind.

Traditional ships had a significant amount of sail area spread across a host of sails. Each sail had a specific name so that sailors could easily communicate. Additionally, each different mast configuration has a different name. Ships can carry up to six masts. A fully-rigged ship is one with square rigs on three or more masts.

Traditional Square-Rigged Sails
Traditional ships came in a variety of sizes. Each ship was built to its own custom specifications. For the sake of simplicity, we’ll look at the rig on an 1850s sailboat.
This boat has three masts and 25 sails in total. Before engine power, sailors relied entirely on the wind to move their ships. Faster ships meant that produce had less time to spoil. The faster your ship was, the more competitive it was. Arriving with the first batch of sugar or fine wine would gather more interest and excitement at the dock than arriving three weeks later.
This ship has four headsails at the front of the boat. The headsails include the flying jib, the outer jib, the inner jib, and the fore topmast staysail.
Each mast has five or six sails, and each sail name on each mast starts with the name of the mast. For example, the most forward mast is the foremast. Each sail is a fore-sail. Thus, the foremast’s sails include the forecourse, fore-topsail, foretopgallant, fore royal, fore staysail, and fore moonsail.
Between the foremast and the mainmast, there are three staysails.
The main mast has the same sails, but each sail name begins with “main” — main course, main topsail, etc.
The mizzenmast, which is located on the aft of the boat, has five sails. Each sail name starts with the word mizzen –
– mizzen topsail, etc.
Finally, at the aft of the boat, there’s a gaff-rigged spanker sail.
As you can see, traditional sailing ships had a large assortment of sails that kept the boat moving in all wind conditions.
Sailors could carry many different sails on a sailboat. If you are into racing, you’ll likely carry a wider variety of sails. Racers often carry sails for every wind condition to get the most speed from their boat. Racing sailboats often have many crew members that don’t mind frequently changing sails.
On a cruising sailboat, the dynamic is different. Often, cruisers may be sailing with just one other person. Space is devoted to supplies and comfort instead of a huge inventory of sails. With a small crew and fewer exacting time restraints, cruisers might not want to change their sails every few minutes.
Cruising sailboats usually carry at least a mainsail and a jib or genoa. In addition, cruising sailboats that spend a lot of time sailing downwind or in light air might have an additional light air sail, such as a spinnaker, gennaker, or a code zero.
How many sails are on a boat?
Most cruising sailboats carry at least two sails, the mainsail, and the jib. Many cruising sailboats carry additional sails such as a staysail, code zero, or storm sail. A racing sailboat might carry up to a dozen sails. Traditional sailboats have many sails– a large sailing ship usually carried around thirty sails.
The number of sails aboard each sailboat depends on the boat’s rig design, the sailor’s goals, sailing area and average wind conditions, and the sailor’s preferences.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.

7 Different Types of Boat Sails
Posted on July 1, 2022

Sails, like boat hulls and engines, have evolved. For example, the ships that traveled the oceans a little over a hundred years ago had multiple masts and may have had eight to ten sails. Likewise, as recreational boats have evolved, so too have many sail types used by wind-powered vessels.
Many of what was and what is are similar. However, early sailboats had different sails made from canvas. Likewise, the sails of today’s boats use space-age materials very different from the canvas sails of yesteryear.
The size and rig of a boat determine the type of sails it will use and the number it employs. For example, small boats like the Optimist pram, Laser, and sunfish use only one sail. While sloops use two sails, a main and jib, cutter-rigged sailboats have two headsails and a mainsail.
At the other end of the spectrum are ships such as the Golden Horizon with 35 sails that can drive it across the world’s oceans. Square sailboats still had mainsails, topsails, and jibs. However, they cannot sail close to the wind, which the gaff and Bermuda rigged boats could.
A square sailed ship can only get within 60 degrees of the direction of the wind. However, small Bermuda-rigged sailboats can get as close as forty degrees to the wind.
A boat that can sail higher (closer to the direction of the true wind) will reach its destination first. The reason is that it will not need as many tacks to make headway and close its distance to its goal.
Along with their diminished usefulness and the advent of steam, gas, and diesel-powered engines, the great sailing ships of yesteryear are mostly gone or in a floating museum somewhere.
However, in the 1960s and 1970s, many boats came to market. From dinghies to hundred-foot-long sailboats and vessels such as the Maltese Falcon and the Golden Horizon, the creativeness of naval architects still comes through with surprises.
Therefore, sailing is long from dead. On the contrary, even those who power huge ships across the world’s oceans have considered adding sails to reduce fuel usage on their travels.
1. Main and mizzen sails

A mainsail is the largest sail of a boat , and you attach it to the back of the main mast. If you have a boat with two masts, the smaller of the two is the mizzenmast, which carries the mizzen sail. The mizzen is smaller than the main on boats that are Bermuda rigged.
However, gaff-rigged ketches and schooners may have a mizzen sail almost the same size as the mainsail.
Headsails (jibs) are set in front of the mast. You can have jibs for light air, medium air, and storms; of course, they all have different names that are often based on their use.
2. Gaff-rigged sailboats

The boating industry changed slowly. When smaller yachts were being built in the early to middle 1950s, many privately owned sailboats still had gaff rigs, as do a few production boats today.
Catboats, which have a single mast and a single sail, are often gaff rigged. However, even today’s gaff-rigged boats use modern technology to make them more efficient than the boats that came before them.
What is a Gaff rigged boat?
Most modern sailboats use a mainsail called a Bermuda or Marconi sail. These sails are triangular and can be formed into a better foil shape than a gaff-rigged sail.
Gaff-rigged boats have a mainsail that hangs in the same place as modern sails. However, they are rectangular and have an upper boom (gaff) and a lower boom that holds the sail open and shapes it.
Although this type of sail and rig are very effective, the Marconi rig is easier to handle. It does not require a crew of husky sailors to raise and lower the sails.
3. Bermuda rigged sailboat — aka the Marconi sail.

The Marconi sail is a variant of the Bermuda rig that has been used in that country since the 1600s. The Marconi rigged sailboat has a similar sail and got its name during the 1899 America’s Cup Yacht race in New York City.
The rig got this name because it reminded sailors of Guglielmo Marconi’s radio antenna. The wires that held the masts upright looked much like those that held Marconi’s radio antennas in place that he used to broadcast the race results to people worldwide.
The Bermuda-rigged sail is easier to handle than a gaff-rigged sail and is lighter; one person can raise and lower this type of sail. This advantage allowed sailors to go venturing alone because the crew is optional, not mandatory, in a Bermuda-rigged boat.
Sailboats with only one mast are sloop-rigged if the boat has only one headsail and a Cutter if the boat has two headsails.
4. Square sails

This type of sail was used on boats pre-1900 and afterward. Square sails have a top-mounted boom. This sail is trimmed by moving the two lower corners with lines leading to the deck. Unfortunately, square sails, and the boats that use them, are not as efficient or as easy to handle as today’s sailboat rigs.
However, the Maltese Falcon uses an automated square rig configuration with DynaRig technology, which is ingenious. With a length of 289 feet, the Maltese Falcon has a crew of 18. However, one person from the well-appointed bridge can control the automated sail system.
5. Mizzen sails

Modern sailboats that carry mizzen sails include yawl and ketch rigged sailboats. A yawl-rigged boat has the mast stepped behind the rudder, and a ketch has the mast stepped in front of the rudderpost. The difference is minor; however, a ketch will carry a larger mizzen sail than a yawl, giving it more sail and power.
Other sailboats with two masts include the Schooner and the Brigantine (brig). However, on these rigs, the aft mast is taller than the foremast, or almost the same height.
6. Top sails

Topsails are used on gaff-rigged sailboats and are set above the sail’s top gaff. They fill the upper triangular area above the main and add sail power. However, topsails aren’t limited to gaff-rigged boats.
Many Marconi rigged ketches and yawls will often set a topsail above the mainsail for more power, especially in light air situations.
7. Foresails have many different names and purposes.

