

Suggestions

George Town Yacht Owner Among Elite Billionaire Seafarers: A 2023 Deep Dive

Key takeaways:
- The ownership of luxury yachts continues to be a symbol of wealth among global billionaires.
- George Town yacht owner holds a significant position among these affluent individuals.
- Yachts, apart from being symbols of luxury, are often equipped with cutting-edge technology and bespoke features reflecting the owners’ personal tastes.
Understanding the Billionaire Yacht Landscape
The world of yacht ownership is a pinnacle of luxury. Often reserved for the ultra-wealthy, owning a yacht is a testament to an individual’s financial success and taste for the finer things in life. From the George Town yacht owner to globally recognized billionaires, the allure of owning a private yacht remains unwavering.
The Influence of Wealth and Taste
While vast wealth makes the purchase of such grand vessels possible, the individual taste of the owners is reflected in the design, features, and functionalities of these yachts. From classical to contemporary designs, luxurious amenities, state-of-the-art technology, and personalized details, these floating residences exhibit the distinct persona of their owners.
The George Town Yacht Owner’s Mark in Luxury Yachting
Among these billionaire yacht owners, the George Town yacht owner’s influence cannot be overlooked. Known for their exquisite taste and an eye for detail, they stand as a significant player in the realm of luxury yachting. The level of comfort, sophistication, and technology in their yacht sets a benchmark for luxury sea travel.
The Most Luxurious Yachts and Their Owners
The list of luxury yachts owned by billionaires is impressive. These range from the Musashi owned by Larry Elisson, the Senses owned by Larry Page, the Dragonfly owned by Sergey Brin, to the Symphony owned by Bernard Arnault, among others. Each yacht, uniquely designed and equipped with incredible features, represents the peak of luxury and technology at sea.
The Irresistible Appeal of the Ocean
Owning a yacht goes beyond flaunting wealth; it represents a love for the ocean and the freedom it offers. The ability to explore the world’s waters in absolute luxury is an irresistible prospect for these billionaires. As the global billionaire list expands, so too does the list of opulent yachts.
The Ever-evolving World of Luxury Yachting
The world of luxury yachting continues to evolve, with new yacht designs, sustainable technologies, and bespoke amenities becoming increasingly common. The trend is moving towards eco-friendly designs without compromising on luxury, a trend that the George Town yacht owner and other influential figures are likely to embrace in the future.
Whether it’s the George Town yacht owner or other billionaires, yacht ownership continues to be a defining aspect of their wealth and influence. As they navigate through the high seas in their luxury vessels, they set new standards for what it means to travel in style and luxury. As we move forward, we can expect to see an increasing emphasis on sustainable practices in the creation of these oceanic wonders, merging ultimate luxury with responsibility towards our planet.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
By using this form you agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. *
Recent Comments

About Levi Keswick

Top Interior Design Trends for the Year 2024

The Most Popular Specialty Rooms for Custom Homes

Factors That Can Shorten the Lifespan of Your Luxury Car

What You Need To Know About In-Law Suites

Dionne Rodrigo
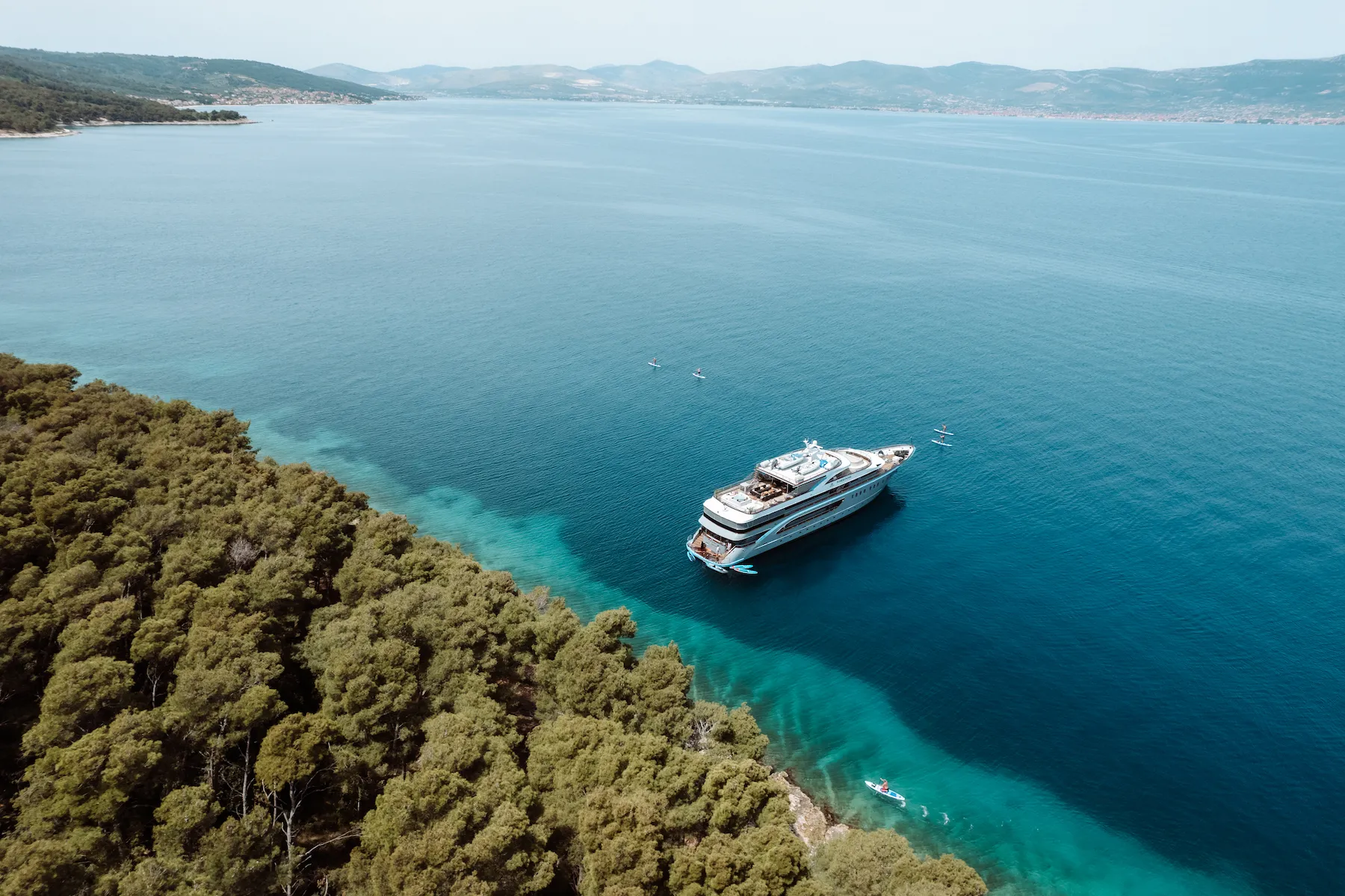

Navigating the Exclusive World of Superyacht Freedom
- Yacht charter
Superyacht Freedom is a rare gem on the high seas and one of only three of its kind in the world. Capable of hosting up to 24 guests across 11 exquisite staterooms, Freedom offers an array of lavish amenities over its four expansive decks, including two master cabins, a cinema, a spa, and a fully-equipped gym.
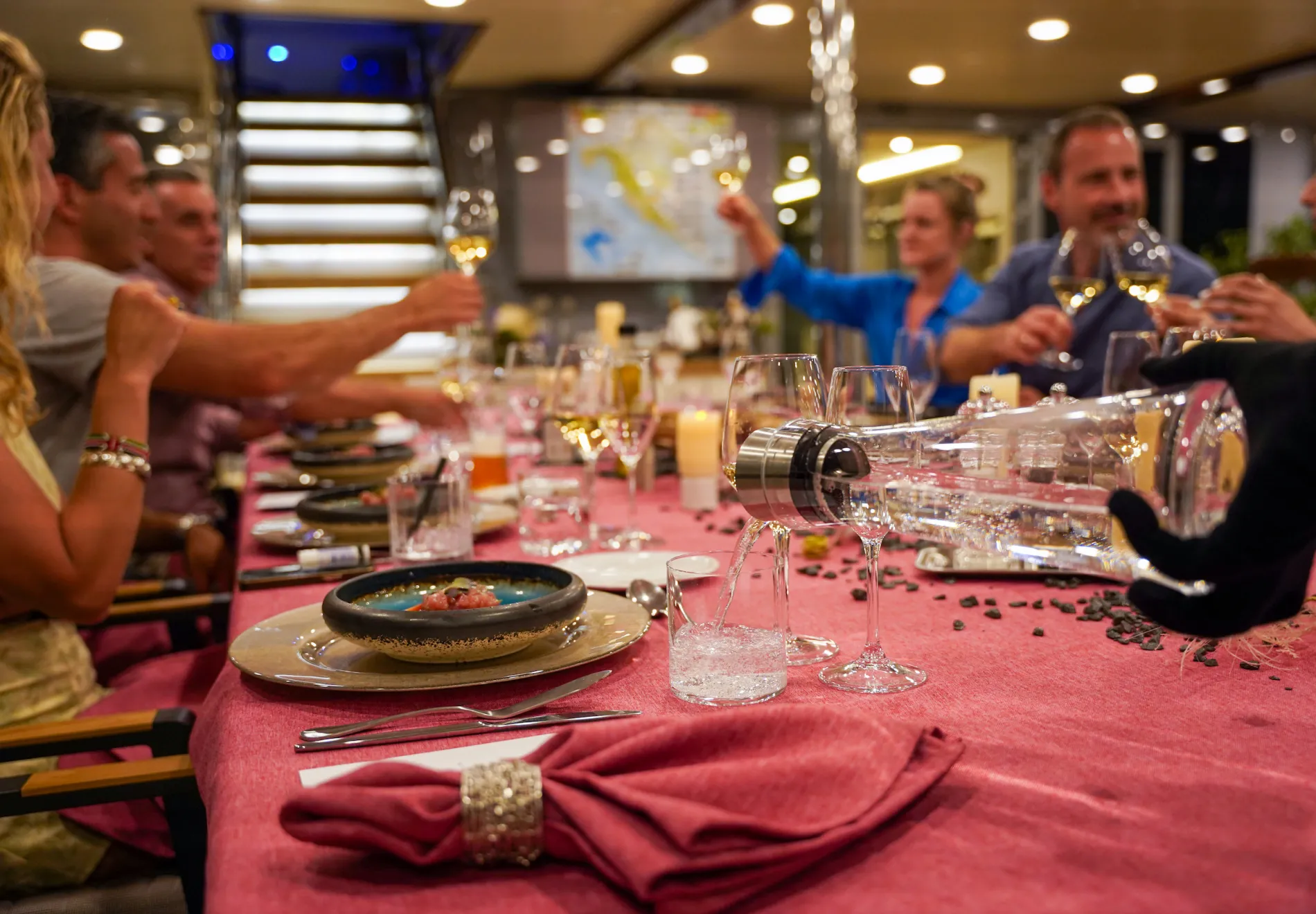
Whether lounging by the sundeck pool, indulging in gourmet organic cuisine, or enjoying the thrill of various water toys, every detail aboard Freedom is meticulously designed for the ultimate in comfort, entertainment, and elegance. This vessel is not just a statement of wealth but a promise of an extraordinary seafaring adventure, enveloped in the highest standards of luxury.

We’re excited to share highlights from some of the articles, which spotlight Freedom's distinctive amenities, the enchanting beauty of Croatia , and the memorable adventures that guests can enjoy while aboard this magnificent superyacht.
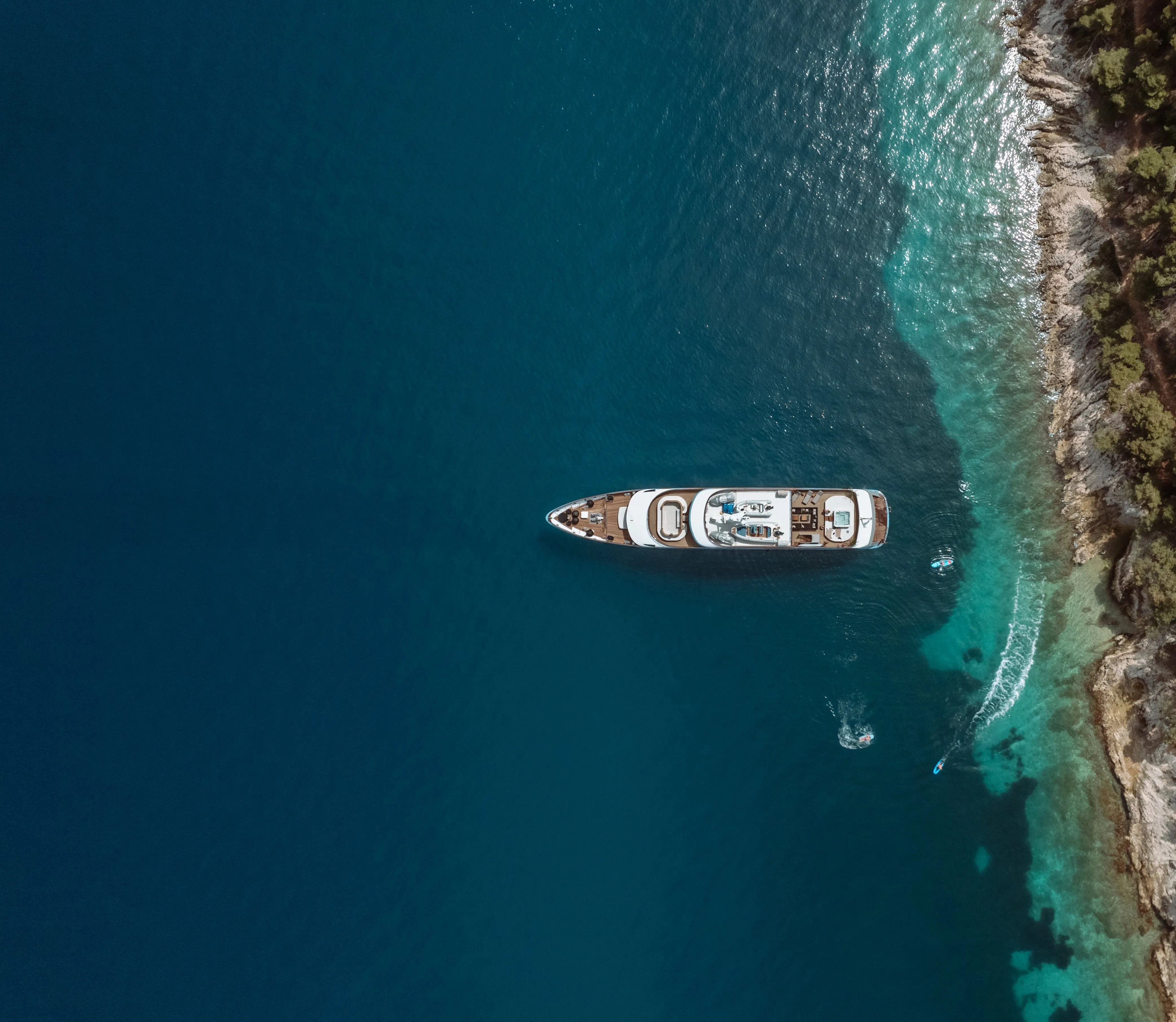

