

Please verify you are a human
Access to this page has been denied because we believe you are using automation tools to browse the website.
This may happen as a result of the following:
- Javascript is disabled or blocked by an extension (ad blockers for example)
- Your browser does not support cookies
Please make sure that Javascript and cookies are enabled on your browser and that you are not blocking them from loading.
Reference ID: 287bda54-164b-11ef-a0a9-f350d050b19e
Powered by PerimeterX , Inc.

- Custom Products
- Product Guides
Flag Sizes for Boats | Nautical Flag Sizes | All Star Flags
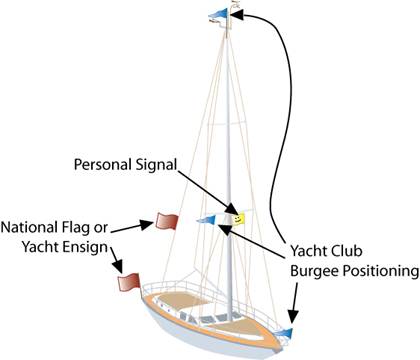
Nautical Flag Sizing
By Chad Creech, All Star Flags
- What flags to fly and where to put them on your boat
For many a recreational sailor, the same questions come to mind every year. Where should I place the flag? And how big should it be? Can I fly the national flag? At sea you’ll often come across a less experienced crew, who seem to have fully-dressed the boat, having decorated it with flags like a Christmas tree. So let's clear up the issue. It never hurts to go over the basic principles, which are actually very simple. So where does which flag belong and what do they mean?
The place at the stern of a yacht is reserved exclusively for one thing:
The Ensign (the national flag of the country under which the boat is registered)
This is the most important flag, which says the most about the boat and crew. This is because ships have the nationality of the state whose flag they fly under (this right is granted by the state together with the issuing of the relevant documents). Ships are then subject to the exclusive jurisdiction of that state on the high seas (which, of course, results in a number of interesting situations). Please note that on coastal seas, the law of the state whose waters you pass through also applies to the vessel.
Where is it flown?
At the stern, ideally on the flagpole (pushpit) or on the stern forestay (flying the flag depends on whether the ship is sailing or mooring). And it must be the largest flag on the ship
This flag should be flown in the correct manner from sunrise to sunset. It must always be hoisted first and lowered last. No other flag may be flown unless the national flag (ensign) is also flown.
How big should the flag be? According to the decree, the flag (if it is the ensign of a boat) should, for example, have a size of 0.75 x 0.50 m (on a recreational yacht).

Don't overlook other useful tips:
How to sail a yacht against the wind
Don’t panic: handling maritime emergencies
Sextant and navigation: survival without GPS
The ultimate yacht cleaning kit
New Year's resolution: let's sail more eco
How to sail a yacht on a tailwind
How to sail a yacht in crosswinds
How to have a nautical Christmas
What to pack for a tropical sailing
The starboard spreader.
The starboard spreader is reserved for courtesy flags. They are flown immediately after the ensign and lowered last before it. What flags should they commonly be?
The flag of the state in whose waters you are sailing
It is placed under the starboard spreader and it isn’t just a courtesy to do so, it is a duty.
However, if you are sailing in Croatia on a Croatian ship, there is no need to fly a courtesy flag.
Boat owner’s flag
The yacht owner can also fly their own national flag on the boat. It can be placed on the starboard spreader, but if the owner deems it appropriate it can be flown on the port side, as it is a flag of lower importance (than the ensign).
The spreader is a mast reinforcement (between the mast and the shroud). It is placed on the mast perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the ship (or points slightly to the stern) and is at right angles to the mast.
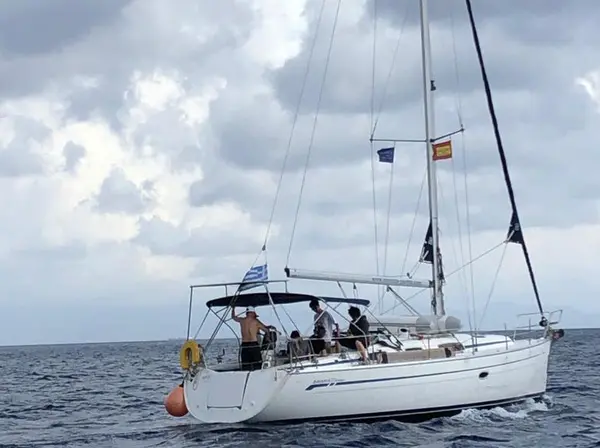

The Port Spreader
All other flags are flown under the port spreader. So what are the other flags you can fly on the yacht?
Signal flags
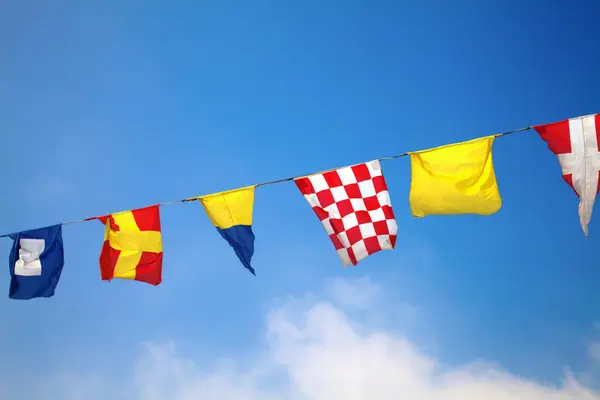

Your national flag
Yes, right here is the place for your own national flag when sailing in Croatia on a Croatian boat.
A burgee is a flag bearing the colours or emblem of a sailing club and should be flown from the main masthead. If this isn’t feasible it should be below the port spreader.
Flags of the nationalities of the crew members
Flags of the countries you’ve visited during the voyage, etc..
How large can the other flags be? They should always be smaller than the ensign.

Special flags and occasions
Can i fly a pirate flag .
The international agreement UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) speaks for itself. Stateless ships, ships flying a foreign flag and ships refusing to fly their ensign may be detained and inspected by warships or civil service ships, even on the high seas.
So if you are flying under a pirate flag out of ignorance or innate rebellion :) (i.e. you hang it on the place where the ensign belongs) you definitely risk an interesting experience. But also be careful not to hang in less risky places, for example, where the burgee should be as there are places and ports where you could get a pretty hefty fine.

How to greet other boats with the flag?
A sharp shot from a cannon is a thing of the past. When ships meet, instead of a verbal greeting you dip the ensign. And after the same response from the other boat it can be raised again. But who greets who first? A merchant ship is first when meeting a warship, a smaller vessel of the same flag when greeting a larger one and when two merchant ships of the same type meet, it is the one with the more junior commanding officer.
When ships meet on the high seas, it is customary to add a port salute. Dipping the flag is accompanied by three prolonged blasts of the horn and the same response is acknowledged with one short blast.
Do you know what dressing the ship is?
Dressing the ship consists of flying national flags on top of the masts and stringing signal flags over the tops of the masts to connect the bow and stern.
When is dressing done? It is a sign of celebration and is done on national holidays. However it can it can be done in a lesser way at the order of the ship's captain on special occasions. The national flags are again placed on the tops of the masts accompanied by flying at least four signal flags from both ends of the mast boom.
Would you also like to set sail and enjoy an adventure at sea? Whether you want to sail under the Croatian, Italian or Greek flags, you’ll find everything you need with us.
Our sailboat offer:
Contact us to get the best deal.

Denisa Nguyenová
- – FlagMagic
- – Pirate Flags & History
- – Boat Flag Facts & Info
- – Pride Flags & History
- – Pride Month 2022
The Definitive Guide To Boat Flag Shapes and Sizes
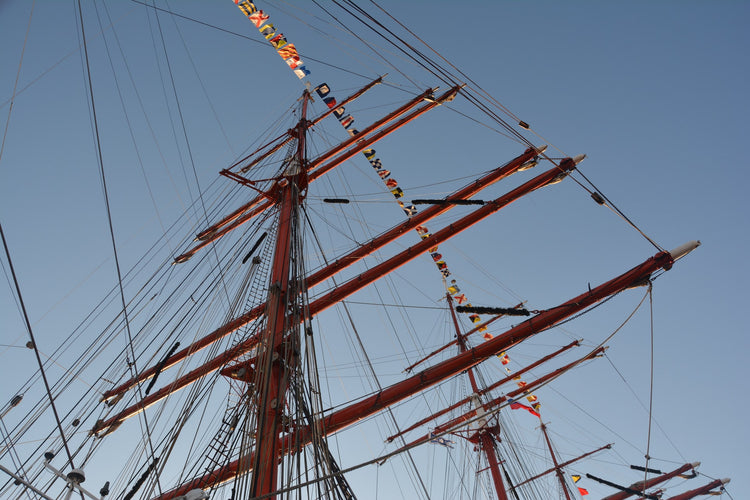

Boat Flag Shapes
Do you know the difference between a boat flag and a boat pennant? How about the difference between a boat flag and a burgee? If not, don't worry - you're about to learn! In this blog post, we will discuss all the different boat flag sizes and shapes. We'll provide information on what each type of boat flag is used for, as well as tips on choosing the right size and shape for your needs.
Boat flags come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but the most common boat flag shape is rectangular. Rectangular boat flags are typically used for decorative purposes , such as flying your country's flag or displaying your boat's name and home port.

Pennants are another popular boat flag shape - they are long and narrow, and often have a pointed end. Pennants are often used to signal distress or indicate that a boat is entering or leaving port.

Burgees are another type of boat flag, and they are usually triangular in shape. Burgees are typically used by yacht clubs or other organizations as a way to identifying their members.
When choosing a boat flag, it's important to consider both the shape and the size. The shape of the flag should be appropriate for the purpose you're using it for, and the size should be appropriate for the boat you're flying it on. If you have any questions about boat flags, or if you need help choosing the right size or shape for your needs, please don't hesitate to contact us - we're always happy to help!
Boat Flag Sizes
The size of a boat flag also varies, but the most common boat flag size is 12 inches by 18 inches. This size is large enough to be seen from a distance, but not so large that it will be blown away in strong winds. This size is large enough to be seen from a distance, but not so large that it will be blown away in strong winds. A general rule is one inch of length for every foot in boat length. It doesn't need to be followed exactly, but gives a good guideline.
If you have a small boat, you may want to choose a smaller flag size. For example, a boat flag size of six inches by nine inches is often used on small boats. This size is still visible from a distance, but it won't overpower the boat or get blown away in strong winds.
It's also important to consider the wind conditions when choosing a boat flag size. If you know you'll be sailing in windy conditions, you may want to choose a larger flag size. A boat flag size of 18 inches by 24 inches is often used in windy conditions. This size will ensure that your flag is visible, even in strong winds.
Common Boat Flag Size and Shape Questions:
Question: What size flag do I need for a 30 foot boat?
Answer: A boat flag size of 18 inches by 24 inches is often used on boats this size.
Question: Can I fly a flag on a pontoon boat?
Answer: Yes you can! Pontoon boats are perfect vessels for flying flags .
Question: What size flag do you fly on a boat?
Answer: The most common boat flag size is 12 inches by 18 inches.
Question: What shape boat flag do I need?
Answer: The shape of the boat flag should be appropriate for the purpose you're using it for. The most common boat flag shape is rectangular.
Question: What is the difference between a boat flag and a boat pennant?
Answer: Pennants are long and narrow, and often have a pointed end. Pennants are often used to signal distress or indicate that a boat is entering or leaving port.
Question: How big is a standard boat flag?
Answer: They can be almost any size, we offer flags in 12" by 18" and 3' by 5'.
Question: Are nautical flags square or rectangle?
Answer: Boat flags come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but the most common boat flag shape is rectangular. Rectangular boat flags are typically used for decorative purposes . Square flags are used for signaling.
Question: What are the 3 sizes of the flag?
Answer: The three sizes of the flag are the width, height, and mast length.
Question: What flag do you put on a boat?
Answer: The only required flag for a boat in the US is The U.S. national ensign, sometimes called "50-star" or "Old Glory." It is the proper and preferred flag for all U.S. vessels. Your boat should wear it from 0800 until sunset, and when you enter or leave port during daylight or at night, weather and rig permitting. After that you can have fun boat flags , signal flags, club pennants, pirate flags , and just about anything else you can think of.
Custom Flag Designers Online
We're creating new, high quality custom flag designers online every day
- About Sailonline
The One Source For Yacht Charters And Charter Yacht Ownership