The foresail triangle is where all the action has been on the innovation of sails. However, the mainsails have changed over the years, but not like foresails.
The advent of full batten sails, and systems that raise and lower sails with the push of a button, has made sailing easier.
Foresails, on the other hand, (the sails in front of the mast) have evolved into many fantastic purposes.
They will continue to evolve as people push the edges of their speed on the water-powered purely by the wind.
Most modern sailboats have one, two, and sometimes three foresails attached to their roller furling systems. This configuration of a sailboat will let you take down one sail and unfurl another while on the fly.
Roller furling sails, from the jib to the mizzen, are wonderful innovations. Roller furling started on headsail and has moved to the entire rig on many boats. The addition of roller furling to main and mizzen sails has caught on and remained popular for a good reason.
A wet foredeck is scary, and the ability to furl and unfurl your sails from the cockpit or cabin makes sailing easy for almost everyone. In addition, these advances have allowed sailors of advanced years to stay on the water longer.
Self-tacking jib

Jibs are set in front of the mast and often have a boom. With a boom or not, self-tacking jibs eliminate a trip to the foredeck. When you change course, and if it is fitted with a boom, you have a lot of control over it. Also, most jibs fit within the fore triangle, eliminating them from being snagged on the rigging as you go from one heading to the next.
Jibs can be lightweight for light air, minimal, and very strong when the wind picks up. Storm jibs are heavily built and may not be much bigger than a small tablecloth. When you need to put this sail in action, you have reached the point of riding it out, whatever ‘it’ happens.

Jib tops have a foot well above deck level, and are used in conjunction with a second jib, usually the staysail. You can also use a jib top with reachers and spinnakers.
Their high foot (the bottom of a sail) keeps them clear of the deck, leaving you free to work the foredeck.
Keeping a jib top sail flying when setting other sails can keep your boat from stalling while raising and lowering spinnakers, reachers, or a Code Zero.
Genoas are jibs, too.
The Genoa is also a headsail and is called a jib, too, because they are. However, some genoas are so big they will overlap your mainsail. Genoas are described by the amount of overlap of the mainsail it covers or its purpose, such as a genoa staysail.
They can have a 50 to 100 percent overlap of the mainsail, and you can use a genoa on sailboats in light to moderate air. Genoa staysails also remain inside the forestay, and you can use them with other genoas and Code Zero sails.
However, over the years, sailmakers have designed sails for any wind. As a result, there are very lightweight sails for days void of much wind and heavily made sails that can keep your boat stable in a blow.
Special foresails for sailboats

Cutter-rigged sailboats have two headsails. The sail set most forward is the Yankee jib, while the aft foresail is the staysail. Modern sailboats often have second and third halyards that give you many options when choosing what headsail to set.
These sailing innovations have effectively turned most modern sloops into cutter rigs, giving you a great deal of control over how you want and need to sail your boat.
The flying jib gets its name because it is much like a spinnaker, so it flies before the wind. So, naturally, they are set in front of the forestay, often on a fixed or retractable bowsprit.
You can use a flying jib with a spinnaker pole to help it keep its shape, especially in light air. The flying jib will give your sailboat a speed jump, whether you are running downwind or on a reach.
Another type of foresail, reachers, are very lightweight and are typically used in winds between one and 15 knots when close-hauled and driving into the wind. However, it is also suitable as a downwind sail in light air.

This is the most easily recognized sail beside a typical main and jib. The spinnaker is the big ballooning sail that boats use to sail downwind. This point of sail is called ‘running’ and can take some boats to planing speeds.
Like spinnakers, Code Zero sails are exclusively for downwind sailing. Drifters and genoas can be used downwind also. However, they are not as efficient because they attach inside the fore triangle and can’t reach as far to the left or right when sailing before the wind.
Like spinnakers, Code Zeros are set outside the fore triangle, and you can set them with a spinnaker pole. The sail is designed to catch every puff of wind possible. Code Zero sails are designed to fill the gaps of the dedicated downwind spinnaker.
Better Sailing

Names of Sails on a Sailboat
Are you a beginner sailor and want to get acquainted with the names of the sails? Are you an experienced sailor and want to learn more details about the sails on a sailboat? Then this article is written for you! Sails form a crucial part of the sailboat because without them, there’s no starting up. For that reason, there are many details about different types of sails concerning their utility, functionality, fabrication materials, and performance. Simply put, each sail serves different purposes when out on the water. Since the sail is the engine of your sailboat, in terms of it being the basic source of propulsion, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why.
Types of Sails on a Sailboat
So, in order to better explain the types of sails, let’s look at their characteristics. The first important distinction between sails is their placement. Generally, the mainsail is placed aft of the mast , which means behind. On the contrary, the headsail is in front of the mast. There are also other sorts of sails that are used for specific conditions. These can be the spinnakers or balloon-shaped sails for downwind use. The second important distinction for the sails is their functionality. The specialized sails have different functionalities and are used in different sailing circumstances and weather conditions. A rule about sails is that large sails are appropriate for downwind use, whereas small sails are good for upwind use. Moreover, large sails perform better on weak winds while small sails are good for strong winds.
The Parts of a Sail and its Shapes
- Head: This is the top of the sail.
- Luff: The forward edge of the sail.
- Leech: Back edge of the sail.
- Tack: The lower front corner of the sail.
- Clew: The bottom back corner of the sail.
- Foot: Bottom of the sail.
There are two sail shapes, the fore-and-aft rigged sails, and square-rigged sails. Nowadays, fore-and-aft sails are more popular, have better performance and maneuverability. To grasp the idea square sails are the ones that Vikings had on their ships and are good at sailing downwind because they run from side to side. But they’re not suitable at all when sailing upwind. On the other hand, a fore-and-aft sail is tied from the front of the mast to the stern and is much better at sailing upwind.

Also Read: What is Sailboat Rigging?
Types and Names of Sails
There are a lot of reasons why you’d want to put one sail over another, but the most important thing to remember has to do with the point of your sail and the wind strength. These points help you understand how your sailboat generates wind power. These points of sail include: into the wind (in irons), beam-reaching, broad-reaching, close-hauled, close-reaching, and running. They all go from windward to leeward and are symmetric from port to starboard . So, let’s get to the point and see the names and explanation of each sail:
- Mainsail : The large sail behind the mast which is attached to the mast and the boom, is called the mainsail. Mainsails cover a lot of surface area concerning incoming winds and by doing that they don’t need very strong winds to provide forward propulsion on a sailboat.
- Headsail or Jib : The small sail placed in front of the mast, attached to the mast and forestay (ie. jib or genoa), is called the headsail. Headsails are smaller than mainsails, thus their surface area is smaller. As a result, they can’t catch the same wind as a mainsail does. However, this is important because in case that the current wind is strong and the mainsail has been enough trimmed, being able to remove the mainsail and depend on the headsail alone, is a good strategy in order to reduce speed.
- Genoa : A genoa is like a large jib and it’s attached to the front of the forestay, like a headsail. When you use a genoa sail then you are expecting light to medium winds. Also, your sailboat would be somehow in a rush point of sail, meaning that the wind comes directly from the rear. Moreover, the surface area of a genoa sail is quite large, so it’s important to use it when winds are relatively low.
- Spinnaker : These downwind sails are symmetrical which makes them more sensitive to the reaching points of the sail and therefore more suitable for the running point of sail. Spinakkers are lighter than other types of jibs, and they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail. Moreover, they remain unattached to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat.
- Gennaker : Gennakers are a mixture of genoa and spinnaker sails. There are small and big gennakers and both are downwind sails. They aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker and aren’t attached to the forestay like a headsail. Furthermore, the gennaker sail is able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of softer winds.
- Drifter Reacher : A drifter is a light air sail, and it’s basically a larger genoa for use in light winds. Its extra sail area offers better downwind performance than a genoa. It’s mostly made from lightweight nylon.
- Code Zero Reacher : This sail is a type of spinnaker, but it looks like a large genoa. However, code zero is designed for better reaching which makes it much flatter than the spinnaker.
- Windseeker : This sail is small, and it’s designed to guide light air onto the lee side of the mainsail. Moreover, it’s tall and thin and ensures a smoother flow of air.
Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you got an idea of the different types of sails on a sailboat, it would also be an advantage to know how these types of sails are related to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast. There are numerous combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, let’s see some of them!
- Cat: A cat is similar to a dinghy and has one mast and one sail. The mast is located at the bow of the sailboat.
- Sloop: The sloop has the classic single mast and a double sail setup. The headsail can be different kinds of jibs, is connected with the forestay on the mast, and runs all the way up to the mast.
- Fractional Rig Sloop: A fractional rig sloop is different from the sloop because its forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast. Its headsail is restricted to a fractional amount of space and this means that less wind can be captured, therefore the speed of the sailboat is reduced.
- Cutter: Having two forestays on the mast and cutters that are able to house two headsails this setup allows easy cruising because it offers a wide combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.
- Ketch: Just like a sloop the ketch has a mast that enables the mainsail and headsail to a full range forestay. However, it also has a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
- Schooner: A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts but it has a couple of sails to manage. A schooner’s aft mast is taller than the forward mast and sometimes a schooner can have up to six masts.
Names of Sails on a Sailboat – Summary
So, how many types of sails are there? In general, sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The rigging also affects the types of sails you can use. As we’ve explained before, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft Bermuda rig. Then, for a headsail, we use a jib or genoa. Most experienced sailors use extra sails to ensure better performance for their sailboat. For example, the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), the gennaker, the code zero (for upwind use), and the storm sail. Keep in mind that every sail has its own use and performance. Want to go downwind fast? Use a spinnaker. Don’t just raise any sail you think suits you best and go for it! It’s of great importance to understand the functionality, use, and performance of each sail.
Peter is the editor of Better Sailing. He has sailed for countless hours and has maintained his own boats and sailboats for years. After years of trial and error, he decided to start this website to share the knowledge.
Related Posts

