
Home » Blog » Gear » Buyers guide to electric boat motors (2023)

Buyers guide to electric boat motors (2023)
By Author Fiona McGlynn
Posted on Last updated: August 3, 2023
Considering making the switch to an electric boat motor? With electric vehicles now commonplace on the roads, it’s no wonder so many boaters are curious about electric boats.
While electric boat motors have been around for a while, in the last several years the technology has taken huge leaps, resulting in more powerful motors, longer-lasting batteries, and ultimately more options for recreational boat owners.
Today, many types of boats can be outfitted with an electric propulsion system including pontoon boats, sailboats, jon boats, powerboats, fishing boats, yachts, and trawlers . If your boat’s combustion engine is in the range of 1 to 135 hp (.75 to 100 kW), you should be able to find an electric substitute.
While electric boating hasn’t gone mainstream—it’s estimated that close to 2% of recreational boats are electric—it’s still a great time to be thinking about making the switch, particularly if you own a tender, sailboat, or boat on a green lake where combustion engines are prohibited.
Table of contents
- 1.1 Benefits
- 1.2 Drawbacks
- 2.1.1 Key features of electric outboard boat motors
- 2.1.2 Electric outboard manufacturers
- 2.2.1 DIY electric inboard boat motor conversion
- 2.2.2 Key features of electric inboard boat motors
- 2.2.3 Electric inboard manufacturers
- 2.3.1 Serial vs. parallel hybrids
- 2.3.2 Key features of marine hybrids
- 2.3.3 Marine hybrid manufacturers
- 2.4.1 Electric pod and sail drive manufacturers
- 3 Batteries
- 4 Ready to catch the electric boating wave?
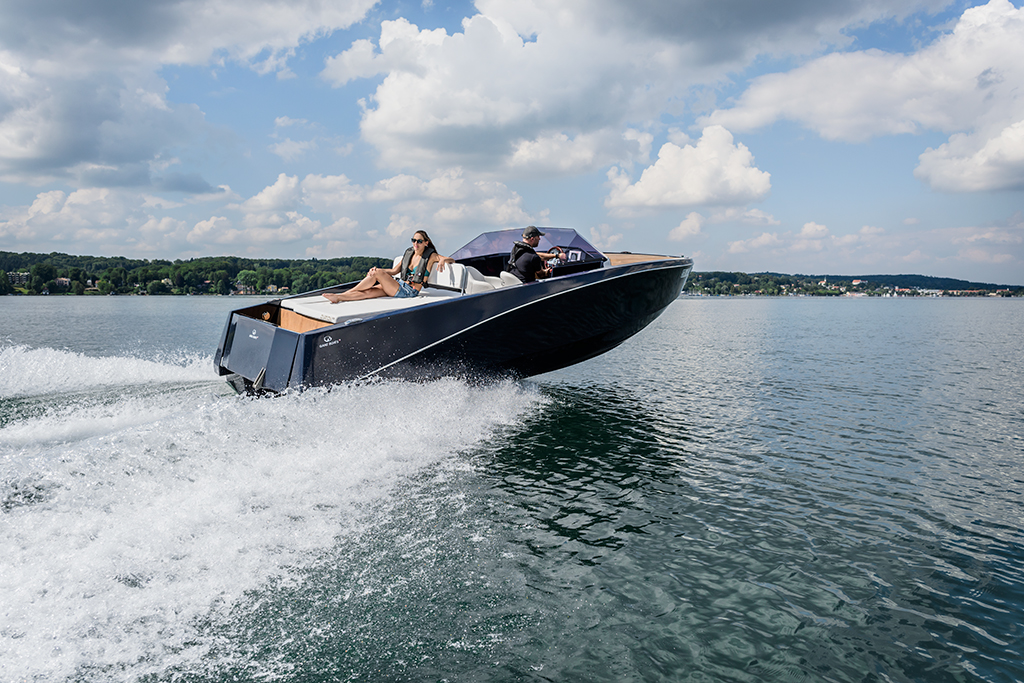

Benefits and drawbacks of electric boat motors
Electric marine motors offer several advantages over internal combustion engines:
- They’re completely silent .
- No noxious fumes or smelly exhaust gases to deal with.
- Instant torque. Electric propulsion provides instant torque, giving you better maneuverability and more consistent speeds in choppy conditions.
- Lightweight. An electric setup (including motor, batteries, and generator) typically weighs less than its diesel counterpart.
- No fuel cost. Charging an electric boat may cost a couple of dollars per charge.
- Easy to maintain. Imagine the maintenance on an outboard with no gas, spark plugs, or oil! Electric motors are simple, more reliable, and virtually maintenance-free.
- Renewable power. Once you’ve gone electric you can get power from renewable sources like wind generators and solar panels.
- Better for the planet. Electric marine motors don’t produce water pollution or produce harmful emissions like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and hydrocarbon (HC).
- Range. The greatest drawback of electric boats is their limited range, which is often measured in the 10s of miles. Range is limited because batteries don’t have the same energy density as fuel — they can’t provide the same energy, pound-for-pound as a tank of gas. A good battery monitoring system, one that displays the remaining range in real-time, can help boaters manage energy consumption and ease range anxiety. For those who want to go farther afield, hybrid propulsion may be a better option.
- Upfront cost. This new technology isn’t cheap. For example, a small electric outboard boat motor may sell for two-and-a-half times the cost of a gas outboard. However, prices are expected to come down as the industry reaches scale.
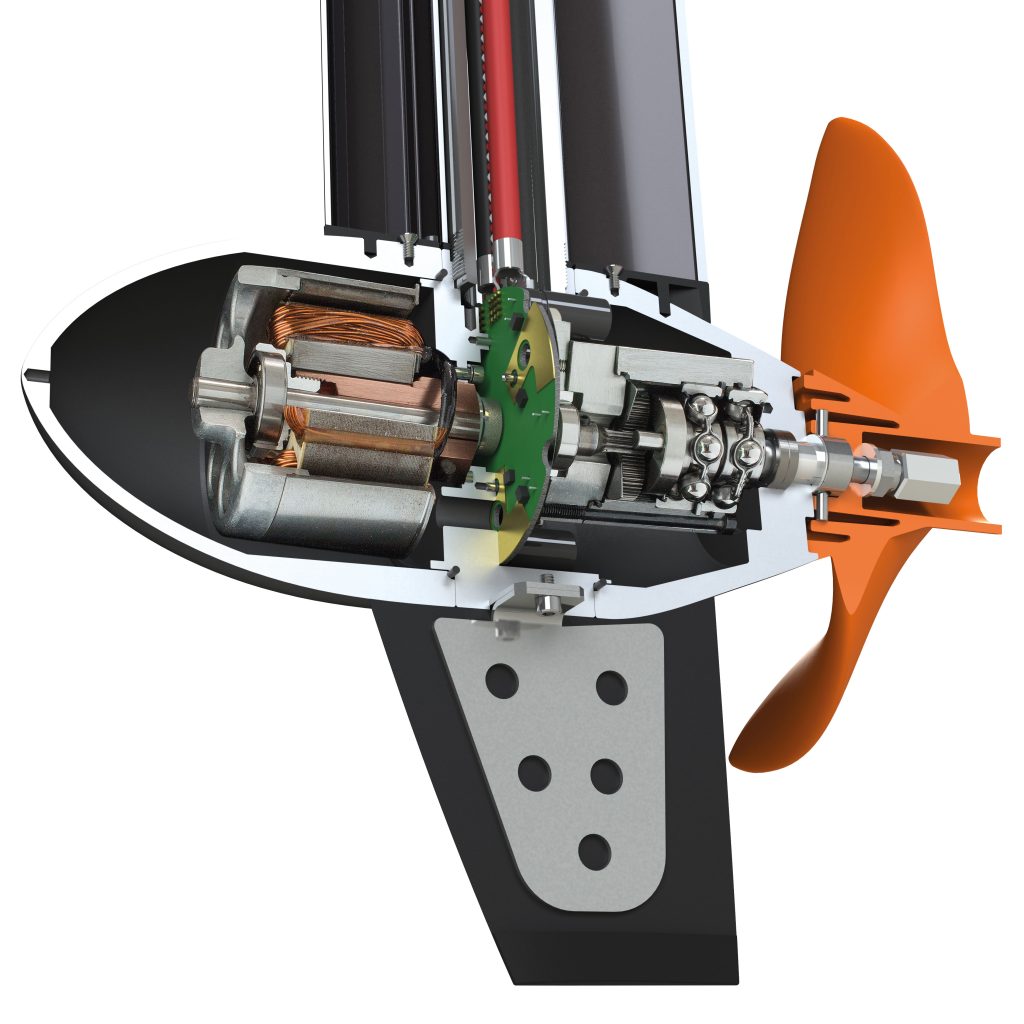
Types of electric boat motors
Electric outboard boat motors.
Some of the first electric outboards to hit the recreational boating market were smaller electric motors, typically used as trolling motors on fishing boats.
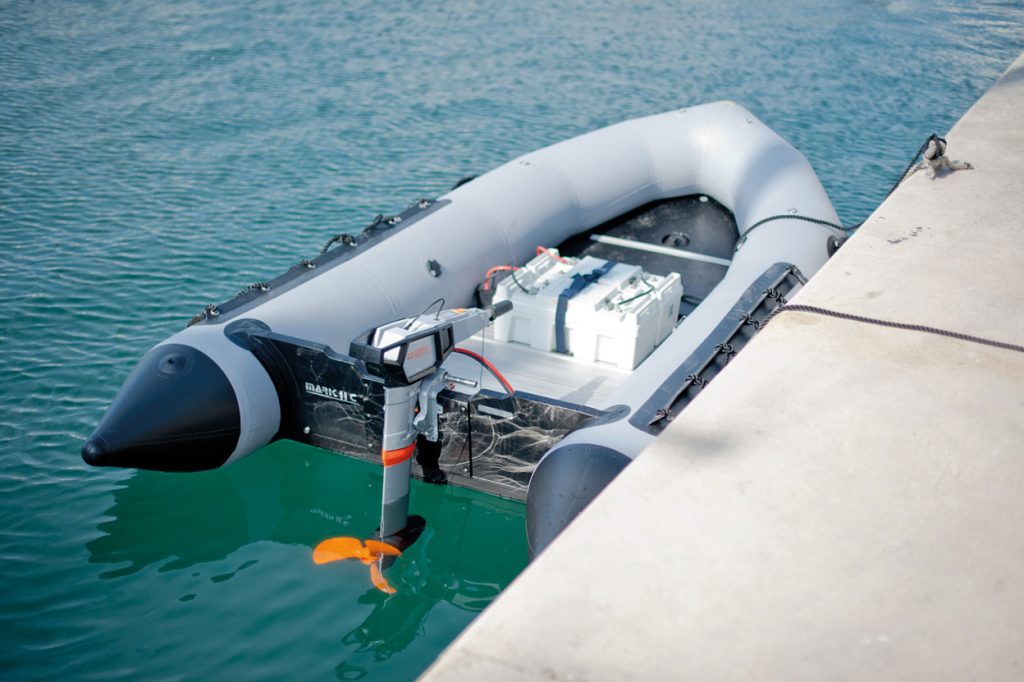
Today, it’s possible to buy far more powerful electric outboard motors in the 1 to 80 hp (.75 to 60 kW) range , with ever more powerful versions hitting the market each year. In 2022, Norwegian start-up, Evoy launched the world’s most powerful outboard to date, the 225kW Storm, a 300-hp beast of an electric outboard!
The range on electric outboard boat motors varies dramatically depending on your boat, total weight, propellor, and battery capacity .
The range also depends on how fast you want to travel. If you go slowly you’ll have a much greater range.
For instance, at a slow speed (5 knots) Torqeedo’s Deep Blue 50R , a 50 kW motor (80 hp equivalent) with a 40 kWh battery, has a listed range of 33-100 nm. But at full throttle (20-25 knots), the listed range drops to 16-20 nm.
To get a better sense of what range to expect on your boat (at both low and high speeds), you can look at the manufacturer’s website. See our list of electric outboard brands below.
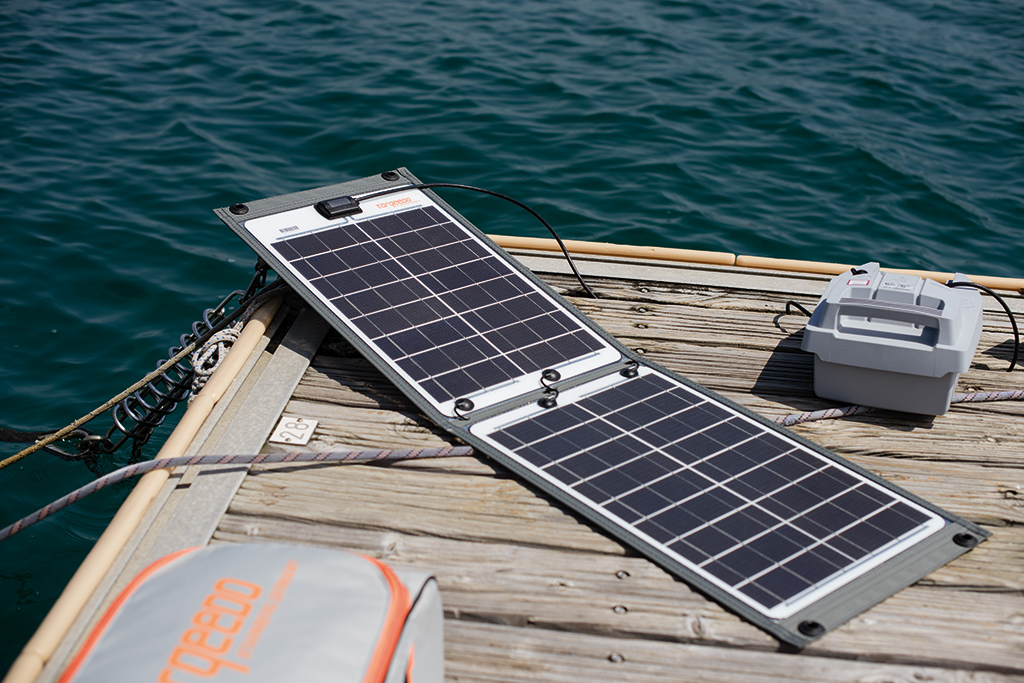