- What is boat chartering
- Choose your best charter type
- Choose your charter company
- Choose a cruising area
- Choose the right boat
- Booking your charter
- Your sailing resume
- Yacht Charter Destinations Chart
- Catamarans vs. monohulls
- Bareboat Destination Skills
- Sailing Area Table
- Caribbean weather info
- What to pack for your charter
- Charter boat checklist
- Internet access on charter
- Briefing your charter crew
- Saving money on charter
- All boat charter tips in 1 file
- Budget Charter Fleets
- Provisioning a charter boat
- Booking directly with a boat owner
- The charter days you really get
- Managing your boat on charter
- Boat charter with kids
- Seasickness tips
- Starting a charter from the USVI
- If you damage a charter boat
- Flotilla charters
- Charter with a handicapped child
- Crewed yacht charter myths
- Organize a crewed charter
- Crewed charter tips
- Browse The Database
- Submit your Boat Listing
- Yacht Management Contract
- Buying a boat with a partner
- Bareboat vs. crewed yacht
- Charter Yacht Phase-out
- Phase-out punch list
- Yacht & Marine Surveyors
- Charter Boat Owners forum
- Yacht financial management tools
- 2nd tier fleets financial comparo
- Active ownership FAQ
- Layman guide to charter boat ownership
- Is Buying A Charter Boat For You?
- Buying a used charter boat
- Yacht buyer representation
- Bareboat vs. crewed yacht ownership
- Active Yacht Ownership
- Customers' Testimonials
- Cruising Logs
- Captain licenses
- 'Heaving to' maneuver: A must
- Charter Boat Seamanship Manual
- Yacht Crew Certification: All answers
- Snorkeling & kayaking safely
- Rules of the Road
- MOB Crash-Stop Maneuver
- 5 Knots you must know
- Flag Etiquette
- Emergencies on charter
- Distress calls at sea
- Navigation on a yacht charter
- Navigation aids sheets
- Estimate distances at sea
- Heavy weather basics
- Caribbean weather information
- VHF use: The basics
- Raising Main Sail | UnPC
- Anchoring technique & hand signals
- Catamaran sailing tips
- Docking: Avoid the embarrassment!
- Mooring technique
- Med-mooring technique
- Dinghy handling: make the best of it!
- Reefing a Catamaran
Remember Me
- Forgot your password?
- Forgot your username?
- Create an account
- Boat flag etiquette

Flag etiquette has been transmitted to us by generations of mariners. Although not often appropriately respected these days, especially not by charterers, we might add, observing flag etiquette can provide some pride of perpetuating a very old tradition as well as some fun. We will not get into deep details and purist fanaticism. However, we will try to show charterers the minimum that is expected for basic respect of rules.
Therefore, we will only talk here about 4 main flags, potentially used by charterers and charter boat owners: the Ensign or the National flag; the club burgee; the Private Signal; and the Courtesy Flags.
Boats should fly the National Flag. Most pleasure boats in US waters have a choice of 2.
The yacht ensign, with its fouled anchor over a circle of 13 stars, the "Betsy Ross" flag. Originally restricted to documented vessels only, it is now commonly flown on recreational boats of all types and sizes instead of the National Flag (see picture).
The 50-star flag "Old Glory" you are familiar with.
The appropriate time to fly the ensign is from 0800 to sunset, except when racing. It is also important to take the flag down prior to leaving the yacht if the ship will be unmanned at the time of sunset.
However, whenever a boat is taken into international or foreign waters, the 50-star U.S. ensign is the proper flag to fly and the yacht ensign cannot to be displayed . In other words, if you own a US boat in the British Virgin Islands, you should not fly the Ensign, but the National Flag.
Boats today fly the ensign from the stern, which provides the best visibility, but it can also be flown from the leech of the most aftersail. When flown from the stern, it should be on a staff (pole) that is sufficiently long and angled, and that is offset to one side (traditionally the starboard side), so the flag flies clear of engine exhaust and rigging.
It is a small flag displaying the symbol of the skipper's yacht club or other sailing organization. It may be flown day and night.
Most people opt to fly the burgee lower in the rig, hoisted to the end of the lowest starboard spreader on a thin flag halyard. While purists rail this practice, it is an accepted adaptation of another tradition, which is that the starboard rigging is a position of honor (when you visit a foreign port, that's where we fly the host country's flag). Besides being reasonable, flying the burgee in the starboard rigging is such a widespread custom that to try to end it would be close to impossible.
Private Signal
It is a small, custom-designed and custom-made flag that carries symbols standing for the owner, so it can basically be anything. The signal may be flown day or night, but is not displayed when another sailor is in command. (The rule is: the private signal and burgee follow the sailor, not the boat.)
On a multi-masted boat, the private signal is flown at the head of the aftermost mast. On a sloop, the private signal may be flown from the starboard rigging, either below the burgee or alone.
Courtesy Flags
As a matter of courtesy, it is appropriate to fly the flag of a foreign nation on your boat when you enter and operate on its waters. There are only a limited number of positions from which flags may be displayed. Therefore, when a flag of another nation is flown, it usually must displace one of the flags displayed in home waters. However, it is hoisted only after the appropriate authorities have granted clearance. Until clearance is obtained, a boat must fly the yellow "Q" flag . All charter boats should carry the national flags of neighboring islands as well as the yellow flag, in case charterers want to visit those islands.
The courtesy flag is flown at the boat's starboard spreader, whether the United States ensign is at the stern staff, or flown from the leech. If there is more than one mast, the courtesy flag is flown from the starboard spreader of the forward mast.
As a side note, some authorities are not amused at all if you fly their courtesy flag using an old, raggy flag. Some will even fine you for disrespect! It happened to a friend of mine who was chartering in Turkey.
Lastly, it is also a common courtesy to fly the national flag(s) of your guest(s) on board, if they have a different nationality than the ensign is showing.
Flags' Dimensions
Flags come in standardized sizes, but there are guidelines about selecting the proper size for your boat.
The size of a nautical flag is determined by the size of the boat that flies it. Flags are more often too small than too large. So in the rules below, round upward to the nearestlarger standard size.
The flag at the stern of your boat: U.S. ensign or national flag should be about one inch for each foot of overall length. For example, on a 40ft. boat, the ensign should be 40 in. i.e. about 3.5ft.
Other flags, such as club burgees, private signals and courtesy flags used on sailboats should be approximately 1/2 inch for each foot of the highest mast above the water. For example, on a 30ft. boat, with 50ft. between the masthead and the water, the burgee should be about 25 in. The shape and proportions of pennants and burgees will be prescribed by the organization which they relate to.
Raising and Lowering Flags
Fly the ensign from morning (8:00 a.m.) to evening (sunset) whether the boat is at rest, under sail, or under power. The exception to this rule is: The ensign is not flown by a boat in a race, which signals to other boats that you are racing.
To prevent wear and tear, the flag may not be flown when out of sight of other vessels or when nobody is aboard. The flag is flown while entering or leaving a port, even at night. For purists: In the morning, the ensign is hoisted rapidly before other flags. In the evening, it is lowered slowly and with ceremony after other flags come down.
Additional sources: Seaflags http://www.usps.org/f_stuff/etiquett.html
- PREMIUM FILES
- Pre-Owned Yachts
- Charter Boat Owners/Buyers Forum
- Favorite Links
Most read articles
- VHF Radio Basics
- Catamarans - Monohulls: Pros and Cons
- Charter Boat Ownership for Dummies
- Charter Boat Owners Group
Copyright ©2000 - 2022 Sailonline.com. Unauthorized reproduction prohibited. Sailonline is not affiliated with any charter company.

Couldn't find the right flag or product? Contact Us! [email protected] Retail Flag Store Location Flag-Works over America, LLC, 16 Kennedy Lane, Concord, NH 03301
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
- Sailboat Flag Etiquette
Sailboat Flag Etiquette: What You Need to Know
Sailboat flag etiquette is steeped in maritime tradition and enshrined in law. If you're new to the world of sailing, you may have wondered about the various flags that you see flying on other sailboats or that you are expected to fly on your own. What do they mean? How should they be displayed? What are the rules and traditions that govern them?

An experienced sailboat skipper will know that flag etiquette is a way of showing respect, courtesy and recognition to other vessels, countries and organizations.
It also helps you communicate important information, such as your nationality, your club affiliation, your intentions or your distress.
For the less experienced we'll explain the basics of sailboat flag etiquette and how it should be applied in practice:
- The types of flags that you can fly on your boat;
- The sizes and positions of the flags;
- The occasions and situations when you should fly certain flags;
- The common mistakes and pitfalls to avoid when flying flags.
The skipper of the Bowman 57 staysail ketch shown here is correctly flying a burgee (the Flying Fish burgee of the Ocean Cruising Club ) from the port spreader, and a courtesy ensign (of Spain in this case) from the starboard spreader.
The ensign, in this case that of the Republic of Ireland, is flown from a flag halyard fom the mizzen mast to the end of the missen boom. Alternatively the ensign could be flown from a staff attached to the taffrail.
The Types of Flags
There are many types of flags that you can fly on your boat, but the most common ones are:
- The ensign: This is the flag that shows the country of registry of your boat and indicates its nationality. It is usually flown at the stern of the boat, as close as possible to the waterline. It is the most senior position for a flag on a boat and it should always be larger than any other flag. A UK flagged boat (sail or power) must wear the national maritime flag, the Red Ensign, unless entitled to wear a special ensign.

- The burgee: This is the flag that shows the yacht club or association that you belong to. It is usually flown at the main masthead of the boat above any other flag, but can be flown from the port spreader unless otherwise stipulated under a special warrant.
- The courtesy flag: This is the flag that shows the national flag of the country that you are visiting or whose waters you are sailing in. It is a sign of respect and goodwill to the host country and it should be flown at the starboard spreader. It should be hoisted as soon as you enter foreign waters and lowered as soon as you leave them.
- The Q flag: This is a yellow flag that indicates that you are requesting clearance from the local authorities when entering a foreign port. It is also flown at the starboard spreader of the boat, below the courtesy flag if there is one. It should be hoisted before you enter the port and lowered after you have been cleared.
- The signal flags: These are flags that have specific meanings in the International Code of Signals. They can be used to spell out messages or to convey information such as your position, your course, your speed, your intentions or your distress. They can be flown individually or in combinations at various locations on the boat.
- The private signal: This is a personal or family flag that has no official meaning or recognition. It can be flown at the port spreader of the boat, below any other flag. It is optional and purely decorative.
The Sizes and Positions of the Flags
The sizes and positions of the flags on your boat are important for both aesthetic and practical reasons. They should be proportionate to your boat size, visible from a distance and clear from any obstruction.
The general rules for sizing and positioning flags are:
- The ensign should be one inch on the fly (the length) for every foot of overall length of your boat. It should be flown on the stern staff or on a gaff if there is one.