Lagoon Catamaran Review: Are Lagoon Catamarans Good?

Best Inboard Boat Engine Brands

Are O’Day Sailboats Good? A Closer Look at a Classic Brand

Why Do Sailboats Lean?
- Buyer's Guide
- Destinations
- Maintenance
- Sailing Info
Hit enter to search or ESC to close.

Types of Sailboats: A Complete Guide

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
Learning the different types of sailboats can help you identify vessels and choose the right boat.
In this article, we'll cover the most common kinds of sailboats, their origins, and what they're used for. We'll also go over the strengths and weaknesses of each design, along with when they're most useful.
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels.
The information found in this article is sourced from boat reference guides, including A Field Guide to Sailboats of North America by Richard M. Sherwood and trusted sources in the sailing community.
Table of contents
Distinguishing Types of Sailboats
In this article, we'll distinguish sailboats by traits such as their hull type, rig, and general configuration. Some sailboats share multiple characteristics with other boats but fall into a completely different category. For example, a sailboat with a Bermuda rig, a large engine, and a pilothouse could technically be called a sloop, but it's more likely a motorsailer.
When discerning sailboat type, the first most obvious place to look is the hull. If it has only one hull, you can immediately eliminate the trimaran and the catamaran. If it has two or more hulls, it's certainly not a typical monohull vessel.
The next trait to consider is the rig. You can tell a lot about a sailboat based on its rig, including what it's designed to be used for. For example, a long and slender sailboat with a tall triangular rig is likely designed for speed or racing, whereas a wide vessel with a complex gaff rig is probably built for offshore cruising.
Other factors that determine boat type include hull shape, overall length, cabin size, sail plan, and displacement. Hull material also plays a role, but every major type of sailboat has been built in both wood and fiberglass at some point.
Sailboat vs. Motorsailer
Most sailboats have motors, but most motorized sailboats are not motorsailers. A motorsailer is a specific kind of sailboat designed to run efficiently under sail and power, and sometimes both.
Most sailboats have an auxiliary engine, though these power plants are designed primarily for maneuvering. These vessels cannot achieve reasonable speed or fuel-efficiency. Motorsailers can operate like a powerboat.
Motorsailers provide great flexibility on short runs. They're great family boats, and they're popular in coastal communities with heavy boat traffic. However, these features come at a cost. Motorsailers aren't the fastest or most efficient powerboats, and they're also not the most agile sailboats. That said, they make an excellent general-purpose sailing craft.
Monohull vs. Multi-hull: Which is Better?
Multihull sailboats are increasingly popular, thanks to advances and lightweight materials, and sailboat design. But are they better than traditional sailboats? Monohulls are easier to maintain and less expensive, and they offer better interior layouts. Multihulls are more stable and comfortable, and they're significantly easier to control. Multihull sailboats also have a speed advantage.
Monohull Sailboats
A monohull sailboat is a traditionally-shaped vessel with a single hull. The vast majority of consumer sailboats are monohulls, as they're inexpensive to produce and easy to handle. Monohull sailboats are proven and easy to maintain, though they lack the initial stability and motion comfort of multi-hull vessels.
Monohull sailboats have a much greater rig variety than multi-hull sailboats. The vast majority of multihull sailboats have a single mast, whereas multi-masted vessels such as yawls and schooners are always monohulls. Some multi-hull sailboats have side-by-side masts, but these are the exception.
Catamaran Sailboats
The second most common sailboat configuration is the catamaran. A catamaran is a multihull sailboat that has two symmetrical hulls placed side-by-side and connected with a deck. This basic design has been used for hundreds of years, and it experienced a big resurgence in the fiberglass boat era.
Catamarans are fast, efficient, and comfortable. They don't heel very much, as this design has excellent initial stability. The primary drawback of the catamaran is below decks. The cabin of a catamaran is split between both hulls, which often leaves less space for the galley, head, and living areas.
Trimaran Sailboats
Trimarans are multi-hull sailboats similar to catamarans. Trimarans have three hulls arranged side-by-side. The profile of a trimaran is often indistinguishable from a catamaran.
Trimarans are increasingly popular, as they're faster than catamarans and monohulls and considerably easier to control. Trimarans suffer from the same spatial limitations as catamarans. The addition of an extra hull adds additional space, which is one reason why these multi-hull vessels are some of the best-selling sailboats on the market today.
Sailboat Rig Types
Rigging is another way to distinguish sailboat types. The rig of a sailboat refers to it's mast and sail configuration. Here are the most common types of sailboat rigs and what they're used for.
Sloops are the most common type of sailboat on the water today. A sloop is a simple single-mast rig that usually incorporates a tall triangular mainsail and headsail. The sloop rig is easy to control, fun to sail, and versatile. Sloops are common on racing sailboats as they can sail quite close to the wind. These maneuverable sailboats also have excellent windward performance.
The sloop rig is popular because it works well in almost any situation. That said, other more complex rigs offer finer control and superior performance for some hull types. Additionally, sloops spread their entire sail area over just to canvases, which is less flexible than multi-masted rigs. The sloop is ideal for general-purpose sailing, and it's proven itself inland and offshore.
Sloop Features:
- Most popular sailboat rig
- Single mast
- One mainsail and headsail
- Typically Bermuda-rigged
- Easy to handle
- Great windward performance
- Less precise control
- Easier to capsize
- Requires a tall mast
Suitable Uses:
- Offshore cruising
- Coastal cruising
Cat (Catboat)
The cat (or catboat) is a single-masted sailboat with a large, single mainsail. Catboats have a thick forward mast, no headsail, and an exceptionally long boom. These vessels are typically gaff-rigged, as this four-edged rig offers greater sail area with a shorter mast. Catboats were popular workboats in New England around the turn of the century, and they have a large following today.
Catboats are typically short and wide, which provides excellent stability in rough coastal conditions. They're hardy and seaworthy vessels, but they're slow and not ideal for offshore use. Catboats are simple and easy to control, as they only have a single gaff sail. Catboats are easy to spot thanks to their forward-mounted mast and enormous mainsail.
Catboat Features:
- Far forward-mounted single mast
- Large four-sided gaff sail
- Short and wide with a large cockpit
- Usually between 20 and 30 feet in length
- Excellent workboats
- Tough and useful design
- Great for fishing
- Large cockpit and cabin
- Not ideal for offshore sailing
- Single sail offers less precise control
- Slow compared to other rigs
- Inland cruising
At first glance, a cutter is difficult to distinguish from a sloop. Both vessels have a single mast located in roughly the same position, but the sail plan is dramatically different. The cutter uses two headsails and often incorporates a large spar that extends from the bow (called a bowsprit).
The additional headsail is called a staysail. A sloop only carries one headsail, which is typically a jib. Cutter headsails have a lower center of gravity which provides superior performance in rough weather. It's more difficult to capsize a cutter, and they offer more precise control than a sloop. Cutters have more complex rigging, which is a disadvantage for some people.
Cutter Features:
- Two headsails
- Long bowsprit
- Similar to sloop
- Gaff or Bermuda-rigged
- Fast and efficient
- Offers precise control
- Superior rough-weather performance
- More complex than the sloop rig
- Harder to handle than simpler rigs
Perhaps the most majestic type of sailboat rig, the schooner is a multi-masted vessel with plenty of history and rugged seaworthiness. The schooner is typically gaff-rigged with short masts and multiple sails. Schooners are fast and powerful vessels with a complex rig. These sailboats have excellent offshore handling characteristics.
Schooners have a minimum of two masts, but some have three or more. The aftermost large sail is the mainsail, and the nearly identical forward sail is called the foresail. Schooners can have one or more headsail, which includes a cutter-style staysail. Some schooners have an additional smaller sale aft of the mainsail called the mizzen.
Schooner Features:
- At least two masts
- Usually gaff-rigged
- One or more headsails
- Excellent offshore handling
- Precise control
- Numerous sail options (headsails, topsails, mizzen)
- Fast and powerful
- Complex and labor-intensive rig
- Difficult to adjust rig single-handed
- Offshore fishing
Picture a ketch as a sloop or a cutter with an extra mast behind the mainsail. These vessels are seaworthy, powerful, excellent for offshore cruising. A ketch is similar to a yawl, except its larger mizzen doesn't hang off the stern. The ketch is either gaff or Bermuda-rigged.
Ketch-rigged sailboats have smaller sails, and thus, shorter masts. This makes them more durable and controllable in rough weather. The mizzen can help the boat steer itself, which is advantageous on offshore voyages. A ketch is likely slower than a sloop or a cutter, which means you aren't likely to find one winning a race.
Ketch Features:
- Headsail (or headsails), mainsail, and mizzen
- Mizzen doesn't extend past the rudder post
- Good offshore handling
- Controllable and mild
- Shorter and stronger masts
- Easy self-steering
- Slower than sloops and cutters
- Less common on the used market
A dinghy is a general term for a small sailboat of fewer than 28 feet overall. Dinghys are often dual-power boats, which means they usually have oars or a small outboard in addition to a sail. These small boats are open-top and only suitable for cruising in protected waters. Many larger sailboats have a deployable dinghy on board to get to shore when at anchor.
Dinghy Features:
- One or two people maximum capacity
- Easy to sail
- Works with oars, sails, or an outboard
- Great auxiliary boat
- Small and exposed
- Not suitable for offshore use
- Going from anchor to shore
- Protected recreational sailing (lakes, rivers, and harbors)
Best Sailboat Type for Stability
Stability is a factor that varies widely between sailboat types. There are different types of stability, and some sailors prefer one over another. For initial stability, the trimaran wins with little contest. This is because these vessels have a very high beam-to-length ratio, which makes them much less prone to rolling. Next up is the catamaran, which enjoys the same benefit from a wide beam but lacks the additional support of a center hull section.
It's clear that in most conditions, multihull vessels have the greatest stability. But what about in rough weather? And what about capsizing? Multihull sailboats are impossible to right after a knockdown. This is where full-keel monohull sailboats excel.
Traditional vessels with deep displacement keels are the safest and most stable in rough weather. The shape, depth, and weight of their keels keep them from knocking over and rolling excessively. In many cases, these sailboats will suffer a dismasting long before a knockdown. The primary disadvantage of deep-keeled sailboats is their tendency to heel excessively. This characteristic isn't hazardous, though it can make novice sailors nervous and reduce cabin comfort while underway.
Best Sailboat Type for Offshore Cruising
The best sailboat type for offshore cruising is the schooner. These graceful aid robust vessels have proven themselves over centuries as durable and capable vessels. They typically use deep displacement keels, which makes them stable in rough weather and easy to keep on course.
That said, the full answer isn't quite so simple. Modern multihull designs are an attractive option, and they have also proven to be strong and safe designs. Multihull sailboats are an increasingly popular option for offshore sailors, and they offer comfort that was previously unknown in the sailing community.
Many sailors cross oceans in basic Bermuda-rigged monohulls and take full advantage of a fin-keel design speed. At the end of the day, the best offshore cruising sailboat is whatever you are comfortable handling and living aboard. There are physical limits to all sailboat designs, though almost any vessel can make it across an ocean if piloted by a competent skipper and crew.
Best Sailboat Type for Racing The modern lightweight Bermuda-rigged sailboat is the king of the regatta. When designed with the right kind of hull, these vessels are some of the fastest sailboats ever developed. Many boats constructed between the 1970s and today incorporate these design features due to their favorable coastal and inland handling characteristics. Even small sailboats, such as the Cal 20 and the Catalina 22, benefit from this design. These boats are renowned for their speed and handling characteristics.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