Set Sail Aboard Superyacht Freedom
You, too, can indulge in the luxury and unparalleled experience that Freedom or other yachts offer. Simply send us an enquiry, and we will ensure that your yachting holiday is as extraordinary as it was for them.
What the Media Say About Superyacht Freedom

»As yacht designers continue to push the envelope on the over-the-top superyachts that are being snatched up by the uber-rich, several ships in the Adriatic are taking a different tack by bumping up the luxury offerings on older ships at a lower price point.«

Boat International
»So, if you want to get a taster of what a fully-fledged superyacht charter in Croatia is all about, Freedom is what you’re looking for. She captures the very best parts without scrimping on the detail.«

»The beauty of a yacht charter is the freedom to write your own rule book in a fully private setting. So you can have breakfast, lunch and dinner served on board by the all-smiling, affable crew — off-piste dietary requests and favourite tipples unblinkingly catered for.«
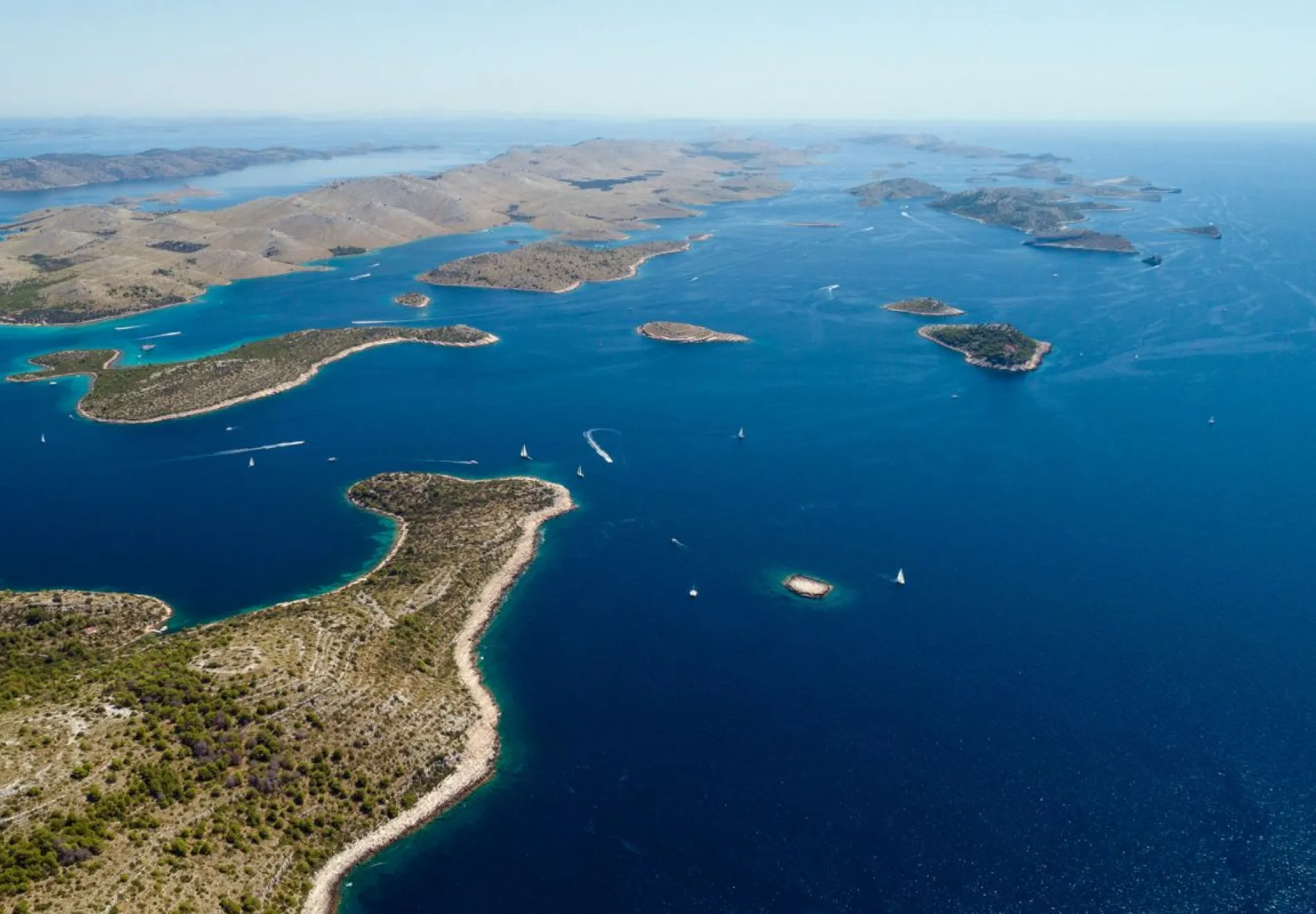

»From a practical perspective, the archipelago is built for sailing. Many of its islands are close to the shore, meaning there’s plenty to explore in a short period of time. Also working in a yacht’s favour is the country’s maritime law, which entitles captains to drop anchor anywhere they wish – and with deep waters so close to shore, this could be mere feet from the beach.«
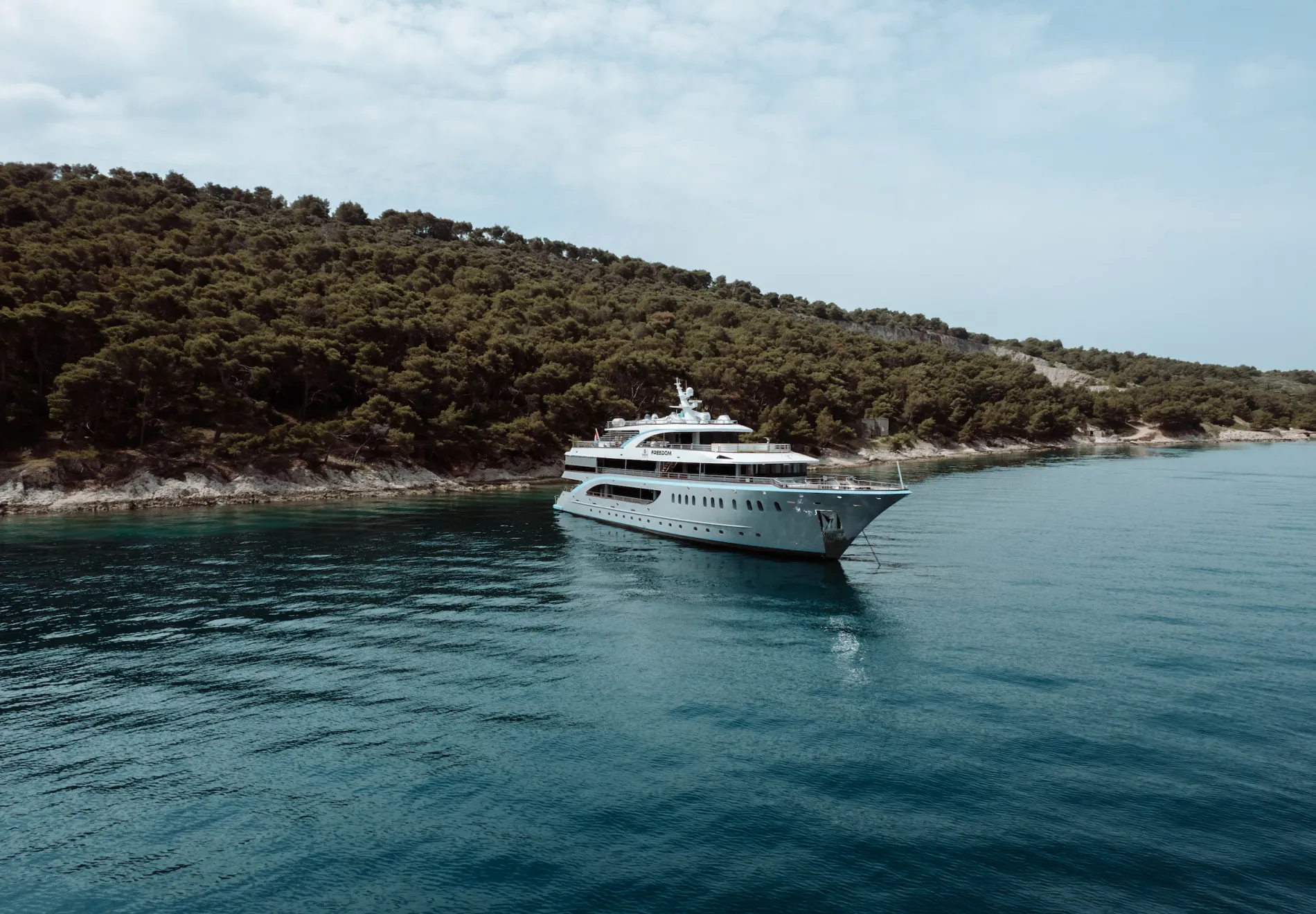

The Superyacht Life
»EU law only permits yachts like Freedom to cruise Croatian waters (with neighbouring Montenegro as the one exception). Freedom costs virtually half the price of a comparable 50 metre yacht and delivers a slice of superyacht life to a far wider audience of potential charterers.«
Jared Watney, director of Ocean Air Media, showcases the yachts around the world, including Superyacht Freedom. Here is what he had to say about this unique luxury vessel:

»Above all else it has to be the personalisation of your holiday. Before boarding you’ll be asked to fill in a preference sheet and work with one of Goolets’ concierges. You’ll have one assigned to you who will listen to everything you want and they'll deliver...«
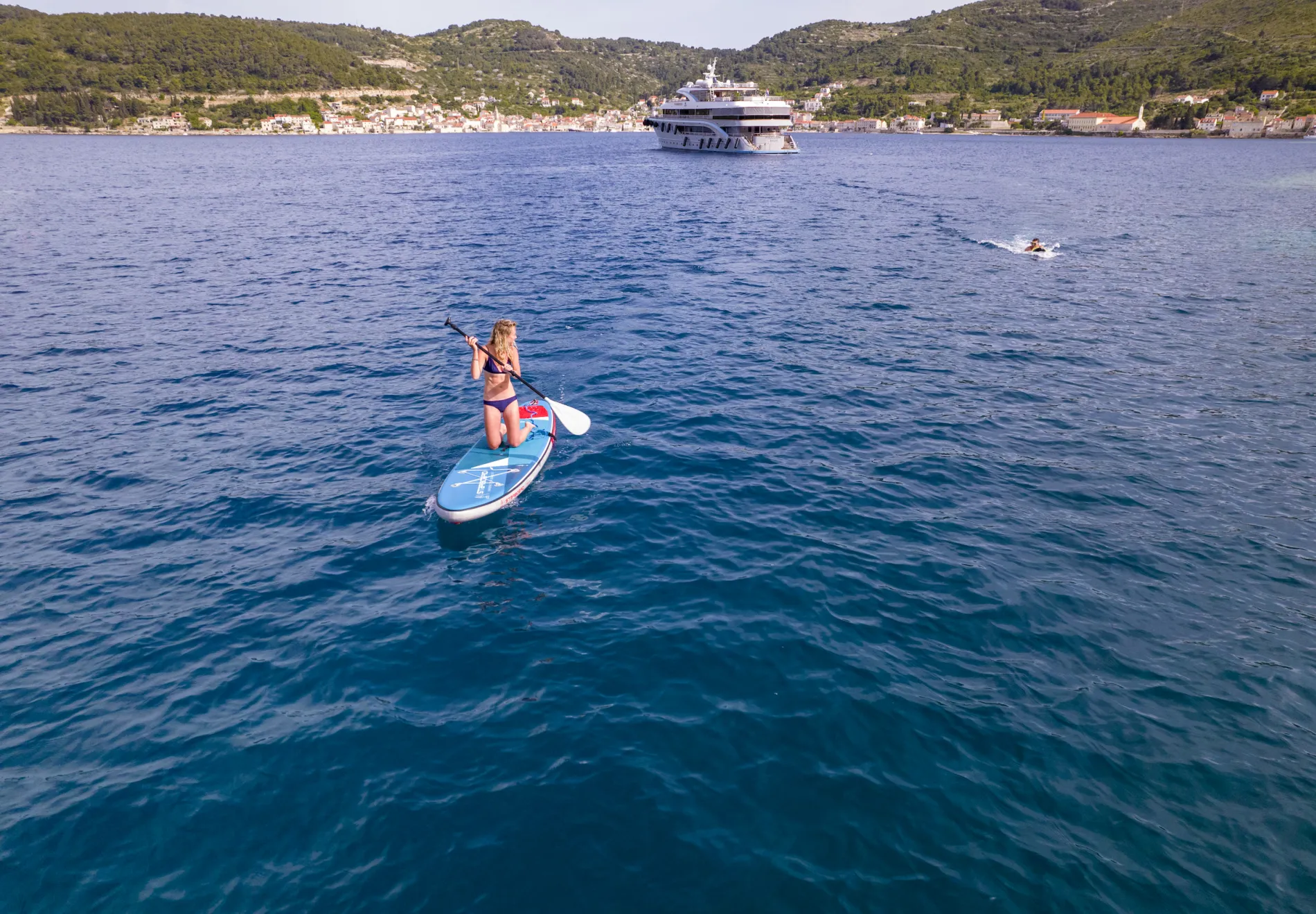

»Maritime law in Croatia means that yacht captains can drop anchor anywhere, so guests can simply fill their days with swim stops and make full use of Freedom’s range of ‘water toys’ – sea bobs, jet skis, paddleboards and rubber rings.«

»So that's roughly £3500 per person, a similar price to going on a regular high-end cruise, for - and let me remind you again - a SUPERYACHT! And this travels to, unlike a regular cruise ship, wherever YOU want, with the people YOU know, and with everything YOU want to do all pre-arranged for you.«
Discover Croatia's landmark destinations that travel vlogger Mitch Summers visited aboard Superyacht Freedom.