- The burgee should be half an inch on the fly for every foot of overall length of your sailboat or five-eighths of an inch for every foot of overall length of your powerboat. It should be flown at the main masthead or on a pigstick (a vertical extension) if there is one.
- The courtesy flag should be the same size as the burgee or slightly smaller. It should be flown at the starboard spreader, preferably on its own halyard.
- The Q flag should be the same size as the courtesy flag or slightly smaller. It should be flown at the starboard spreader, below the courtesy flag if there is one, on its own halyard.
- The signal flags should be sized according to their function and meaning. They can be flown individually or in combinations at various locations on the boat, such as the masthead, the yardarm, the bow or the stern of the boat.
- The private signal should be the same size as the burgee or slightly smaller. It should be flown at the port spreader, below any other flag, on its own halyard.
The Occasions and Situations When You Should Fly Certain Flags
The occasions and situations when you should fly certain flags on your boat depend on where you are, what you are doing and who you are with. Some flags are mandatory, some are optional and some are forbidden.
The general rules for flying flags are:
- You must fly your ensign at all times in daylight, especially when near to or in sight of land or another boat. You must also fly your ensign when entering or leaving a foreign port and on demand. You can fly your ensign at night if you wish, but it is not required.
- You can fly your burgee at any time, but it is customary to hoist it at 0800 and lower it at sunset. You can also fly your burgee at night if you wish, but it is not required.
- You must fly the courtesy flag of the country that you are visiting or whose waters you are sailing in as soon as you enter their jurisdiction and until you leave it. You must also fly the Q flag when entering a foreign port until you have been cleared by the local authorities. You can lower the Q flag after you have been cleared, but you should keep the courtesy flag until you leave the port or the country.
- You can fly signal flags whenever you need to communicate with other boats or shore stations using the International Code of Signals. You can also fly signal flags for decorative purposes, such as dressing your boat for a special occasion, but you should avoid using flags that have specific meanings or that could cause confusion.
- You can fly your private signal whenever you want, but it has no official significance or recognition. It is purely a personal or family emblem.
The Common Mistakes and Pitfalls to Avoid When Flying Flags
Flying flags on your boat can be fun and rewarding, but it can also be tricky and challenging. There are some common mistakes and pitfalls that you should avoid when flying flags, such as:
- Flying an incorrect, damaged, wrongly sized or otherwise invalid ensign. This is a breach of law and etiquette and could lead to fines or penalties.
- Flying a special ensign without being entitled to do so. This is a privilege granted by a warrant from the Admiralty or by an Act of Parliament and it requires certain conditions to be met.
- Flying a burgee that does not match your ensign or that is higher than your ensign. This is a sign of disrespect and ignorance and could offend other boats or authorities.
- Flying more than one burgee at a time. This is considered sloppy and excessive and could imply that you are showing off or indecisive.
- Flying a courtesy flag that is larger than your burgee or that is above your burgee on the same halyard. This is a sign of subservience and inferiority and could insult your own country or club.
- Flying a Q flag when you have already been cleared or when you are leaving a port. This is unnecessary and confusing and could cause delays or misunderstandings.
- Flying signal flags that have specific meanings or that could cause confusion for decorative purposes. This is irresponsible and dangerous and could lead to accidents or incidents.
- Flying a private signal that resembles an official flag or that has an offensive meaning. This is misleading and rude and could provoke anger or hostility.
- And you should never, ever, fly a skull-and-crossbones flag. There is nothing amusing or glamorous about pirates.
Sailboat Flag Etiquette: A Few FAQs...
Why do some British sailboats fly a White or Blue Ensign rather than the traditional Red Ensign?
Some British sailboats fly a white or blue ensign because they belong to certain yacht clubs or organisations that have special permission to use these ensigns.
The white ensign is a variation of the national flag that is normally used by the Royal Navy, but it can also be worn by yachts owned by members of the Royal Yacht Squadron , which is a privileged yacht club with a long history and close ties to the monarchy.
The blue ensign is another variation of the national flag that is normally used by government vessels, but it can also be worn by yachts that belong to one of the 32 yacht clubs or associations that have a warrant from the Admiralty or the relevant authority to use the undefaced blue ensign.
Additionally, some yachts can wear a blue ensign defaced with the badge of their club or association, if they have a warrant for that as well. There are 57 yacht clubs or associations that have this privilege.
These special or privileged ensigns are considered a mark of distinction and honour, and they should only be flown with proper authorisation and following the rules and regulations of wearing them.
What is the difference between an ensign and a burgee?
An ensign is a flag that shows the nationality of the vessel and must be worn at the stern or as close to it as possible. A burgee is a flag that shows the membership of a yacht club or sailing association and can be worn at the masthead or the port spreader.
What is a special ensign and how can I get one?
A special ensign is a variation of the national flag that can be worn by certain yachts that belong to a privileged yacht club or organisation. To get one, you need to apply for a warrant from the Admiralty or the relevant authority and follow the rules and regulations of wearing it.
How big should my flags be and how should I hoist them?
The size of your flags depends on the length of your vessel, but as a general rule, your ensign should be about one inch for each foot of overall length. Your burgee and courtesy flag should be smaller than your ensign, but not too small to be seen. You should hoist your flags using halyards or staffs and make sure they are not tangled, faded, or torn.
When should I raise and lower my flags?
You should raise your flags at 0800 hours or when you leave harbour, whichever is later, and lower them at sunset or when you enter harbour, whichever is earlier. You should also lower your flags when out of sight of other vessels or when nobody is aboard.
Can I fly more than one burgee or other flags on my vessel?
Traditionally, you should only fly one burgee at a time, but some yachts may choose to fly more than one to show their affiliation with different clubs or associations. However, you should always make sure that your burgee matches your ensign if you are wearing a special one. You can also fly other flags, such as signal flags, house flags, or personal flags, but they should not take precedence over your ensign, burgee, or courtesy flag.
How should I salute other vessels or authorities with my flags?
You can salute other vessels or authorities by dipping your ensign, which means lowering it halfway down the staff or halyard and then hoisting it back up. You should only do this if you receive a salute first or if you are passing by a naval vessel, a Coast Guard vessel, or a foreign warship.
What are the rules for flying flags in a race?
The rules for flying flags in a race may vary depending on the organising authority, but generally, you should not fly your ensign during a race, as this signals that you are not racing. You should also follow any instructions given by the race committee regarding signal flags, class flags, or protest flags.
What are the consequences of not following flag etiquette?
Not following flag etiquette may result in fines, penalties, or even confiscation of your vessel if you break the law or offend the host country. It may also cause confusion, misunderstanding, or disrespect among other sailors or authorities. Therefore, it is advisable to learn and follow the proper flag etiquette whenever you go sailing.
I wrote this article using GPT-4, OpenAI’s large-scale language-generation model, as a research assistant to develop source material. I wrote the final draft in its entirety and believe it to be accurate to the best of my knowledge.
Dick McClary
Recent Articles
Westerly Oceanranger 38 for sale
May 19, 24 04:09 AM
Hunter Passage 450 for sale
May 18, 24 03:46 AM
Used Sailing Equipment For Sale
May 15, 24 02:04 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com

- CLASSIFIEDS
- NEWSLETTERS
- SUBMIT NEWS

Flag Etiquette on a sailing boat today

Related Articles

Currency: GBP
- Worldwide Delivery
Mooring Warps and Mooring Lines
- LIROS 3 Strand Polyester Mooring Warps
- LIROS Green Wave 3 Strand Mooring Warps
- LIROS Braided Dockline Mooring Warps
- LIROS Handy Elastic Mooring Warps
- Marlow Blue Ocean Dockline
- LIROS Super Yacht Mooring Polyester Docklines
- 50 metre / 100 metre Rates - Mooring
Mooring Accessories
- Mooring Compensators
Mooring Strops and Bridles
- V shape Mooring Bridles
- Y shape Mooring Bridles
- Small Boat and RIB Mooring Strops
- Mooring Strops
- Mooring Strops with Chain Centre Section
Mooring Assistance
- Coastline Bow Thruster Accessories
- Max Power Bow Thrusters
- Bonomi Mooring Cleats
- Majoni Fenders
- Polyform Norway Fenders
- Ocean Inflatable Fenders
- Dock Fenders
- Fender Ropes and Accessories
Mooring Components
- Mooring Swivels
- Mooring Shackles
- Mooring Cleats and Fairleads
- Mooring Buoys
Mooring Information
- Mooring Warps Size Guide
- Mooring Lines - LIROS Recommended Diameters
- Mooring Rope Selection Guide
- Mooring Warp Length and Configuration Guide
- How to estimate the length of a single line Mooring Strop
- Mooring Ropes - Break Load Chart
- Mooring Compensator Advisory
- Rope Cockling Information
- Fender Size Guide
- Majoni Fender Guide
- Polyform Norway Fender Inflation Guide
Custom Build Instructions
- More Article and Guides >
Anchor Warps Spliced to Chain
- LIROS 3 Strand Nylon Spliced to Chain
- LIROS Anchorplait Nylon Spliced to Chain
Anchor Warps
- 50 / 100 metre Rates - Anchoring
- Drogue Warps and Bridles
- Leaded Anchor Warp
- LIROS 3 Strand Nylon Anchor Warps
- LIROS Anchorplait Nylon Anchor Warps
- Aluminium Anchors
- Galvanised Anchors
- Stainless Steel Anchors
Calibrated Anchor Chain
- Cromox G6 Stainless Steel Chain
- G4 Calibrated Stainless Steel Anchor Chain
- Lofrans Grade 40
- MF DAMS Grade 70
- MF Grade 40
- Titan Grade 43
- Lewmar Windlasses
- Lofrans Windlasses
- Maxwell Windlasses
- Quick Windlasses
- Windlass Accessories and Spares
Chain Snubbers
- Chain Hooks, Grabs and Grippers
- Chain Snubbing Bridles
- Chain Snubbing Strops
Anchoring Accessories
- Anchor Connectors
- Anchor Trip Hooks and Rings
- Anchoring Shackles
- Bow Rollers and Fittings
- Chain and Anchor Stoppers
- Chain Links and Markers
Anchoring Information
- How To Choose A Main Anchor
- Anchoring System Assessment
- Anchor Chain and Rope Size Guide
- The Jimmy Green Guide to the Best Anchor Ropes
- What Size Anchor Do I Need?
- Anchor Size Guides
- Anchor Rope Break Load and Chain Compatibility Chart
- How to Choose Your Anchor Chain
- How to Establish the Correct Anchor Chain Calibration?
- Calibrated Anchor Chain - General Information
- Calibrated Anchor Chain Quality Control
- Calibrated Chain - Break Load and Weight Guide
- Galvanising - Managing Performance and Endurance expectation
- Can Galvanised Steel be used with Stainless Steel?
- Windlass Selection Guide
- More Articles and Guides
Stainless Steel Wire Rigging and Wire Rope
- 1x19 Wire Rigging
- 50 / 100 metre Rates - Wire and Fibre
- 7x19 Flexible Wire Rigging
- Compacted Strand Wire Rigging
Dinghy Rigging
- Dinghy Rigging Fittings
- Fibre Dinghy Rigging
- Stainless Steel Dinghy Rigging
- Wind Indicators
Fibre Rigging
- DynIce Dux Fibre Rigging
- LIROS D-Pro Static Rigging
- LIROS D-Pro-XTR Fibre Rigging
- Marlow Excel D12 MAX 78 Rigging
- Marlow M-Rig Max Rigging
Wire Terminals
- Cones, Formers, Wedges, Ferrules, Rigging Spares
- Hi-Mod Swageless Terminals
- Sta-Lok Swageless Terminals
- Swage Terminals
- Headsail Reefing Furlers
- Plastimo Jib Reefing
- Selden Furlex Reefing Gear
Furling Systems
- Anti-torsion Stays
- Straight Luff Furlers
- Top Down Furlers
Guard Wires, Rails and Fittings
- Guard Rail Fittings
- Guard Rails in Fibre and Webbing
- Guard Wire Accessories
- Guard Wires
Wire Rigging Fittings
- Babystay and Backstay Adjustment
- Terminal Backing Plates and Coquilles
- Turnbuckles and Rigging Screws
Rigging Accessories
- Rigging Chafe Protection
Standing Rigging Assistance
- More Articles and Guides >
- Cruising Halyards
- Performance Halyards
- Dinghy Halyards
Rigging Shackles
- Captive and Key Pin Shackles
- hamma™ Snap Shackles
- Soft Shackles
- Standard Snap Shackles
- Wichard Snap Shackles
Classic Ropes
- Classic Control Lines
- Classic Halyards
- Classic Sheets
- Cruising Sheets
- Performance Sheets
- Dinghy Sheets
Sail Handling
- Boom Brakes and Preventers
- Lazy Jack Sail Handling
- Rodkickers, Boomstruts
- Sail Handling Accessories
50 / 100 metre Rates - Running Rigging
- 50 / 100 metres - Cruising Ropes
- 50 / 100 metres - Dinghy Ropes
- 50 / 100 metres - Performance Ropes
Control Lines
- Cruising Control Lines
- Performance Control Lines
- Dinghy Control Lines
- Continuous Control Lines
Running Rigging Accessories
- Anti-Chafe Rope Protection
- Lashing, Lacing and Lanyards
- Mast and Boom Fittings
- Rope Stowage
- Sail Ties and Sail Stowage
- Shock Cord and Fittings
- LIROS Ropes
- Marlow Ropes
Running Rigging Resources
- Running Rigging Rope Fibres and Construction Explained
- How to Select a Suitable Halyard Rope
- How to select Sheets and Guys
- Dyneema Rope - Cruising and Racing Comparison
- Dinghy Rope Selection Guide
- Rope Measurement Information
- Running Rigging - LIROS Recommended Line Diameters
- Running Rigging Break Load Comparison Chart
- Colour Coding for Running Rigging
- Selecting the right type of block, plain, roller or ball bearing
- Replacing your Furling Line
- Recycling Rope
- Running Rigging Glossary
Custom Build Instructions for Sheets, Halyards, Control Lines
Plain bearing blocks.
- Barton Blocks
- Harken Element Blocks
- Low Friction Rings
- Selden Yacht Blocks
- Wichard MXEvo Blocks
- Wooden Yacht Blocks
Control Systems
- Ratchet Blocks
- Stanchion Blocks and Fairleads
- Snatch Blocks
- Genoa Car Systems
- Traveller Systems
- Block and Tackle Purchase Systems
Ball Bearing Blocks
- Harken Ball Bearing Blocks
- Selden Ball Bearing Blocks