Choosing the Right Boat for Your Sailing Adventure
T he pleasure derived from sailing is largely contingent on the kind of boat employed and, crucially, the sailor's ability to navigate it. A sailor will find it greatly more enjoyable to sail a boat that they are proficient and at ease with compared to one where they don't fully understand its operations.
Ideally, the latter circumstance should be avoided as it elevates the risks of sailing. The open sea can pose significant threats. Hence, navigating a boat under challenging conditions should only be undertaken by individuals who are thoroughly knowledgeable about their actions.
In this article, we'll introduce you to the most common small vessels so you can keep them in mind when choosing the right boat for your time on the water.
Types of Boats
Ski and wakeboard boats.
Ski and wakeboard boats are primarily designed for water sports activities and are not typically used for cruising. Depending on the model, they may come equipped with various features tailored to water sports.
These features might include ballasts for cruise control, wave enhancement, a heating system to prolong the boating season, and a tower for skis, attaching ropes, and wakeboards.
Uniquely, a wake boat utilizes an internal engine and a shaft propulsion system instead of a conventional sterndrive, enhancing the safety of skiers and wakeboarders. However, these boats have their drawbacks.
They are not well-suited for cruising or navigating choppy waters due to their flatter hull design and configuration, making sailing through waves uncomfortable or even downright unpleasant.
Additionally, these boats are generally more expensive and consume significant fuel when used for water sports.
Pontoon Boats
Whether you're sailing on an Arizona lake or an Atlantic seaboard bay, pontoon boats are a common sight. These boats don't rely on a fiberglass hull but instead float on two or three aluminum “logs.”
These boats were often slow, unattractive, and not particularly seaworthy in the past, but those days are long gone. Modern pontoon boats are quick, aesthetically pleasing, and incredibly comfortable.
While it's true that they may not be the best choice for waters that frequently see large waves, their stability is unparalleled, they offer plentiful deck space, and their flexibility allows for a myriad of seating configurations. You can even enhance them with features like wet bars, towing arches, and more.
High-performance Boats
Similar to sports cars, high-performance boats offer an unrivaled cruising experience. Their striking colors and sporty designs ensure you won't blend into the crowd when out on the water.
Thanks to their higher cruising speeds , these boats can traverse longer distances and quickly transport you to far-off places. Their speed and pronounced V-shape hull make them capable of handling choppy waters with ease.
While their fuel consumption at lower speeds matches smaller vessels, it increases significantly at higher speeds. However, their ability to reach destinations quicker reduces the time spent consuming fuel, thus narrowing the gap with other boat types regarding fuel efficiency.
One intriguing aspect of these sporty high-performance boats is that, due to their narrower beam and lower height, even larger models over 30 feet can be towed, a feat impossible with cruisers of the same size.
This feature allows exploring new, remote bodies of water or ones off-limits to other vessels.
On the downside, these boats come with high-performance mechanical parts, which means they carry a higher purchase price and maintenance cost.
High-quality boats are less comfortable and accommodating than cruisers of the same length. This is especially true as recent years have seen more balanced models replaced by extreme boats. Additionally, the insurance costs for these boats are also on the higher side.
Some people relish the sensation of wind blowing through the sails, even though sailing necessitates a unique skill set that isn't required for motorboating. If you're drawn to sailing , mastering the art is essential, and the ideal way to start is by taking a beginner's sailing course.
The absence of a motor means your journey is entirely at the mercy of the wind, which could be thrilling if you have an adventurous spirit. A detailed online directory of various boat types can also assist you in making informed decisions.
Console Boats
?Typically, console boats feature an open hull with ample deck space or seating at the front and central controls for steering and ignition. They are specifically engineered to endure offshore waters, making them perfect for ocean fishing.
The boat cover design ensures it doesn't hinder a fisherman's casting. These boats are spacious and have facilities to store fish in icy conditions.
Despite rough seas, they provide both safety and comfort. There's plenty of room for gunwale rod holders, outriggers, and bait wells. Outboard engines power all console boats. Their size can vary from 18 to 65 feet and reach speeds of 30 knots or more.
Personal Watercraft
Personal watercraft (PWCs) are widely recognized for their superior maneuverability and ease of operation. They are relatively inexpensive, easy to tow even with a car, and allow for exploration of various bodies of water.
Their distinctive turbine propulsion system requires less water depth than traditional vessels, making them suitable for areas larger boats can't reach.
Some models boast impressive engine power, allowing for higher speeds that enhance the thrill of the ride. Compared to other crafts, the upkeep expenses of these watercraft are comparatively minimal.
On the downside, their operation costs can be relatively high due to increased fuel consumption caused by their high-speed capability. This also impacts insurance costs.
The limited onboard space, accommodating one to three passengers depending on the model, also restricts the possibility of group trips unless you're in company with other boaters. This often results in a solitary experience, which may not appeal to everyone.
Dinghy Boats
Rubber-made, inflatable small boats, also known as dinghies, come in three distinct types: those with air floors, rigid bottoms, and a hybrid featuring jointed or slatted bottoms. These dinghies are typically stowed on larger vessels and utilized in shallow areas inaccessible to their larger counterparts.
Often referred to as inflatables or rowboats, these dinghies are equipped with oars and a compact outboard engine. Their ability to navigate shallow waters makes them ideal for fishing activities in such locations. They are also commonly brought along on camping trips.
RIBS (Rigid Inflatable Bottoms), which are inflatables with rigid bottoms, are favored due to their lightweight nature and stability. They can be deflated for easy storage, and their soft-sided design prevents any potential damage to the motherships they are carried on.
One can confidently assert that the majority of these vessels are multi-functional. A compact fishing boat could easily double as a recreational boat and the other way round.
The ideal type of boat for you hinges on several factors, such as your preferred type of water body, the duration of your sea journey, and your storage needs. A thorough investigation can guide you towards the perfect boat tailored to your requirements.
This story is brought to you in partnership with Supra Boats.
The post Choosing the Right Boat for Your Sailing Adventure appeared first on Go Backpacking .
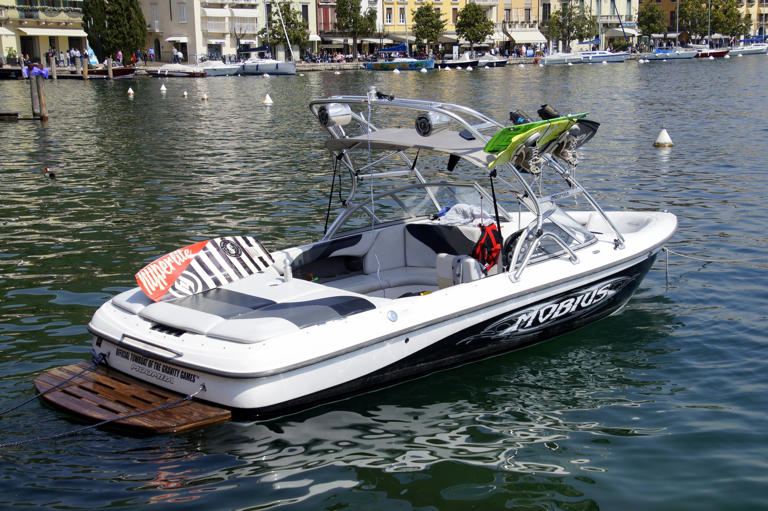