»If you get the chance to travel by yacht, board it. Even better, do it in Croatia. Just be prepared to return spoiled and catch yourself later, on other perfectly lovely getaways, thinking with a sigh: “If only this were Croatia.«
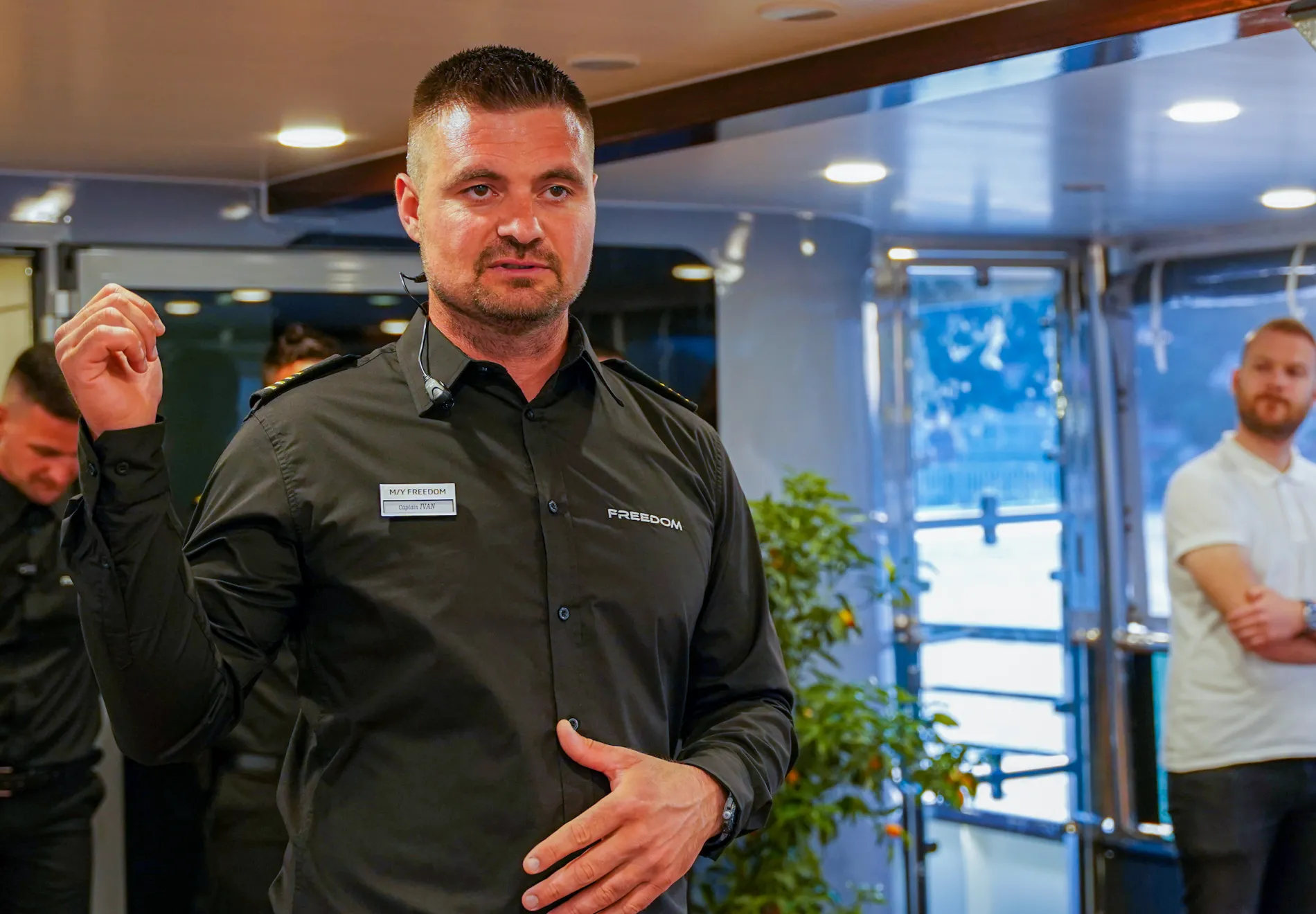

»Having local experience helps in determining where to cruise, wherever you are sailing. Our captain, Ivan, who also owns Freedom, devised an activity-packed but never overloaded route from Split, where there’s a modern airport that is relatively easy to get to via international flight connections.«

»You don't need to get off Freedom to enjoy it, though. The yacht has a cinema, a top-deck Jacuzzi, and a dining room where private chefs act like genies, granting culinary wishes.«

»With the sun beating down even in October, it beats any hotel pool. Throw in experiences like touring the infamous Blue Caves, or the number of isolated beaches dotted along the coast’s small islets, and simply stopping to create your own floating paradise is something that feels like a true one-off in a world filled with locations promising something unique.«
Check out the walkthrough video and discover Freedom's upgraded features.
Embark on a journey of ultimate luxury and breathtaking experiences aboard superyacht Freedom. Let the pristine waters of Croatia and the immaculate services on the yacht captivate your senses, creating memories that will linger long after your voyage. Dive deep into a realm of opulence where every moment is tailored to exceed your expectations and elevate your sense of delight and satisfaction.
Unveil the extraordinary and start planning your unforgettable yachting holiday today. Send us an enquiry for a bespoke offer and detailed insights. Your journey towards a magnificent seafaring adventure begins now.
Ultimate Yacht Charter Guide: Discovering Croatia's 6 Top Beaches
A Yachter's Guide to Croatia's Best National Parks
Other articles

Savoring Local Flavors: Culinary Excellence Aboard DS Yacht Cristal

Why Goolets is The Premier Yacht Charter Expert in Croatia

The Irresistible Allure of Renting a Yacht in Eastern Europe

Gulet Charters in Croatia Closer Within Reach

Miha Menegalija's Mastery in Designing Your Dream Yacht Charter

Behind the Scenes with Blaž Feguš About Crafting Bespoke Yacht Charters

Understanding your wishes
We continuously monitor availability, quality, and accuracy of pricing, of well over 500 gulets and yachts in eleven different charter destinations.
What kind of boats are for you?
Find out which boat will suit you best in this short and fun quiz.
© 2024 Goolets. All Rights Reserved
Privacy Policy Terms of Service Cookies

Yachts for Sale
Selling a Yacht
Tenders & Toys
Recent Sales

NEVER SAY NEVER AGAIN

Yachts for Charter
Destinations
Experiences
Charter Management
Charter Guide
Yacht Marketing
How to Charter

Superyacht Management
Crew Structure

THE WELLESLEY
Superyacht Construction
New Yachts for Sale
Yacht Design
Yacht Shipyards
Custom Construction
Built on Trust

Heesen 55m Steel

Benetti Oasis
Yacht Shows
News & Blog

Freedom Yacht for Charter
Overview | Exterior | Interior | Accommodation | Photos | Layout | Price

Freedom PRICE
From:115,000€p/week
Freedom CHARTER YACHT
Enquire about freedom.
Contact our charter brokers about chartering this yacht.
Related Yachts
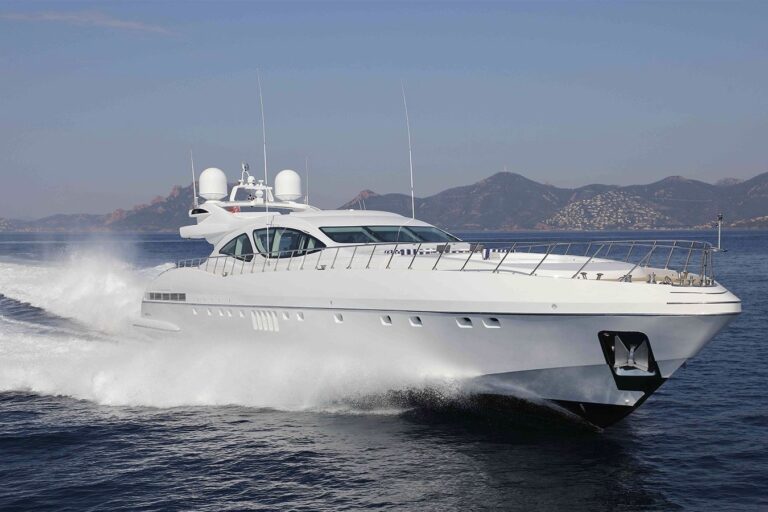

VENI VIDI VICI
40m | Overmarine | 2006
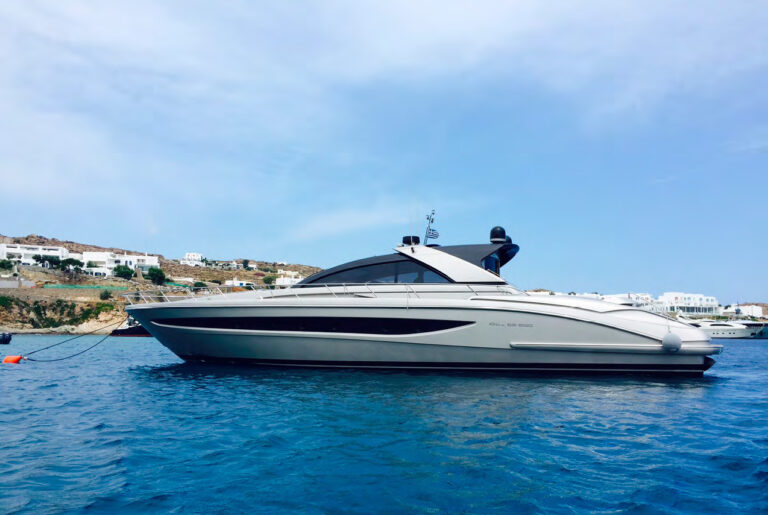

20.8m | Riva | 2005

SILVER BREEZE
23m | Riva | 2010
DESTINATIONS

ABC Islands

YACHTS FOR SALE
YACHTS FOR CHARTER
CHARTER MANAGEMENT
+377 97 77 67 57
Privacy Policy
SEO by The Agency

Yachts for sale
Selling a yacht
Recent Sale
REQUEST BROCHURE
Leave us your contact details and our team will be in touch shortly to provide you with your quick request.
REQUEST AVAILABILITY
Request layout, request itineraries, request virtual tour.
Leave us your contact detail and our team will be in touch shortly to arrange your virtual visit aboard this yacht.
REQUEST VIDEO
Leave us your contact detail and our team will be in touch shortly to provide you with your quick request.
THANKS FOR YOUR ENQUIRY
TELL US MORE ABOUT YOUR CHARTER AND OUR TEAM WILL PROVIDE YOU WITH A RELEVANT YACHT SELECTION.
Please use a modern browser to view this website. Some elements might not work as expected when using Internet Explorer.
- Landing Page
- Luxury Yacht Vacation Types
- Corporate Yacht Charter
- Tailor Made Vacations
- Luxury Exploration Vacations
- View All 3576
- Motor Yachts
- Sailing Yachts
- Classic Yachts
- Catamaran Yachts
- Filter By Destination
- More Filters
- Latest Reviews
- Charter Special Offers
- Destination Guides
- Inspiration & Features
- Mediterranean Charter Yachts
- France Charter Yachts
- Italy Charter Yachts
- Croatia Charter Yachts
- Greece Charter Yachts
- Turkey Charter Yachts
- Bahamas Charter Yachts
- Caribbean Charter Yachts
- Australia Charter Yachts
- Thailand Charter Yachts
- Dubai Charter Yachts
- Destination News
- New To Fleet
- Charter Fleet Updates
- Special Offers
- Industry News
- Yacht Shows
- Corporate Charter
- Finding a Yacht Broker
- Charter Preferences
- Questions & Answers
- Add my yacht
FREEDOM Interior & Exterior Photos
70m / 229'8 benetti 2000 / 2016.
- Previous Yacht
- Amenities & Toys
- Rates & Regions
- + Shortlist

Charter Freedom
To charter this luxury yacht contact your charter broker or
SIMILAR YACHTS FOR CHARTER

66m | Oceanco
from $487,000 p/week ♦︎

63m | Codecasa
from $360,000 p/week

77m | Amels
from $645,000 p/week

Elegant 007
72m | Lamda Nafs Shipyards
from $568,000 p/week ♦︎

63m | Oceanco
from $310,000 p/week

69m | Oceanfast
from $411,000 p/week ♦︎

69m | Austal
from $480,000 p/week

72m | Austal
from $593,000 p/week ♦︎

72m | Feadship
from $471,000 p/week ♦︎
NOTE to U.S. Customs & Border Protection
SIMILAR LUXURY CHARTER YACHTS
Here are a selection of yachts which are similar to the current charter yacht. To view all similar luxury charter yachts click on the button below.