One of the great things about electric outboards is that they can use renewable power sources. So, for instance, you could plug your boat into a portable solar panel while picnicking and get an extra boost for the trip home.
Some electric outboard boat motors can even generate power! Motors with hydro regeneration capabilities can charge the batteries while the boat is being towed or under sail.
While hydro regeneration is a fairly new feature for electric outboards, some manufacturers, like EPropulsion, are offering it across their outboard product line.
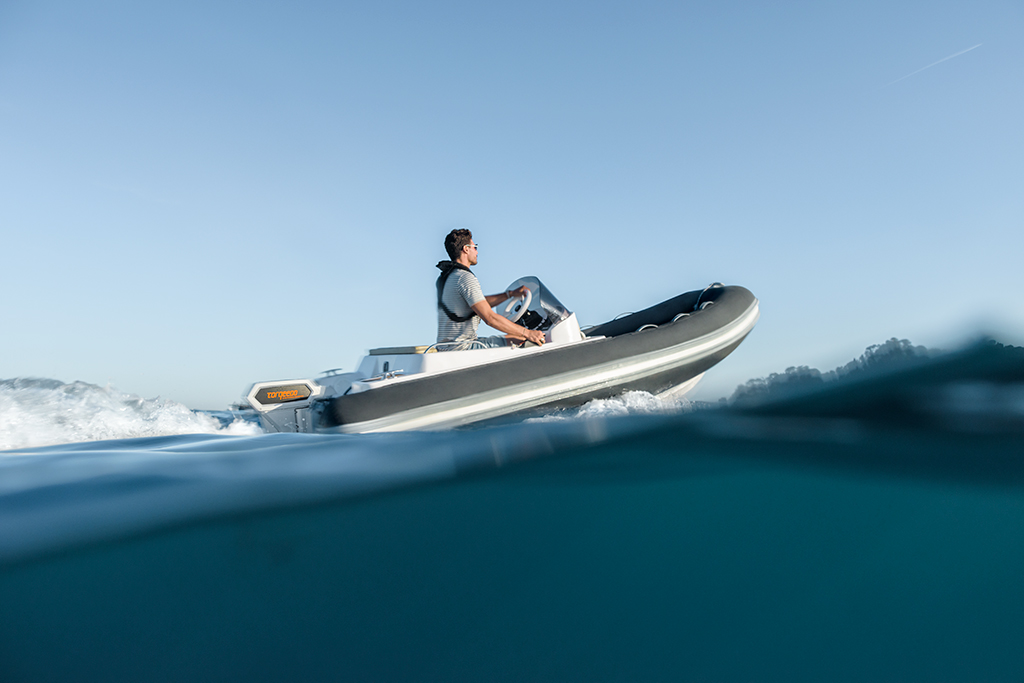

Key features of electric outboard boat motors
Each electric outboard motor brand has slightly different standard offerings and add-on features. Here are some of the key features and options to look for.
- Waterproof. Some electric outboards are fully sealed and designed to withstand immersion
- Remote controls. Choose between tiller and remote throttle controls
- On-board computers . Some electric outboards come with chartplotter connectivity, navigation functions, sonar, GPS anchoring, and autopilot features
- Built-in or stand-alone batteries. Some of the smaller motors come with built-in batteries, while the larger ones have separate battery packs
- Battery monitoring and tracking systems that calculate and display the remaining range in real-time
- Shaft length. Electric outboards come in both short and long shaft lengths to accommodate a variety of applications.
- Hydro regeneration capabilities
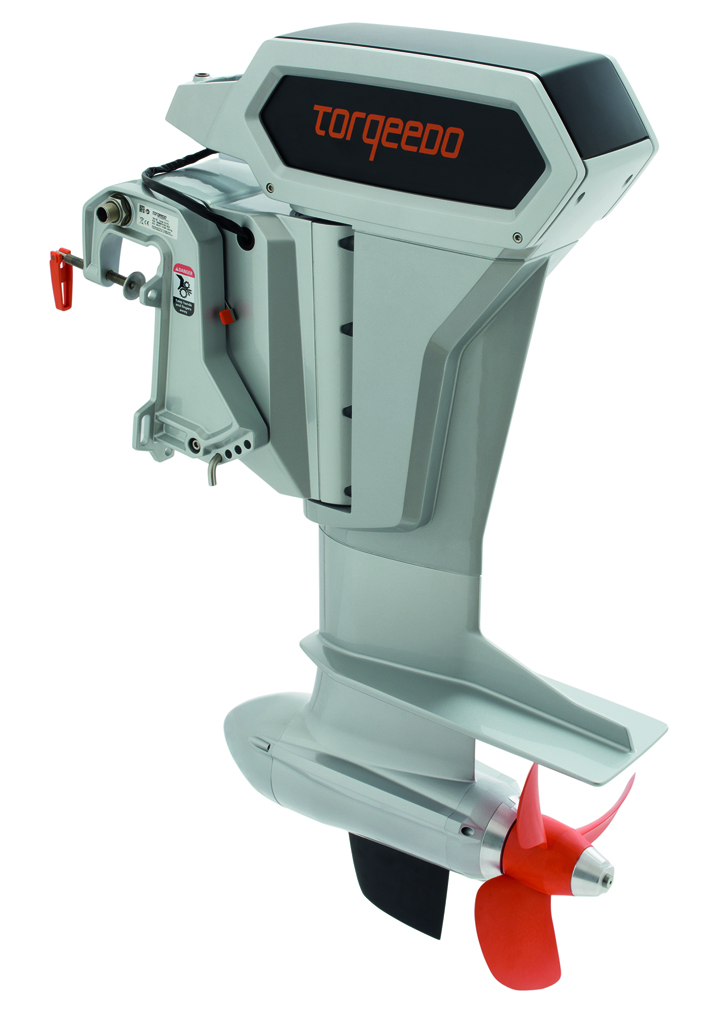

Electric outboard manufacturers
These electric outboard boat motor manufacturers (listed in alphabetical order) range from small startups to large companies and serve the North American market.
If you’re looking to learn more about what each of these companies offers (and how they compare) I’d highly recommend checking out the Plugboats’ electric outboard guides and directories . Jeff Butler, the editor at Plugboats has done a great job of compiling motor specifications from across the market.
Headquartered in San Diego, California, Bixby makes a small electric motor system for kayaks, inflatable boats, canoes, and paddleboards.
Elco has been building electric motors for 125 years and counts the likes of Henry Ford and Thomas Edison among their customers. Their award-winning electric marine motors range from 5 to 50 hp. The company is based in Lake George, New York, and its electric motors can be found on boats around the world.
Flux Marine
Flux Marine was founded by mechanical engineering Princeton grads and offers three outboard models—a 40 hp, 70 hp, and 100 hp. In 2021, they won an award for the best new green product at the Newport International Boat Show.
Joe Grez, a consumer product developer from Washington, invented the EP Carry , a compact, ultralight electric outboard system because he was concerned about exposing his young daughter to the carbon monoxide (CO) emissions produced by gas outboards.
The EP Carry retails for $1,600 and is a great size for small vessels like dinghies, canoes, inflatable boats, and kayaks.
ePropulsion
ePropulsion , based in Guangdong, China, manufactures 3 to 9.9-hp electric motors for sailboats, fishing boats, as well as dinghies and tenders. They all come with hydro regeneration capabilities.
Mercury Marine launched the Avator 7.5 electric outboard (3.5 hp equivalent) in early 2023. The leading outboard manufacturer is currently developing more powerful 20e and 35e models which it plans to release later this year.
In 2023, Newport , a well-known US-based inflatable boat manufacturer, launched three small outboards ranging from 1.8 to 3 hp.
If you’re into fishing, you’re probably familiar with the Minn Kota name, derived from MINNesota North DaKOTA, prime fishing country where the company has its roots. They introduced their first electric trolling motor back in 1934 and they’ve been making them ever since.
Pure Watercraft
Pure Watercraft was founded by CEO Andy Rebele in Seattle in 2011. Their 25 kW (50 hp) motor starts at $16,500.
Ray Electric Outboards
Ray Electric Outboards is a 3rd generation family-owned business based in Cape Coral, Fl. They manufacture one outboard model that can be operated at different power ratings ranging from 10 to 22 hp.
Stealth Electric Outboards
The 50 and 75-hp Stealth electric outboards were developed by Scott Masterston of Houston, Texas.
German manufacturer, Torqeedo , has been leading the propulsion industry for years and sells some of the best e outboard motors in the 1 to 80-hp range
Vision Marine Technologies (formerly The Canadian Electric Boat Company).
Based in Quebec, Canada, Vision Marine Technologies has been in the boating industry for 25 years and produced some very innovative electric boats. In 2021, they launched E-Motion 180E, one of the most powerful electric outboards on the market.

Electric inboard boat motors
Today’s electric inboard motors can provide anywhere from 3- to a whopping 330 hp (2 to 246 kW) and are used in a range of applications from heavy displacement vessels to fast, planing powerboats.
Similar to outboards, the range on electric inboard engines will vary based on your boat, load, battery capacity, and boat speed (among other things).
However, with an inboard electric boat motor, you have the option of a hybrid motor which can significantly extend your range. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of hybrid boat motors later in this post.
Sailors may also want to consider choosing an inboard electric motor with hydro regeneration capabilities. These electric power motors can charge the battery while the boat is under sail.

DIY electric inboard boat motor conversion
One way to save money on an electric inboard is to do the installation yourself. There are a few DIY electric inboard boat motor conversion kits available on the market.
I’ve spoken with a few sailors who’ve had great success replacing their inboard diesel engines with these electric boat motor conversion kits from Thunderstruck-EV , an electric drive manufacturer in Santa Rosa, California.
Key features of electric inboard boat motors
Each brand has a slightly different set of electric inboard motor options. Here are some of the key features and options to look for.
- DIY conversion kits
- On-board computers and touchscreen display
- Waterproof system components
Electric inboard manufacturers
US manufacturer, Elco Motor Yachts , has been building electric motors for over 125 years, having gotten their start in 1893, supplying electric boats for the Chicago World’s Fair. They have seven inboards ranging from 6 to 200 hp.
Electric Yacht
Electric Yacht is a US supplier focused on providing plug-and-play electric motors for DIY installations on sailboats. Their electric propulsion systems range from 10 to 30. They’ve had over 450 installs in 10 years of production.
Oceanvolt is a leader in regenerative systems and their electric inboard motors are popular among sailors. They offer shaft drive systems ranging from 6 to 60 hp.
Torqeedo, a German manufacturer, is the world’s leader in electric boat motors. They have two lines of inboards, one for displacement boats and another for fast planing boats. Their Deep Blue inboard systems range from 25 kW to 100 kW (40 to 135 hp)
Hybrid systems
Hybrid systems combine an electric motor and combustion engine, so you can cruise in silence (but know you’ve got enough gas to get home). These systems offer many of the benefits of pure electric motors, without the limited range.
If you want additional power for onboard luxuries like air-conditioning, hybrids can also provide a significant increase in house-side fuel efficiency.
The downside to any hybrid solution is that the systems are far more complex . Not only do they require more equipment, but, for an optimized system, you’ll need highly sophisticated software to manage multiple power sources and switch back and forth between diesel and electric.
Unsurprisingly, the increased complexity adds cost, making hybrids less economical than either a conventional or pure electric install.
Serial vs. parallel hybrids
As with cars, there are two types of hybrid systems: serial and parallel. A serial hybrid uses a generator to power a large electric motor connected to the drive shaft. Whereas, a parallel hybrid has both a conventional combustion engine and a small electric motor connected to the drive shaft.
There are plenty of factors to consider when choosing between a parallel and serial system. Marine mechanics and electrical expert, Nigel Calder, does a great job of explaining serial and parallel hybrids in detail.
In general, serial systems may be a better fit for boats that can get most of their propulsion energy from renewable sources (e.g., a sailing catamaran). Whereas, a parallel system makes more sense on boats that regularly require sustained propulsion (e.g., Greenline’s power yachts ).
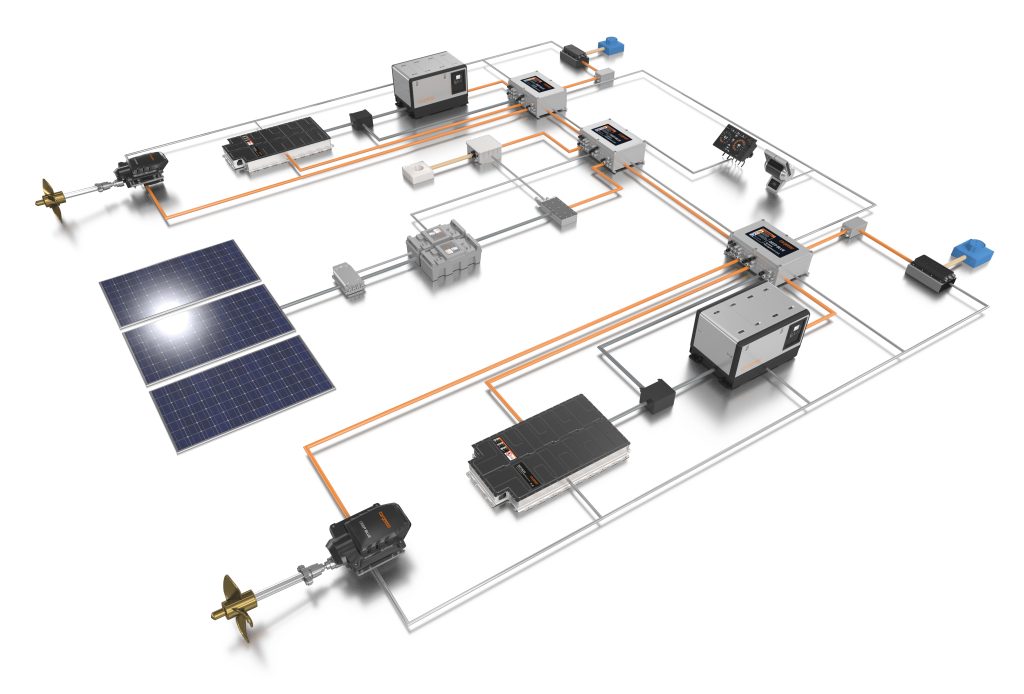
Key features of marine hybrids
- Parallel and serial hybrid options
- Integrated energy management systems
Marine hybrid manufacturers
Elco motor yachts.
Elco manufactures serial, parallel, as well as a combined serial-parallel system. Their systems can be used on sailboats, trawlers, yachts, and boats up to 85′ feet.
Hybrid Marine Ltd.
Hybrid Marine sells parallel hybrid systems in the 10 to 230 hp range. Beta, John Deere, and Yanmar’s hybrids all incorporate Hybrid Marine technology.
Finnish manufacturer, Oceanvolt , offers serial hybrid systems for both sailboats and powerboats.
Torqeedo makes hybrid systems for yachts up to 120 feet as well as powerful motorboats.
Electric pod drive and sail drive
Several manufacturers are now making electric pod and sail drives. These electric drive systems are more efficient and can save space onboard.
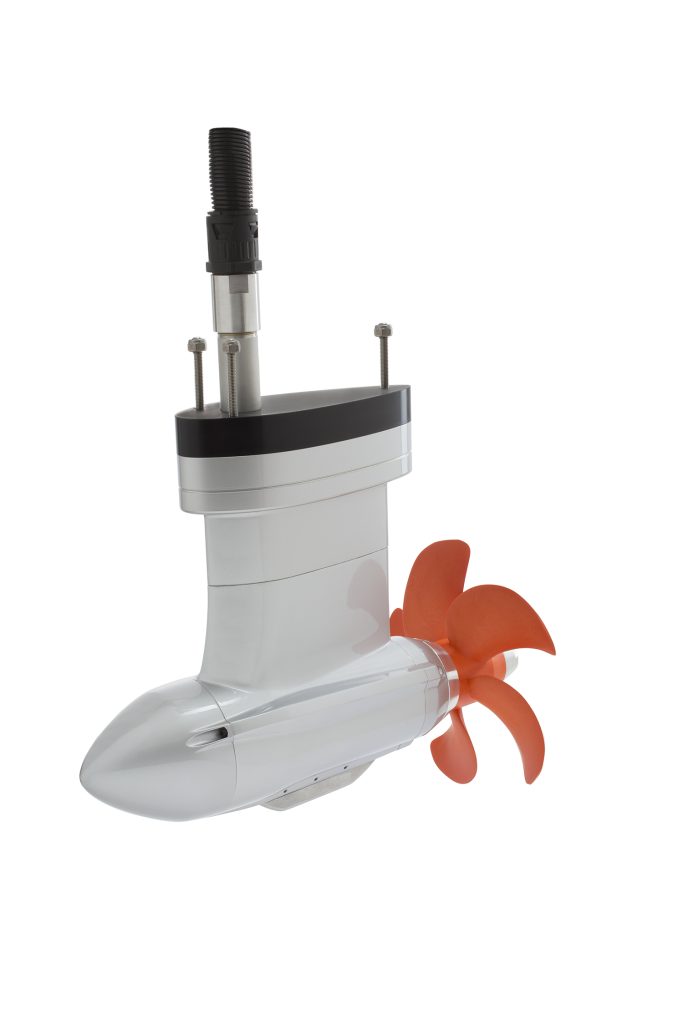