Roller Bearing Blocks
- Harken Black Magic Blocks
- Selden Roller Bearing Blocks
Deck Fittings
- Bungs and Hatches
- Bushes and Fairleads
- Deck Eyes, Straps and Hooks
- Pad Eyes, U Bolts and Eye Bolts
- Pintles and Gudgeons
- Tiller Extensions and Joints
- Harken Winches, Handles and Accessories
- Barton Winches, Snubbers and Winchers
- Lewmar Winches, Handles and Accessories
- Winch Servicing and Accessories
Clutches and Organisers
- Barton Clutches and Organisers
- Spinlock Clutches and Organisers
- Lewmar Clutches
- Harken Ball Bearing Cam Cleats
- Barton K Cam Cleats
Deck Hardware Support
- Blocks and Pulleys Selection Guide
- Barton High Load Eyes
- Dyneema Low Friction Rings Comparison
- Seldén Block Selection Guide
- Barton Track Selection Guide
- Barton Traveller Systems Selection Guide
- Harken Winch Selection Guide
- Karver Winch Comparison Chart
- Lewmar Winch Selection Guide - PDF
- Winch Servicing Guide
Sailing Flags
- Courtesy Flags
- Red Ensigns
- Blue Ensigns
- Signal Code Flags
- Flag Staffs and Sockets
- Flag Accessories
- Flag Making and Repair
- Webbing only
- Webbing Soft Shackles
- Webbing Restraint Straps
- Webbing Sail Ties
- Sail Sewing
- PROtect Tape
Fixings and Fastenings
- Screws, Bolts, Nuts and Washers
- Monel Rivets
Hatches and Portlights
- Lewmar Hatches
- Lewmar Portlights
- Fids and Tools
- Knives and Scissors
General Chandlery
- Carabiners and Hooks
- Antifouling
Chandlery Information
Flag articles, flag size guide.
- Bending and Hoisting Methods for Sailing Flags
- Courtesy Flags Identification, Labelling and Stowage
- Courtesy Flag Map
- Flag Etiquette and Information
- Glossary of Flag Terms and Parts of a Flag
- Making and Repairing Flags
- Signal Code Message Definitions
Other Chandlery Articles
- Anchorplait Splicing Instructions
- Antifoul Coverage Information
- Hawk Wind Indicator Selection Guide
- Petersen Stainless - Upset Forging Information
- Speedy Stitcher Sewing Instructions
- Thimble Dimensions and Compatible Shackles
Jackstays and Jacklines
- Webbing Jackstays
- Stainless Steel Wire Jackstay Lifelines
- Fibre Jackstay Lifelines
- Jackstay and Lifeline Accessories
Lifejackets
- Children's Life Jackets
- Crewsaver Lifejackets
- Seago Lifejackets
- Spinlock Lifejackets
Floating Rope
- LIROS Multifilament White Polypropylene
- LIROS Yellow Floating Safety Rope
Guard Wires, Guardrails and Guardrail Webbing
Lifejacket accessories.
- Lifejacket Lights
- Lifejacket Rearming Kits
- Lifejacket Spray Hoods
- Safety Lines
Seago Liferafts
- Grab Bag Contents
- Grab Bags and Polybottles
- Liferaft Accessories
- Danbuoy Accessories
- Jimmy Green Danbuoys
- Jonbuoy Danbuoys
- Seago Danbuoys
Overboard Recovery
- Lifebuoy Accessories
- Purchase Systems
- Slings and Throwlines
Safety Accessories
- Fire Safety
- Sea Anchors and Drogues
Safety Resources
- Guard Wires - Inspection and Replacement Guidance
- Guard Wire Stud Terminal Dimensions
- Webbing Jackstays Guidance
- Webbing Jackstays - Custom Build Instructions
- Danbuoy Selection Guide
- Danbuoy Instructions - 3 piece Telescopic - Offshore
- Liferaft Selection Guide
- Liferaft Servicing
- Man Overboard Equipment - World Sailing Compliance
- Marine Safety Information Links
- Safety Marine Equipment List for UK Pleasure Vessels
Sailing Clothing
- Sailing Jackets
- Sailing Trousers
- Thermal Layers
Leisure Wear
- Accessories
- Rain Jackets
- Sweatshirts
Sailing Footwear
- Dinghy Boots and Shoes
- Sailing Wellies
Leisure Footwear
- Walking Shoes
Sailing Accessories
- Sailing Bags and Holdalls
- Sailing Gloves
- Sailing Kneepads
Clothing Clearance
Clothing guide.
- What to wear Sailing
- Helly Hansen Mens Jacket and Pant Size Guide
- Helly Hansen Womens Sailing Jacket and Pant Size Guide
- Lazy Jacks Mens and Womens Size Charts
- Musto Men's and Women's Size Charts
- Old Guys Rule Size Guide
- Sailing Gloves Size Guides
- Weird Fish Clothing Size Charts
The Jimmy Green Clothing Store
Lower Fore St, Beer, East Devon, EX12 3EG
- Adria Bandiere
- Anchor Marine
- Anchor Right
- August Race
- Barton Marine
- Blue Performance
- Brierley Lifting
- Brook International
- Brookes & Adams
- Captain Currey
- Chaineries Limousines
- Coastline Technology
- Colligo Marine
- Cyclops Marine
- Douglas Marine
- Ecoworks Marine
- Exposure OLAS
- Fire Safety Stick
- Fortress Marine Anchors
- Hawk Marine Products
- Helly Hansen
- International
- Jimmy Green Marine
- Maillon Rapide
- Mantus Marine
- Marling Leek
- Meridian Zero
- MF Catenificio
- Ocean Fenders
- Ocean Safety
- Old Guys Rule
- Petersen Stainless
- Polyform Norway
- PSP Marine Tape
- Sidermarine
- Stewart Manufacturing Inc
- Team McLube
- Technical Marine Supplies
- Titan Marine (CMP)
- Ultramarine
- Waterline Design
- William Hackett
Clearance August Race Boat Cleaning Kit £26.00
Clearance LIROS Racer Dyneema £55.08
Clearance Folding Stock Anchor £123.25
Clearance LIROS Herkules £0.00
Clearance Barton Size 0 Ball Bearing Blocks - 5mm £10.13
Clearance Marlow Blue Ocean® Doublebraid £18.48
Mooring Clearance
Anchoring clearance, standing rigging clearance, running rigging clearance, deck hardware clearance, chandlery clearance, safety clearance, yacht flags sizing guide, traditional yard sizing for flags.
The yard sizing (traditional diagonal measurement) is nominal and may vary slightly due to the nature of the production/sewing process.
- The Yard Size refers to the outside diagonal measurement, e.g. from the top corner of the hoist to the bottom corner of the fly end.
- The fly is measured along the horizontal length, top or bottom.
- The hoist is measured down the vertical length of the left-hand side next to the staff.
- The Fly end is the opposite end to the hoist = the end that flies in the breeze.
The yard sizing (traditional diagonal measurement) is nominal and may vary slightly due to the nature of the production/sewing process.
Nominal length and height measurements are tabled in the guide below.
Selecting the appropriate size for your Courtesy Flags:
Generally, yachts up to about 60 feet (18 metres) in length look properly "dressed" with half yard (18" x 12" or 45x30cm) courtesy flags.
There is a smaller size range (12"x8") not available from Jimmy Green because these flags look insignificant from deck level when hoisted aloft.
There is an old rule of thumb for courtesy flags: a half inch on the fly for every foot of overall vessel length, e.g. 18 inches = ½ yard for a 36-foot yacht.
3/4 yard Courtesy Flags are available for larger yachts or skippers who wish to 'make a statement'.
What Size Ensign do I Need?
As a guide, your Ensign should be proportionate to the LOA and the style/design of the yacht.
An old rule of thumb for the size of your Ensign is an inch per foot of yacht length, but this may look rather small for modern yachts to look "well dressed".
The Ensign hoist measurement also needs to be compatible with the length of the flagstaff. i.e. The length of the flagstaff between the truck (head) and the cleat must be, at the very least, greater than the hoist measurement so there is sufficient room to tension the hoist line or halyard.
The gap between the bottom of the hoist and the cleat is a matter of personal choice.
A more modern interpretation of suitable Red Ensign yard size is suggested in the chart below, but...
Ultimately, the size of a Red Ensign is entirely up to the owner's discretion, and if it looks right, then it is right.
Flag Size Chart Glossary: Yard Size: the traditional method of measurement = length of the diagonal Finish: Sewn = individual panels stitched together to complete the flag
Finish: Printed = one screen-printed piece of fabric Fly: nominal length, may vary slightly due to the nature of the production/sewing process Hoist: nominal height, may vary slightly due to the nature of the production/sewing process Staff Length: the length overall of the flagstaff N.B. the measurement between the truck and the cleat will be less than the overall length LOA = Yacht Length Overall
Flag Toggles
Top-quality wooden toggles are available at a reasonable cost and can be fitted to the loop at the top of the hoist if required:
Wooden Flag TOGGLES