As Featured In
The YachtCharterFleet Difference
YachtCharterFleet makes it easy to find the yacht charter vacation that is right for you. We combine thousands of yacht listings with local destination information, sample itineraries and experiences to deliver the world's most comprehensive yacht charter website.
San Francisco
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Follow us on Instagram
- Find us on LinkedIn
- Add My Yacht
- Affiliates & Partners
Popular Destinations & Events
- St Tropez Yacht Charter
- Monaco Yacht Charter
- St Barts Yacht Charter
- Greece Yacht Charter
- Mykonos Yacht Charter
- Caribbean Yacht Charter
Featured Charter Yachts
- Maltese Falcon Yacht Charter
- Wheels Yacht Charter
- Victorious Yacht Charter
- Andrea Yacht Charter
- Titania Yacht Charter
- Ahpo Yacht Charter
Receive our latest offers, trends and stories direct to your inbox.
Please enter a valid e-mail.
Thanks for subscribing.
Search for Yachts, Destinations, Events, News... everything related to Luxury Yachts for Charter.
Yachts in your shortlist
Off the Hook Yachts Acquires Georgetown Yacht Basin
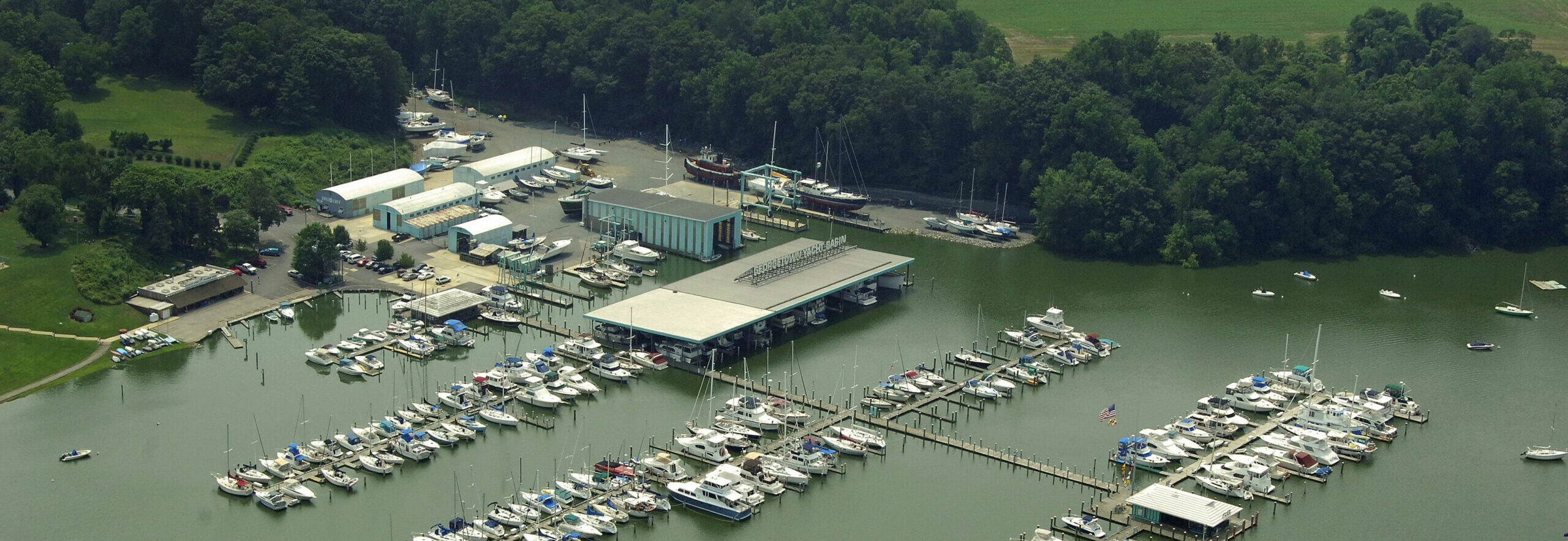

Jan 10, 2023
Off the Hook Yachts Acquires 300-Slip Marina in Georgetown Maryland

The Acquisition
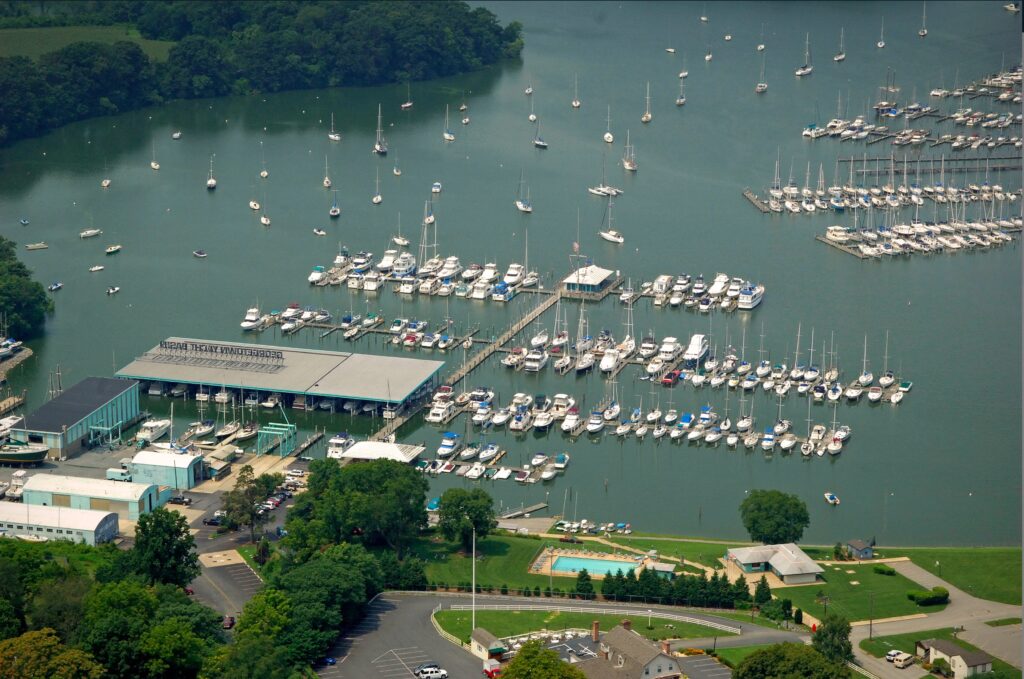
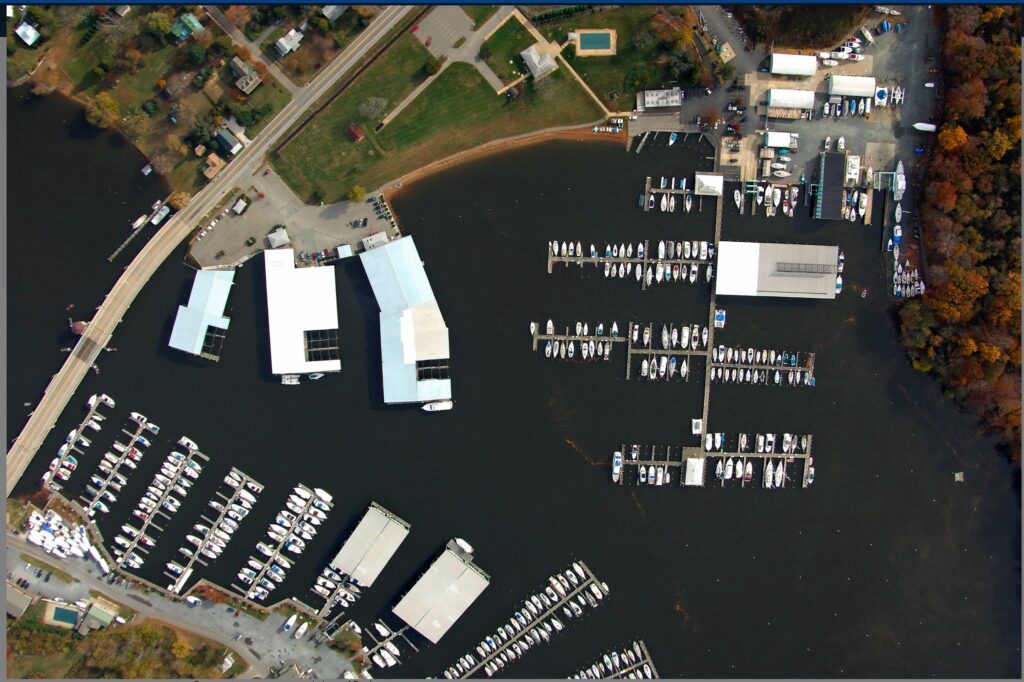
Off the Hook Yachts is proud to announce the acquisition of Georgetown Yacht Basin (GYB) now rebranding under Georgetown Yacht Haven – a 300-boat slip full-service marina located on the Sassafras River in Georgetown, MD. Off the Hook plans to restore the yacht basin to its former glory and reconnect with the local community in order to establish it as a household name in the area.
As our founder is originally from Maryland, this will complement our current presence in the area, along with our MD sales team, which currently operates out of Bay Bridge Marina. The acquisition of the marina will allow us to expand on sales, service, and custom-built Nor-Tech Performance Boat sales in the region. Georgetown Yacht Haven has 300 slips, two paint sheds that can hold up to a 110-foot yacht, a 110-ton travel lift, a fuel dock, a swimming pool, bathhouses, and a complete ship store, along with many other amenities. GYH controls the largest travel lift in Northern Chesapeake Bay.

About Off the Hook Yacht Sales
Off The Hook Yacht Sales NC, LLC, based in Wilmington, North Carolina, was founded in 2012 by Jason Ruegg and has now become the largest marine wholesaler in North America. The company provides wholesale purchasing services for brokerages, new boat dealers, and private individuals, and has become a household name at the largest brokerages and dealerships in the Country. Off the Hook Yachts headquarters is in Wilmington, North Carolina, where it remains today. We have 12 other locations currently in the USA, with expansion plans for 2023. Additionally, OTH is proud to represent Nor-Tech Hi-Performance Boats from Georgia to Maine and Yellowfin Boats from Miami to the Florida Keys.
About Georgetown Yacht Haven
Georgetown Yacht Haven was originally constructed in 1949. The marina is situated on 14.26 acres along the Sassafras River. This river is known for its very deep brackish to freshwater – making it ideal for boating in the Upper Chesapeake area. Georgetown Yacht Haven is a full-service marina and shipyard with a restaurant and hotel on site. For more information contact Tristan Price at (410) 648-5112 / [email protected] .

Have a Boat to Sell?
- Select a Year
- Select a Make
- AB Inflatables
- Action Craft
- Albury Brothers
- American Custom Yachts
- American Tug
- Argos Nautic
- Arrow head ski
- Austin Parker
- Barker Boatworks
- Bass seeker
- Bass Tracker
- Boca Grande
- Boston Whaler
- Buddy Davis
- Californian
- Cap-N-Squid
- Carolina Cat
- Carolina Classic
- Carolina Skiff
- Carolina Skimmer
- Center Console
- Chaparral Vortex
- Chris-Craft
- Cinco Boatworks
- Competition
- Correct craft
- Cruisers Yachts
- Custom Carolina
- Custom Line
- Cypress cay
- De Antonio Yachts
- Deep Impact
- El ShaddieFla
- Fathom Yachts
- Ferretti Yachts
- Forest River
- Fountaine Pajot
- Freedom Boat Works
- Front Runner
- Gamefisherman
- Glacier Bay
- Grady-White
- Grand Banks
- Hacker-Craft
- Harris FloteBote
- Hunt Yachts
- Hydra sports
- Hydra-Sports
- Inmar Inflatable
- Intermarine
- Island Runner
- J&H Performance
- Jarrett Bay
- Jersey Cape
- Jet Williams
- Jones Brothers
- Judge Yachts
- Kadey-Krogen
- LaserPerformance
- Lazzara Yachts
- Lexington Pontoon
- Liquid Glass
- Little Harbor
- Macgregor/Venture
- Magnum Marine
- Maimi sport
- Malcolm Tennant
- Marine trader trawler
- Mastercraft
- Mathews Brothers
- Maverick Boat Co.
- Mckee Craft
- Midnight Express
- Miller Marine
- Misty Harbor
- Monte Carlo
- Monte Carlo Yachts
- Nautic Star
- Nordic Tugs
- North Coast
- OBX Boatworks
- Ocean Alexander
- Ocean Master
- Ocean Runner
- Ocean Yachts
- Outer Banks
- Outer Limits
- Pacific Mariner
- Pair Customs
- Palmer Johnson
- Polar kraft
- Pontoon Air Cruiser
- Ranger Tugs
- Reef Runner
- Release Boatworks
- Rockharbour
- Rodriguez Yachts
- Schaefer Yachts
- Seaswirl Striper
- Sessa Marine
- Shallow Sport
- Siar Moschini
- Silver wave pontoon
- Smoker Craft
- Smokercraft
- Steiger Craft
- Sun Tracker
- Tahoe tritton
- Tecnomar Yachts
- Tiara Sport
- Tiara Yachts
- Tracker Grizzly
- Tracker Marine
- Tracker pro160
- Tracker Tahoe
- Tracker Tahoe Q4 Ski
- True World Marine
- United marine
- Vintage Hickman
- Water Mocassin
- Williams Jet Tenders
- Williamscraft
- Windsor Craft
- Winter Custom Yachts
- Wooden sailing Dinghy
- Yamaha Boats
- yamaha linux
- ZAR Formenti
- Length (ft)
- 100 ft
- 101 ft
- 102 ft
- 103 ft
- 104 ft
- 105 ft
- 106 ft
- 107 ft
- 108 ft
- 109 ft
- 110 ft
- 111 ft
- 112 ft
- 113 ft
- 114 ft
- 115 ft
- 116 ft
- 117 ft
- 118 ft
- 119 ft
- 120 ft
- 121 ft
- 122 ft
- 123 ft
- 124 ft
- 125 ft
- 126 ft
- 127 ft
- 128 ft
- 129 ft
- 130 ft
- 131 ft
- 132 ft
- 133 ft
- 134 ft
- 135 ft
- 136 ft
- 137 ft
- 138 ft
- 139 ft
- 140 ft
- 141 ft
- 142 ft
- 143 ft
- 144 ft
- 145 ft
- 146 ft
- 147 ft
- 148 ft
- 149 ft
- 150 ft
- 151 ft
- 152 ft
- 153 ft
- 154 ft
- 155 ft
- 156 ft
- 157 ft
- 158 ft
- 159 ft
- 160 ft
- 161 ft
- 162 ft
- 163 ft
- 164 ft
- 165 ft
- 166 ft
- 167 ft
- 168 ft
- 169 ft
- 170 ft
- 171 ft
- 172 ft
- 173 ft
- 174 ft
- 175 ft
- 176 ft
- 177 ft
- 178 ft
- 179 ft
- 180 ft
- 181 ft
- 182 ft
- 183 ft
- 184 ft
- 185 ft
- 186 ft
- 187 ft
- 188 ft
- 189 ft
- 190 ft
- 191 ft
- 192 ft
- 193 ft
- 194 ft
- 195 ft
- 196 ft
- 197 ft
- 198 ft
- 199 ft
- 200 ft