Electric pod and sail drive manufacturers
Electric Yacht produces a range of sail drives that can replace diesel engines up to 75 hp.
propulsion sells a 3 hp, 6 hp, and 9.9 hp fixed pod drive.
Oceanvolt’s sail drives range from 6 kW to 15 kW (8 to 20 hp)
Torqeedo sells a 40 hp and 80 hp equivalent electric sail drive as well as electric pod drives in the 6 to 25 hp range.
While it’s possible to power an electric motor with a conventional lead-acid battery, there are many good reasons to upgrade to lithium-ion batteries.
Their increased usable capacity is roughly double what you can get out similarly sized lead-acid battery. More battery capacity means more range—and hours of fun—on your electric boat.
They also charge more quickly and have a longer life span than lead-acid batteries. Unlike flooded lead-acid batteries, which need to be watered, lithium-ion batteries are practically maintenance-free.

The downside is that lithium-ion batteries are far more temperature-sensitive and can’t be charged much above 113 F (45 C) or below 32 F (0 C).
They can also present major safety issues . Lithium-ion batteries can go into what’s known as thermal runaway—a self-heating process that can cause the battery to catch fire.
Simply put, lithium-ion batteries are NOT a drop-in substitute for lead-acid batteries. They need to be specially designed for the marine environment and paired with a robust battery management system.
Electric motor manufacturers often provide complete solutions (including motor, batteries, and battery management system). It’s a good idea to work with a manufacturer with extensive marine experience and an ABYC-certified technician on any installation.
The other catch is that lithium-ion batteries cost two to four times as much as lead-acid batteries. However, the increased capacity and longer life span may make lithium batteries a better value option over the long run.
Ready to catch the electric boating wave?
With ever more powerful and feature-packed electric options launching each year, it’s an exciting time to be in the market for a new motor or engine. If you have any doubts about whether an electric boat motor is right for you, head to your local boat show and see, first hand, what all the buzz is about.
Fiona McGlynn is an award-winning boating writer who created Waterborne as a place to learn about living aboard and traveling the world by sailboat. She has written for boating magazines including BoatUS, SAIL, Cruising World, and Good Old Boat. She’s also a contributing editor at Good Old Boat and BoatUS Magazine. In 2017, Fiona and her husband completed a 3-year, 13,000-mile voyage from Vancouver to Mexico to Australia on their 35-foot sailboat.
Douglas McQuilken
Sunday 30th of January 2022
Great article!
For those who wish to collaborate with prospective & current electric boaters, highly recommend this forum - https://groups.io/g/electricboats
Thanks for the suggestion, Douglas!
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy

All About Electric Sailboat Motors: Efficiency & Performance
Exploring the Environmental Benefits of Electric Boat Motors

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan E4 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan E4" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-E4.png"><h3><strong>E4</strong> - 34' 9" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan E5 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan E5" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-E5.png"><h3><strong>E5</strong> - 39'3" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan E6 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan E6" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-E5.png"><h3><strong>E6</strong> - 50'2" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan i43 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan i43" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/I43-YACHTS-Sideview.png"><h3><strong>IMPRESSION 43</strong> - 43'8" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan i50.1 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan i50.1" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-i501.png"><h3><strong>IMPRESSION 50.1</strong> - 49'10" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan GT5 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan GT5" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-GT5.png"><h3><strong>GT5</strong> - 43'4' ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan GT6 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan GT6" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-GT6.png"><h3><strong>GT6</strong> - 49'9" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan GT6 X - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan GT6" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/GT6X-YACHTS-Sideview.png"><h3><strong>GT6 X</strong> - 49'8" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan i40.1 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan i40.1" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-i401.png"><h3><strong>IMPRESSION 40.1</strong> - 39'4" ft</h3>
- <img title="Elan Yachts - Elan i45.1 - sideview" alt="Elan Yachts - Elan i45.1" src="https://media.elan-yachts.com/img/YACHTS-Sideview-i451.png"><h3><strong>IMPRESSION 45.1</strong> - 45'5" ft</h3>
- Elan Yachting Experience
- Distributors
- Elan Technology

What You Need to Know Before Buying an Electric Sailing Yacht or Sailboat
It’s no secret that we’re approaching, or have maybe even passed the moment in history where most buyers are considering buying an electric vehicle. The awkward early adopter phase is long gone, doubters few and far between, and every car manufacturer has at least some EV options, while others focus exclusively on electric and are experiencing massive growth. Mass adoption is here, the prices are falling, and infrastructure and legislature are hurrying to catch up.
All of this has left many people wondering why not bring sailing boats into the electric world? Sailing was never about motoring, never about engine speed – it is about that connection to nature, the serenity of the sea and the challenge. So why not get rid of the “dirty and loud” diesel engine, and simply exchange it for “clean and quiet” electric propulsion? Motor out of the marina or bay in silence, then use the sun, wind and waves to continue your journey.
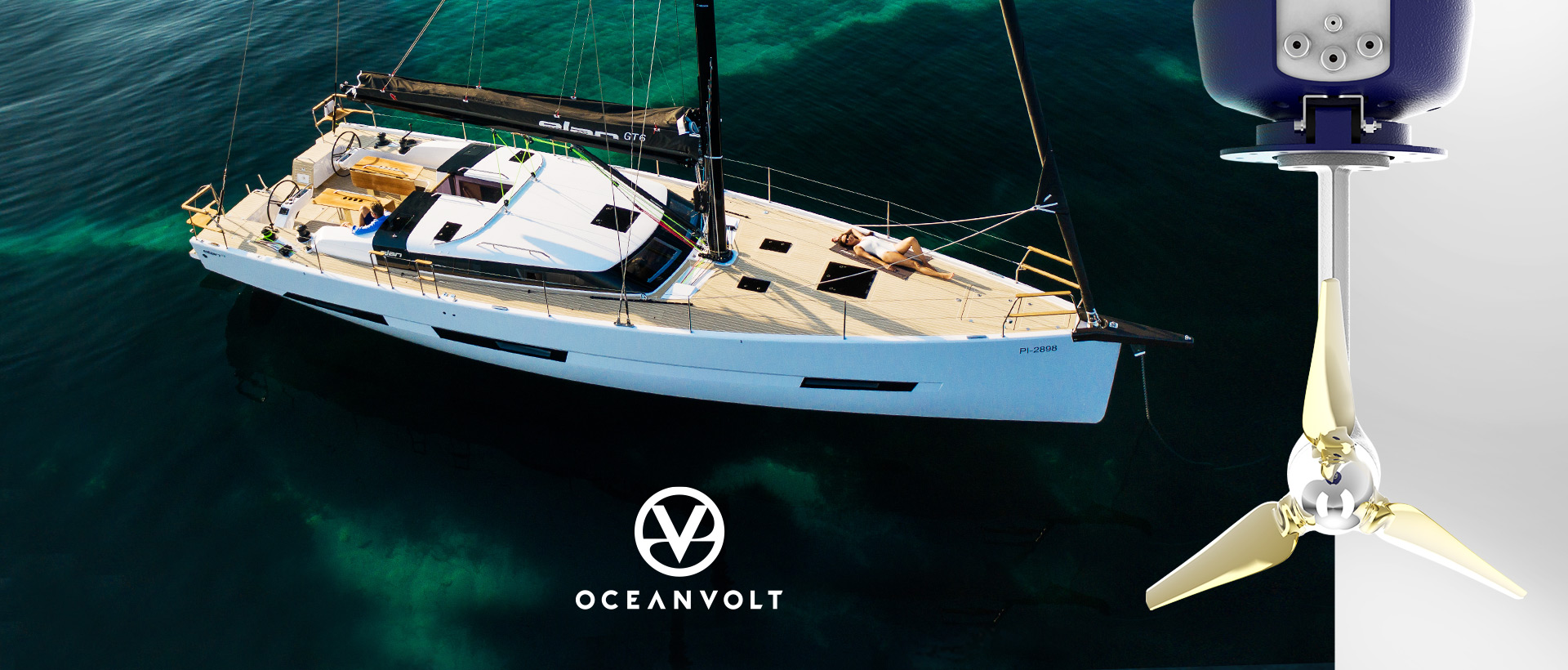
Well – it turns out that like all good things in life, it’s not that simple, but it can be completely viable if approached correctly, and Elan and Oceanvolt have partnered-up to offer just that.

EARLY ADOPTER PHASE
Unlike the automobile industry, electric-powered yachting is still in the early adopter phase. That is why picking experienced manufacturers is crucial. Elan Yachts, for instance, had built various highly successful projects with Oceanvolt in the past and were part of the pioneering few boatbuilders to take on the challenge. The partnership flourished and matured so that Elan is now working exclusively with Oceanvolt and has extended the offer to their whole range of yachts. But what does being an early adopter mean for the buyer? Mostly that the technology is here, but the price is high. For a well-rounded, high-quality and reliable system, you can expect to pay 20-30% more than a comparable diesel-powered sailing yacht. And since a large part of that cost is for the batteries, do not expect that to change very soon as the demand for Lithium-ion batteries is only increasing.
FOR SERIOUS SAILORS
However, let’s assume that the price is not a problem. You want to be among the first few with a zero-emissions yacht – no noise, no exhaust, no smell and no environmental restrictions. You want to sail without the use of fossil fuels. You want the famous instant power output benefits of electricity in emergency situations, no engine rev settling, no pre-start waiting and low maintenance costs. You want to use the wind and the sun to re-charge. All of these are actual benefits of electric yacht propulsion, but what are the downsides? For committed sailors, there are not many. The operating range of high-end electric propulsion systems like the one from Oceanvolt is from 25 to 70 miles at 5 knots (and more, depending on the battery pack options and power generation), which is more than enough to get you in and out of marinas and bays and still have plenty left over to get you out of a bind. The rest, you sail. And if the yacht is fast, the winds are fair and you achieve 5 knots or more, Oceanvolt’s hydrogeneration kicks in and generates power for recharging the battery bank. Hydrogeneration creates drag of only 0.1 knot at a boat speed of 7.0 knots – so it is barely noticeable. If you can go even faster, the power generation increases exponentially (see GRAPH 1).
GRAPH 1: Elan E4 Power generation prediction