Types of Sails on a Boat: A Comprehensive Guide
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 13, 2023 | Sailing Adventures

Short answer: Types of sails on a boat
There are several types of sails commonly used on boats, including mainsails, jibs, genoas, spinnakers, and staysails. Each sail serves a specific purpose and is designed to optimize performance in different wind conditions.
An Overview of the Different Types of Sails on a Boat
Title: Raising the Mast: A Deep Dive into the Different Types of Sails on a Boat
Introduction: Ahoy, fellow seafarers! As we embark on our nautical journey across the vast blue horizon, there’s one crucial aspect that majestically propels us forward – sails . These magnificent structures of fabric work in harmony with the winds, enabling us to harness their power and sail gracefully through both calm waters and tempestuous seas. In this blog post, we set sail to explore the various types of sails found on boats today. From traditional mainsails to cutting-edge spinnakers, let’s unfurl our knowledge and bask in the breezy wonders of these essential components .
1. The Mainstay Mainsail: The mast’s trusty companion, the mainsail, is undoubtedly the cornerstone of sailing. Positioned aft, it captures direct wind force and is responsible for powering your vessel ahead. With its triangular or trapezoidal shape and mounted perpendicular to the keel, this versatile sail allows you to navigate efficiently against headwinds or calm conditions alike.
2. Raising Eyebrows with Jibs: Next up in our lineup is a sail that often raises eyebrows – jibs! Situated at the bow (front) of a boat, jibs complement the mainsail’s performance by generating additional lift. These smaller triangular sails come in various designs such as standard jibs and genoas (larger jibs), each serving specific purposes like improving light wind maneuverability or achieving balanced sailing dynamics.
3. Reaching New Heights with Spinnakers: Ready for a daredevil display? We now dive into spinnakers – sails built for reaching new heights – literally! Used primarily for downwind sailing when speedy pursuits become paramount, spinnakers are characterized by their impressive ballooning shapes that excel at catching even a whiff of gusty breezes. Harnessing the power of a tailwind, these vibrant sails resemble colorful parachutes, propelling boats forward in exhilarating fashion.
4. Mini Wonders – Staysails: Sometimes the unsung heroes of the sailing world, staysails find their abode on smaller vessels or as an additional sail on larger ships. These versatile triangular sails are often positioned between the mast and forestay (a cable-like structure supporting the mast). Whether acting as supplementary propulsion in fair winds or assisting with stability during heavy weather conditions, staysails prove their worth time and time again.
5. Dynamic Daring – Gennakers: Picture this: smooth seas and steady wind guiding your vessel towards its destination. Enter gennakers! Merging elements from genoas (large jibs) and spinnakers, these specialized downwind sails are crafted specifically for light or moderate wind speeds. Gennakers serve as spirited performers for sailors eager to embrace adventure while maintaining control – think of them as your reliable accomplice when it comes to effortlessly handling cruising boats.
Conclusion: As we lower anchor and conclude our exploration of various sail types, it’s evident that each design carries a unique purpose in enhancing a boat’s performance across diverse sailing conditions. From mainsails that stand tall as the primary driving force to spinnakers that encourage unforgettable downwind escapades, understanding the different sails allows us to adapt to changing winds with confidence and grace. So next time you set sail, raise your spirits along with those sails high above towards the never-ending horizon – a true testament to man’s enduring relationship with the raw power of nature’s breath!
Exploring the Functionality and Benefits of Different Sail Types on a Boat
Title: Sail Away to New Horizons: Unveiling the Functionality and Benefits of Different Sail Types on a Boat
Introduction: Ahoy, fellow seafarers! Set sail with us as we embark on an exciting journey to unravel the secrets behind the mesmerizing sails that gracefully propel boats across vast oceans. In this blog, we will dive deep into the functionality and benefits offered by various sail types for navigating the open waters. From traditional square sails to modern asymmetrical spinnakers, let’s unfurl their hidden potential together!
1. Square Sails: Nostalgia Meets Elegance Picture yourself transported back in time to an era when explorers valiantly sailed uncharted waters; here are where square sails reign supreme. Known for their iconic silhouette resembling a quadrilateral canvas canvasing the sky, these sails embody elegance and nostalgia simultaneously. Traditional square rigs like those found on tall ships provide incredible downwind performance and boast simplicity in operation. While fore-and-aft rigging has largely replaced square sails in modern recreational boating due to maneuverability concerns, they remain indispensable in historical reenactments or vessels seeking a touch of maritime magnificence.
2. Fore-and-Aft Sails: The Versatile Workhorses For sailors craving agility and adaptability while navigating diverse wind directions, fore-and-aft sails emerge as unparalleled champions. This sail type facilitates close-hauled sailing, optimizing upwind performance by cleverly harnessing every gust of air with finesse. Be it Bermuda rigs adorning yachts or gaff-rigged adaptations commanding historic charm; it’s hard not to admire their ability to slice through headwinds efficiently.
3. Topsails: A Glimpse into Mastery Want to elevate your sailing skills through innovation? Look no further than topsails – sophisticated companions that augment existing sail systems without demanding radical transformations onboard your boat. Placed atop masts, these additional sails provide extra surface area to trap atmospheric currents efficiently. By mastering the art of handling topsails, sailors can fine-tune their vessels’ response to different wind speeds or reduce reliance on multiple sail changes during fluctuating conditions.
4. Spinnakers: Unleashing the Wind’s Power Prepare to be swept away by the unrivaled power and grace displayed by spinnakers! These brightly colored billowing wonders are designed specifically for reaching or sailing downwind courses in lighter winds . Their expansive configuration allows them to scoop up even the slightest zephyr, propelling any vessel into a thrilling glide across tranquil waters . Asymmetrical spinnakers add a modern twist whilst facilitating easier handling for solo sailors or those aspiring for swifter maneuvers.
5. Code Zero Sails: Embrace Optimal Performance Yearning for enhanced performance and exhilarating speeds? Code Zero sails answer your call with fervor. These versatile creations bridge the gap between traditional genoas and asymmetrical spinnakers by finding their sweet spot in moderate overlapping headsail territory. Particularly beneficial while sailing close-hauled coupled with light airs, Code Zero sails empower you to defy nautical limitations without compromising maneuverability – igniting your boat ‘s potential even in challenging conditions.
Conclusion: With each sail type playing its part in perfect harmony, it becomes evident that selecting appropriate sails based on prevailing conditions is an art form mastered only through experience and careful consideration. Whether you’re chasing historical fantasies aboard historic tall ships or embracing technological advancements alongside sleek modern yachts, understanding sail functionality empowers you as a sailor, enabling unforgettable experiences beneath vast skies and endless horizons. So weigh anchor, unfurl your chosen sail type, and embark on incredible adventures while whispering gratitude to these magnificent fabrics that have graced our world since time immemorial!
Step-by-Step Guide: Choosing the Right Sail for Your Boat
Title: Step-by-Step Guide: The Quest for the Perfect Sail – A Voyage to Find the Right Match for Your Boat