A Yard and a Half Sewn Red Ensign on Roshni, Azuree 46

A Yard and a Half Printed Red Ensign on Max, Moody 47
Choosing between Printed and Sewn Flags:
Printed courtesy flags are generally accepted everywhere you may visit.
Sewn courtesy flags may prove far too expensive on an extended voyage.
Printed courtesy flags are lighter and therefore fly better in a light breeze.
However, there are two distinct schools of thought regarding your Red Ensign (or national flag), and either is acceptable.
- Printed - is less than half the cost and ‘will soon be blown out anyway'.
- Sewn - is the only proper flag to fly, will last longer and is worth 'every penny.'
Shop for Flags
FREE Shipping Available Orders $75+*
- Call us: 800-858-8776
- Sign In & Register
- Gift Certificates
- Recently Viewed
Your 2024 Guide to Nautical Flag Etiquette
Ever wonder why there are so many boat flags ? How do the sailors know which flag to put first and when? Nautical flag etiquette is an essential part of sailing. The seven most common types of boat flags are Skin Diver flags , Storm Warning flags , Coast Guard boat flags , US Jack flags , Maritime flags and Pennants, Yacht Ensign & Officer flags , and most importantly the International Code Signal flags .
Code signal flags and are frequently used by boats to send messages to other boats. They are made with a sequence of twenty-six square flags that represent a letter of the nautical alphabet. Ten numbered flags, one answering pendant, and three repeaters also form part of the nautical flag sequence.
As with most yesteryear traditions, the popularity of boat flags as a common communication tool is slowly reducing with the introduction of technology. This does not mean that we should discard this sacred tradition.
The world of nautical flags is broad, and we cannot possibly cover them all in this article. Navies, yachts and fishing boats have variations in the meaning of some flags.
While the need for nautical flags might be dwindling in the boating world, they are still pleasing to the eye. Learning when to use nautical flags and how to use them is a skill every sailor and thalassophile should have. Not only is it essential for safety reasons, but boat flags can also a lot of fun. Take a gander at our fun maritime flags and pennants !
Word of the Day: A thalassophile is someone that loves the sea!
This article will teach you the hows and whens of nautical flag etiquette. We will also provide you with a glossary of terms because, let's face it, some boating terms are pretty confusing even for a seasoned sailor.
So put your best sailor's cap on and join us on this great sea signal voyage.
What is Nautical Flag Etiquette?
Glossary of flag terms, flag courtesies.
As silly as it might seem, boat flag etiquette is crucial. In a worst-case scenario, it could mean the difference between life and death. Generally speaking, the nautical flag etiquette is a combination of years of maritime tradition and laws that help boats communicate messages to each other.
Different countries have varying legal requirements that should be observed for boats that enter and leave their waters or ports. So it is helpful to be mindful of sailing the vessel’s legal obligation for various countries. No one likes to pay a fine for something as simple as forgetting or putting up the wrong flag signal.
As we have stated before, the world of boating is vast and sometimes confusing. The terminology used is pretty unique. The key to understanding nautical etiquette is to know what everyone is talking about first.
Even professional sailors don't always get it right. So to help you brush up on your boating terms, we've put together this glossary with definitions. We hope this will help you to understand the nautical phrases that we will use in this article.
ABAFT - refers to the rear end or stern of a ship
AFT – means towards stern of the boat (the back of the boat)
ASTERN – it means to go towards the back of the boat
BOW - refers to the front of the ship
BUTT DIAMETER - is the width of the bottom of the flagpole.
CANTON - the rectangular part of a flag, usually at the top hoist corner of a flag, which occupies about a quarter of the total surface area of the flag
CLOSE UP - it means that the flags are now fully hoisted
COLORS - refers to the raising and taking down of the flags at 8:00 am and at sunset, respectively
COURTESY FLAG - is the national flag of the country that a boat is entering. Ex: Boats entering the United States would display an American flag as a courtesy flag.
DIP - means to lower a flag by turning it forward from an upright position to 45° or horizontal as a sign of deference or respect
ENSIGN - means a flag showing nationality of the boat, i.e. the country where the boat is registered. Ex:
- The Red Ensign can be flown by a merchant vessel
- The White Ensign can be flown by war or naval ships
- The Blue Ensign can be flown by public or government vessels
- The Civil Ensign is flown by civilian vessels
- The Yacht Ensign is flown by yachts and is typically the largest flag on board; the flag may be flown at stern staff
- The USPS ensign is flown by the United States Power Squadrons and is flown to signal that the boat is commanded by an active member of the USPS.
FLAG STAFF AT THE STERN - a pole at the stern/ back of the ship where the ship's country of registry flags is flown
FLY - refers to the length of the flag, measured from the heading to the fly end
GAFF - is a rig that extends from the flagpole that allows for more flags to be hoisted, which usually rises at an angle and represents the mast of a ship
HALYARD - rope or stainless steel cable used to hoist and lower flags
HOIST - the raising of flags
HOIST END - the edge of the flag that is closest to the flagpole
HOUSE FLAG - refers to the emblem that shows the company or commercial house that a merchant ship belongs to and also refers to a yacht owner's personal flag
INTERCO - stands for the International Code of Signals used in the maritime system
JACK - mean the additional national flags flown by warships (and certain other vessels) at the head of the shi
MASTHEAD - is the tallest part of a ship's mast or the lower section of a mast
NAUTICAL –refers to everything associated with maritime travel
NAUTICAL FLAGPOLE --refers to a flagpole with a yardarm and or gaff
PENNANT - is a triangular-shaped flag
PRATIQUE - refers to the license or permission to use a port from the host country
STARBOARD - is the right-hand side of the boat when you are facing the bow.
STARBOARD SPREADER - is the most forward part on the mast (if there is more than one) where the courtesy and q flags are flown
STEM – refers to the most forward part of the bow
STERN – refers to the back of the boat
STERN LINE – is the docking line that comes from the stern
TACK LINE - is the length of the halyard; it's used to separate the group of flags
UNDERWAY – means a vessel in motion
YARDARM - refers to the horizontally mounted and tapered pole attached to a flagpole to create a "t" or a cross
Now that we are familiar with some common terminology used in nautical language, let's move on to the order in which the flags must be arranged in terms of nautical flag etiquette rules.
This order is universal across the globe. We must follow the order to avoid confusing other ships. The flag with the highest honor should be flown at the highest point.
The order is as follows:
- Gaff (reserved for the national ensign/ country flag)
- Flagstaff at the stern
- Starboard yardarm (Halyard)
- Truck of mast (masthead)
- Port yardarm (Halyard)
First, we need to establish the system that governs these nautical flag rules. INTERCO is the International Code of Signals. The system is used worldwide to communicate nautical messages related to navigation, safety, and maritime.
Signal flags like the ones we are discussing in this article form part of INTERCO's signals. The other signals include radiotelegraphs or radiotelephones, ALDIS lamps, hand signals and some sound signals to name a few.
Knowing and understanding the basics of the INTERCO signaling system is extremely important for anyone interested in sailing. Whether privately or otherwise.
The National Ensign/Flag
Let's talk about nautical etiquette rules that apply for the most critical flag signal, the national ensign.
The U.S. national ensign is the preferred flag for all U.S. vessels. This ensign is also known as the “50-star of “Old Glory.” This is also the preferred ensign for yachts, especially when sailing in international or foreign waters.
Great honor is given to the national flag of the country in which the ship is registered. On the order of positioning for the flags, the national ensign is given that most senior position; the gaff. If your boat does not have a gaff, then you should fly the ensign from the flagstaff at your boat's stern.
The second rule is that you can fly no other flag above the national ensign on the same halyard. Additionally, the Jack and the National Ensign should not be hoisted together. The Jack is only hoisted when the ship is at anchor or made fast to the shore or to buoy, never when the ship is underway, when the last line is cast off, and when the anchor is aweigh. We do not recommend hoisting the Jack for recreational purposes.
The scenarios where a national ensign should be flown include:
- When dressing the ship
- When occupying foreign waters during the daylight hours
- When moving along a foreign port or a combat ship (man of war)
The Courtesy Flag
Flying the courtesy flag is a centuries-old tradition that is still relevant in these modern times. The act of flying a foreign nation's flag as your ship passes through or enters its waters is not only a sign of respect, it is an essential etiquette to observe. While there is no legal requirement to fly a courtesy flag, it is a polite custom to which you should adhere.
The only legal requirement for vessels in foreign water is to fly the red ensign flag.
Where does the courtesy flag fly? As per tradition, the courtesy flag is flown at the starboard spreader. If your boat has more than one mast, you must fly the courtesy flag from the forward most mast. The courtesy flag is tied and hoisted after the authorities have granted your vessel clearance to enter their space.
Key rules for courtesy flag etiquette include:
- Never fly the national ensign and the courtesy flag on the same mast because that will be interpreted as a sign of you are challenging the foreign nation's authority
- Never fly a courtesy flag that is in terrible condition; this is a sign of disrespect
- If you have guests on your boat that are of another nationality, then you should also fly their national flags as a courtesy, but never on the same mast
- When you return to your home country, always take down the foreign country's flag
Additional courtesy flag etiquette includes:
- If your boat is mastless, then the courtesy flag can replace any flag which is normally flown at the bow of the boat
- If your boat has a mast with a spreader, the courtesy flag is flown at the starboard spreader
However, you must keep in mind that these rules or traditions vary from one country to another, so always make sure that you look for the correct information.
Nautical Flag Etiquette Entering a Foreign Port
The Q flag is the first flag that you must raise when entering foreign waters or a foreign port. It signals to the port authorities that your ship is healthy and you require free practice.
We always fly the Q flag in international waters before customs clears you for entry. After clearing, you then replace the Q flag with the courtesy flag. You often fly the Q flag on the starboard yardarm.
Dressing the Ship
Certain occasions require that your vessel be decked up with all the flags that it can hold. We call this dressing the ship.
It is reserved for special occasions such as public holidays or when the ship is beginning its maiden or last voyage. Dressing the ship is only done when the ship is not underway.
The ship's full splendor will be on display, so this is the time to have fun. The dressing begins at 08.00 am at anchor unless it is the ship's maiden or last voyage, then the dressing can occur at sea.
The national ensign is first. All the other flags will follow, lining up from the waterline forward to the waterline after using the stem or bowsprit end and the masthead.
We have barely scratched the surface of all the rules and customs you need to follow to observe proper nautical flag etiquette. However, we hope that we have simplified some of the most important customs in maritime tradition. Hopefully, the next time you are on a boat, you will understand the meaning of the signals and flags better. Happy sailing!
Recent Posts
The best american flag: a durability study.
At Flags.com, we're not just passionate about providing the best American flags; we're also commi
Army Flag FAQ
As a symbol of one of America’s oldest military branches, the Army flag is proudly flown by servi

Boats & Flags: 11 Answers You Should Know (For Beginners)
The flags on a boat can signify many different things.
Mostly, they can seem confusing to a layperson or a new boater.
Flying the wrong flag at the wrong position can confuse other boaters and result in a fine!
Here’s what you need to know about how and when you can use flags on a boat:
Table of Contents