(Source: Oceanvolt)
LIVING ABOARD
Buying an electric-powered yacht is still far from an off-the-shelf experience. You need a trusted team of specialists who will guide you through the process and make sure they create a custom solution according to your needs and a good partnership between the shipyard and the electric propulsion provider is crucial. Why is this so different from a car? A yacht is an independent element on the sea and, unlike a car, it will need to provide its owner with much more than just propulsion. It is imperative therefore to consider everything, from the way the yacht is built to the equipment on board. Since you will spend most of your time sailing, you need a yacht that performs well and is easy to sail. A good, reliable sail plan and rig, like the one on Elan yachts, will give you enough options to substitute the practicality of a diesel engine. Elan’s VAIL technology keeps the weight down, its short-handed sailing approach and comfort-centric design will keep you comfortable even when sailing for longer periods, and the high-end electronics are designed to keep consumption low. That is crucial because you will need to bear in mind cooking, refrigeration, water and cabin heating and entertainment, as well as the availability of ports/marinas with good electrical infrastructure. Of course, there are fossil fuel solutions for all these challenges, and Elan’s and Oceanvolt’s partnership offers a hybrid option with a 48V DC generator, which is very practical, if on the pricier side. Purists, however, will want to go full electric. And for them, more renewable power generation options like photovoltaics, a wind generator or a humbler approach to on-board living will be crucial, especially in colder climates. Bear in mind that experienced shipyards like Elan Yachts will be able to provide a complete solution, including solar panel procurement and installation.
POWER OPTIONS
How powerful are electric motors on sailboats? Well, Oceanvolt offers two different propulsion systems. The Finland-based company has developed a 6, 8, 10 and 15kW SD saildrive, as well as a special 10 and 15kW ServoProp with even better hydrogeneration, thanks to its patented and DAME-awarded software-controlled propeller blades, which change pitch to generate as much power as possible. Depending on the yacht, the entry-level SD saildrive enables 5 knots of cruising speed and a top speed of 7 knots on the 30 ft Elan E3. Bear in mind that power consumption and speed is inverse in relation to power generation – as you go faster, you consume exponentially more power (see GRAPH 2) The good part is that the motor and the saildrive weigh only 42.5 kg, which offsets some of the battery weight. In addition, all of the motors are all closed-circuit liquid-cooled, so there is no annoying spluttering.
GRAPH 2 : Elan E3 RANGE PREDICTION

Source: (Oceanvolt)
Want to go electric?
Get in touch with Elan Yachts, and request the configuration of your ideal electric-powered sailboat. Elan is the only yacht manufacturer offering complete electric propulsion solution for the whole range of yachts. Contact our experts, build an energy balance sheet for your needs and your new Elan, taking into account the type of sailing, the environment, living habits and other possible criteria, to create the optimal setup.
E Line Crossover

IMPRESSION Cruising

IMPRESSION 43 - 43'8"

IMPRESSION 50.1 - 48'8"
Gt line luxury performance.

GT5 - 40'9"

GT6 X - 49'8"
Get in touch.
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
The Promises and Pitfalls of an All-Electric Yacht
- By Tim Murphy
- Updated: November 8, 2021
This past October, I saw one of the most interesting exhibits in more than 500 new cruising sailboats I’ve reviewed over two decades. It was the Arcona 435Z, built in Sweden and introduced by Graham Balch of Green Yachts in San Francisco. Balch describes his business as “a new brokerage dedicated to the electric revolution on the water,” and it was the “Z” in the boat’s name, which stands for “zero emissions,” that made this boat so interesting. This was the first electric propulsion system—not hybrid but all-electric —I’d ever seen on a cruising sailboat.
Electric propulsion isn’t new. Since 1879, electric motors have propelled boats; a fleet of some four-dozen electric launches transported visitors around the 1893 Colombian Exposition in Chicago. But cruising sailboats are not launches, and the open sea is not a protected canal. When we’re using cruising boats as they’re meant to be used, they seldom end their day plugged into a shore-power outlet. Cruising boats comprise many devices —stove, refrigerator, freezer, windlass, winches, autopilot, radar, lights—whose power typically comes from a tank of fossil fuel. And today’s cruising sailors are accustomed to using diesel auxiliary power to motor through lulls or punch into headwinds and seas.
Starting about 15 years ago, we saw a wave of diesel-electric and hybrid propulsion systems on production and custom cruising boats ( see “Perpetuated Motion,” CW , March 2005 ). Both of those systems ultimately start with an onboard internal-combustion engine. A diesel-electric propulsion system relies on a running genset to directly power the electric motor that turns the propeller. A hybrid system relies on batteries to power the electric motor, plus an internal-combustion genset to recharge the batteries. One of the promises of a hybrid system is the ability to regenerate electrical power. Regeneration means using boatspeed under sail to turn the propeller, whose spinning shaft sends electrons from the electric motor back through an electronic controller to recharge the batteries. In such a system, the boat’s propeller is both an electrical load (when running under power) and a charging source (when sailing in regeneration mode).
The Arcona 435Z was different from both of these systems: It incorporates no onboard fossil-fuel engine at all. Instead, it has a bank of lithium batteries, several solar panels, and a proprietary propulsion leg that looks like a saildrive. “This boat,” Balch said, “has the very first production unit in the world of Oceanvolt’s newest electric propulsion system, called the ServoProp.”
For our sea trial, Balch was joined by Derek Rupe, CEO of Oceanvolt USA. “If you can sail the boat and you have some solar, you can go anywhere in the world, and you can make all your power underway while you go,” Rupe said. When we spoke in October 2020, he touted three high-profile sailors who were using the Oceanvolt electric propulsion system: Alex Thomson, for his Hugo Boss Open 60 Vendée Globe program; Jimmy Cornell, for his Elcano 500 expedition; and Riley Whitelum and Elayna Carausu, who had been teasing their new boat for months on their popular Sailing La Vagabonde YouTube channel.
The efficiency of Oceanvolt’s ServoProp and the regeneration from it is the promised game-changer in each of these boats. The ServoProp is a leg with a feathering propeller that can be set for optimal pitch in three modes: forward, reverse and regeneration.
“You don’t need fuel,” Rupe said. “You don’t need to dock; you can go anywhere you want to go and always have the power for living and propulsion.”
That’s the promise. But are there also pitfalls?
Innovation and Risk
Marine electric propulsion is an emerging technology. Compared with the mature and settled technology of diesel engines and lead-acid batteries, electric-propulsion systems—with their electronic controllers and lithium batteries—are in a stage of development best described as adolescent. Every sailor has his or her own tolerance for technical innovation. For the promise of fewer seconds per mile, grand-prix-racing sailors willingly trade a high risk of expensive damage to the sails, rig or the boat’s structure itself; cruising sailors, by contrast, tend to favor yearslong reliability in their equipment as they seek miles per day.
Folks who identify as early adopters take special joy in the first-wave discoveries of a new technology; if they’re clear-eyed about supporting an ongoing experiment, they see themselves as partners with the developers, accepting failures as opportunities for learning. Sailors motivated primarily by changing the trajectory of climate change might be especially willing to modify their behavior to limit their own output of greenhouse gases. Investing in any emerging technology asks you to start with a clear assessment of your own risk tolerance. We’ll return to this theme with one or two real-life examples.
The American Boat and Yacht Council, founded in 1954, sets recommended standards for systems installed on recreational boats. For decades, ABYC has published standards related to installations of diesel and gasoline engines, as well as electrical systems based around lead-acid batteries. By contrast, it was only three years ago that ABYC came out with its first electric-propulsion standard (revised July 2021). And only last year it published its first technical-information report on lithium batteries (a technical-information report is an early step toward a future standard). The takeaway is that if you need help servicing your diesel engine or electrical system built around lead-acid batteries, you can pull into any reasonable-size port and find competent technicians to help you. With electric propulsion and lithium batteries, that pool of skilled talent is significantly scarcer.
To say that a technology is mature simply means that we’ve learned to live with it, warts and all, but that it holds few remaining surprises. Certainly, diesel-propulsion and lead-acid-battery technologies each leave plenty of room for improvement. When a charge of fuel ignites in the combustion chamber of a diesel engine, some three-quarters of the energy is lost in heat and the mechanical inefficiencies of converting reciprocating motion to rotation. Lead-acid batteries become damaged if we routinely discharge more than half of their capacity. During charging, they’re slow to take the electrons we could deliver.
Lithium batteries are comparatively full of promise. Their power density is far greater than that of lead-acid batteries, meaning they’re much lighter for a given capacity. They’re capable of being deeply discharged, which means you can use far more of the bank’s capacity, not merely the first half. And they accept a charge much more quickly; compare that to several hours a day running an engine to keep the beers iced down.
But the pitfalls? Let’s start with ABYC TE-13, Lithium Ion Batteries. Some of its language is bracing. “Lithium ion batteries are unlike lead-acid batteries in two important respects,” the report says. “1) The electrolyte within most lithium ion batteries is flammable. 2) Under certain fault conditions, lithium ion batteries can enter a condition known as thermal runaway, which results in rapid internal heating. Once initiated, it is a self-perpetuating and exothermic reaction that can be difficult to halt.”
Thermal runaway? Difficult to halt? Self-perpetuating?
“Typically, the best approach is to remove heat as fast as possible, which is most effectively done by flooding the battery with water,” TE-13 continues, “although this may have serious consequences for the boat’s electrical systems, machinery, buoyancy, etc.”
If you were following the news in January 2013, you might remember the story of Japan Airlines Flight 008. Shortly after landing at Boston’s Logan Airport, a mechanic opened the aft electronic equipment bay of the Boeing 787-8 to find smoke and flames billowing from the auxiliary-power unit. The fire extinguisher he used didn’t put out the flames. Eventually Boston firefighters put out the fire with Halotron, but when removing the still-hissing batteries from the plane, one of the firefighters was burned through his professional protective gear.
Samsung Galaxy cellphones, MacBook Pro laptops, powered skateboards—in the past decade, these and other devices have been recalled after their lithium batteries burned up. In that period, several high-end custom boats were declared a total loss following failures from lithium batteries. In March 2021, a 78-foot Norwegian hybrid-powered tour boat, built in 2019 with a 790 kW capacity battery bank, experienced thermal runaway that kept firefighters on watch for several days after the crew safely abandoned the ship.
Yes, experts are learning a lot about how to mitigate the risks around lithium batteries. But we’re still on the learning curve.
ABYC’s TE-13 “System Design” section starts, “All lithium-ion battery systems should have a battery management system (BMS) installed to prevent damage to the battery and provide for battery shutoff if potentially dangerous conditions exist.” It defines a bank’s “safe operating envelope” according to such parameters as high- and low-voltage limits, charging and discharging temperature limits, and charging and discharging current limits.
Graham Balch takes these safety recommendations a step further: “To our knowledge, the BMS has to monitor at the cell level. With most batteries, the BMS monitors at the module level.” The difference? “Let’s say you have 24 cells inside the battery module, and three of them stop working. Well, the other 21 have to work harder to compensate for those three. And that’s where thermal events occur.”
Balch followed the story of the Norwegian tour boat this past spring. He believes that the battery installation in that case didn’t meet waterproofing standards: “The hypothesis is that due to water intrusion, there was reverse polarity in one or more of the cells, which is worse than cells simply not working. It means that they’re actively working against the other cells. But if the BMS is monitoring only at the module level, you wouldn’t know it.”
On the Green Yachts website, Graham lists five battery manufacturers whose BMS regimes monitor at the cell level. “If I were sailing on an electric boat, whether it be commercial or recreational, I would feel comfortable with having batteries from these five companies and no other,” he said.
The broader takeaway for today’s sailors is that lithium batteries bring their own sets of problems and solutions, which are different from those of conventional propulsion and power-supply technologies. A reasonably skilled sailor could be expected to change fuel filters or bleed a diesel engine if it shuts down in rough conditions. With lithium-ion batteries aboard, an operator needs to understand the causes and remedies of thermal runaway, and be ready to respond if the BMS shuts down the boat’s power.
Real-World Electric Cruising Boats
When we met Oceanvolt’s Derek Rupe a year ago, he and his wife had taken their all-electric boat to the Bahamas and back the previous season. Before that, he’d been installing electric-propulsion packages for six years on new Alerion 41s and other refit projects. “My real passion is on the technical side of things—installations, really getting that right. That’s half the picture. The technology is there, but it needs to be installed correctly.”
When talking to Rupe, I immediately encountered my first learning curve. I posed questions about the Oceanvolt system in amps and amp-hours; he responded in watts and kilowatt-hours. This was yet another example of the different mindset sailors of electric boats need to hold. Why? Because most cruising boats have just one or two electrical systems: DC and AC. The AC system might operate at 110 or 220 volts; the DC side might operate at 12 or 24 volts. On your own boat, that voltage is a given. From there we tend to think in terms of amps needed to power a load, and amp-hours of capacity in our battery banks. Going back to basics, the power formula tells us that power (watts) equals electrical potential (volts) times current (amps). If your boat’s electrical system is 12 volts and you know that your windlass is rated at 400 watts, it follows that the windlass is rated to draw 33 amps.
But an all-electric boat might comprise several systems at different voltages. A single battery bank might supply cabin lights at 12 volts DC; winches and windlasses at 24 volts DC; the propulsion motor at 48 volts DC; and an induction stove, microwave and television at 110 volts AC. A DC-to-DC power converter steps the voltage up or down, and an inverter changes DC to AC. Instead of translating through all those systems, the Oceanvolt monitor (and Derek Rupe) simply reports in watts coming in or going out of the bank.
“We keep all our thoughts in watts,” Rupe said. “Watts count in the AC induction. They count in the DC-to-DC converter. They count the solar in. They count the hydrogeneration in. And the power-management systems tracks it that way for shore-power in.
“On a boat like this, maybe I have 500 watts coming in the solar panels,” he continued. “So then I can think: ‘Well, my fridge is using 90 watts. My boat has an electric stove. When I cook a big meal, I can see that for every hour we cook, we lose about 10 to 12 minutes of our cruising range.’”
During his Bahamas cruising season, Rupe observed that on days that they were sailing, the combination of solar panels and hydroregeneration supplied all the power he and his wife needed. “When we weren’t sailing,” he said, “we found that we were losing 8 percent each day, in the difference from what the sun gave us to what we were using for the fridge, lights, charging our laptops, and all that stuff.”
Rupe’s solution? “Twice in Eleuthera and once outside Major’s, we went out and sailed laps for a couple of hours because the batteries were below 30 percent of capacity. It was good sailing, and the wind was coming over the shore, so we didn’t have any sea state. We did a couple of hot laps on nice beam reaches, and generated about 700 watts an hour.”
Of the three sailors Rupe touted in October 2020—Alex Thomson, Jimmy Cornell and the Sailing La Vagabonde couple—only Cornell can report back on his all-electric experiences with Oceanvolt. Alex Thomson ended his circumnavigation abruptly last November, just 20 days after the Vendée Globe start, when Hugo Boss collided with an object in the South Atlantic. And at press time in early fall 2021, Riley and Elayna had just recently announced the build of their new Rapido trimaran; keep an eye on their YouTube channel for more about their experiences with the Oceanvolt propulsion system.
As for Cornell—circumnavigator, World Cruising Routes author, creator of the transoceanic rally, and veteran of some 200,000 ocean miles—he suspended his planned Elcano 500 round-the-world expedition solely because of the Oceanvolt system in his new Outremer catamaran. His Aventura Zero Logs on the Cornell Sailing website, particularly the Electric Shock article posted on December 2, 2020, are essential reading for any sailor interested in sailing an electric boat. “Sailing around the world on an electric boat with zero emissions along the route of the first circumnavigation was such a tempting opportunity to do something meaningful and in tune with our concern for protecting the environment that my family agreed I should do it,” Cornell wrote. “What this passage has shown was that in spite of all our efforts to save energy, we were unable to regenerate sufficient electricity to cover consumption and top up the batteries.”
Cornell’s experience in that article is raw, and his tone in that moment bitterly disappointed. We recommend it as essential reading—not as a final rejection of the electric-boat concept or of Oceanvolt’s system, or even as an endorsement of Cornell’s own decision that the system didn’t work. I suspect that I may have arrived at the same conclusion. Yet given the same boat in the same conditions, one imagines that a new breed of sailor—a Graham Balch or a Derek Rupe—may have responded differently to the constraints imposed by an all-electric boat, as nearly every cruising sailor today habitually responds to the inconvenient constraints of diesel engines and lead-acid batteries.
“If you bring electric winches, electric heads and an induction stove, and then sail into a high-pressure system, you’ll set yourself up for failure,” Balch said. “You have to balance your power inputs and your power outputs.
“Sailing an electric boat is a return to the tradition of sailing that the crutch of a diesel engine has gotten us away from,” he added. “Magellan’s fleet got all the way around the world, and they didn’t have a diesel engine.”
Tim Murphy is a Cruising World editor-at-large and longtime Boat of the Year judge.
- More: Green Wakes , Hands-On Sailor , navigation , print nov 2021 , sailboat review , Sailboat Reviews
- More Sailboats
New to the Fleet: Pegasus Yachts 50
Balance 442 “lasai” set to debut, sailboat review: tartan 455, meet the bali 5.8, route planning in the face of climate change, how to rig everything in your favor, imtra named employee-owned company of the year.
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter

Ericson 34-2 Finds Sweet Spot

How to Sell Your Boat

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Solar Panels: Go Rigid If You have the Space…

Leaping Into Lithium

The Importance of Sea State in Weather Planning

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

When Should We Retire Dyneema Stays and Running Rigging?

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

What Your Boat and the Baltimore Super Container Ship May Have…

Check Your Shorepower System for Hidden Dangers

DIY survey of boat solar and wind turbine systems

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?

The Scraper-only Approach to Bottom Paint Removal

Can You Recoat Dyneema?

How to Handle the Head

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions


Cockpit Drains on Race Boats

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Safer Sailing: Add Leg Loops to Your Harness

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Systems & Propulsion
Electric and Hybrid Propulsion for Sailboats
Practical sailor looks at the players in the developing field of electric auxiliary engines.

How soon will electric auxiliary propulsion be available to everyman? That depends on whom you ask. Opinions differ widely not just on what type of drive system might surge to the forefront, but even on whether the concept itself is viable. While a handful of companies forge ahead, notably Glacier Bay and Electric Marine Propulsion on this side of the Atlantic, some expected participants are waiting on the sidelines.

Photos courtesy of Manufacturers
One of the big issues that divides promoters and detractors alike is whether the appropriate way to go in a sailboat is with a pure diesel-electric drive train, with a hybrid electric drive with a diesel generator as back-up, or as a pure electric drive with regeneration capability. We’ll take a look at these and other options later in this article. For now, the short answer is that no single approach suits every sailor all the time.
Simply put, in the diesel-electric system, the electric motor runs only when the diesel-driven generator is running. Such arrangements have long been employed in railway locomotives, submarines, and commercial vessels of many types. In the hybrid system, a large bank of batteries provides the energy for the electric motor and the diesel generator recharges the batteries. On the face of it, the hybrid system offers a certain degree of redundancy in that, assuming the batteries are kept well charged, the boat has a measure of emergency power should the generator fail at an inopportune moment. The hybrid also is capable of recharging its batteries when sailing: Driven by the turning propeller, the motor becomes a generator.
Each of these approaches has its strengths and weaknesses, and while we’ll leave it to their developers to work out the technical issues, we would like to urge anyone contemplating installing an electric drive, or purchasing a boat that has one, to first look very closely at how they expect to use the boat. There’s more entrained in the choice than in picking a flavor at Baskin-Robbins. More on this later.
Among the electric drives currently available in one form or another, or as components, the big variable is operating voltage. Motors are available that run on 24, 36, 48, 72, and 144 volts, and, in the case of Glacier Bay’s diesel-electric system with Ossa Powerlite technology, 240-volt DC. Each supplier will discourse at length on the merits of their voltage choice, but an inconvenient fact haunts the entire field: High-voltage DC is deadly, potentially more so in some circumstances than AC.
While neither form of high-voltage is “safe,” we have a lot more experience with AC aboard recreational vessels than with high-voltage DC. An extensive body of knowledge exists on which to base AC installations so as to make them safe as well as reliable. High-voltage DC is used in a variety of marine and non-marine commercial applications, but these installations are well protected from access by untrained operators.
What voltage constitutes high voltage? That, again, depends on whom you talk to. The American Boat & Yacht Council (ABYC), which sets voluntary standards for the marine industry, defines it as 50 volts and above. Prompted by rapid adoption of high-voltage services in small commercial craft and bigger yachts, though not specifically in propulsion systems, the ABYC is in the process of drawing up guidelines for voltages higher than the 48 volts covered by existing standards.
An absence of standards might not deter individuals from installing an electric drive, but it might impede widespread adoption of the technology. If a surveyor can’t state in an insurance survey that a boat is built according to ABYC standards, that could affect its insurability.
Jim Nolan, who manages the underwriting department for BoatUS, said the company has no clear cut guidance regarding insuring boats with electric propulsion. Each boat is dealt with on a case-by-case basis. A new boat with a factory-installed system would be a good deal easier to underwrite than a one-off or do-it-yourself project, especially in the absence of a standard practice. Lagoon Catamarans’ 72-volt-DC hybrid system, for instance, has qualified for the European standard (CE) certification on the strength of following industrial standards that apply to such applications as fork-lift trucks. Anyone contemplating an electric drive would be well advised to discuss it ahead of time with an insurer and even get a surveyor involved from the outset.
Because of the safety issues surrounding the voltages involved in electric propulsion, Fischer Panda has decided to limit its DC product line to boats weighing 10 tons or less. A company representative we spoke to said that while Fischer Panda currently sells DC generators up to 48 volts in the USA for marine use, it “won’t touch” high-voltage DC because it’s lethal.
A proposed collaboration with Catalina Yachts to fit a diesel-electric system in a Catalina-Morgan 440 never came to fruition due to budget constraints, according to Fischer Panda. But in Europe, Fischer Panda teamed up with Whisperprop to equip a Bavaria 49. (Beyond the fact that one of its boats was used, Bavaria Yachts was not involved in the project.) According to Fischer Panda, after evaluating the Bavaria project, the company decided that the diesel-electric AC system is a niche product that wouldn’t interest their prime market: original equipment builders.
“Although the AC system has some advantages in the improved response of the electric motors … and the quietness of the system, the desired fuel efficiency and weight savings were not evident,” Fischer Panda reported.
Fischer Panda considers the DC system to be more suitable for its North American customers. Although it’s limited in output due to its limited battery voltage of 48 volts, it is still able to power multihulls up to 10 tons.
Currently, much of the movement toward electric drives is taking place in the catamaran world. This makes sense when you consider that a single diesel generator can, in theory, provide all the boat’s electrical needs and also take the place of two diesel-propulsion engines. Taking the lead in the field, Lagoon Catamarans introduced in 2006 the Lagoon 420. Originally offered only as a hybrid, it now is also available in two diesel versions. Corsair Marine is building the Corsair 50 catamaran around the Glacier Bay diesel-electric drive, but the boat’s launch date—formerly set for this summer—has been postponed.
Dick Vermeulen, president of Maine Cat, tried the Glacier Bay system in a prototype power cat, but it failed to meet performance expectations, so production models will have conventional diesels. A number of other cat builders have announced hybrid or diesel-electric projects, but feedback on how they perform is scan’t.
So much for the mainstream—but backwater sailors will go their own way, as they always have. As more vendors and components enter the market, the options for do-it-yourselfers or custom-boat customers become broader and more attractive. However, before going ahead with an installation, make sure it’s appropriate to how you plan to use your boat, and even then be prepared to adapt the way you sail to take best advantage of the system’s characteristics. Here’s a rundown of the various types.
Electric Drive Only
Duffy Electric Boats has for years been building electric launches and lake boats that have the simple capability of puttering around in sheltered waters for a period of time determined by battery capacity and speed maintained. A battery charger powered by shore power charges the batteries overnight. Transferring that approach to a sailboat up to about 25 feet used for daysailing and kept near an electrical outlet shouldn’t be too difficult. It won’t offer the assurance of diesel when trying to get home against current or wind, but a proven 36- or 48-volt system will keep you out of uncharted standards territory.
For a bigger boat, more power, a greater range, or a combination of these requirements, it will be necessary to install a large battery bank and almost certainly will entail going to a higher voltage to keep the amps and the cabling needed to carry them manageable. The boat’s range under power will be limited by the weight of batteries, and while lighter lithium-based technology is on the horizon, for now the standard is lead/acid. The fast charging, but expensive pure lead thin plate (PLTP) Odyssey batteries have attracted particular interest among propulsion enthusiasts.
Electric Drive with Regeneration

The next level up in complexity is a “reversible” system. When the boat is sailing, the propeller turns the motor, which then becomes a generator. The electricity it makes is used to recharge the batteries. The capability to regenerate extends the boat’s potential range, but the drag on the propeller slows the boat measurably. One hour of regen will not restore the power consumed by one hour of motoring, but if sailing time sufficiently exceeds motoring time, this arrangement offers considerable range.
A regenerating system does have the potential to overcharge the batteries once they become fully charged and the boat continues to sail fast. The solution is, ironically, to give the motor some “throttle,” which reduces the drag on the propeller and consequently the power output. This phenomenon gives rise to a new technique, that of “electro-sailing” in which sails and an electric motor complement each other. At present, the “throttle” must be adjusted by hand, but developers are working on automatic controls. Field trials of existing regen motors such as the Solomon systems suggest that a small regen motor’s ability to match the output of a much higher-rated diesel have been overstated.
Hybrid Electric Drive
A hybrid system adds to the mix an onboard generator, which is used primarily to maintain charge in the batteries, both those for the propulsion motor and for the house services. This arrangement extends the boat’s capability to lie for long periods at anchor, independent of shore power for electricity and without the need to go sailing for the sole purpose of charging the batteries. A hybrid can motor constantly, as long as there is fuel, but it cannot sustain full speed for long periods. This is because the generator is usually rated at a far lower horsepower than that required to drive the boat at full speed.
Diesel-Electric Drive
In a pure diesel-electric, the electric propulsion motor runs only when the generator is running. Storage batteries are not needed for propulsion purposes, and the generator is the source for all onboard electrical power needs. The rationale behind diesel electric lies in the relationship between a diesel engine’s rate of fuel consumption and the load it’s working under. It burns fuel more efficiently when heavily loaded than when lightly loaded. When the diesel engine is disconnected from the propeller, it can be controlled so that it is working in the upper range of its efficiency regardless of how fast the propeller is turning. Nigel Calder’s series of articles in Professional Boatbuilder magazine (www.boatbuilder.com) beginning with the June/July issue delves deeply into the efficiency discussion surrounding these engines. Systems on large vessels are built around multiple generators that switch on or off according to the power demands of the moment. Translating those efficiencies into a smaller boat scenario has proven to be challenging.
Hype vs. Experience
Maine Cat’s Vermeulen, on the company’s website, describes the sea trials he performed in the Maine Cat 45, a power catamaran. He began with a Glacier Bay diesel-electric system with two 25-kW generators, each weighing about 550 pounds.
“With both generators putting out their full power of 25 kW each … our top speed was a disappointing 8.4 knots, and the assumption that electric horsepower was somehow more powerful than conventionally produced horsepower was in serious doubt.”
He replaced the propellers with a pair with less pitch, which allowed the electric motors to reach their full rating of 1,100 rpm, but that only increased the speed to 9.1 knots.
“These are about the same speeds and fuel burns we get on our Maine Cat 41 sailing cat … powered by twin 29-horsepower 3YM30 Yanmar diesels with saildrives and two-bladed, folding propellers.” At the time he installed them, the 25-kW generators were the highest power available from Glacier Bay.