Introduction: Sailing is a metaphorical dance between wind, water, and your boat. To truly enjoy and maximize your sailing experience, you need the perfect sail tailored to your boat’s needs. However, navigating through the vast sea of options can be overwhelming. Fear not! In this comprehensive step-by-step guide, we will chart a course towards finding the ideal sail for your boat. So hoist those sails, grab your compass, and let’s embark on this nautical journey.
1. Knowing Your Boat – Unveiling Its Personality: Every boat has its own personality – a unique blend of size, weight, shape, and purpose. Understanding these characteristics is paramount when choosing the right sail . Begin by identifying whether you have a cruising or racing vessel as this distinction will play a crucial role in selecting sails that align with its intended use.
2. Consulting Charts & Weather Reports – Determining Sailing Conditions: Just as a ship’s captain consults navigational charts before setting sail, get acquainted with local weather patterns and prevailing winds in your preferred sailing area. This knowledge will enable you to envision the conditions under which you’ll be hoisting your sails and help identify suitable sail types .
3. Setting Course for Sail Types – Main Options on Display: a) Mainsails: The core of any sail setup is the mainsail. Do you prefer traditional Bermuda or modern square-headed designs? Each offers distinct advantages regarding efficiency and performance. b) Headsails: These front-facing sails include genoas, jibs, or spinnakers. Genoas excel in upwind sailing; jibs are perfect for lighter winds or cruising; while spinnakers embrace downwind challenges. c) Specialty Sails: Depending on your ambitions and voyage requirements, consider other specialty sails like gennakers, code sails, or asymmetrical spinnakers for enhanced performance in specific conditions.
4. Material Matters – Choosing the Right Fabric: The quality and material of your sail significantly impact its durability and performance. Common materials include Dacron, laminate blends, or carbon fiber. Assess factors such as longevity, cost, stretch resistance, and weight to make a wise decision that suits both your budget and sailing aspirations.
5. Seeking Professional Assistance – Finding a Sailmaker: Consulting an expert sailmaker is akin to enlisting the services of an experienced navigator who knows every secret passage on the water . They will meticulously measure your boat’s dimensions and listen attentively to your requirements, ultimately crafting a bespoke sail that fits like a glove.
6. Rigging It Up – Completing Your Sail Setup: Selecting the right sail doesn’t end with simply choosing it – you must ensure proper rigging. Elements like mast height, boom length, sheet angles, halyard tensioning systems all affect how efficiently the chosen sails perform. A professional rigger can guide you through this crucial step to optimize your sail setup.
7. Test Drive on the Open Seas – Fine-Tuning Your Sails: Once rigged up with your newfound sails, take them for a spin! Be observant while sailing at different angles to gauge their efficiency whilst noting any adjustments needed in trim lines or settings. This firsthand experience allows you to fine-tune your sails’ performance based on their behavior amidst natural elements.
8. Maintenance & Longevity – Keeping Your Sails Shipshape: To extend the life of your sails and retain optimal performance over time, establish regular maintenance routines such as cleaning off saltwater residue after each outing and inspecting for signs of wear and tear between voyages. Proper storage techniques also play a vital role in preserving sail integrity.
Conclusion: Choosing the ideal sail for your boat is not just about function; it’s an art form that merges physics, craftsmanship, and your boating desires. By following this comprehensive step-by-step guide, you are well-equipped to embark on the journey of selecting a sail tailor-made for your boat – a match that will ensure smooth sailing and unparalleled adventures upon the open seas.
Frequently Asked Questions about Types of Sails on a Boat Answered
Frequently Asked Questions about Types of Sails on a Boat Answered: Everything You Need to Know
When it comes to sailing, choosing the right type of sail for your boat is crucial. With various options available, it’s essential to understand the different types and their purposes. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner looking to set sail , we’ve got you covered. Below, we answer some frequently asked questions to help you navigate through the world of sails with confidence.
1. What are the main types of sails?
The main types of sails found on boats are mainsails, jibs/genoas, spinnakers/gennakers, and storm sails. Each sail serves a specific purpose and performs differently depending on wind conditions and your desired course.
– Main sails: This is the largest sail on most boats and is attached to the mast. It provides primary power and helps control the boat’s direction . – Jibs/Genoas: These forward-facing sails are positioned closer to the bow of the boat than the mainsail. They capture wind from ahead or alongside, providing additional power when sailing upwind. – Spinnakers/Gennakers: Designed for downwind sailing, these large colorful sails add speed by catching wind from astern or at an angle behind the boat. – Storm Sails: Smaller in size but built for heavy weather conditions, storm sails help maintain control during strong winds and storms.
2. How do I choose the right type of sail ?
Selecting the appropriate sail configuration depends on several factors such as wind conditions, boat size , intended course, and personal preferences. Here are some considerations:
– Wind Conditions: Every sail has a recommended range of use based on wind strength. Ensure you match your chosen sail with appropriate wind conditions to optimize performance without compromising safety. – Boat Size: Smaller boats generally require fewer but versatile sails since they lack dedicated storage space. Larger boats, on the other hand, can carry a more diverse inventory to suit various wind conditions. – Course: Are you planning an upwind, downwind, or mixed direction voyage? Knowing your intended course will help determine which sails are most suitable for your journey.
3. What materials are sails made of?
Sails can be made from different materials, including Dacron, laminates (such as Mylar or Kevlar), and even exotic materials like carbon fiber. Each material has its advantages and is suited to specific sailing styles and budgets.
– Dacron: Durable and versatile, Dacron is commonly used for cruising sails. It provides good performance across a wide range of wind conditions and requires less maintenance. – Laminates: These high-performance sails offer increased strength-to-weight ratios due to their layered construction. While Mylar suits racing sailors seeking speed, Kevlar provides excellent shape-holding capabilities. – Carbon Fiber: Top-of-the-line racing yachts often employ carbon fiber for its lightweight and ultra-responsive features, optimized for maximum speed.
4. Can I use multiple sails simultaneously?
Yes! Using multiple sails together on a boat is called “sailtrimming” or “sail combinations.” It allows sailors to harness the wind’s power more efficiently in different directions.
Pairing a mainsail with one or more headsails can improve overall efficiency by capturing wind from various angles. For instance, hoisting a jib/genoa alongside the mainsail enables you to tackle upwind challenges effectively. Additionally, deploying spinnakers/gennakers can boost downwind speeds significantly.
5. How do I maintain my sails?
Proper sail maintenance ensures longevity and optimal performance:
– Cleanliness: Rinsing your sails with fresh water after each sail helps remove salt buildup that may lead to damage over time. – Storage: Invest in proper storage solutions such as bags or UV-resistant covers to protect your sails from prolonged sun exposure. – Repairs: Regularly inspect your sails for signs of wear and tear. Promptly repair any damaged areas, as even small tears can compromise their performance.