1. What Are The Main Types Of Flags Flown On Boats?
On any non-commercial vessel, you can usually find these four different types of flags:
- Ensign – a variety of national flag
- Burgee – a flag representing a boating organization
- Private Signal – a small custom-made flag for the boat owner
- Courtesy – the flag of a foreign country for an onboard guest or when you are in foreign waters
2. What is an Ensign Flag, and When Do I Use It?
An ensign is a flag from the nation from which the boater originates.
They are slightly different from their national flags. Ensign flags used to be restricted to documented vessels only.
Now it is common courtesy to fly the national flag on all types of recreational boats.
It is proper etiquette to only fly ensign flags from 0800 to sunset unless you’re in a boat race outside those hours. It is also important to take this flag down before leaving your boat if it is unmanned at sunset.
If you take your boat into international waters, you should fly your national flag. These days ensign flags are flown off of the stern.
If you do this, make sure it is on a staff-pole and that the pole is long and angled.
If you offset it to one side (like the starboard side), it’ll fly clear of the engine’s exhaust.
This will also keep it clear from the rigging.
3. What is a Burgee Flag, and When Do I use That?
A burgee flag is a small flag with the skipper’s sailing organization or yacht club on it.
It follows the skipper from boat to boat. These are flown day and night.
Traditionally, sailing vessels hoisted these flags on a “pigstick” at the top of the highest mast. Because of instruments that are often at the top of the mast, it is more common to hoist a burgee on a spreader halyard.
Of course, this is the modern way to fly it.
The starboard rigging is known as a place of honor (when it comes to flags). That’s why you fly the host country’s flag there when visiting a foreign port.
4. What is a Private Signal, and When Do we use Those?
These are small flags that are custom designed (and custom made) specifically for the boat owner.
It’s flown day and night but is only flown when the owner is in command of the boat.
If a different sailor is in command, they are to fly their own private signal.
Private signals are flown at the aftermost mast’s head (if you have a multi-mast boat). On a sloop, fly private signals on starboard rigging, below the burgee.
Unless you don’t have a burgee, then you can fly it alone.
5. What’s a Courtesy Flag, and When Do I Fly That?
Courtesy flags are flown when you are in a foreign nation’s waters.
It also comes into play when you have someone from a foreign country on your vessel.
You can only fly a courtesy flag if certain conditions are met:
- Only after authorities from the country have granted you clearance.
- After you remove your yellow “Q” flag.
- If you have a flag that is in the proper condition.
- If you fly a courtesy flag, do so at the boat’s starboard spreader.
- If there is more than one mast, then it must be flown off the starboard spreader of the forward most mast.
By “proper condition,” you must fly a flag that is not old or in a disrespectful state.
If you do fly a ratty old flag, you could be fined for being disrespectful!
6. What About International Signal Flags?
There is a system of internationally recognized numerical and alphabetical pennants and flags known as the International Code of Signals.
This helps communicate when you’re out in the open water.
The messages these flags send can be about navigation or even safety.
Signals can be sent by:
- Flag semaphore
- Signal lamp (otherwise known as “blinkers”)
- Radiotelephony
- Radiotelegraphy
There are so many different communication methods because it is important when the crew’s safety is concerned—especially when you’re in open water.
Boaters use nautical signal flags in several different ways:
- With each spelling out a letter of a message
- With a flag symbolizing a specific message (For example, an “A flag” is flown by diving support vessels when they can’t move from their current location.)
- In a yacht or dinghy race, with each flag flying as code (For example, a “P flag” is used to stand for “Prepare,” which indicates that the race is about to start.)
Some boaters use signal flags to dress their ships for holidays by hoisting the national ensign at the stern staff first.
A rainbow of flags can then be arranged, reaching from the waterline forward to the aft, from the bowsprit end (or stem).
7. Why are There so Many Boat Flags?
Flags are flown for multiple reasons but remember that when you’re out at sea, this is the easiest way to recognize other boats.
It’s like the license plate on a car. Different countries have different license plates.
Within each country, different states or provinces can also have different license plates.
Then, you can have symbols that signify clubs or organizations on your license plate in each state.
This is a way you can express yourself on your vessel.
Check out our article about what colored flags on houses are all about.
8. Why are Some Flags Flown at Half-Mast?
Just like on land, flags are sometimes flown at half-mast in respect for someone who has passed.
This isn’t required in all places, nor is it mandated by any law.
However, it’s good to note why you might see this when you are out in the water.
Some boaters will also dip their flags (drop it down to half, then raise it again) as a friendly signal to a passing boater.
9. What Size Are Boat Flags?
Generally, boat flags come in different sizes, depending on the type of boat that you have.
For aesthetic purposes, most flags are roughly 1” per foot of the length of your boat.
Also, the staff should be twice the length of the height of your flag.
For example, if you have a powerboat that is 33’ long, you should have flags that are 24” x 36” on a staff that is 48”.
This is the recommended proportion of ensign flags. Burgee and private signals are approximately half that size. For the same powerboat example above, you might get burgee and private signal flags, which are 12” x 18”.
10 What do “Fishing Flags” Mean?
Fishing flags are signal flags that have representations of various types of fish on them.
Flying one (or more, if you’re lucky) lets other boaters know what sort of fish you’ve caught that day. It also lets other boaters know what sort of fish are in the area that day.
Fishing flags should be placed on the port rigger, spaced at least one flag length apart. This will let the proper authorities or other boaters count your catch easily.
It should also be placed in order of size, with the biggest species of fish on top.
Certain rules follow certain types of fish so make sure you read up on the fish flag etiquette in fishing manuals.
In the past, if a fisherman tagged a fish, they would fly the species flag with a white “T” under it to let others know of their tag. If they hoisted the species flags upside down, that signifies that they had caught and released that particular fish.
If they did so with multiple fish of the same species, they hoisted several red triangle pennants under that species flag.
However, today most fishermen are doing the opposite when they practice catch and release. They fly a fish right-side-up to signify that it swam away healthy after being released.
While an upside-down species flag signifies a fish caught and harvested.
11. How Much do Boat Flags Cost?
Boating flags can range from $12 for a single flag to $175 for a set.
The average cost for an ensign flag is roughly $20.
Final Thoughts
There is a long history of nautical flag use.
Using the wrong flag or flying a flag in the wrong position can get you into trouble. Thus, it is important to brush up on the meanings of different flags before using them.
It is important to have a boat handling book or flag manual on your boat in case of emergency. The US Power Squadron is a good source for their publication “ How to Fly Flags, Nautical Flags Display .”
If you are out with your family and an emergency occurs, they must know how to call and signal for help in different ways: including using a flag signal.
Flags aren’t just important for you and your boat, however.
It is also important to recognize what different flags may mean when you run across other boats.
Click to share...
For FLAGS, BANNERS, BURGEES....LEAVE it to BEAVER FLAGS!

- my account Sign in Register Gift Certificates
FREE SHIPPING TODAY on $99+ Orders! All of our flags are MADE IN THE USA !
US Ensign Sizes
The flag at the stern of your boat is either a U.S. ensign, a yacht ensign, or a USPS ensign. A national ensign flown at the flagstaff should be one inch on the fly for each foot of overall length of the vessel. So a 30 foot vessel should fly a national ensign that has at least a 30 inch fly. All other flags on power boats should be 5/8 inch on the fly for each foot of overall length.
© 2024 Beaver Flags All rights reserved. | Sitemap

- Forums New posts Unanswered threads Register Top Posts Email
- What's new New posts New Posts (legacy) Latest activity New media
- Media New media New comments
- Boat Info Downloads Weekly Quiz Topic FAQ 10000boatnames.com
- Classifieds Sell Your Boat Used Gear for Sale
- Parts General Marine Parts Hunter Beneteau Catalina MacGregor Oday
- Help Terms of Use Monday Mail Subscribe Monday Mail Unsubscribe
American Flag etiquette
- Thread starter mark Johnson
- Start date Feb 24, 2005
- Hunter Owner Forums
- Ask A Hunter Owner
mark Johnson
I want to add a fix flag mast on the stern of my 33 Cherubini, from which I'll fly an American flag. With the boarding ladder locate on the center line of the stern - which side of the stern should the American flag be placed? I've asked many people and researched the internet and still don't have a firm answer. Confused!
Starboard I have a center walk through on my H36. The flag holder came from the factory on the starboard side.
Rick Dalton
Ensign/National Anyplace on the stern is fine. On the center line would be the most collegiate location but I too have the center thru-way on my h380 and the Flag staff was factory installed/welded to the immediate port stantion.
Cactus Jack
Clip to shroud? My used Catalina came with a small American flag with clips to attach to a stay. The clips are too small to easily clip to the backstay; does flag etiquette allow clipping to a shroud? Jack
Ensign From the USPS: The fifty star, 13 stripe American flag is flown only between 0800 and sunset. It is mounted on the stern staff at center or on the starboard side.
I clip mine to the split backstay No idea which side is best, and didn't even think about it. I used these little 4-screw clamps you can buy that attach to cable (all sizes), then attach w/ a plastic wire tie. I would think lower on the stern would get dirty from diesel exhaust.
If clipped to a shroud... ...it must be on the starboard side. It may then be considered a "courtesy" flag. You will need to check on that. But when I had a C25, I put the American flag on the starboard burgee line under the spreader.
FLYING THE FLAG While in port the flag is flown on the stern mount between 0800 and sunset unless it is lit by a light that is dedicated to the flag. While underway the flag is flown from the yard arm (spreader bar) - (not on the stern mount) at all times while underway. No dedicated lite is required while underway. While flown from the yard arm it is the top most flag. No other flag (read burgee) is ever flown above the stars and stripes. God Bless America RD
FLYING THE FLAG While in port the flag is flown on the stern mount between 0800 and sunset unless it is lit by a light that is dedicated to the flag. While underway the flag is flown from the yard arm (spreader bar) - (not on the stern mount) at all times while underway. No dedicated lite is required while underway. The flag should not be flown from a stern mount while underway. The flag should not be flown from a shroud or other such line while in port - only from a stern mount. While flown from the yard arm it is the top most flag. No other flag (read burgee) is ever flown above the stars and stripes. God Bless America RD
Les Blackwell
No rules for flying the "colors" Every now and then, this subject comes up on one web site or another. I have research this subject several times including checking in with the Library of Congress and my senator's staff. I know I will upset a number of person when I tell you there are NO rules for flying flags on your pleasure craft. There are rules for the military and for elements of the government but none for pleasure craft. Most guidelines come from Chapman's Piloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling tomes but what most people don't know is that Franklin D. Roosevelt, then assistant secretary of the Navy during World War I was given the assignment to mobilize the then growing population of pleasure power boats. He then requested Chapman (who was editor of a new magazine called Motor Boating) to come up with some policies to mobilize our new fleet of power boats, probably our first Homeland Defense act. On a frontest page of a 1917 edition of Chapman's Practical Motor Boat Handline, Seamanship and Piloting, it states in part, "Adapted for the yachtsman interested in fitting himself to be of service to his Government in time of war." While there are no federal laws pertaining to flying a flag on your boat, many of the suggestions made in recent years are taken from both British and American tradition of early sailing ships. Hence, we show our "colors" from the stern of our ships. It is a signal and nothing more. We can also enjoy raising other signals such as our yacht club burgees, and courtesey flags when entering another country, You do not have to fly your colors (American Ensign) if you do not wish. Indeed in years gone by many clipper ships flew the flag of their owner so one could tell what boat was coming into the harbor. The tradition of flying a signal, as most flags are considered, from the starboard yards or spreaders comes from the time when ships lay their port side along a wharf and showed their signals on starboard to let incoming ships know who was in the harbor The 1917 edition of Chapman's on flags and Colors (colors are the US. Flag only) is entertaining since it writes about the owner's private signal (who owned the boat), the church Pennant (flown during devine services), guests flags, the owners dinner flag and the crew's meal pennant. Aha, I never wanted to eat with my crew either. There was also an owner's absent flag (damn, I forgot to put that up when I left my boat today). One signal which confuses me is a Night Pennant of which I have never found the reason for flying it--to tell me it was night? My oh my. The size of the flag flown on your boat also has no rules along with where you fly your "colors." When we had sailboats with gaff rigged mains, we flew the flag from the gaff because it was up and out of the way as well as where another boat could see it. But there was never a rule that said we had to fly it off our back stays at three quarters of the way up. That is only tradition. Flying your flags from 8 AM to dusk is another tradition that come from a peace time Navy that was borrowed by Chapman. While it is a traditon that I like it is only suggestive. The same goes with flying the flag at night--you do not need a light. Makes sense but is not required. Before you get upset with what I'm saying here about flying your signals, here is what Chapman said in 1917. "Yachting etiquette, including the proper colors to fly, and their correct locations, is largely governed by custom, but the fundamental rules in this respect were established many years ago before the advent of the motor boat. They are not in every instance well suited to the modern craft." I wonder what Chapman would think abour Hunter and the lack of a backstay. As an aside, it is interesting that Chapman said very little about sailboats in his 1917 edition except to suggest "...we (the power boater) stay out of their way. " I go for that. (Peggie, my luv, are you paying attention?) If you disagree with any of this, I would be perfoundly grateful if you would give me the resource or rule that prompts your disagreement. As I stated earlier, as of this moment, there are no federal laws pertaining to flying the flag on a pleasure craft. Les Blackwell
I fly obove the rudder
From The Stern Boats today fly the ensign from the stern, which provides the best all-round visibility. It should be on a staff that is sufficiently long and angled, and that is offset to one side (traditionally the starboard side), so the flag flies clear of engine exhaust and rigging. For many years, until around World War II, most ensigns were flown from the leech of the aftermost sail—a sloop or cutter's mainsail or a ketch or yawl's mizzen. That position is still available. On a Marconi rig, the ensign may be flown about two-thirds of the way up; on a gaff rig, just under the gaff. In either case the flag may be sewn into the leech or hoisted on a halyard through a leech cringle (reinforced hole) so the ensign can be lowered to avoid chafe, say on a permanent backstay. Source: http://www.sailnet.com/collections/articles/index.cfm?articleid=rousma0041
newly anonymous
US Yacht Ensign Piggybacking on Les Blackwell's comments, I've heard it said that the US Yacht Ensign should only be flown in US waters, and that in foreign ports one must resort to the US National Ensign. Does anyone know of a definative regulation regarding this? I also once read in a magazine that the only boats that were entitled to fly the US Yacht Ensign were documented yachts, and that they indeed are required to fly that ensign. True?
There was a rule about the U.S. Yacht Ensign John, you are correct as usual. At one time the U.S. yacht ensign was mandatory for use on documented yachts. The reason was that most boats in the early 1900's whether they were working boats (commercial craft) or pleasure craft looked alike. Both had paid crew and were made of wood. No plastics yet. At that time, the ports had fees for the commercial craft much like airports charge commercial airlines today. But the ports couldn't tell the difference between the comercial vessels and the pleasure vessels and since almost all the pleasure vessels at that time were documented, they were required to fly the yacht ensign (the U.S. type flag with the fowled anchor on it. But in the late 1980s (I'm now trying to find out the exact date) congress receinded ALL the laws pertaining to the U.S. Flags including the Yacht Ensign requirement for documented vessels. Anyone now can now fly that flag. Let me put my head on the chopping block one more time. If I were traveling around the world in my boat at the present time I believe I would like to have a number of Flags from different countries that I could hang off my stern. In spite of how I (and other Americans) feel about our flag, there are a number of places in the world that do not like American boats. I might fly the flag of Iceland or Singapore until I could make eye to eye contact. This procedure has been done many times in the past, particularly between America and England. Maybe I would design my own personal flag instead of a pennent and fly that. There are many U.S. commercial tankers and freighters who fly "flags of convience" from small countries so as not to have to pay large taxes to U.S. Ports. I wonder where they got that idea, eh? Good point, John. Thanks. Les
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…