Vermeulen replaced the diesel-electric system with twin 160-horsepower Volvo diesels. At 9.1 knots, they together burned 2.2 gallons per hour, considerably less than the 3 gallons per hour that the Glacier Bay system burned at the same speed. With the twin Volvos maxed out at 3,900 rpm, the boat made 24.5 knots.
Also among the unconvinced is Chris White, well-known designer of ocean-going catamarans. “To date, I’ve not seen any system that makes sense for a cruising boat,” he says, but he might change his mind, “if someone can show me by building one that delivers an advantage in performance, weight, or cost.”
White sees the current bubble of interest in diesel-electric drives as a fad. In the end, he says, you’re getting the horsepower the diesel creates at the crankshaft, which is basically the same whether it’s delivered to the prop via a conventional reduction gearbox or via a generator and an electric motor. Besides, he says, diesel engines and diesel fuel are understood and available anywhere in the world you might take a sailboat. Complex, electronically controlled electric motors are not.
White’s reservations notwithstanding, it’s in the world of catamarans that we’re seeing most of the applications. At first sight, it does seem logical that replacing three diesel engines—two propulsion and one generator—on a fully equipped cruising cat would result in fuel savings. Still, if the generator is big enough to drive the boat at cruising speed (which in a cat is expected to be in the vicinity of 10 knots) and run the air conditioning at the same time, it will be overkill for the times it’s only needed to operate the boat’s services. For this reason, commercial and military diesel-electric systems employ multiple generators that can be switched on and off according to the power demand of the moment.
Corsair Marine hopes that by installing a diesel-electric system in its 50-foot catamaran, it will be able to descend the weight spiral. Where a conventional installation would involve two 75-horsepower saildrives plus a 6-kW genset, it’s fitting a pair of 28-horsepower electric motors, one 25-kW generator, and a 40-amp, 230-volt battery bank. It expects to save about 700 pounds in equipment weight, some of it through the use of high-voltage, low-current systems, which will in turn reduce the rig requirement, thus the structural weight, and so on toward an estimated overall weight savings in the thousands of pounds.
Corsair’s David Renouf estimates that the boat will cruise at 8 knots and be capable of short bursts at 10. He admits that, until the first boat is launched, his information is “based on extrapolation, not proven numbers.” He says that some clients will add a second 25-kW genset to assure longer periods at 10 knots. Currently, the project is running behind schedule, with a launch scheduled before the end of the year.
Cost and Other Benefits
At the present time, there appears to be no reason to install any proprietary electric drive of any description in the expectation of bettering the economics of a standard diesel drive. The motors and their electronic controllers are sophisticated and expensive. A battery bank sufficient to provide a useful motoring range is a big investment in weight, space, and money. When you add a generator and its peripherals, the cost and weight take another upward leap.
Only the simplest system will begin to pay itself off in terms of fuel not burnt, and then only if the boat sees a great deal of use. A diesel-electric system designed to closely dovetail with the way you use the boat may prove to be more efficient over time than a conventional diesel installation, but until enough systems have been installed and used and data from that use compiled and compared, we can’t know that.
So why even consider going electric? Cleanliness and silence of operation are two qualities that make electric propulsion an attractive proposition for a sailboat, but in order to enjoy them, we have to accept the limitations they impose.
A hybrid or a diesel-electric system enables us to have a single fossil-fuel power source for both propulsion and onboard appliances, but whatever fuel we might save as a consequence of motoring more efficiently for a couple of hours will be inconsequential if we run the generator all night to power the air conditioning.
Conclusions
As we go to press, pickings are slim for sailors looking for an electric solution to the diesel problem. Suppliers of components are few, prices are high, and the feedback on long-term reliability is nonexistent. On top of all this is the elephant in the room: the unexplored safety ramifications that accompany high-voltage DC.
However, none of this should deter the dedicated tinkerer who has funds to match his curiosity and who can live within the parameters imposed by electric propulsion.
Practical Sailor encourages our readers to explore the technology, because ultimately, it is the experimenters who bring us the equipment we eventually come to take for granted.
- Pricing Electric Power for a 30-foot Sailboat
- Special Report
- Electric Engines
- Success in the Real World is a Matter of Perspective
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
What your boat and the baltimore super container ship may have in common.
I have gotten excited about repowering my Freedom 30 with an electric motor. A fellow Freedom 30 owner completed his refit about 8 months ago and is very happy with the result, although he wishes he had gone with larger Lipo batteries. He chose a motor from electricyacht.com which sells a 10KW package (quietTorque 10) including motor, performance display, throttle and shaft coupler for $6K. Batteries and charger are extra. The motor does does feature a regen capability. Figure a $10K investment. Big bucks for sure but equivalent to a yard installed diesel repower. I would do the install myself.
I am not a cruiser but have done some lengthy passages from San Francisco to Hawaii. Ideal conditions for regen. I expec between regen and a hundred watts of solar, I could have kept the bank topped up the whole way down despite AP loads, etc. The way back? Not so much. Realistically you would need a small generator and a good stock of gas if you wanted to do much motoring, Having said that, one of the boats that sailed down there with me came home with an outboard as his aux power. I think he had ten gallons of gas.
But I am not planning ocean passages in future, I will be sailing the SF Bay and coastal cruising. When I think about eliminating the engine noise, engine maintenance, fuel tank and tank maintenance, diesel hoses, diesel smell, diesel soot, diesel leaks, r=two boxes of hoses and spares. oil changes, coolant changes, transport and disposal of all the waste to the local recycling facility, lugging fuel jugs down to the boat, storing fuel, filling fuel, buying fuel, worrying about spilling fuel. I mean it just goes on and on.
Frankly, I can’t wait. In terms of range, well, I plan to get a hefty battery bank but I also intend to become a better sailor. I’ll slow down and do more sailing. Gee wiz, what a concept. I’ll be more mindful of time and tide, I’ll take advantage of favorable currents and I’ll be ready to anchor and chill when they are not favorable.
Meanwhile, Elon and his competitors are improving battery technology rapidly. Couple of years from now maybe I double range. But, by then, I won’t be worrying about it because I will be a real sailor.
I look forward to reading an update on the state of electric sailboat propulsion 13 years later…
Most of the time we leave the dock, motor for under half a nautical mile to get out of tiny Wilmette harbor and get the sails up, turn off our much abused Yanmar 3GMF, sail around, turn on the engine, lower the sails, and travel another half a nautical mile back to the dock. Almost all at a very low RPM. But, on occasion we motor or motor sail long distances for hours on end, so a battery only system would not work. But how nice it would be if we had electric propulsion for getting in and out of the harbor.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

40-Footer Boat Tours – With Some Big Surprises! | Boat Tour

Electrical Do’s and Don’ts

Bahamas Travel Advisory: Cause for Concern?

Island Packet 370: What You Should Know | Boat Review
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

Electric yacht: What are the options for going electric?
- Will Bruton
- July 17, 2020
The options for having an electric yacht or a hybrid-electric yacht are growing in popularity; we outline the current options for those making the switch

The Arcona 380Z is a standard production yacht that has been adapted for electric propulsion. Note the increased solar panel surface area with soft panels bonded to the sails. Credit: Jukka Pakainen
A modern electric yacht can come in all shapes and sizes, from the latest high-tech speed boats with recently developed high-performance electric engines, to a traditional tender with an electric outboard on the back. Increasingly yachts are going electric too as electric engines become increasingly capable of propelling boats weighing several tonnes, and with the rigging for sails, at a reasonable speed for an acceptable length of time.
Since the invention of the marinised engine , there has never been the capacity to store enough fuel to cover significant distances in boats that are smaller than a tanker, with fuel capacity always being the limiting factor. As such the best way to cover long distances on a boat fit for a small number of passengers was, and remains, wind power.
For all the many green attributes that using the power of wind offers, there is no escaping that for most, fossil fuels still represent some part of sailing – whether that be a diesel engine to motor in light winds, onto and off a mooring , or to generate power for onboard electronic systems. Even a small tender used to go from ship-to-shore is often fitted with an outboard motor.
Recent advances in electric power, however, have started to make electric propulsion a reasonable alternative to fossil fuel power. Range will always be an issue but that has long been true of a traditional diesel engine. Improvements in lithuim-ion battery performance is, and likely will continue to, increase range every year.
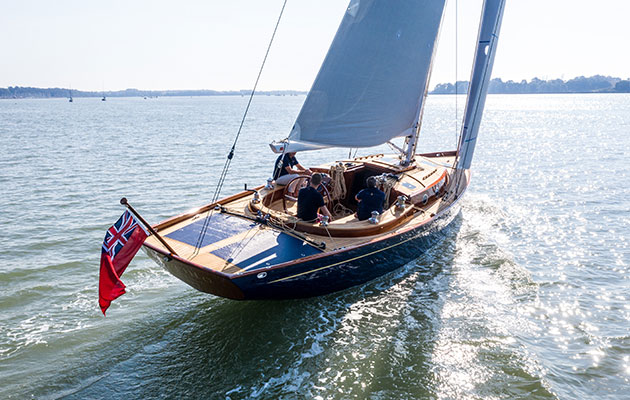

Spirit Yachts 44e – the ‘e’ stands for electric
Additionally electric power and batteries offer the bonus of being able to be recharged via solar panels , a wind turbine or hydroelectric power – via a hydrogenerator mounted on the stern of a boat sailing.
At first glance the electric yacht market could appear in its infancy, but like every revolution, the will of the people is driving forward technology that only a few years ago was seen as the stuff of fantasy.
The market has responded to demand, and battery and motor technology has come on leaps and bounds, driven in part by the rapid development of electric cars.
It may not be commonplace yet, but electric yachting is here, even available ‘off the shelf’, so is it time to get onboard?

The Spirit 111 is a bold hybrid yacht, promising 30 miles motoring under electric power alone. Credit: Ian Roman/Waterline Media
A cutting edge electric yacht
Like Formula One, it’s the cutting edge of electric yachting that trickles down into mainstream production in no time at all.
For Spirit Yachts, a builder defined by a unique blend of traditional and state-of-the-art, electric yachting has been driven by demanding clients that want their yachts to be at the cutting edge.
Spirit Yachts have now produced a number of projects aimed at the all electric luxury yacht market including the Spirit 44e electric yacht and a recent project, the Spirit 111, had all the hallmarks of a superyacht project and the team had to earn their keep delivering to brief.
Managing Director Nigel Stuart explained how it works.
‘The 111 combines several cutting-edge technologies to deliver a something that’s never really been done before. A lithium-ion powered electric drive system can be charged by hydrogenation and also two high-wattage diesel generators.
‘Each generator is 22kw, meaning they can pack a lot of power into the system in a short period of time, they don’t need to run for long to fully recharge.
‘The prop is both a means of drive and power generation, so no separate hydrogenerator is needed. She will be capable of motoring under electric alone for more than 30 miles.
‘When you take on a project that’s electric, it makes you think hard about efficiency so the air conditioning, water heaters and everything in the galley has also been carefully selected to use less power.
‘For her owner there is very little compromise and some major advantages.’
Whilst it’s a long way from the average cruising yacht, the trickle-down effect of projects like the Spirit 111 can’t be underestimated.

Calypso , a Contessa 32, was the yard’s first foray into electric-powered yachts. Credit: Jeremy Rogers
Traditional electric yacht
Jeremy Rogers’ yard in Lymington is the birthplace of the iconic Contessa designs and a veritable temple to long keeled , traditional craft.
Less well known is the yard’s interest in electric auxiliary engines, something they have been involved in for more than 10 years.
Their first project, the refit of a Contessa 32 called Calypso, was an experiment by the Rogers family to see what was possible.
‘ Calypso was a test bed in the technology’s infancy,’ explains Kit Rogers of this early electric boat.
‘Inevitably, we didn’t get it all right, but we learned a lot about the dos and don’ts of electric yachting. The end result was a hybrid. The more we did, the more interesting the project became.
‘It’s not just the obvious, silent peaceful propulsion; it’s also the things you take for granted about a cruising boat. For example, no gas, we didn’t need it because we had electric power.
The yard has also worked on an electric folkboat conversion for a foreign customer.
‘The client, first and foremost, loves to sail. He sees the electric as an auxiliary option, along with the rowing and is excited to own a boat that’s quietly different.
‘He’s looking for a more connected experience and an electric boat helps him achieve it. When you’ve been motoring in and out of marinas under chugging diesel engines for years, the electric motor is something of a revelation.

Arcona has installed solar sails on its latest 380Z electric yacht
Off-the-shelf electric yacht
Perhaps the biggest indication of the future of the electric boat is the willingness of production and semi-production builders to pin their flags to the mast and embrace it.
One of the first was Hanse, who developed a version of their 315 utilising a Torquedo electric pod system.
Providing around the same amount of power as a 10 horsepower diesel, a 4.4kWh lithium ion battery pack powers the system.
Arcona, Dufour, Elan and Delphia also have electric boat models and are each taking their own direction on entering the market.
Arcona’s 380Z (the ‘Z’ stands for ‘zero emission’) fully electric boat has solar panel covered sails, capitalising on the large surface area to top up batteries under sail.
In the multihull market, there is even more scope for solar, wind and hydrogenation due to the horizontal surface area available for solar charging.
What are the options for an electric yacht?
Pure electric.
Purely electric systems can be broadly divided into two categories, high and low voltage.
The latter is the simplest option in terms of how it works and requires less specialist knowledge to install.
Kit Rogers installed a 48v Ocean Volt system in his latest project and remarked on the experience.
‘The advantage of the low voltage system is its inherent lack of complexity. Whilst we’ve coupled it with lithium ion battery technology, it can also be wired up to conventional lead acid batteries. There are pros and cons to both. What surprises everyone is the size, it’s a tiny motor and is surrounded by lots of space where the engine would normally sit.’
High voltage systems are more advanced, and utilising lithium-ion technology, their capacity is improving year on year.
For larger yachts this is generally seen as a better option.
A partnership between BMW and Torqueedo has led to the development of the Deep Blue 315v high voltage battery.
Effectively the same unit as found in the BMWi3 electric cars now often seen on the high street, the system produces a lot of power and is being used on the Spirit 111 project as well as catamarans.
Electric hybrid
One big barrier to entry exists for most potential electric yacht buyers – range.
Even the most advanced set-ups are limited to a maximum of a few hours motoring at cruising speed.
‘The electric motors excel at two things in particular,’ explained Kit Rogers.
‘The first is as auxiliary power for getting in and out of marinas. The second is engaged at low power to very efficiently motor-sail in light airs. If you want to do more than that, at present, you need to add a way of packing in the charge into the battery quickly whilst at sea; which means a generator’ .
As with electric cars and as enthusiasm builds for the technology, a hybrid option, pairing a generator with an electric drive system, is already proving popular and is probably the most practical option for those planning to cruise any distance.
Using a large generator, charge can be quickly put into the system when needed.
Once under sail, the yacht’s propeller becomes a hydro generator, meaning that diesel power is not needed day-to-day.
Solar can also be used to add additional charging capacity.
‘When a fully integrated electric hybrid system is incorporated into a cruising yacht from the outset, its possibilities really become clear,’ explains John Arnold, UK manager at Torqeedo.
‘Sailing for days on end with no engine noise is entirely possible. There are other less obvious benefits too. Electric drives have no long rotating shaft, so can be used as pod drives as well, meaning the boat is far more manoeuvrable than even a yacht equipped with bow and stern thrusters.’