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- Boat Pro Home
- Pricing Plan
- Superyacht Insight
- Product Features
- Premium Content
- Testimonials
- Global Order Book
- Tenders & Equipment
$10 million price cut on Benetti's 70m superyacht Reverie at OCI
Almost a year to the day since I reported that the 70m motor yacht Reverie had come on the market with Michael White and Peter Thompson at Ocean Independence , comes news of a $10 million price reduction.
At the time of her build in 2000 she was the largest superyacht by tonnage built by Benetti and, despite her size, Reverie sleeps just 12 guests for charter in eight cabins with a further two cabins available for personal staff. A major attraction though, is that she can accommodate 18 to 24 guests for private use.
Internally, her six decks (all united by a lift) include one that is largely devoted to the owner. This includes a master suite that revels in a magnificent bedroom with panoramic forward views over the private terrace, sumptuous his and hers bathrooms and vast walk-in dressing rooms. The deck also offers two further family cabins (each with a double and a single bed), a study, an owner’s saloon and a circular inside-outside dining room.
Of the remaining guest cabins, four are identically sized double cabins with en suite bathrooms situated on the lower deck and an impressive VIP cabin, which occupies the forward element of the main deck superstructure.
Lying in Genoa, Reverie is now asking $65 million.
More stories
Most popular, from our partners, sponsored listings.
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
Cruising the Moskva River: A short guide to boat trips in Russia’s capital
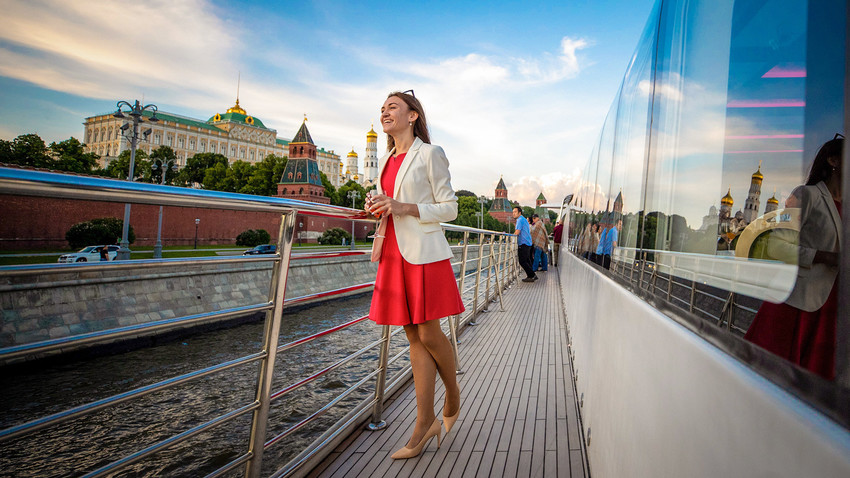

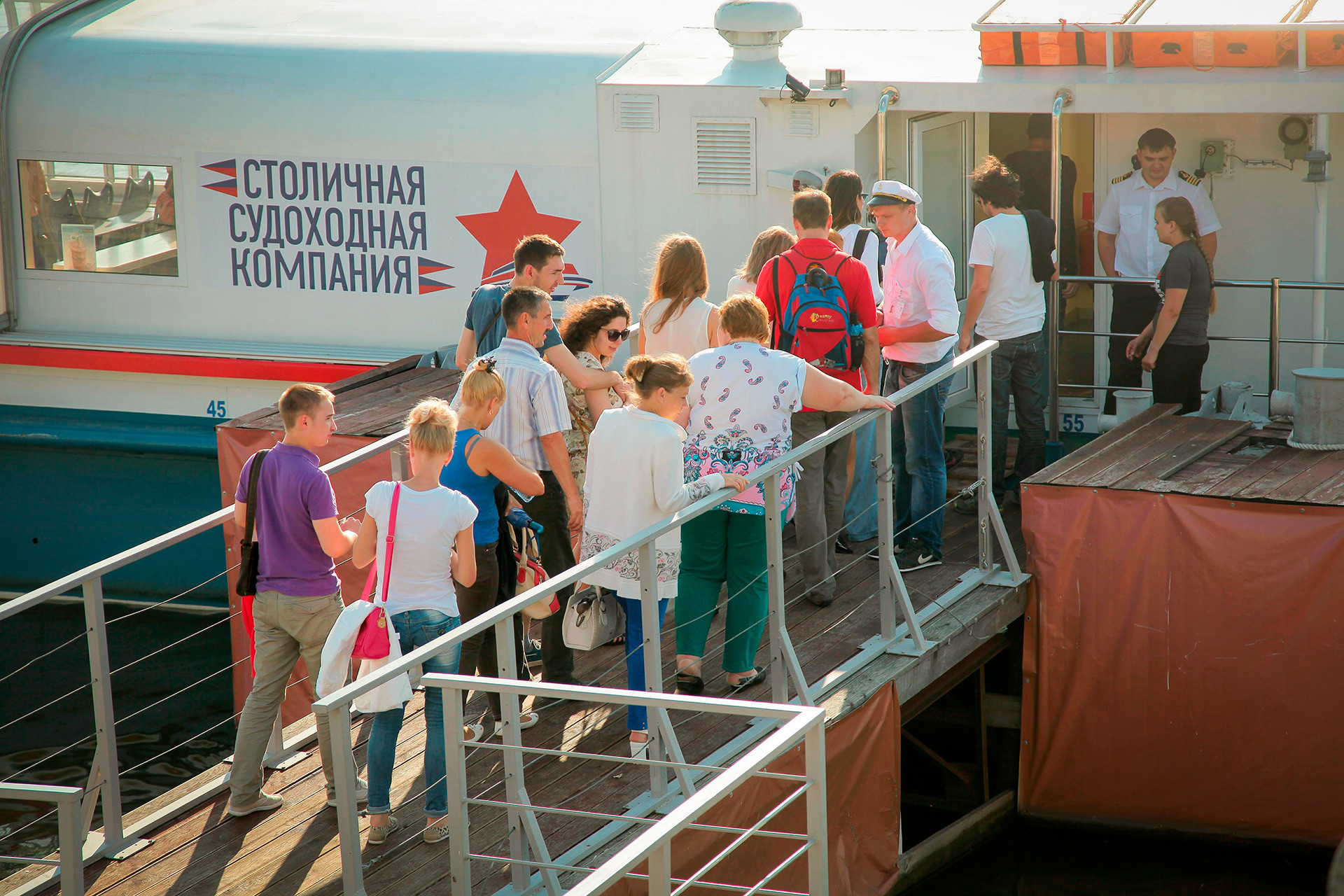
There’s hardly a better way to absorb Moscow’s atmosphere than on a ship sailing up and down the Moskva River. While complicated ticketing, loud music and chilling winds might dampen the anticipated fun, this checklist will help you to enjoy the scenic views and not fall into common tourist traps.
How to find the right boat?
There are plenty of boats and selecting the right one might be challenging. The size of the boat should be your main criteria.
Plenty of small boats cruise the Moskva River, and the most vivid one is this yellow Lay’s-branded boat. Everyone who has ever visited Moscow probably has seen it.
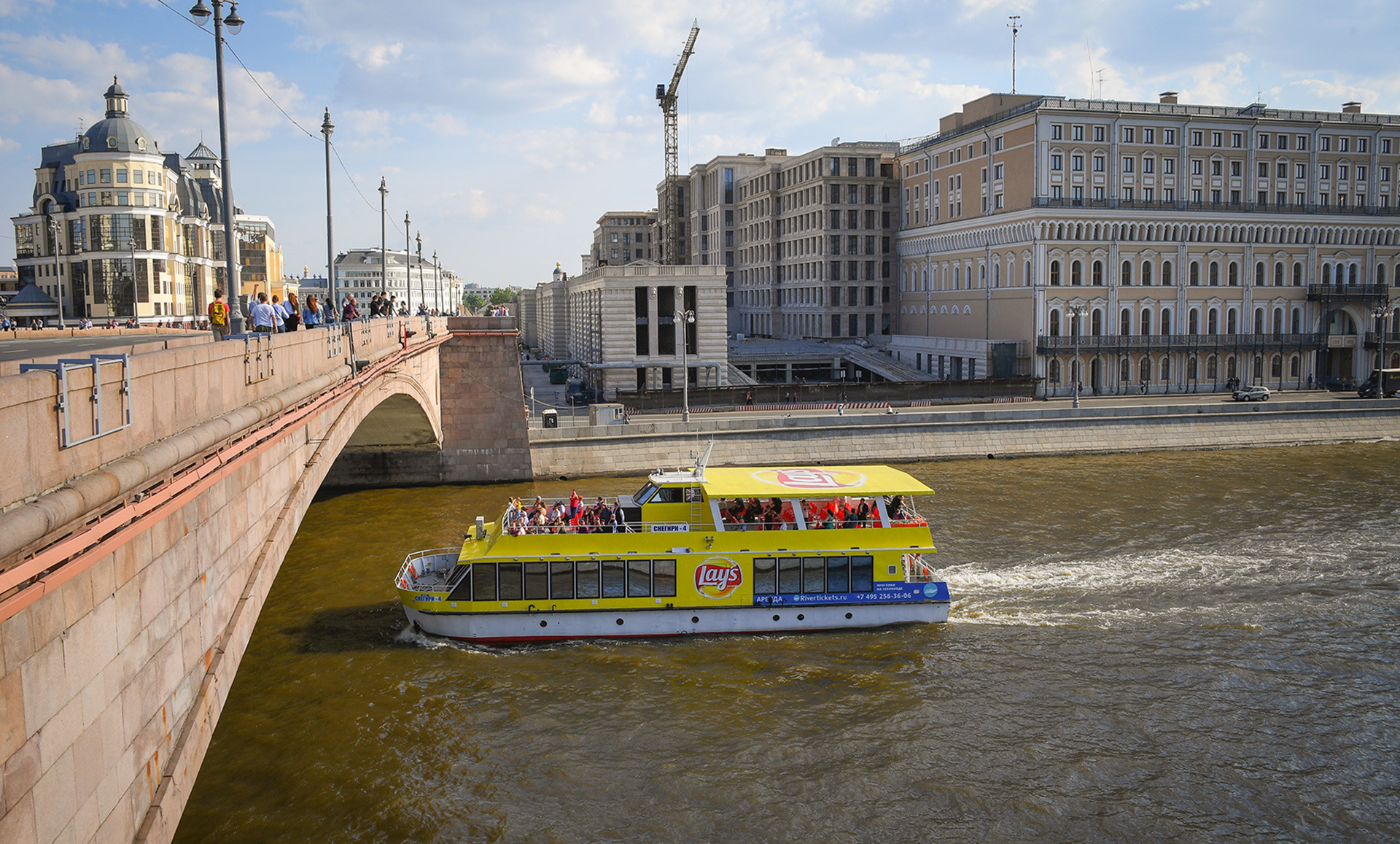

This option might leave a passenger disembarking partially deaf as the merciless Russian pop music blasts onboard. A free spirit, however, will find partying on such a vessel to be an unforgettable and authentic experience that’s almost a metaphor for life in modern Russia: too loud, and sometimes too welcoming. Tickets start at $13 (800 rubles) per person.
Bigger boats offer smoother sailing and tend to attract foreign visitors because of their distinct Soviet aura. Indeed, many of the older vessels must have seen better days. They are still afloat, however, and getting aboard is a unique ‘cultural’ experience. Sometimes the crew might offer lunch or dinner to passengers, but this option must be purchased with the ticket. Here is one such option offering dinner for $24 (1,490 rubles).

If you want to travel in style, consider Flotilla Radisson. These large, modern vessels are quite posh, with a cozy restaurant and an attentive crew at your service. Even though the selection of wines and food is modest, these vessels are still much better than other boats.
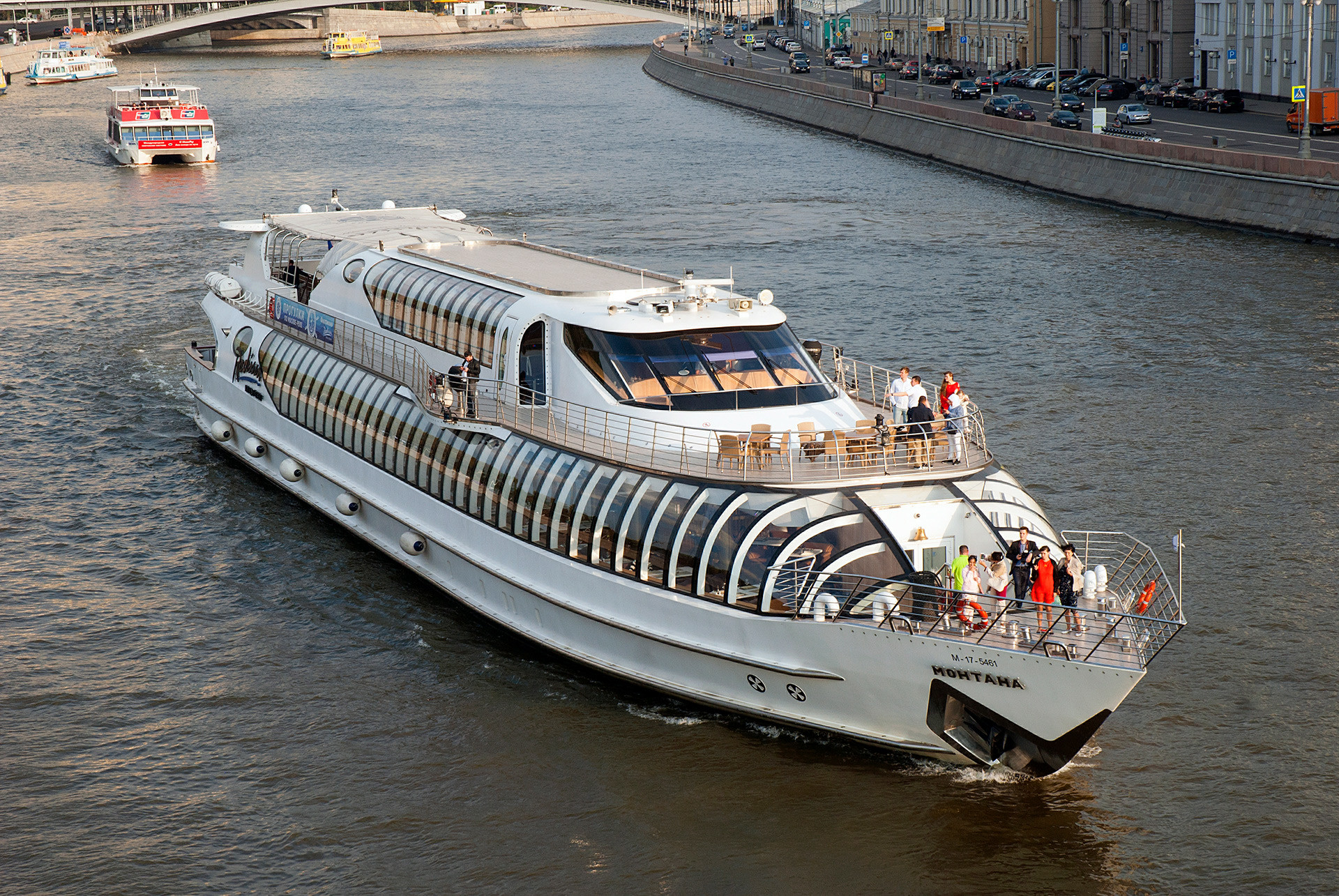