By understanding the characteristics of different types of sails and taking care of them, you can enjoy safer, more efficient, and thrilling sailing experiences.
In conclusion, choosing the right type of sail for your boat involves considering various factors such as wind conditions, boat size, intended course, and personal preferences. By familiarizing yourself with the main types of sails available and understanding their purposes in different conditions, you can navigate confidently on your next sailing adventure. Remember to prioritize maintenance to ensure your sails remain in top shape for years to come.
Understanding How Different Sails Impact the Performance of Your Boat
When it comes to sailing, the performance of your boat heavily relies on the type of sails you use. Understanding how different sails impact your boat can make all the difference in achieving optimal speed, efficiency, and maneuverability on the water. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate world of sail selection and explain how each type influences your boat ‘s performance.
Firstly, let’s familiarize ourselves with some common types of sails. The most basic is a mainsail – a large triangular sail attached to a mast that captures wind from behind the boat. This solidifies its role as the primary driving force. However, there are variations such as square-headed mainsails that offer increased surface area for greater power.
Additionally, we have headsails or foresails which include genoas, jibs, and spinnakers. These sails are situated at the front of the boat and are responsible for fine-tuning maneuverability and handling in various wind conditions.
Now let’s explore how different sails impact performance:
1. Mainsail Dominance: As mentioned earlier, the mainsail acts as your boat’s primary driving force. Its size and shape significantly affect both speed and stability . The larger surface area provides more power but can also lead to excessive heeling – when a boat leans heavily on one side due to strong winds. Conversely, reducing sail area can improve control during stormy conditions.
2. Jib & Genoa Efficiency: When it comes to headsails like jibs and genoas, their primary function is to optimize maneuverability by complementing the mainsail. Jibs are smaller and tend to be used in higher wind conditions or when sailing upwind (towards where the wind is coming from). On the other hand, genoas have a larger overlap with the main sail and maximize power while sailing downwind or in lighter winds.
3. Spinnaker Magic: The spinnaker, often dubbed as the “go-fast” sail, is designed for downwind sailing. Its unique shape resembles a parachute and captures wind from the front side of the boat , generating additional speed during favorable wind angles. Using a spinnaker requires skillful handling and control but can truly make your boat fly on the water .
It’s important to note that selecting the appropriate sail combinations depends on various factors such as wind conditions, seascape, boat type , crew experience, and personal preferences. Having a diverse inventory of sails allows sailors to adapt to different situations seamlessly.
In summary, understanding how different sails impact your boat’s performance is crucial for any sailor seeking optimal speed and maneuverability on the water. The mainsail acts as the primary driving force while headsails fine-tune handling in different wind conditions. By considering factors like size, shape, and purpose of each sail type – mainsails, jibs/genoas, and spinnakers – sailors can harness their power to conquer varying challenges while enjoying the exhilarating thrill of sailing . So go ahead and set sail with confidence knowing that you are equipped to navigate any nautical adventure!
Pro Tips: Expert Advice on Optimizing Your Sailing Experience with the Right Type of Sail
Introduction:
When it comes to sailing, one crucial factor that can significantly enhance your experience is having the right type of sail. From maximizing speed to ensuring stability and control, choosing the proper sail for your boat is essential. In this blog post, we will provide you with pro tips and expert advice on optimizing your sailing experience by selecting the right type of sail.
1. Understanding Different Types of Sails:
Before delving into specific types of sails, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the various options available. The three main categories are:
a) Cruising Sails: These are designed for comfort and durability during long journeys or leisurely cruising. They prioritize longevity over speed and are typically made from resilient materials like Dacron.
b) Racing Sails: As the name suggests, racing sails are built for performance and speed in competitive sailing events. They are lightweight, often made from technologically advanced materials such as carbon fiber or Kevlar.
c) Offshore Sails: Ideal for sailors embarking on extensive offshore voyages, these sails strike a balance between durability and performance. They can withstand harsh weather conditions while still delivering a decent level of speed.
2. Matching Sail Type to Boat Characteristics:
To optimize your sailing experience further, it’s vital to match the sail type with your boat ‘s characteristics:
a) Boat Size: Consider whether you have a small dinghy or a larger cruising yacht. Smaller boats generally benefit from lighter sails that allow for easy maneuverability, while larger vessels may require heavier-duty sails for enhanced stability .
b) Rigging Configuration: Different boats have varying rigging configurations such as sloops, cutters, ketches, or schooners. Each setup requires specific types of sails to ensure optimal performance.
c) Water Conditions: The type of water you plan to sail in also influences the appropriate choice of sail. Factors like wind strength and prevailing weather patterns should dictate whether you opt for a racing sail for high-speed performance or a cruising sail better suited for comfort in mild conditions.
3. Aerodynamics and Sail Shape:
Understanding the principles of aerodynamics and sail shape is crucial to maximizing your sailing experience . Here are a few considerations to keep in mind:
a) Surface Area: Larger surface area generates more power, translating into increased speed. However, it also creates more drag that can hinder maneuverability. Finding the right balance is key.
b) Mainsails vs. Headsails: Mainsails provide primary power, while headsails complement them by optimizing airflow around the boat . Experimenting with different combinations can help find the perfect synergy.
c) Sail Trim: Proper sail trim ensures optimal airflow over the sails, minimizing drag and maximizing efficiency. Investing time in mastering this skill will greatly enhance your sailing experience .
4. Additional Tips and Tricks:
To further optimize your sailing experience, consider the following pro tips:
a) Regular Maintenance: Ensure your sails receive regular maintenance and repairs as needed to prolong their lifespan and maintain peak performance.
b) Seek Expert Advice: Consult with experienced sailors or professionals who are knowledgeable about various types of sails and can offer personalized advice based on your specific needs.
c) Trial and Error: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different types of sails to find what works best for you and your boat. Each sailing excursion presents an opportunity to learn more about your craft’s capabilities.
Conclusion:
Sailing is an exhilarating pastime that becomes even more enjoyable when you harness the power of the right type of sail for your boat . By understanding different types of sails, matching them with suitable boat characteristics, considering aerodynamics and sail shape, implementing proper maintenance practices, seeking expert advice when needed, and embracing trial and error, you’ll be well on your way to optimizing your sailing experience like a true expert sailor. So hoist those sails high and prepare for an unforgettable journey on the open waters!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Text: A A A Print ECNS Wire
World's first river-sea electric container ship sets sail.