Download Our FREE Boat Flag Size Chart
Get the pefect size burgee or flag for your boat.
Fill out the form on the right to download a FREE PDF of our boat flag sizing chart.
Regardless of the size of your boat make sure that you have the appropriately sized flag or burgee on the water this year. A great resource to keep with you on your boat or for the future. Enjoy!
Fill out the form to Download our Free Chart!
Download Our FREE Flag Size Chart
“I wanted to send a sincere thank you for all of your work and help on the street banners….Looking forward to our next project with you.”
P. Schepens Eye Research Institute
"Just wanted to send you a note to thank you and your crew for the great, fast work on the banner! It looked fantastic!"
C., Boston University
"Our building really needed some color and identity and Accent Banner’s ideas were right on target."
"I could not be more pleased with the process or with the results. I recommend them with real enthusiasm and with NO hesitation."
Yelp Review
"Accent Banner is the place to go. These guys have always come through with the best pricing and quality work for my company. Next time your driving through, take a look at the banners on the light poles. If they are not hanging square and straight, that means that Accent Banner didn't do them"
Google Plus Review
"My experience with Accent Banner has been amazing. They have exceeded all of our expectations when it came to different projects. The projects they have completed for us have enhanced our facilities 10-fold."
UMASS Boston
About Accent Banner
Recent Posts / RSS Feeds
Visit us:, contact us:.

Racing Signals: Sailing Flag Meanings

Last Updated by
Gabriel Hannon
August 30, 2022
Where other competitions have umpires and referees right next to the players, sailing race committees have to rely on flags to communicate with sailors.
In this article, we are going to explain the meanings of all the flags used at regattas to communicate with sailors. The flags can give information about starting procedures, course information, and on-the-water judging, so a basic understanding is a crucial part of general seamanship.
While nautical flags all have defined meanings in a historical context, they have very specific meanings in the context of racing competition. For instance, in the general nautical world, the Z-flag means that you are in distress and are in need of a tow or relief from a tug boat. At a regatta, the race committee may fly the Z-flag to indicate an additional penalty for any boat that has crossed the line early. Moreover, even though there are certain flags that have well-defined roles, race committees may stipulate additional meanings or introduce new flags via an announcement in the sailing instructions for the event, so we will cover some of these more common changes as well. We will break down the meanings into the various categories of usage.
A secret that I have learned over many years of regattas at every level from proverbial ‘beer-can’ races to national championships is that, as well as both you and the race committee can recite the racing flag rules on land, someone is always going to make a mistake or misunderstand these symbols. That is why I will be going through the official flag meanings and rules from the Racing Rules of Sailing for 2021-2024 to clarify any questions that you might have when the race committee flies a flag that hasn’t been seen since we used Clipper Ships to cross the oceans. Hopefully this article will help break down all the most common signals so that when your friend turns to you and asks ‘is that the flag that tells us it's time to go in,’ you’ll be able to help out!
Table of contents
Flags at the Start
The start of a race is often the most confusing part of a regatta and is where the most flags must be used. We will be going over the rules for the flags at a basic 5-minute start. These can be modified for 3-minute dinghy starts, 5-minute match race starts, 6-minute Olympic starts, or 10-minute big boat starts, but the same logic applies.
A few flags are crucial to set everything up on the starting line prior to the starting sequence.

To begin, the race committee must have an Orange Flag visibly displayed, as this demarks the exact location on the boat from which the line is called. If there is a pin boat, they will often fly an Orange Flag as well, but if it is just a buoy, then the buoy serves as the other end of the line.

Next, the RC will additionally fly the L Flag if they are ready for competitors to check-in at the beginning of the race day. This helps them confirm that everyone is sailing under the correct sail number, which is often a logistical nightmare. They will blow one horn when raising this flag. If this flag is raised at any point later in the day, it is meant to tell competitors to come by the committee boat again.

Finally, the AP Flag is a general purpose postponement flag. The race committee may raise this on land to indicate that the harbor start has been delayed or on the water to indicate that there will be a delay in the starts. While there are other flags that are used for abandonment situations, particularly the N Flag, the AP is commonly used in informal situations. Two sounds accompany the raising of the AP, and it can be said that competitors are ‘under AP’ until it is dropped, along with one sound. If it is dropped on land, competitors may immediately launch. If it is dropped on the water, the next start may begin in as little as one minute.

The final note with the AP Flag is that the race committee may indicate the end of racing for the day by flying ‘AP over A.’ Again, the AP could technically be replaced with the blue and white checkerboarded N Flag, but the two serve very similar purposes at most levels.
Starting Flags

Once the race committee is set up and everyone is ready to go sailing, the next task is to get the right fleets to the starting line for their start. At the warning signal, one loud horn that indicates that the 5-minute countdown to the start has begun, the race committee will raise some type of Class Flag that indicates which type of boat will be starting. Above we have the different class flags for the different competition rigs for the ILCA-Dinghy, formerly known as the Laser, which would be raised to indicate which rig is starting.

This is a convention even if there is only one class on the water. Sometimes this is replaced with raising the Orange Flag itself, or some other flag as laid out in the sailing instructions. Often classes have been assigned a numeral pennant, of which 1-4 are displayed above, in place of the highly specific Class Flags. Still, some flag of this nature goes up at 5-minutes and remains up until go, at which point it is dropped.

At 4-minutes, the RC will sound another horn, known as the preparatory signal, and raise some combination of the above flags.
The P Flag is always required to go up, and it is simply the ‘Prep Flag,’ which signals to the racers that they need to get serious about the race. Once the P Flag is raised, all the right-of-way rules that apply during the start switch on and racers, particularly in team and match racing, are allowed to begin tactically engaging with each other (though in team racing this would happen at minute 2 of the 3-minute start). Moreover, racers can talk with their coaches until the prep signal, and race committees may alter the course up until this moment. Afterwards, all coaching is banned and all course changes on the current leg are not allowed. This belies the fact that a 5-minute starting sequence is actually a 4-minute sequence with a warning signal at 5-minutes, but that is a purely semantic detail.
Depending on how rowdy the competitors are, the race committee may raise any combination of the I, Z, U, or Black Flags. Each of these flags deals with boats that start ‘on-course side’ (OCS), essentially a false start for sailing. If any of these flags is raised, a boat is not allowed to be anywhere within the triangle formed by the starting line and the first mark of the course after the 1-minute signal during the start. These flags essentially help the RC ensure that they can get off a clean start and ensure that they can identify any boats that are OCS at go. When they are flown, the following penalties are added beyond requiring a boat to clear itself by dipping back under the line:
- I Flag: Conventionally referred to as the ‘one-minute rule,’ this requires that any boat over the line after a minute also has to sail around an end of the line in order to start the race fairly. This punishes a boat for being over by potentially making it a little harder to clear themselves if they are over on a large line.
- Z Flag: Often flown in combination with the I Flag, this flag adds that any boat that is OCS will get a 20% penalty on top of their score in that race, regardless of whether they clear themselves or not. This further hurts any boat that is ‘pushing the line’ by ensuring that even if they manage to clear themselves and come back, they will still see an impact on their scoreline that is equivalent to immediately being passed by 20% of the fleet.
- U Flag: Now we’re getting into harsh territory. When the RC is really trying to brush the fleet back off the plate, this flag immediately disqualifies a boat that is over after a minute with no course for redress. If these boats are identified, they tend to be told to stop sailing the race by a notice board at the top mark.
- Black Flag: The black flag serves a very similar purpose to the U Flag, except it is a step harsher. It disqualifies you after a minute and even prevents you from sailing in a restart of the race or a race abandoned halfway through.
The I Flag is by far the most common flag, and is often effective at keeping boats from being over. The U Flag rule was introduced in 2013 as an option and formally codified in the Racing Rules in 2017 and is massively more popular than the Black Flag, which is considered overly punitive. In particular, when many sailors are over in a Black Flag start, such that the RC cannot determine who was over, they are forced to make unfair decisions that carry over to the restart, so the U is now almost universally used in its place. Additionally, as the U has become more popular, people tend to shy away from the Z flag, which is considered cumbersome for scorers and confusing to sailors.
In general, while these flags are supposed to be raised in conjunction with the P Flag, often the RC will only raise the most punitive of the flags, as any of them can essentially be considered as a prep flag.
As the starting sequence continues, any prep flag(s) raised must be lowered at the 1-minute signal. The class flag is then lowered at go, leading to the next category of flags: Recall Flags
Recall Flags
After the pain of raising and lowering all those start flags, the RC then has three possible jobs. If the start is clean, they shout ‘All Clear!’ and can then relax until they have to start another race or record finishes for the race in progress. Unfortunately, this is often not the case, as they likely will need to ‘recall’ certain competitors for being ‘OCS,’ i.e. false starting. They have two choices here.

If only a few, easily-identifiable boats have started early, the RC will raise the X Flag along with a single sound in what is referred to as an individual recall. This indicates to the boats on the course that there are some competitors who are currently OCS and must clear themselves. If the I Flag had been flown for the start, competitors have to round an end; if not, they can just dip back behind the starting line and restart from there.
While the X is suitable on its own to inform a boat that it has been called over, it is an oft practiced courtesy for the RC to hail an OCS boat’s sail number over a megaphone, a radio, or other transmission device. The X Flag is dropped when all OCS boats have cleared themselves or after 4 minutes from go, whichever comes first.

If more boats than can be easily identified are called over, the RC can blow two horns and fly the First Substitute Flag, indicating a general recall. In this case, the race is fully reset and the committee will initiate another entire starting sequence for that fleet. After a general recall, the RC will often, but not always employ the next level of penalty flag for the restart in an attempt to get the race off cleanly.
Sometimes, as in college sailing or as stipulated by other sailing instructions, any general recall immediately implies the I Flag for the next sequence if it had not been flown previously. As such, the RC does not necessarily have to fly the I if it is unavailable. Still, such stipulations are almost always written out explicitly for a given event and are often accompanied by a verbal announcement as a courtesy.
Still, outside some usages of the AP or N Flags to abandon or delay starts already in sequence, these are all the flags that deal with general housekeeping and the starting sequence.
While Underway
While the starting flags are by far the most complicated of the flag rules, there are still other flags to keep track of while racing. The first among these are...
Course Change Flags
Although course changes are relatively rare, race committees often pull them out when conditions change substantially during races or if there has been a problem with one of the marks.

When wind or time constraints require, the race committee may send an official to any mark of the course that no boat has yet rounded and have it raise the S Flag along with two sounds. This indicates that the fleet shall finish at that mark, cutting off the race earlier than written in the sailing instructions.

In the case of any other change to the course, such as a minor adjustment to the angle or distance of an upcoming leg, a race committee boat will go to the preceding mark and raise the C Flag along with repeated sounds.
This is sometimes accompanied by a Red Square or a Green Triangle to indicate that the mark has been moved to port or starboard respectively. Although during less formal events, you can change the positions of any marks so long as there are no competitors currently sailing on that leg of the course, it is considered poor form if at all possible to inform competitors, particularly in longer races. Sailors make decisions based on the position of the marks, and if this has been changed without them noticing, that can drastically affect the outcomes of strategic decisions, so in large competitions the C Flag is a must.

If, meanwhile, something odd has happened to a mark of the course, any official boat may fly the M Flag with repeated signals. This serves to inform the competitors that they have become a replacement for the missing mark. This is relatively uncommon, but anchors do occasionally snap on marks, so it is always good to have a support boat with the M if possible.