Surprisingly, the luxurious boats are priced rather modestly, and a single ticket goes for $17-$32 (1,100-2,000 rubles); also expect a reasonable restaurant bill on top.
How to buy tickets?
Women holding photos of ships promise huge discounts to “the young and beautiful,” and give personal invitations for river tours. They sound and look nice, but there’s a small catch: their ticket prices are usually more than those purchased online.
“We bought tickets from street hawkers for 900 rubles each, only to later discover that the other passengers bought their tickets twice as cheap!” wrote (in Russian) a disappointed Rostislav on a travel company website.
Nevertheless, buying from street hawkers has one considerable advantage: they personally escort you to the vessel so that you don’t waste time looking for the boat on your own.

Prices start at $13 (800 rubles) for one ride, and for an additional $6.5 (400 rubles) you can purchase an unlimited number of tours on the same boat on any given day.
Flotilla Radisson has official ticket offices at Gorky Park and Hotel Ukraine, but they’re often sold out.
Buying online is an option that might save some cash. Websites such as this offer considerable discounts for tickets sold online. On a busy Friday night an online purchase might be the only chance to get a ticket on a Flotilla Radisson boat.
This website (in Russian) offers multiple options for short river cruises in and around the city center, including offbeat options such as ‘disco cruises’ and ‘children cruises.’ This other website sells tickets online, but doesn’t have an English version. The interface is intuitive, however.
Buying tickets online has its bad points, however. The most common is confusing which pier you should go to and missing your river tour.

“I once bought tickets online to save with the discount that the website offered,” said Igor Shvarkin from Moscow. “The pier was initially marked as ‘Park Kultury,’ but when I arrived it wasn’t easy to find my boat because there were too many there. My guests had to walk a considerable distance before I finally found the vessel that accepted my tickets purchased online,” said the man.
There are two main boarding piers in the city center: Hotel Ukraine and Park Kultury . Always take note of your particular berth when buying tickets online.
Where to sit onboard?
Even on a warm day, the headwind might be chilly for passengers on deck. Make sure you have warm clothes, or that the crew has blankets ready upon request.
The glass-encased hold makes the tour much more comfortable, but not at the expense of having an enjoyable experience.
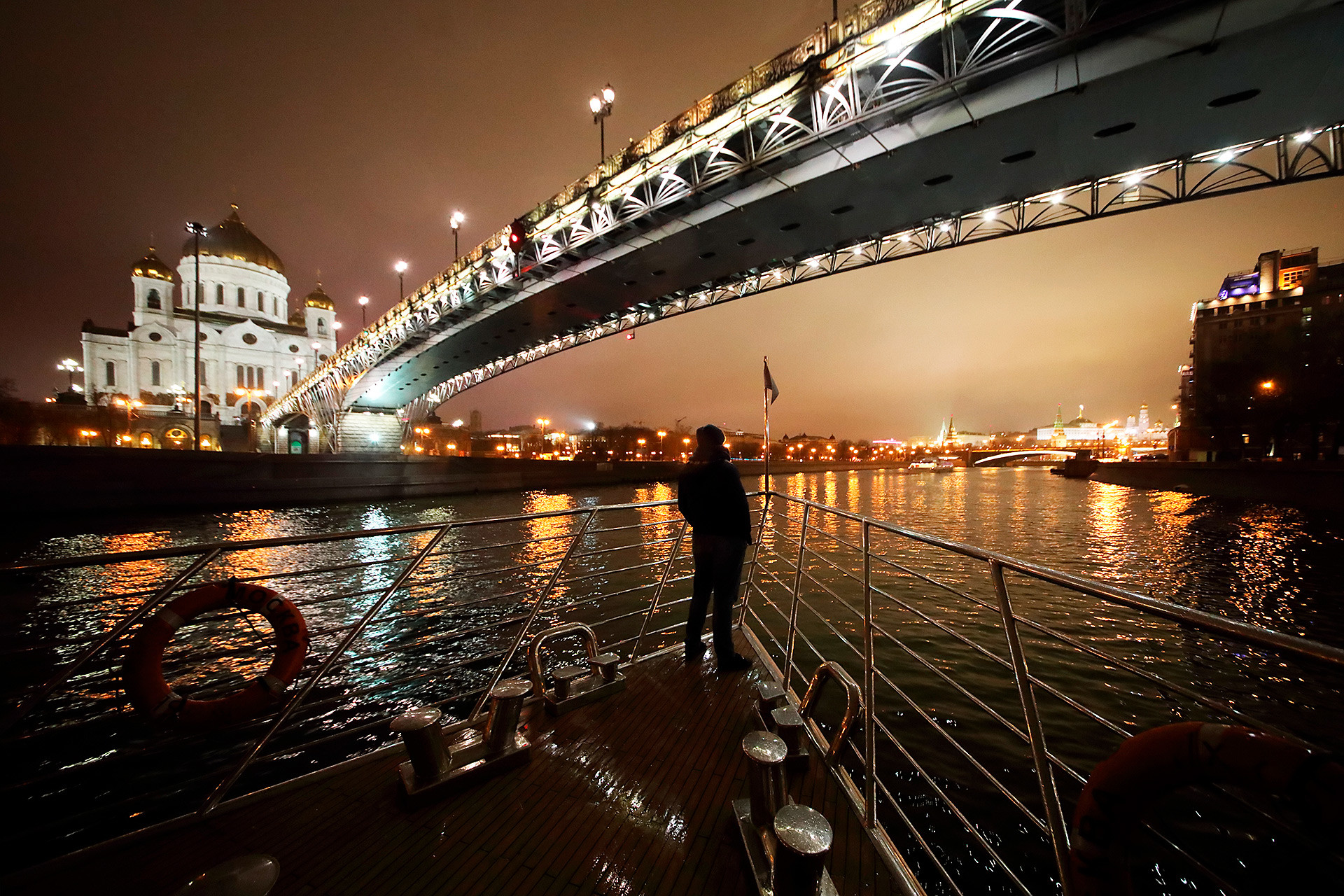

Getting off the boat requires preparation as well. Ideally, you should be able to disembark on any pier along the way. In reality, passengers never know where the boat’s captain will make the next stop. Street hawkers often tell passengers in advance where they’ll be able to disembark. If you buy tickets online then you’ll have to research it yourself.
There’s a chance that the captain won’t make any stops at all and will take you back to where the tour began, which is the case with Flotilla Radisson. The safest option is to automatically expect that you’ll return to the pier where you started.
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
- What to do in Moscow City, if you’re not mega-rich
- Moscow after dusk: 10 places to drink, dance, and groove
- 5 things you must do in Moscow in 2018 between football matches (or without them)
- Sandwiched between Moscow and St. Petersburg: How to spend a perfect weekend in Tver
- 24 or 48 hours in Moscow: Where to go and what to do in 2019
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.
- George Town Tourism
- George Town Hotels
- George Town Bed and Breakfast
- George Town Vacation Rentals
- Flights to George Town
- George Town Yacht Club
- Things to Do in George Town
- George Town Travel Forum
- George Town Photos
- George Town Map
- All George Town Hotels
- George Town Hotel Deals
- George Town
- Things to Do
- Restaurants
- Vacation Rentals
- Travel Stories
- Rental Cars
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travelers' Choice
- Help Center
A free shuttle to and from the airport - George Town Yacht Club
- Caribbean
- Cayman Islands
- Grand Cayman
- George Town
- George Town Restaurants
“A free shuttle to and from the airport” Review of George Town Yacht Club

I was stuck in the Owen Roberts Airport for 6 hours and I had already turned in my rental car. I asked one of the airport employees with the CIAA T-shrt what a person does for six hours. She said she'd leave and suggested that she would call the free shuttle that would take me to the yacht cub. She said the food there was good. The shuttle driver showed up in minutes.. The yacht club was noisy--a marathon's finish line was there. On the other hand, the food was good--so much better than anything at the airport that it is difficult to describe. I had the calamari with pickled apples--really tasty. There is outdoor seating with views of the marina, but inside with the air conditioning the view was very nice as well. I explained my plight to my server who invited me to stick around as long as I wanted--which I did. She kept my soda glass filled and did not at any time suggest that I move on. Eventually, it was time to go and my server arranged to have the shuttle driver ready in a few minutes. I would go back if confronted with hours in the airport, but the noise was bothersome.
- Excellent 164
- Very good 81
- All languages
- English (281)
- German (3)
- French (1)
- More languages
- English (281)
- Italian (1)
186 - 190 of 286 reviews
Flavor and what a staff! I had the Soup of the day, fresh, tasty, and hot. My Father had the burger, and it was black angus, semi rare, with sweet potatoes, plus fish burgers, it was just like homemade. Huge sit down horseshoe bar, incredible friendly staff. Amazing....!
This is the third time we have dined at this restaurant. Twice last year and then again on our trip this year. Our only disappointment was that we could not dine outside because of a downpour that got all the tables wet. Nice atmosphere, beautiful view and a very attentive staff. We split the Wahoo Cerviche for an appetizer. It was so good an an ample portion for two. Every meal comes with a basket of fried bread. For my entree I had the grilled chicken with garlic butter sauce, for my two sides I chose the sautéed mushrooms and macaroni and cheese with truffle oil. The sides are huge and the so much chicken there was plenty to bring for lunch the next day. Every thing was delicious and I would definitely recommend this restaurant. Very affordable for the Cayman Islands.
Given the lack of choice in the area, we were quite pleased to find this little gem of a restaurant! It's in a nice location overlooking the marina - just out the front doors of the airport, down the road and past the roundabout. The food was excellent! We were served some tasty fried bread with butter as soon as we sat down. My husband and I ordered the appetizer of conch fritters with jerk mayo and the lion fish tacos with pickled fennel and arugula as our main dishes. The ingredients were fresh, with just enough heat. The server was very nice and efficient, answering any questions that we had. And the prices were quite reasonable for the Caymans. If you have a layover at the Grand Cayman airport or you just happen to be in the area, I would highly recommend the George Town Yacht Club.
One of our favorite places in Cayman for lunch or dinner. In fact we always make it a first stop for a drink & food when arriving in Cayman, because it's right beside the airport. Also visiting by boat is really nice & the pool is a wonderful social spot
Travelers who viewed George Town Yacht Club also viewed
Been to george town yacht club share your experiences, owners: what's your side of the story.
Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
Browse nearby
Find anything you save across the site in your account
Moscow, a Newspaper City
By David Remnick