Spirit Yachts 44e
How much does it cost to convert a yacht to electric power?
The technology exists, but anyone seriously considering going electric will want to crunch the numbers.
In the case of taking out a traditional inboard diesel and replacing it with an electric system, it’s relatively easy to work this out.
However, unless you include an auxiliary generator, you will be limited to battery range alone.
For this reason, we’ve done a like for like comparison for a 35ft yacht engine refit, including the cost of a generator to make the system a practical hybrid.
Unsurprisingly, at the moment, there’s a big difference in cost, but at between three to six times the cost, it is gradually coming into the realms of possibility, and prices should continue to drop as technology develops and evolves.
Ocean Volt SD10 Motor system (including batteries, charger and 6kw generator): £30,825.16
Beta Marine Beta 20hp Marine Diesel: £4,100
If you enjoyed reading this….
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
Taking a small dinghy with an electric outboard motor on your sailboat can provide a means of quick and reliable transportation.
While electric outboard motors can have difficulty moving full-size sailboats around, they are more than powerful enough to get a small dinghy going fast. While trolling motors are only good for slow speeds, an electric outboard motor can get a boat going fast as long as the boat is small enough.
Electric outboard motors can be a better choice than gas motors. As well as being powerful enough, they are lighter, more compact, and more reliable. You can count on motors from ePropulsion and Torquedo to last for a while.
If your sailboat is large enough, you should always take a dinghy with you. As well as being a potential lifesaver in an emergency, a dinghy is useful any time you need to drop anchor and make it to shore. A dinghy with a motor is cheap compared to a sailboat, so a sailor should always have a dinghy with them.
Table of contents
How fast can you go with an electric outboard motor?
If you are running a powerful motor on a small boat at full speed, you might be able to do 15 knots or better. Usually, you won't go that fast when you are in a dinghy and running an electric motor.
If you want to make it as far as possible, you will run the motor on much less than full power. Fifteen knots is what you might get if you are running a powerful 6000 watt motor on a small boat. Normal speeds are slower - you might move at less than five knots if you want to travel as many miles as possible before the battery dies.
How far can you make it in a dinghy with an electric motor?
Something like 20 miles is a rough, ballpark figure, although with some motors, you might be able to make it 70 miles at a slow speed. Don't take any risks when it comes to whether or not your battery will run out in the middle of the sea. Be on the safe side.
You will do much better if you run your motor at a slower speed. If you run your motor as fast as possible, you might make it only a fraction of the maximum distance before your battery runs out. Distances high above 20 miles are sometimes possible if you go slow, although it depends on the boat and the motor.
How is power measured for electric motors?
The power of an electric motor is usually measured in watts, not horsepower. Sometimes the power of an electric motor is given in horsepower, but usually in watts.
Boat motors vary greatly in how powerful they are. A motor that is only 10hp, 5hp, or 3hp is common even though outboard motors can be 20hp or more.
Usually, you can go more like 5 knots than 15 knots with an electric or gas motor. To go 15 knots, you might need something like a 100hp motor - this is too expensive and not what people are likely to put on a small dinghy.
What are the advantages of gas motors?
In the long run, electric motors can save you money because it costs less to keep them running. After the first few years, electric motors are the cheaper choice.
The maintenance cost per hour of use is much higher for petrol motors. After only a few hundred hours of use, a petrol motor's cost will exceed the cost of an electric motor.
One disadvantage of electric motors is that they run on batteries, which take time to charge. You will have to charge your batteries overnight, compared to quickly refueling a gas engine.
One way out of this problem is to use a solar charger. With a solar charger, you can charge your batteries anywhere as long as the sun is out.
Electric outboard motor advantages
As well as being effectively cheaper than gas motors, electric motors are much quieter. Compared to a gas engine, an electric motor is almost silent. You will hear almost nothing and will not scare fish away.
Electric motors are also much cleaner to deal with than gas motors. If you use an electric motor, you won't have to deal with engine grease. You can get engine grease on your boat and not just on your hands and clothes with a gas motor.
Gas motors also have exhaust fumes, so an electric motor is better for your health. Electric motors are also simpler than gas motors, so you won't have to repair them as often.
Is it possible to buy high powered electric outboard motors?
Yes, you can find an electric motor with a power equivalent to an 80 horsepower gas engine. Not many people put such powerful motors on their dinghies, though. Dinghies mostly have weaker motors, often less than five horsepower.
Is it easy to break a propeller if you hit something?
You can definitely do expensive damage to a propeller if it hits a rock. A small bump won't damage it - most propellers are made well and are reasonably durable. If your motor does not come with a propeller guard, you should buy one separately.
Are 3hp motors good enough for many boats, or are they too weak for most purposes?
If you are using a small dinghy that weighs less than two tons, and do not intend to go very fast, a 3hp motor is good enough. You can go much faster than trolling speed with only a 3hp motor if your craft is small enough. For a small sailboat that weighs more like six tons than one or two tons, a 10hp motor may be enough.
Best electric outboard motors
Make sure you buy a high-quality motor because these are not tiny investments. You can lose more than a little money if you buy a shoddy product that does not have a good warranty. Put a bit of time into verifying the reliability of whatever you purchase.
1) ePropulsion Spirit 1.0 Plus
If you are fine with a fairly weak 3HP motor, the Spirit 1.0 Plus is a great product with few disadvantages. The Spirit 1.0 Plus from ePropulsion is built to last, uses power efficiently, and doesn't cost a fortune.
At full speed, the Spirit will only last for about 90 minutes on a single battery. With a 12 foot boat, you can go about 9 km/h - not bad for a relatively low power engine. You also do not need to run the boat on full power to approach your boat's maximum speed.
If you run the Spirit on 1/4 power, you can keep it going for 6 or 8 hours. Batteries are fairly heavy, but you can keep the motor running for a long time if you bring extra batteries. The motor can save you in a dangerous situation and is great for non-emergency uses as well.
Another advantage of the Spirit is that the battery floats, so it won't sink if you drop it in the water. The Spirit is also light, even with the powerful battery it comes with. The digital display that shows how much battery power you have left is accurate.
Like other electric boat motors, the Spirit is more environmentally friendly and healthier than a gas engine. Gas engines have fuel leakage and fumes; an electric motor avoids these problems. The Spirit even comes with a 180W solar panel to charge it, although this is not the only or the fastest way of charging the battery.
The motor even has a remote control, so you can steer it and adjust the speed with a console. If the Spirit has a disadvantage, it is that the range on a single battery is unimpressive. You can make it a little more than 20 miles, but many other electric motors let you go farther on a single battery.
2) ePropulsion Navy 6.0
If you are looking for something longer lasting than and more powerful than the Spirit 1.0 Plus, ePropulsion also offers the more powerful Navy 6.0 . The Navy 6.0 is equivalent to a 10Hp engine, so it won't struggle to move a relatively big boat.
The range on the Navy 6.0 is impressive. The battery is powerful enough that you can travel 40 miles before having to recharge. If you want to bring more than one battery, the Navy 6.0 can be compatible with other companies' batteries.
The Navy 6.0 also has a propeller that will stop immediately if it hits anything. This can save your engine from damage if the propeller hits a rock or anything else. There is also an emergency stop kill switch to
The Navy 6.0 works just as well in freshwater as in saltwater. It is advantageous to have an electric motor on a lake because there are laws against gas motors in some lakes.
3) Torquedo Travel 1003
One thing that makes the Torquedo Travel stand out is its onboard GPS computer, which can calculate how far you can travel before the battery runs out. The computer will continuously update how far you can travel based on how much battery power is left, how fast you are going, and how much power you are using.
While the Torquedo Travel can run for 10 or 11 hours on a full charge, it can only move a small boat at 1.5 or 2 knots for that long. If you run the engine at half throttle, it will last for 3.5 hours at 3 knots. If you travel faster, the battery runs out very fast - it will only last half an hour at 5 knots.
If you want a solar charger for the motor, you can buy it separately from the company. It is costly, but the solar panels do work well and give you a way to charge the battery at sea.
The Torquedo Travel is also a small and light motor that does not take up much room. Without the battery, it weighs only 8.9 kilograms. You can easily remove and store the engine.
Another useful feature is the kill switch that allows you to stop the motor immediately in an emergency. You can also use the engine/battery as a power source for electronics through a USB.
The Torquedo is a reliable engine backed by a two-year warranty. It is equivalent only to a 3HP engine, so it is not powerful enough for everyone.
4) Torquedo Cruise 4.0 T
The Torquedo Cruise is the best choice if you want a more powerful alternative to the Torquedo Travel. The Torquedo Cruise electric outboard motor is equivalent to an 8HP gas engine. If you need a motor for a boat that weighs three or four tons instead of one or two tons, get the Cruise instead of the Travel.
The Torquedo Cruise will stay completely waterproof for a long time and not develop small leaks quickly. Small leaks can ruin some of the cheaper engines on the market. The Torquedo Cruise is also very corrosion resistant, so you can use it in saltwater for a long time without damage.
The Torquedo Cruise has the same onboard GPS computer, emergency off switch, and two-year warranty as the Torquedo Travel does. The only disadvantage compared to the Torquedo Travel is the higher price. Not everyone needs a more powerful motor, but it is an excellent engine if you do.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Sailboat Upgrades
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

Best Trolling Motors For Pontoon Boats
Jacob Collier
February 1, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat

9 Best Trailerable Sailboats
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

- Subscribe Now
- Digital Editions

Best electric outboard motors: 11 top options for zero-emissions propulsion
- Electric boats
- Top stories
Electric outboard motors seem to be springing up all over the place right now. We round up 11 of the best electric outboards on the market…
Electric outboard motors are nothing new, after all the humble electric trolling motor has been around for decades, but in the past couple of years a new breed of more powerful units has emerged.
Capable of powering everything from a tender to a 50-knot sportsboat, this new generation of electric outboard motors will surely play a big role in the growing trend towards all- electric boats .
We’ve rounded up 11 of the best options available on the market right now to help you track down the right one for cutting down your boat’s carbon footprint.
Compact electric outboard motors for your tender

Torqeedo 603 Travel
Weight: 15.5kg Power: 600W / 0.8hp Battery: 500Wh Range: 11nm Price: £1,499
Torqeedo has been making electric outboard motors for quite a while now, and their latest offering slots into the travel range of electric outboards between the 503 (1.5hp) and the 1103C (3hp).
All the usual Torqeedo refinements are present and correct. IP67 rated as totally waterproof, the 603 Travel has a magnetic kill cord and an onboard computer providing instant readouts of operating range at current RPM and battery-charge status displayed on the tiller arm.
You can link it to an Apple or Android app and gain even more information including a map-based range indicator.
Read more about the Torqeedo 603 Travel

Mercury Avator 7.5e
Weight: 27.1kg Power: 750W / 1hp Battery: 1kWh Range: 34nm Price: $1,500
Announced in early 2022 and launched less than a year later, the Mercury Avator 7.5e is the first electric unit from the world’s biggest builder of outboard engines .
The whole top plate hinges up to reveal the battery, which can be quickly removed from your electric boat or replaced for convenient charging.
It’s by no means the lightest electric outboard motor on the market, but its claimed range at 25% throttle is very impressive – we look forward to putting one to the test.
Not resting on its laurels, Mercury launched the Avator 20e and 35e this summer as well. These units are no bigger than the 7.5e, but need wiring in to an on-board battery bank.
Read more about the Mercury Avator 7.5e
Read more about the Mercury Avator 20e and 35e

Weight: 14.5kg (inc. bracket) Power: 1kW / 3hp Battery: 1,085 Wh Range: 14nm Price: £2,185
The idea behind the Remigo One electric outboard makes perfect sense; rather than mounting the battery on top of the shaft, like the engine on an old-school petrol outboard, the Slovenian company has integrated it into the shaft and shaped it like a rudder to minimise drag and maximise steering effect.
It is backed by a 2-year warranty and has a magnetic key/kill cord. There are some other neat ideas too. The rudder casing is waterproof to IP67 above the water and IP69 below the water so it will survive a dunking, and it’s held in place by a clamp mechanism that allows you to adjust the shaft length to suit your boat with the aid of an allen key.
The transom bracket is separate to the motor so you can leave the bracket attached to the boat and simply slot the motor on and off. The tiller also folds and locks parallel to the blade so you can use it as a perfectly balanced carry handle.
Watch our test drive video of the Remigo One electric outboard

The Kicker is exceptionally light and surprisingly powerful
Thrustme Kicker
Weight: 4.4kg Power: 1kW / 3hp Battery: 259kWh Range: 5nm Price: £1,250
If it’s light weight and value that you prioritise over cruising range, then this Norwegian option is hard to beat.
Launched in 2021, the Kicker boasts enough range and grunt to get one person from ship to shore and back again in calm conditions, as editor Hugo proved in a week-long test.
The only downside is that the battery isn’t removable, which can make charging a little more difficult.
Read more about the Thrustme Kicker