Lvshui 01, the world's first river-sea electric container ship, arrives at Shengdong Wharf of Yangshan Port in east China's Zhejiang Province, April 22, 2024. (Photo/China News Service)
(ENCS) -- Lvshui 01, the world's first river-sea electric container ship, arrived at Shengdong Wharf of Yangshan Port in east China's Zhejiang Province on Monday, setting new records for the world's first and largest vessel of its type.
It will operate on a regular route from Nanjing to Yangshan Port.
The ship is 119.8 meters long, 23.6 meters wide, and 9 meters deep with a design draft of 5.5 meters. It has a gross weight of 8,261 metric tons and can achieve a maximum speed of 19.4 kilometers per hour.
It is outfitted with 36 containerized battery boxes, reaching a total capacity of more than 50,000 kilowatt hours.
As the world's first ship of it type, Lvshui 01 is equipped with several innovative new technologies. It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 12.4 metric tons per 100 nautical miles, saving 3,900 kilogram of fuel and an energy cost of about 33,500 yuan ($4,623).
It is expected to reduce 2,472 metric tons in exhaust emissions for the whole year, including about 2,362 tons of carbon dioxide.
This ship is set to drive the green, low-carbon and intelligent transformation of the shipping industry and promote green development.

Qingdao illuminated in celebration of 75th founding anniversary of Chinese PLA navy

Preview of International Horticultural Exhibition 2024 Chengdu

Rongshan Yangtze River Bridge connected in Sichuan

Chinese PLA navy celebrates 75th founding anniversary

China's first deep-sea multi-functional vessel launched in S China

Light show staged to mark 9th Space Day of China in Wuhan

Pearl River basin in S China braces for flood

Cradle of civilization: The Cangjie Temple

In numbers: China-Slovenia relations

Culture Fact: UN Chinese Language Day

Tunnel boring machine Yongzhou installed in E China

4th China International Consumer Products Expo concludes

Centuries-old tree blooms in Hangzhou

China Post issues commemorative stamps of Chengjiang Fossil Site

In Numbers: China's economic indicators in Q1 of 2024

China receives 38 cultural relics returned from U.S.

Storm dumps heaviest rain ever recorded in UAE

Panda strolls in flowers

Historic Copenhagen stock exchange in flames

China ready to launch Shenzhou-18 crewed spaceship

Products of Chinese culture shine at CICPE 2024

Flame for Paris 2024 Summer Olympic Games lit in Ancient Olympia

Blooming water lilies in West Lake resemble Monet's painting

Xi meets German chancellor, calls for achieving mutual success

In pics: 798 Art Zone

Pear blossoms accentuate the beauty of Hanfu

Transportation hub undergoes load testing in Greater Bay area

National Security Education Day marked in Hong Kong

135th Canton Fair opens with over 29,000 exhibitors

Notre Dame Cathedral restoration nears completion after 5 years

Culture Fact: Shangsi Festival

UN Security Council holds emergency meeting after Iran's retaliatory attacks on Israel

German Chancellor Olaf Scholz starts China visit

In Numbers: China, Germany cooperation yields fruitful results

Cradle of Civilization: Zuojiang Huashan Rock Art

China is committed to managing Ren'ai Jiao issue through dialogue and consultation: FM spokesperson
Most popular in 24h, more top news.
- Expert lists multiple mistakes in U.S. criticism of China's ‘overcapacity’
- Highest, largest wind farm installs first turbine in Himalayas
- China continues to create jobs, pledges continued enhancement
- G7 meddling in internal affairs condemned
- China firmly rejects manipulation of China-related issues at G7 FM Meeting: spokesperson

Earth Day Everyday: Choose the planet over plastics

China launches new remote sensing satellite


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn about the different types of sails and rigs on a sailboat, from mainsail and headsail to spinnaker and gennaker. See pictures and diagrams of sail shapes, parts, and functions for various conditions and mast configurations.
Learn about the different kinds of sails and how they are used on sailboats depending on the wind conditions. Find out the advantages and disadvantages of mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker sails.
Learn about the 8 types of sails for sailboats, from mainsails and headsails to spinnakers and storm jibs. Find out how to use them in different wind and weather conditions and sailboat types.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker. While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily ...
Spinnaker sails are a type of downwind sail that can be used to increase boat speed when sailing in light winds. They are typically used in wind conditions below 10 knots, which are considered light air sails. Spinnakers come in two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Author: Ken Heaton CC BY-SA-4..
The Most Popular Types Of Sails On A Sailboat. A sloop-rigged sailboat typically features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker. The mainsail is rigged aft of the mast, while the headsail is attached to the forestay. The two most commonly used headsails are the Genoa and Jib.
Mainsails are essential for providing the boat with forward propulsion and play a significant role in steering and balancing the vessel. There are two primary types of mainsails: full-batten and partial-batten. Full-batten mainsails have horizontal battens that run the entire width of the sail, providing additional support and shape.
Type of Sails Names: Decoding the Terminology. Mainsail and Foresail. The mainsail, as mentioned earlier, is the principal sail that catches the wind to move the boat forward. Foresail is a general term that includes various sails positioned near the bow of the sailboat, such as the jib and genoa. Genoa and Jib.
Basic Types of Sails. Sails are an essential part of any sailboat. They are used to harness the wind to propel the boat forward. There are several types of sails available for sailboats, and each serves a different purpose. Here are the three basic types of sails: Mainsail. The mainsail is the most critical sail on a sailboat. It is a large ...
Types of Sails. There are four main types of sails that you will encounter when outfitting your sailboat: mainsails, headsails, spinnakers, and storm sails. Each type of sail serves a specific purpose and is designed for different sailing conditions. Mainsails. The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailboat and is attached to the mast and boom.
Learn about the most popular types of sails on sailboats, such as mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker. Also, discover the different sail and mast configurations, such as sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat.
Short answer different types of sails: There are several different types of sails used in sailing, including mainsails, headsails (jibs and genoas), spinnakers, gennakers, and storm sails. Each type is designed for specific wind conditions and sailing techniques, contributing to the overall performance and maneuverability of a sailboat.
Short answer types of sails for sailboats: Sailboats typically use four primary types of sails: mainsails, genoas/jibs, spinnakers, and staysails. Mainsails are the largest and provide forward propulsion. Genoas/jibs enable efficient sailing upwind. Spinnakers are used for downwind sailing and maximizing speed. Stay-sails provide stability in heavy wind conditions.
The shape of the sail plays a crucial role in how it works. Sails are designed to be curved, much like an airplane wing. This curvature creates differences in air pressure: the wind flowing over the curved side of the sail travels faster and creates lower pressure, while the wind on the flat side (facing the wind or windward) remains relatively slower with higher pressure.
Types of Sails on a Sailboat. Sailors could carry many different sails on a sailboat. If you are into racing, you'll likely carry a wider variety of sails. Racers often carry sails for every wind condition to get the most speed from their boat. Racing sailboats often have many crew members that don't mind frequently changing sails.
Short answer: Sail types. Sail types refer to the various designs and configurations of sails used in sailing vessels. Common sail types include the square sail, fore-and-aft sail, and lateen sail. Each type has unique characteristics and is suited for different wind conditions and sailing maneuvers.
Although this type of sail and rig are very effective, the Marconi rig is easier to handle. It does not require a crew of husky sailors to raise and lower the sails. 3. Bermuda rigged sailboat — aka the Marconi sail. The Marconi sail is a variant of the Bermuda rig that has been used in that country since the 1600s.
Learn the different types of sails on a sailboat, such as mainsail, headsail, genoa, spinnaker, gennaker, and more. Find out how they are placed, shaped, and used in different wind conditions and points of sail.
Short answer sailboat types of sails: There are several types of sails used in sailboats, including the mainsail, jib, genoa, spinnaker, and staysail. Each sail type serves a specific purpose and is designed to perform optimally under different wind conditions and points of sail. Introduction to Sailboat Types of Sails: A Comprehensive GuideIntroduction to Sailboat
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels. The information found in this article is sourced ...
A compact fishing boat could easily double as a recreational boat and the other way round. The ideal type of boat for you hinges on several factors, such as your preferred type of water body, the ...
Short answer: Types of sails on a boat There are several types of sails commonly used on boats, including mainsails, jibs, genoas, spinnakers, and staysails. Each sail serves a specific purpose and is designed to optimize performance in different wind conditions. An Overview of the Different Types of Sails on a BoatTitle: Raising the Mast:
As the world's first ship of it type, Lvshui 01 is equipped with several innovative new technologies. It can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 12.4 metric tons per 100 nautical miles, saving ...