At his dacha in the woods outside Moscow, Mikhail Gorbachev climbed into the back seat of a Zil limousine and headed north, toward the Kremlin. It was the morning after Christmas, and suddenly the Soviet Union was a half-remembered dream and its last general secretary a pensioner. Gorbachev wanted to take care of some final meetings and clean out his desk before starting a few weeks of vacation. The Russian government had promised him a peaceful day or two before it took up residence in the Kremlin. But when he arrived at his office he saw that his nameplate had already been pried off the wall. “Yeltsin, Boris Nikolaevich” was there, gleaming brassily, in its place. Inside the office, Yeltsin was sitting behind the desk. For days, there had been an air of self-pity about Gorbachev, and this petty incident seemed to transform it into fury. Never mind Gorbachev’s own assaults on Yeltsin over the years. “For me, they have poisoned the air,” he complained to a reporter. “They have humiliated me.”
This was a historic moment in Moscow: for the first time, an elected President occupying the Kremlin; the hammer and sickle gone from the flagpole; the regime and the empire dissolved. And yet history felt like nothing more than a miserable winter day; the Western press corps roamed Red Square in search of passion or comment. “You care, we don’t,” an old woman from the provincial city of Tver told a clutch of reporters. With that, she stormed off in search of potatoes and milk for her family.
In the afternoon, Gorbachev’s press secretary, Andrei Grachev, invited a small group of aides, foreign reporters, and Russian editors to a reception at the Oktyabrskaya Hotel. A farewell party, Grachev called it, and he could not have chosen a more appropriate stage. For years, the hotel, across the street from the French Embassy, was a symbol of the Communist Party’s kitschy opulence. The lobby and the dining rooms are heavy on marble and mirrors. Every fixture, it seems, was designed with a certain solicitude for the aging members of the Central Committee—feudal lords of the provinces—who would visit Moscow a few times a year for their plenary sessions and shopping sprees. The Communist Party discovered in its dying days that its financial situation had declined dramatically, and that the only solution was the quick sale of its assets. The Oktyabrskaya Hotel, once known to Muscovites as the Waldorf-Astoria of the Central Committee, is now open for the high-end tourist trade.
At a few minutes before five o’clock, the reporters and the editors stood waiting at the top of the marble stairs for Gorbachev to arrive. By chance, I took my place near two of the city’s best-known newspaper editors: Len Karpinsky, the editor-in-chief and a columnist of the weekly Moscow News ; and Vitaly Tretyakov, a young defector from Moscow News , who had started Nezavisimaya Gazeta ( Independent Newspaper ), the closest thing Russia has ever had to a Western daily. Standing there, I was struck by the fact that Gorbachev’s resignation meant a transition from Karpinsky’s generation of intellectual idealists to a breed of younger men and women like Tretyakov—business neophytes, scholars, hustlers, newspaper editors—who would build a new world not so much out of the jagged ruins of the old experiment as out of fragmentary notions gathered from the West.
Karpinsky is what Muscovites call a shestidesyatnik —someone who came of age in the early nineteen-sixties, during the exhilarating thaw under Nikita Khrushchev, and grew disillusioned when Soviet tanks crushed the Prague Spring, in 1968. That generation harbored the dream of a humane socialism in Russia. Its members did not dare take the risks of full-blown dissidence but found a measure of independence and sanity in their work. There were scholars who fled the oppressive scrutiny of Moscow for institutes in provincial cities from Tartu to Novosibirsk; there were journalists who fled Pravda for Prague and wrote for Problems of Peace and Socialism . Some shestidesyatniki even found it possible to work and think in small, relatively liberal pockets of the Communist Party apparatus in Moscow. Karpinsky first met Gorbachev thirty years ago, when both were prominent in the Komsomol, the Young Communist League. Shared hints of dissatisfaction, of irony, made them comrades of a sort. But Karpinsky was both ambitious and angry, and he had long since veered into the dangerous terrain of what he always called “my life as a half-dissident.” Gorbachev’s appearance as a leader of reform, in 1985, was what Karpinsky had been waiting for all his adult life. Under Gorbachev, Karpinsky went from disgrace to rehabilitation, then on to real stardom in the new world of journalism. When Gorbachev, in the last months of his rule, made serious miscalculations and proved unable to act decisively against the hard-liners who eventually placed him under house arrest for three days in the Crimea, Karpinsky quit the Party and put his hopes in Yeltsin. Yet that conversion, after the assault on Lithuania, in January of 1991—a conversion nearly unanimous among the Moscow intellectuals of Karpinsky’s age and background—was a kind of afterword, a coda to the failed dream of perestroika . Now, as Gorbachev was leaving center stage, so was Karpinsky. Moscow News , which had broken one taboo after another in the first years of perestroika , had become a tired paper: still interesting at times, still honest, but one that spoke to a generation that now seemed, with Gorbachev, exhausted.
“It’s good that Gorbachev’s leaving now, but I am moved to the core,” Karpinsky told me. “How can I deny that I have just finished the most important chapter of my life?”
That day in Moscow, Vitaly Tretyakov was thirty-nine years old—a quarter of a century younger than Karpinsky. In just one year, Tretyakov had developed a paper totally alien to what had been the Soviet Union. From its first issue, in December of 1990, Nezavisimaya Gazeta had never known government interference or censorship, and its language was free of ideology. The first issue appeared just as Eduard Shevardnadze resigned as Foreign Minister and made his uncanny prediction of an incipient dictatorship. The paper’s coverage of the rise of the hard-line counter-revolution and the August coup was unmatched. Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s combination of news, conflicting commentaries, highbrow essays, and satire made Moscow News seem hopelessly earnest and a little antique. While the pages of Moscow News were filled with the avuncular columns and the hand-wringing of old and worn-out men, reporters in their twenties at Nezavisimaya Gazeta were filching Party documents, printing the confessions of military spies, and conducting irreverent interviews with government leaders. Tretyakov gave free rein to people like Tatyana Malkina, who is twenty-four years old and once worked as a researcher at Moscow News . At a news conference held by the eight conspirators during the August coup, Malkina asked the most penetrating question of the hour. Fixing her eyes on the half-drunk pretender to power, Gennadi Yanayev, she said, “Tell me, please, do you realize that you have carried out a state coup? And which comparison would you find more appropriate—1917 or 1964?” Yanayev’s hand began to quiver uncontrollably as he careered through his reply.
“I’m supposed to be young, but sometimes I feel a hundred years old when I watch what my reporters dare to do,” Tretyakov told me later. “They are the first generation that knows no fear. Journalism is not a mission for them, as it was for us at Moscow News . It’s a terrific game.”
It was now five o’clock, and everyone at the top of the stairs was looking down, to see if Gorbachev would appear. Then the front doors opened and a few of Gorbachev’s closest advisers walked through—owlish little men in mouse-gray overcoats, among them Aleksandr Yakovlev, Georgi Shakhnazarov, and Anatoly Chernyaev. These were the bookish apparatchiks who had warned Gorbachev of the enemies in their midst, and had failed, ultimately, to penetrate their man’s gigantic, and tragic, self-possession. Just behind them was Gorbachev, wearing a coat the color of smoke. He looked up at the crowd and seemed embarrassed; there was something feeble in his smile. For years, he had played the press corps so easily. At first, it was enough that he was ambulatory and reasonably fluent in his own language—that he was not Brezhnev or Chernenko—but with time it was clear as well that he had an apparently effortless ability to connect, to seem to recognize a face in a crowd. And he had the gifts of surprise and agility. Now, at the end, if he was going to remain a force in politics and become Yeltsin’s moderate opposition he would want to give a decent performance at this reception. As Gorbachev shed his coat and began climbing the stairs, the reporters and the photographers began applauding; the applause was hesitant at first, but then it grew louder, and the sound reverberated from the marble and the high windows. Gorbachev clasped his hands together and shook them, more relieved than triumphant.
In a reception room, near tables covered with huge platters of smoked fish and roasted meats, Gorbachev gave a wheezy little speech, made all the worse by a horrendous public-address system. His clichés about the great missions of the past few years came out like the muffled, echoing announcements at a bowling alley. His aides looked bored and weary. But then, with that ritual over, Gorbachev threw himself into the event with gusto. He polished off a shot of lemon vodka and a slice of pickled herring, dangling the herring between forefinger and thumb and dropping it onto his tongue. In a voice of tricked-up cheer, he held his glass up to the guests and the cameras and said, “You think I can’t do it, but now I can afford to.” As Gorbachev worked the room, moving from one cluster of questioners to another, he made it clear that he had no intention of fading away. “I have big plans,” he said. “I am not leaving the political scene.” The later it got, the more pointed his gibes about his successors became. “I just could not go on,” he said. “Everything I did in the last few months, Yeltsin was always opposing. There was just no way. No way. It’s easy to be against Gorbachev, always against Gorbachev all the time. They have always been in opposition. So now I’m gone. There’s no one for them to oppose. So now let them do what they can.”
The transition in Russia these past few months has been far more profound than the turn from Gorbachev to Yeltsin. Genuine democracy is only now in the making, and economic reform remains a distant hope. So far, the great change in Russia has been one of mind and attitude.
The regime knew that it could not modernize without entering the age of information. And it was information—the truth about Soviet history and the failure of ideology—that brought an end to the regime. In the first years of perestroika , the intellectual, spiritual, and journalistic leaders of that change of mind were the shestidesyatniki —men and women like Karpinsky, idealists who suddenly provided an open, civil discourse where there had been none. In the past year, these people have given way to the new generation, less encumbered by the past or by self-doubt, more hardheaded, cynical, practical. Its members are businessmen who travel to Europe for weekend meetings; young academics specializing in the works of Hayek, Mill, and Burke; journalists who find their models in American investigative reporters and, not infrequently, the New York Post . The transition in journalism from Moscow News to Nezavisimaya Gazeta was perhaps the quickest and most visible of these shifts. To witness Len Karpinsky’s transformations—in print and in person—over the Party, socialism, and Gorbachev, and then to confront an army of kids, untroubled by the murk of ideology or by the censor’s pen, was to get a sense of the transition of Russian generations which is now in play.
Len Karpinsky’s parents were Old Bolsheviks. He was named in honor of his father’s mentor and friend Lenin. “ ‘Len’ was pretty common then, and so was ‘Ninel’—‘Lenin’ backward—or ‘Vladilen,’ for Vladimir Ilyich Lenin,” Karpinsky told me at his office one afternoon. “I’m just glad I didn’t get a name like ‘Elektrifikatsiya’ or some others my friends were stuck with.”
Karpinsky’s father, Vyacheslav Karpinsky, belonged to a generation of revolutionary romantics, the fin-de-siècle Communists. He joined the Communist Party in 1898, and in 1903, after his activities as a political organizer got him into trouble with the police in the Ukrainian city of Kharkov, he went into foreign exile, according to an interview that was published in “Voices of Glasnost,” by Stephen F. Cohen and Katrina vanden Heuvel. In Switzerland, he became Lenin’s aide and copy editor. In Moscow, after the revolution, he helped Lenin assemble his personal archives and held various posts at Pravda and the Central Committee’s Department of Propaganda. He received three Orders of Lenin, and in 1962 became the first journalist ever named a Hero of Socialist Labor.
For the Karpinsky family, a life in revolution provided an elevated existence. From 1932 to 1952, they lived in the famous House on the Embankment—a huge pile across the river from the Kremlin. Other tenants were the Kremlin élite: generals, Central Committee members, agents of the secret police. There were special dining halls stocked with groceries of a sort unknown to the rest of the socialist paradise. There were billiard halls, swimming pools, and, for the children, Special School No. 19. When Len Karpinsky was a boy, he was friendly with a couple of Stalin’s nephews. At a birthday party once, Stalin appeared in a doorway. “Children!” one of the adults announced. “Joseph Vissarionovich is here!” Stalin waved and smiled. The children all waited in silence until he left, and then resumed their games.
That was in 1935. In the coming years, Karpinsky watched dumbstruck as one after another of his friends in the building lost parents, aunts, uncles, and grandparents to Stalin’s purges. Nearly every night, secret-police vans would arrive and there would be arrests—an admiral, a lecturer on Marxism-Leninism, the sisters of a spy in a foreign embassy. “There was a knock and then they disappeared,” Karpinsky said. It had been the world of Yuri Trifonov’s novella “The House on the Embankment”—a world where “a life went on that was utterly different” from the life of ordinary people. Now it was a world where the most devoted revolutionaries, the most obsequious ministers, suddenly found themselves declared “plotters” and “infiltrators” and “enemies of the people.” Karpinsky’s family was, by the standards of the building, not hard hit. One of his aunts and her two brothers were sent off to the camps. To this day, Karpinsky does not quite understand why his father, the very sort of Lenin loyalist who so threatened Stalin, was not arrested and executed. The only reason he can think of now, he says, is that by 1937 or 1938 his father was semi-retired and out of politics.
From the moment I moved to Moscow, in January of 1988, until leaving, four years later, I read Moscow News , and particularly Karpinsky, avidly. Everyone did. The leadership had installed Karpinsky’s old friend Yegor Yakovlev as editor-in-chief of the newspaper in 1986, and almost from that point it was clear that Moscow News would be the paper of the thaw generation, the one that would subtly break the taboos formed over seventy years. From time to time, I visited Karpinsky at the Moscow News office, on Pushkin Square, and he always seemed to me an honest man, if a limited writer—a representative figure, whose life had been, as he remarked to me, “an inner conflict between the ambition to be a boss in the Communist Party and the almost involuntary development of a conscience.” His appearance today, waxen and drawn, speaks of that struggle. His face is long, lined, and worn. The fingers of his right hand are yellowed up to the first knuckle, from tobacco. More often than not, when I called and asked how he was he would say dryly, “My health is awful. I’m spending the week in a sanatorium. I may die.”
Karpinsky is so unassuming, and so ironic about his own failures and hesitations, that it is hard to believe he was once an ambitious Communist, a dutiful apparatchik who believed deeply in Communism and in himself—in his entitlement to success. After entering Moscow State University, in 1947, he began working as a “propaganda man” at factories and construction sites during the days before the Party’s single-candidate elections. “My assignment was to make the workers get up at 6 a.m. and go to the polls,” he told me one afternoon. “There was a competition among the propaganda men over whose group would be the first to finish voting. The deadline was midday, by which time the whole Soviet people was supposed to have voted. That was a decision of the Party. We eighteen-year-olds were supposed to carry on propaganda among the workers, and our only tool was the promise to improve their housing conditions. They lived in horrible slums, or in railway cars, with no toilets, no heat. I loved the work, thought it was a great service—and, yes, a stepping stone. At the university, Yuri Levada, who is now a well-known sociologist, wrote an article about me called ‘The Careerist.’ And it was true. I did it all with the idea of getting to the top. That was what it was all about—to be one of the bosses.”
After a pause, Karpinsky ground out a cigarette and went on, “But, having said that, I have to say a few words in self-defense. Society during the Stalin era left open no real opportunities for self-realization or self-expression except within this perverted system of the Communist Party. The system destroyed all the other channels—the artist’s canvas, the farmer’s land. All that was left was the gigantic hierarchic system of the Party, wide at the base and growing narrower as one climbed to the top. You had to have a Party membership just for admission. That was your only opportunity. When you are engaged in that work, you forget about the social and political implications and just do it. Gradually, though, this sort of life bifurcates your mind, your intellect. You do eventually begin to understand that life is life and it’s better to do something good for thy neighbor than to climb upward stepping on his bones. It all depends on moral principles. I suppose my first doubts came when I went to Moscow State University. A Jewish friend of mine named Karl Kantor was attacked by the university’s Party committee at the beginning of Stalin’s anti-Jewish campaign. That was just the start of a long transformation.