Weight: 15kg Power: 1kW / 3hp Battery: 740Wh Range: Up to 1hr Price: €2,850
A brand new option from France, the TEMO-1000 doesn’t look anything like a traditional outboard motor.
The design doesn’t have any rectangular box on top, just a rudder-shaped shaft with an electric motor at the bottom and a long slim battery that simply slides down into it, connecting automatically to your electric boat without having to plug wires into it.
The tiller arm does the same, meaning it disappears completely when not in use and yet it is never detached and therefore never mislaid.
Read more about the TEMO-1000

Haswing Ultima 3
Weight: 16kg Power: 1kW / 3hp Battery: 1.03kWh Range: 18nm Price: £1,570
A top-of-the-range option from trolling motor stalwarts Haswing, the Ultimate 3 is suitable for boats up to 7m long.
The brushless DC motor produces 3hp (claimed to be equivalent to a 4hp petrol outboard motor), and it’s available in short and long shaft versions as well as the standard length.
Not only is the detachable battery unusually light at 5kg (lightest in class, according to the manufacturer), it also connects to the engine in a single simple operation without the need for connecting cables or other fiddly parts – no bad thing when you’re bobbing about in a tender!
Read more about the Haswing Ultima 3

ePropulsion Spirit 1.0 Plus
Weight: 19.3kg Power: 1kW / 3hp Battery: 1,276Wh Range: 22nm Price: £1,600
The original Spirit 1.0 has actually been in production for six years with over 10,000 units built. Featuring a 1,000W brushless motor, this electric outboard motor is claimed to be equivalent to a 3hp petrol engine, ideal for tender duties or small to medium sized dinghies.
This Plus version, launched in 2020, is the same weight, size and power – the big gain is where it’s needed most, run time. It has been achieved by upgrading the battery from 1,018Wh to 1,276Wh.
At the same time, the power cord has been upgraded for durability and reliability, and the voltage has been changed from 40.7V to 48V, making it compatible with an external 48V battery. The battery will even float if dropped overboard!
Read more about the ePropulsion Spirit 1.0 Plus
Most powerful electric outboard motors for day boats

Yamaha Harmo
Weight: 55kg Power: 3.7kW / 9.9hp Battery: Sold separately Range: Depends on battery Price: £TBC
Announced in 2022 and tested on a 12m Venmar water taxi, the Yamaha Harmo electric boat drivetrain may be a rather modestly powered 3.7kW motor, equivalent to a 9.9hp petrol engine, but it is being seen as a major statement of intent from the Japanese brand synonymous with big, powerful four-stroke outboards.
Intriguingly, the Harmo is neither an outboard engine nor a sterndrive but a new propulsion package that borrows ideas from both camps.
It is mounted on the transom just above the waterline much like a sterndrive leg, but in keeping with the outboard engine ethos it’s an entirely self-contained unit that includes the motor and steering mechanism.
Read more about the Yamaha Harmo electric rim drive

RAD Propulsion RAD40
Weight: 100kg Power: 40kW / 55hp Battery: 20-60kWh Range: 100nm Price: £28,000 (ex. battery)
The RAD40 drive from British start-up RAD Propulsion appears to be far more than just a conventional outboard leg with an electric motor bolted on top.
Every single element of it has been designed from the ground up to maximise the benefits of electric power. The result is a brand new drive system that is not only much cleaner, quieter and more efficient than a petrol outboard engine but also smaller, lighter, cheaper to maintain and even more manoeuvrable.
In its current 40kW guise (equivalent to around 55hp) it’s powerful enough to propel everything from a 25-knot planing RIB to a 10-knot displacement craft but with a larger 160hp RAD120 as well as a portable tiller steered RAD2 already in development, it’s clear that RAD Propulsion has its eyes set on a much wider market.
Read more about the RAD Propulsion RAD40 electric outboard

E-Motion 180E
Weight: 580kg Power: 110kW / 180hp Battery: 70kWh Range: 70nm Price: $78,990
Launched in 2021 by Canadian firm Vision Marine Technologies, the E-Motion 180E looks like a genuine alternative to the 150-200hp petrol outboard motors that power the vast majority of 18-25ft sportsboats and RIBs.
The outboard engine itself weighs around 180kg, compared to 216kg for a 200hp V6 Mercury Verado, but that relatively modest saving pales into comparison next to the 400kg weight of the 70kWh battery pack.
Admittedly, a fair chunk of that will be offset by the lack of fuel tank and starter batteries, but unlike a petrol boat, the battery pack’s weight stays constant whether full or close to empty.
Read more about the E-Motion 180E

The Evoy Storm looks, feels and goes like a well-matched petrol outboard engine
Weight: 350kg Power: 222kW / 300hp Battery: 2x 63kWh Range: 25nm Price: €144,700
Although currently still in development, the Evoy Storm is a working prototype that has already been fitted to a number of partner brands’ boats, including an Iguana amphibious craft and an Axopar 25 that we tested at last year’s Cannes Yachting Festival .
Despite a 450kg weight penalty over a fully fuelled petrol boat, and five passengers, we still recorded a top speed of over 50 knots – vastly quicker than any other electric boat we’ve tested and not far off the world speed record for a production electric boat of 57.7 knots (held by a Goldfish X9 powered by a 400hp Evoy inboard).
The anticipated price for this electric Axopar 25 is €185,000 (ex tax), which looks pretty good value given that the price of the motor alone is €74,900 plus another €69,800 for the batteries. Whether Axopar can maintain, or even reduce, that price once the Evoy Storm enters production in 2024 remains to be seen.
Read more about the Evoy Storm
Tip of the iceberg
If this seems like a lot of choice, there are even more options coming down the pipeline in 2024. MBY understands that several major outboard manufacturers are planning on entering the electric outboard market, so watch this space…
If you enjoyed this…
Be first to all the latest boats, gadgets, cruising ideas, buying advice and readers’ adventures with a subscription to Motor Boat & Yachting . Available in both print and digital formats, our monthly magazine will be sent directly to your home or device at a substantial discount to the usual cover price. See our latest offers and save at least 30% off the cover price.
New Cauldwell outboard motor: Petrol performance & diesel reliability?
‘we had no real plan for how to get back onto our boat’ – lessons from a man overboard, the new ‘transformer’ megayacht concept that expands at anchor, latest videos, fairline targa tour: sensational new british sportscruiser, navan s30 & c30 tour: exceptional new axopar rival, galeon 440 fly sea trial: you won’t believe how much they’ve packed in, parker sorrento yacht tour: 50-knot cruiser with a killer aft cabin.
Posted 2024-03-28 21:03
Contact Information:
1984 14 ft SmokerCraft Johnson 9.9 & electric motors - $1,700

QR Code Link to This Post
post id: 7731973135
posted: 2024-03-28 21:03
♥ best of [ ? ]
refresh the page.
1984 14 ft SmokerCraft Johnson 9.9 & electric motors - boats - by...
1984 14 ft SmokerCraft SMK Aluminum V-Hull boat, Johnson 9.9 with both electric and pull start, Diehard 25lb thrust electric motor and 2nd electric troll motor, Hummingbird fish finder 565 with case...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
With the Spirit 1.0 Evo electric sailboat motor, you can go 5.5 mph (8.8 kph) at top speed on the 21 ft RS21 sailing boat, or troll for 20 hours continuously at 2.2 mph (3.5 kph) according to our test. This electric sailboat motor with regeneration allows you to recover energy from the prop while under sail.
Cheoy Lee Clipper on Lake Superior. Jan 2, 2023. Sailing with an Electric Motor In 2021 we installed the QuietTorque™ 10.0 Electric Motor by Electric Yacht on our 1972 Cheoy Lee Clipper Sailboat, which we use for day charters from May through October on Lake Superior. We have been extremely satisfied with the...
Electric motors achieve instant torque with Electromotive Force while internal combustion engines need to build RPMs gradually by increasing piston firing frequency. Hydro Generation At sailing speeds over 6 knots Oceanvolt systems are able to generate significant power for recharging the battery bank by activating at the touch of a button.
Electric motors possess comparable power to diesel motors, while offering additional features that make them highly suitable for marine propulsion. They exhibit greater efficiency, typically 2 to 3 times more efficient than diesel motors, enabling an electric motor with one-third the size and weight to match the power output of a diesel motor.
Whether quietly maneuvering through a harbor or motor-sailing on low-wind days to create your own apparent wind, our electric solutions will enhance and extend your sailing enjoyment. Oceanvolt offers Hybrid or Electric systems as a power & propulsion option in partnership with many leading monohull boat builders - adding new partners continuously.
The 5 models range in listed power from 12/19kW to 35/57kW • Voltage: There 48 and 96 Voltage availble for all models. • Current: 50, 92, 120, 150, 200 • HP: At 1800/3600 RPM they range from 25/39 to 47/76. Motor Type: PMAC (Permanent Magnet AC), PMS (Permanent Magnet Synchronous) • Air cooled.
Based in Quebec, Canada, Vision Marine Technologies has been in the boating industry for 25 years and produced some very innovative electric boats. In 2021, they launched E-Motion 180E, one of the most powerful electric outboards on the market. Frauscher 740 Mirage Air with Torqeedo Deep Blue 100i 2400.
13. 48. L: 681 W: 290 H: 271 (motor + controller in frame) 76 (motor + controller in frame) 1450. Asynchronous - Air. With information about 150 electric inboard boat motors from 17 manufacturers, welcome to what we believe is the most complete guide to electric inboard.
An Electric Sailboat Motor's Range Is Greater Than You Think. While electric sailboat motors have a limited range compared to gas or diesel motors, this is less of an issue than you might think. Most sailors use a motor primarily to get in and out of a harbor, a task easily accomplished by an electric motor.
Absolutely everything you need to know about electric motors on sailboats is right here, in this episode where we have an in-depth discussion with Dan and Ki...
How powerful are electric motors on sailboats? Well, Oceanvolt offers two different propulsion systems. The Finland-based company has developed a 6, 8, 10 and 15kW SD saildrive, as well as a special 10 and 15kW ServoProp with even better hydrogeneration, thanks to its patented and DAME-awarded software-controlled propeller blades, which change ...
This was the first electric propulsion system—not hybrid but all-electric—I'd ever seen on a cruising sailboat. Electric propulsion isn't new. Since 1879, electric motors have propelled boats; a fleet of some four-dozen electric launches transported visitors around the 1893 Colombian Exposition in Chicago.
August 24, 2021 Jeff Butler 2305 Views 0 Comments Arcona, Oceanvolt, Sweden, The Gussies. Sweden's Arcona Yachts has announced that their new Arcona 415 has Oceanvolt electric propulsion as a standard feature, a first for series-produced sailing yachts. Having electric as standard on a boat like the 415 marks a big change.
35 feet 7.9 knots (9.1mph) With an electric outboard motor, or any kind of auxiliary motor, boat speed depends on the hull type, waterline length, and total displacement weight (including passengers, food, and baggage), as well as the motor thrust. Speed factors also include the waves, current, and wind, relative to your heading.
288. Vermeulen replaced the diesel-electric system with twin 160-horsepower Volvo diesels. At 9.1 knots, they together burned 2.2 gallons per hour, considerably less than the 3 gallons per hour that the Glacier Bay system burned at the same speed. With the twin Volvos maxed out at 3,900 rpm, the boat made 24.5 knots.
Supporting Electric Marine Conversions Since 2007. When we're not at the race track you may find us out on the water! Convert your sailboat to a clean, quiet electric drive! Eliminate noxious diesel fumes and the cost of filling up at the pump. Enjoy your sailboat to the fullest, with a quiet drive and truly fresh air.
Perfectly matched system integration rather than an assortment of components. The most powerful electric saildrives come from Torqeedo series production. The Deep Blue 25 SD propels sail yachts of up to 40 feet in length to speeds of up to almost ten knots (18 km/h), or smaller boats even faster when planing. This makes cruising with large sail ...
The Cruise FP models are installed in a fixed position (therefore the abbreviation FP - fixed pod) as generally desired for sailboats and also for some motorboats. The eletric pod motors for sailboats are available with folding propellers. Other boats would choose our standard, highly efficient propellers. Choose from performance classes from ...
Categories: 48 Volt Systems, Electric Motors. $ 4,995.00 $ 4,495.00. The QuietTorque™ 10.0 Sport is a cost effective 10kW electric propulsion system designed for the day sailing and coastal cruising sailboats up to 35' (LOA) and 12,000 lbs displacement. Typically programmed and sized to push boat at cruising or harbor speed.
The Arcona 380Z is a standard production yacht that has been adapted for electric propulsion. Note the increased solar panel surface area with soft panels bonded to the sails. Credit: Jukka Pakainen. A modern electric yacht can come in all shapes and sizes, from the latest high-tech speed boats with recently developed high-performance electric ...
I have installed an electric inboard in my Catalina 30 sailboat. This is a handy installation guide to help you with your own install, or to help satisfy you...
Like other electric boat motors, the Spirit is more environmentally friendly and healthier than a gas engine. Gas engines have fuel leakage and fumes; an electric motor avoids these problems. The Spirit even comes with a 180W solar panel to charge it, although this is not the only or the fastest way of charging the battery.
Specs. Weight: 15.5kg. Power: 600W / 0.8hp. Battery: 500Wh. Range: 11nm. Price: £1,499. Torqeedo has been making electric outboard motors for quite a while now, and their latest offering slots into the travel range of electric outboards between the 503 (1.5hp) and the 1103C (3hp). All the usual Torqeedo refinements are present and correct.
John Peeters, holder of over 60 race-boat records, at the helm. Woody Marshall. Big Bird will be familiar to racing fans as the vessel, built by legend Ed Karelsen, which won many races powered by gas engines.Big Bird was designed for an outboard up to 1,100 cc. Now, the canopied race boat features a permanent magnet AC motor weighing just 65 pounds.
Halevai's Model2050 electric boat will commence production this summer at its new White Bluff, Tennessee facility. 35 initial builds are slated for 2024, equating to one or two boats per week.
1984 14 ft SmokerCraft SMK Aluminum V-Hull boat, Johnson 9.9 with both electric and pull start, Diehard 25lb thrust electric motor and 2nd electric troll motor, Hummingbird fish finder 565 with case and box. Floor in boat with multiple rotating seats , multi anchors, ropes, lights for boat, paddles, life vests.