Finally, as mentioned before, if conditions have deteriorated to the point that a race is considered no longer possible, due to lack of wind, fear of foul weather, or some form of interference -- I’ve seen it happen because cruise ships wanted to pass through a dinghy course, and you don’t say no to them -- the race committee may abandon the race using the N Flag. Still, this flag is relatively rare as you will often see the AP in its place for convenience, as they are functionally similar.
Miscellaneous Flags
While we have covered the bulk of the flags necessary for racing at any level, there are a few more flags from across different disciplines and classes that are worth mentioning, if only to let you in on these quirky parts of the racing world! This starts with what one could reasonably call…
The Cheating Flag

Calling the O Flag the cheating flag is certainly a bit of a misnomer. The O Flag does, however, suspend Rule 42 of the Racing Rules of Sailing. Rule 42 is particularly notorious, as it bans pumping, rocking, ooching, sculling, and excessive maneuvering, all of which are methods to make your boat go substantially faster. While Rule 42 is worth an article in and of itself, the larger point is that it is meant to keep anyone from gaining an unfair advantage over their competitors.
Certain competitive classes, however, including the Olympic class 470s and Finns and many of the new foiling fleets, allow competitors to ignore Rule 42 in certain conditions, typically in heavy breezes that are referred to as ‘planing’ conditions. There are differences across the classes, but whenever it is allowed and the RC flies the O Flag, Rule 42 is switched off and competitors can ooch, pump, rock, and tack their boats all around the racecourse. This allows for a much more physical style of sailing and is a rule that many different classes and sectors of sailing are beginning to consider.

If conditions no longer meet the threshold for that class’s rules regarding suspension of Rule 42, an official boat will raise the R Flag at some point during the race. They can only do so at a mark of the course so that it is fair to all the competitors throughout the fleet. This is relatively rare, and is normally done between races, but is still a key part of the O Flag rule.
Judge and Umpire Flags
On the topic of Rule 42, there are certain fouls in sailing that can be actively enforced on the water by judges or umpires, depending on the context.
Rule 42 is enforced by judges with a Yellow Flag, which they will point at an offending boat along with a sound signal and a direct sail number hail. That boat may clear themselves from their first Yellow Flag by taking their two-turn penalty, but, unless otherwise noted in the sailing instructions, any subsequent violation can entail disqualification.
Finally, certain levels of modern match and team racing, with the addition of high-performance racing like SailGP, have full on-the-water umpires who actively follow the racing to make calls on fouls and other plays. While this is not the spot to go through the intricacies of team and match race calls, the basic gist is as follows.
In any interaction, any boat involved in the race may call in the umpires if they believe that their opponent has fouled them. If the opponent clears themselves quickly, essentially admitting fault, the umpires will not get involved. If no boats clear themselves, the umpire has to make a call on whether there has been a foul. If they determine that the maneuvers were clean, they will make one sound and fly a Green Flag, thus exonerating all boats in the interaction. If they determine there was a foul, they will fly a Red Flag with a singular sound and hail the offending boat.
Beyond that, if a boat is found to have broken a rule not related to an interaction, the umpires may come in and fly the Red Flag without being directly invited into the situation. Further, if a boat is found to be in violation of sportsmanship or refuses to take a penalty as assessed by an umpire, the umpire may fly a Black Flag, disqualifying them from the race.
While there are differences at each event and in each discipline, these general guidelines are followed in most umpired races, with specific flags used at various events, generally depending on availability.
With that, we have made it from land, through the start, a few general recalls, all the way to umpire flags! I hope this has helped you get a grasp of the various flags used across sailing. While this has not scratched the specifics of the various alterations made for kiteboards and windsurfers, nor some of the annoyances of protest flags and more, we have gone through the bulk of regularly used race committee and umpire signals.
The ‘Wear Your Life Jacket!’ Flag

Finally, we have a safety flag. At big boat regattas, the race committee may, if it chooses, fly the Y Flag at any point prior to a start to inform competitors that they must wear personal floatation devices, which is not always strictly necessary.
The Most Important Flag
While I wish I could tell you that everyone uses their flags properly and accompanies them with the proper timing and sound signals, that is far from the truth. Everyone’s flag set is slightly incomplete or out of date, and invariably there is going to be a miscommunication somewhere, where the race committee forgets to put the I Flag up but really should have; I’ve certainly done that a time or two. Still, there’s nothing quite like being on the water, so, despite the endless mutual griping between racers and their race committees, hopefully everyone comes back to shore flying the ‘Happy Flag.’
Happy sailing!
Related Articles
I have been sailing since I was 7 years old. Since then I've been a US sailing certified instructor for over 8 years, raced at every level of one-design and college sailing in fleet, team, and match racing, and love sharing my knowledge of sailing with others!
by this author
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
Daniel Wade
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Basics Of Sailboat Racing Explained
May 29, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Everyday Flag Etiquette. All boats operating in inland waters can fly the U.S. "Old Glory" 50-star flag, or the U.S. Yacht Ensign, the 13-star "Betsy Ross" flag with the fouled anchor. Flags are flown, traditionally from 8:00 a.m. to sunset, from the stern staff (when under way or occupied), or onboard sailboats —on aftermost sail 2/3 ...
All other flags on board should be smaller in size. Generally speaking, the yacht ensign should be approximately one inch in width for every foot of boat length. For example, a 33-foot vessel would use a 24x36" yacht ensign with a private boat flag of 12x18". To take the guesswork out of determining the correct boat flag size for your ...
This page displays a nautical flag size chart for how big your flags should be per length of boat. View this flag sizes for boats chart at All Star Flags! 1.800.868.3524. The Quality is in Every Star! ... Recommended Yacht Flag Sizes. Sailboat. Length of Boat: Size of Private & Club Signal: Size of Yacht Ensign: 20 ft: 10" x 15" 16" x 24" 25 ft ...
Boat owner's flag. The yacht owner can also fly their own national flag on the boat. It can be placed on the starboard spreader, but if the owner deems it appropriate it can be flown on the port side, as it is a flag of lower importance (than the ensign). The spreader is a mast reinforcement (between the mast and the shroud).
Answer: They can be almost any size, we offer flags in 12" by 18" and 3' by 5'. Question: Are nautical flags square or rectangle? Answer: Boat flags come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but the most common boat flag shape is rectangular. Rectangular boat flags are typically used for decorative purposes.
20' Flagpole Maximum Top flag 4'x6', Bottom (2nd flag) 3'x5'. 40' Flagpole-Minimum Top flag 6'x10', Bottom (2nd flag) 5'x8'. 40' Flagpole Maximum Top flag 8'x12', Bottom (2nd flag) 6'x10'. Keep in mind that there are certain variable that may change the size of flags that you can fly on your flagpole. Some of these variables include the ...
Here is a handy chart to help you find what size flag you need for your vessel. Power Boat: Length of Boat Under (feet) Size of Private Signal & Club Signal (inches) Size of Yacht Ensign: 20' 8 x 12" ... On a sailboat, the courtesy flag is flown at the boat's starboard spreader, whether the United States ensign is at the stern staff, or flown ...
So in the rules below, round upward to the nearestlarger standard size. The flag at the stern of your boat: U.S. ensign or national flag should be about one inch for each foot of overall length. For example, on a 40ft. boat, the ensign should be 40 in. i.e. about 3.5ft. Other flags, such as club burgees, private signals and courtesy flags used ...
When ordering an ensign, or American Boat Flag, we recommend a flag that measures one inch for each foot of boat length. For smaller vessels, a 12x18" flag is usually suffice, while larger boats may opt for the 2x3' flag. Burgee and personal Custom Boat Flags are generally smaller than the ensign, but can measure up to half an inch for each ...
BOAT FLAG SIZES TO Power Boat Boat Length Under 20' 20' ... Yacht Ensign / Country Flag 12x18" 12x18" 16x24" 16x24" 24x36" 24x36" 24x36" 2.5x4' 2.5x4' 2.5x4' 3x5' 3x5' 4x6' 4x6' Sailboat Boat Length 20' 25' 30' 35' 40' 45' 50' 60' 70' 80' 90' 100' ... 30x48" 30x48" Yacht Ensign / Country Flag 16x24" 16x24" 24x36" 24x36" 24x36" 2.5x4' 2.5x4' 2 ...
As a calculation almost every flag size is a multiple of those two sizes in this case: 6x10, or 4x6 etc.. There are one or two odd sizes, and some are manufactured to rare custom sizes. An inch per foot of boat is an the most generally accepted rule but you can see the difficulty here; those with boats in the 30-40ft range have no choice but to ...
What size lags should I order for my boat? Use this chart as a helpful guide. View Cart. Toggle navigation. Home; ... SAILBOAT. Length of Boat Under: Size of Private Signal & Club signal: Size of Yacht Ensign: 20 feet: 10" x 15" 16" x 24" ... Flag-Works over America, LLC, 16 Kennedy Lane, Concord, NH 03301 ...
Sailboat flag etiquette is a combination of law and maritime tradition. It is a way of showing respect, courtesy and recognition to other vessels, countries and organizations. ... The Q flag should be the same size as the courtesy flag or slightly smaller. It should be flown at the starboard spreader, below the courtesy flag if there is one, on ...
Flags are more often too small than too large. So in the rules below, round upward to the nearestlarger standard size. The flag at the stern of your boat: The ensign or national flag should be about one inch for each foot of overall length. For example, on a 40ft. boat, the ensign should be 40 in. i.e. about 3.5ft.
A sailboat with a 55-foot length should have a non-ensign flag that is 27″ long. For power boats, all other flags should be 5/8″ long for each foot of overall length. A 56-foot boat should have a 35-inch long flag. Proper boat flag size varies depending on the size of the boat in question. Semaphore flags (discussed below) are always made ...
Generally, yachts up to about 60 feet (18 metres) in length look properly "dressed" with half yard (18" x 12" or 45x30cm) courtesy flags. There is a smaller size range (12"x8") not available from Jimmy Green because these flags look insignificant from deck level when hoisted aloft. There is an old rule of thumb for courtesy flags: a half inch ...
12 x 18 inches. 37 to 48 feet. 16 x 24 inches. 49 to 60 feet. 20 x 30 inches. 61 to 72 feet. 24 x 36 inches. Boating Main Page. CRW Flags Inc. offers recommended sizes for boat flags.
Nautical flag etiquette is an essential part of sailing. The seven most common types of boat flags are Skin Diver flags, Storm Warning flags, Coast Guard boat flags, US Jack flags, Maritime flags and Pennants, Yacht Ensign & Officer flags, and most importantly the International Code Signal flags. Code signal flags and are frequently used by ...
Generally, boat flags come in different sizes, depending on the type of boat that you have. For aesthetic purposes, most flags are roughly 1" per foot of the length of your boat. Also, the staff should be twice the length of the height of your flag. For example, if you have a powerboat that is 33' long, you should have flags that are 24 ...
So a 30 foot vessel should fly a national ensign that has at least a 30 inch fly. All other flags on power boats should be 5/8 inch on the fly for each foot of overall length. Powerboat or. Sailboat Length. US Ensign Size. up to 20'. 12x18" flag. 21' to 24'. 16x24" flag.
Robert. Feb 25, 2005. #9. FLYING THE FLAG. While in port the flag is flown on the stern mount between 0800 and sunset unless it is lit by a light that is dedicated to the flag.u000bu000bWhile underway the flag is flown from the yard arm (spreader bar) - (not on the stern mount) at all times while underway. No dedicated lite is required while ...
Download Our FREE Boat Flag Size Chart . Get the Pefect Size Burgee or Flag for your Boat. Fill out the form on the right to download a FREE PDF of our boat flag sizing chart. Regardless of the size of your boat make sure that you have the appropriately sized flag or burgee on the water this year. A great resource to keep with you on your boat ...
Z Flag: Often flown in combination with the I Flag, this flag adds that any boat that is OCS will get a 20% penalty on top of their score in that race, regardless of whether they clear themselves or not. ... 10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why) Daniel Wade. December 20, 2023. 7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat. Daniel Wade. December 20, 2023 ...