“After graduation, I was sent to the city of Gorki for Komsomol work. At that point, Stalin had one more year to live. I got to know the working class and the peasants in Gorki. I saw the utter degradation, the ruin. I saw Soviet society as it had really emerged. Some people still think, erroneously, that the life of the apparatchik breeds only conformists and subjects loyal to the regime. Actually, the regime splits people into two opposing factions—those who believe they can make it only through conformism and timeserving, and those who, thanks to a different structure of mind, dare to question the surrounding reality.”
He paused again, and then said, “So when Stalin died I realized perfectly well what he had been all about. Still, I went to the funeral in Moscow, out of curiosity. I felt like one of those prisoners in the camps who threw their hats in the air and cried, ‘The man-eater has finally kicked the bucket!’ My father’s reaction to Stalin’s death was interesting. By then, he was retired, working for the Central Committee only as a consultant. He sat there in his office, typing on an old Underwood, which he had brought from the offices he shared with Lenin in Switzerland. He called me into his study and said, ‘Son, Comrade Stalin has passed away. And, having been an epigone of Lenin, he created all the necessary conditions for our cause to triumph.’ It was so strange. My father had never before in his life talked so formally to me. I think he talked that way because his generation had always carried the burden of promoting the Party line at all times, and he felt that it was his duty to pass that down to his children. But this was a man, eighty years old, who had conceived his idea of the Party before the revolution and while living in exile. He had to convince not me but himself. He was talking to himself.”
When Karpinsky returned from Gorki to Moscow for good, in 1959, Khrushchev was the general secretary, and the thaw was in full swing. Novy Mir , Aleksandr Tvardovsky’s monthly journal of literature and opinion, was publishing texts critical of the old regime. Khrushchev himself read Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn’s “One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich,” and sanctioned its publication in Novy Mir . Karpinsky’s friends Yevgeny Yevtushenko and Andrei Voznesensky were winning a following with their foppish lyrics and performances. In various pockets of the Central Committee apparatus, young apparatchiks wrote proposals and outlines of economic and political reform—though all within certain boundaries of ideology and language. Karpinsky, for his part, worked as the head of the Komsomol’s Department of Propaganda and Agitation and as the editor of Molodoi Kommunist ( Young Communist ). Then, in 1962, he joined the empyrean of the adult Communist world. He was promoted to Pravda ’s editorial board, to head the department of Marxism-Leninism. He had made it.
“Once I was back in Moscow from Gorki, my critical approach weakened somewhat,” Karpinsky said. “I was part of the élite again, and not merely as my father’s son but as a real member. I was part of the top nomenklatura , and the nomenklatura is another planet. It’s Mars. It’s not simply a matter of good cars or apartments. It’s the continuous satisfaction of your own exclusivity; it’s the way an army of bootlickers allows you to work for hours. All the little apparatchiks are ready to do everything for you. Your every wish is fulfilled. You can go to the theatre on a whim, you can fly to Japan from your hunting lodge. It’s a life in which everything flows easily. No, you don’t own a yacht or spend your vacations on the Côte d’Azur, but you are at the Black Sea, and that is really something. The issue is your relative well-being. You are like a king: just point your finger and it is done.”
Karpinsky’s potential as a man of the Communist Party élite was unlimited. It is conceivable that he could have won eventual appointment to the Politburo. He was a Soviet Ivy Leaguer: bright, ambitious, a Legacy. One afternoon, at a Kremlin ceremony, two of Khrushchev’s most powerful partners in the leadership, Mikhail Suslov and Boris Ponomarev, called Karpinsky their golden boy, their comer. One of them said that Karpinsky was like “a son of the regiment” to them, and that they saw for him a great future in the ideological department of the Communist Party. “We are pinning our hopes on you,” Suslov said.
Working in that rarefied atmosphere, Karpinsky got to know nearly every figure who would make a difference (one way or the other) during perestroika . He was friendly with Yegor Yakovlev, the Lenin biographer, who became the editor of Moscow News ; Yuri Karyakin, a Dostoyevski scholar, who was among the leading radical deputies in the Congress of People’s Deputies; Aleksandr Bovin, the gargantuan journalist who propagandized the “new thinking” in foreign policy at Izvestia ; the reform-minded economists Gavriil Popov and Nikolai Shmelyov and the sociologist Yevgeny Ambartsumov; Otto Latsis, the son of an Old Bolshevik and an editor at Kommunist ; Gennadi Yanayev and Boris Pugo, who helped lead the August coup; and even the leading triumvirate of reform, Eduard Shevardnadze, Aleksandr Yakovlev, and Mikhail Gorbachev.
“I first met Gorbachev when I was working at Pravda and he was in Stavropol working in the Komsomol organization there,” Karpinsky said. “He was not very well known at the time, but I must tell you that Gorbachev was saying the same things then that he said at the beginning of perestroika . He was in Moscow on some business trip or other—I forget what it was about—but we met for a couple of hours, and I was impressed. He talked about the outrage of paying combine operators by their mileage, and not by their output. To put it in a nutshell, he spoke about the absurd system of incentives, or lack of them, in the economy. He was excitable but somehow very rational. And for the first two or three years of perestroika Gorbachev was the same sort of innovator he had been when he was young. The innovative projects were always limited, within certain boundaries, and that, of course, was significant later on. Well, I understand him. Like all of us, Gorbachev had to have a dual nature. It was in his mind, in his soul. He knew well that the idea of reward for work well done was considered out of the ordinary but not quite heretical. You could experiment with something limited like that. But we were not allowed to make any political or philosophical conclusions suggesting that the system itself was a failure. In your mind, you avoided such conclusions. You were simply incapable of thinking that way. To think that way was not only career suicide but a form of despair. And so, like the rest of us, Gorbachev hedged—outwardly and within himself.”
Karpinsky and his friends were at first not much upset by Brezhnev and Suslov’s overthrow of Khrushchev, in 1964. When Karpinsky heard the news, he and Yegor Yakovlev celebrated over a bottle of cognac. Khrushchev had long since tightened restrictions on the press and the arts, and had become prone to unpredictable decisions—a manic “voluntarism,” as the Party language had it. Only years later, when Khrushchev was a sad old man living in exile at his dacha, did Karpinsky call him, to wish him well on his birthday. Karpinsky said that he was calling on behalf of “the children of the Twentieth Party Congress,” and that Khrushchev should know that one day history would make clear to everyone the importance of that session, in 1956, at which he levelled his first attacks against Stalin’s “cult of personality.”
“I have always believed this, and I am very pleased that you and your relatively young generation understand the essence of the Twentieth Congress and the policies I initiated,” Khrushchev replied. “I am so happy to hear from you in my twilight years.”
It did not take Karpinsky or anyone else long to realize that Brezhnev had no intention of making reforms. Just the opposite. A neo-Stalinist movement was in the works. One night at dinner with Yevtushenko and Otto Latsis, Karpinsky began to speak out about what was happening to his generation, to its cast of mind. “Our idea was this: when one has an education in philosophy and a certain intellectual background, one begins to understand the inner properties of reality—something I termed intellectual conscience,” he told me. “It’s not a natural, inborn conscience but a conscience that stems from a kind of thinking that links you with a moral attitude toward reality. If you understand that everything in this society is soaked in blood, that the society itself is heading toward collapse, that it is all an anti-human system—if you understand this instinctively and intellectually—then your conscience cannot remain neutral. Look, I never really took any risks, and didn’t want to. I was sort of compelled by my conscience to take what steps I did. And, once compelled to take those steps, I could never foresee the bad consequences. Every time, I thought I’d get away with it. And, every time, I didn’t.”
Karpinsky made his first real foray into the netherworld of “half-dissent” in 1967, and it was a personal disaster. He and a friend at Pravda , Fyodor Burlatsky, wrote an article in Komsomolskaya Pravda calling, in a euphemistic way, for an easing of censorship in the theatre. Karpinsky now says that the piece was “half-rotten,” especially its solipsistic arguments that the best way to eliminate anti-Soviet sentiments from the theatre would be to let the people, and not the official censors, decide. That way, the authors said, the playwrights would have no right to complain about the government, and so would be deprived of a source of anger and subject matter. But the article, “On the Road to the Première,” contained one idea, plainly stated, that caused an uproar when it appeared: the personality cult, Karpinsky and Burlatsky said, had been criticized only lightly, and the censors were preventing anything deeper.
Brezhnev, who had already begun the ideological rehabilitation of Stalin, was furious when his aides brought the piece to his attention. He took the article as a personal attack. By chance, the article had appeared on the same day that a member of the Central Committee criticized the military industry, which had been Brezhnev’s province before he became general secretary. Karpinsky, Burlatsky, and the editor of Komsomolskaya Pravda were fired. Karpinsky was quickly appointed to a job at Izvestia , but after he made a few critical remarks at a meeting of that paper’s Communist Party committee he was eased out of there, too.
Despite his inherited romantic view of Bolshevism and his own pleasure in the perquisites of power, Karpinsky could no longer hide his disaffection. The invasion of Czechoslovakia, in August of 1968, was for Karpinsky and many of his friends a breaking point. He did not join the seven young protesters who went to Red Square with banners and were arrested and sent to prison or a psychiatric hospital or into exile. Nor did he form any links with Andrei Sakharov or other leading intellectuals who had decided, once and for all, to give up their lives in the hierarchy for the dangers of political dissidence. But he did act. Under the pen name L. Okunev, Karpinsky wrote a long article called “Words Are Also Deeds,” for circulation only among a select group of friends and would-be reformers within the world of the Party and its official academies. (The article was published abroad in 1982 in Stephen F. Cohen’s book “An End to Silence.”) The pseudonym was an inside joke: “Karpinsky” derives from “carp,” and “Okunev” from “perch.” In the article Karpinsky argued that free thought—and not “rows of armed soldiers, insurgent crowds, columns of revolutionary sailors, or a volley from the cruiser Aurora”—would one day challenge the Soviet system. Furthermore, the state structures and ideological machinery would not be able to resist, for the system “lacks any serious social basis. It cannot convince anyone of its fertility and hangs on only by the instinct of self-preservation,” he wrote. “The farce of neo-Stalinism we are passing through is just the outward expression of the ‘uneasy forebodings’ the petty tyrants feel. They long for the old regime, the ‘Stalin fortress,’ but they find only decrepit foundations, too weak to support such a structure.”
The article, like nearly all of Karpinsky’s writings, is clogged with indirection and filler, great clots of the undigested verbiage of the typical Party apparatchik. It was, however, remarkable not only for its moments of clarity and daring but also for its prescience. Here was an apparatchik (“We are pinning our hopes on you,” Suslov had said) who now believed no more in the viability of the Bolshevik state than did Berdyaev, Sakharov, Amalrik, or Solzhenitsyn.
“Our tanks in Prague were, if you will, an anachronism, an ‘inadequate’ weapon,” Karpinsky wrote. “They ‘fired’ at—ideas. With no hope of hitting the target. They ‘dealt with’ the Czechoslovak situation the same way that at one time certain reptiles ‘dealt with’ the coming of the age of mammals. The reptiles bit at the air, gnashing their teeth in the same ether that was literally seething with the plankton of renewal. At the same time, fettered by their natural instincts, they searched for ‘hidden stocks of weapons’ and diligently occupied the postal and telegraph offices. With a fist to the jaw of thinking society, they thought they had knocked out and ‘captured’ its thinking processes.”
Karpinsky also provided an insider’s view, identifying within the monolith of the Party structure “a layer of Party intellectuals.” He went on to say, “To be sure, this layer is thin and disconnected; it is constantly eroded by coöptation and promotion, and is thickly interlaced with careerists, flatterers, loudmouths, jesuits, cowards, and other products of the bureaucratic selection process. But this layer could move toward an alliance with the entire social body of the intelligentsia if favorable conditions arose. This layer is already an arm of the intelligentsia, its ‘parliamentary faction’ within the administrative structure. This faction will inevitably grow, constituting a hidden opposition, without specific shape and not aware of itself, but an actually existing and widely ramified opposition at all levels within the administrative chain.”
And that is precisely what happened between 1985 and 1988. The dissidents were the bravest and most clear-minded of all, but in the early Gorbachev years they did not provide, in numbers or in force, an adequate army. As if from nowhere, intellectuals within the Party, the institutes, the press, and the literary, artistic, and scientific worlds slowly took a Soviet leader at his word that this would be a different age. For once, the purposes of a Kremlin leader and the liberal intelligentsia intersected.
The tragedy was that by the time Gorbachev came to power there were so many broken lives: great minds lost to emigration, drink, suicide, despair, or sheer cynicism. “So many people had been destroyed,” Karpinsky said. “You can maintain that split way of thinking for a while, but then you begin to degenerate and start to speak only what is permitted, and the rest of the conscience and the soul decays. Many people did not survive to perestroika . We had to create an internal moral system, and not everyone could sustain that indefinitely. Solzhenitsyn spoke about this in his essay ‘Live Not by Lies.’ I understood his viewpoint, and we tried not to live by lies, but we couldn’t always manage it. If you ignore the regulations of the state completely, and go into total dissidence, then you can’t have a family: you don’t know where you will get rent money, and your children would have to go into the streets to scrape up a living. To fulfill this principle of not living under a lie in every aspect is just impossible, because you live in a certain time.
“Compared with the people who were not afraid of prison, my friends and I were not heroes. We abstained from direct acts. This position was itself a compromise. But it was the sort of compromise you make when you are in a cage with a lion. It is understandable, though nothing to be proud of. When I myself was in the position of having to say what I felt, I said it. I just didn’t deliberately try to put my head in a noose. I used Aesopian language. I had to use hints about progress—nothing more. What we did publish only hinted at our real thoughts.”
But “Words Are Also Deeds” went far beyond Aesopian language. In 1970, Karpinsky gave a copy of his text to Roy Medvedev, the Marxist historian. A few months later, Medvedev called Karpinsky and told him that the K.G.B. had ransacked his apartment and taken every manuscript in sight, including “Words Are Also Deeds.” For a few years, Karpinsky was oblivious of the trouble he was in. He bounced around from job to job, from a sociology institute to editing Marxist-Leninist works at Progress Publishers. But in 1975, when he was caught working on the manuscript of his friend Otto Latsis’s book “On the Eve of a Great Breakthrough,” an analysis of collectivization and Stalinism, the K.G.B. called him in. Naturally, the interrogator was an old friend: a Komsomol colleague named Filipp Bobkov, who had become one of the most infamous figures in the Soviet secret police. Karpinsky tried to soften up Bobkov. “When you came to me, there was tea and cookies,” he told him. “You don’t even offer me tea. It’s not very polite.” Bobkov was not amused. He passed the damning documents along to the Communist Party Control Committee, and Len Karpinsky, the son of Lenin’s friend and the Party’s great hope, was expelled. Suslov, for one, viewed Karpinsky’s transgressions as a personal betrayal.
Now Karpinsky did whatever he could to make a living—among other things, commissioning paintings and monuments for a state agency, for which he received a minuscule salary. He kept up his friendships, talked politics, and for a while lived at the dacha he had inherited from his father. The moment of reckoning he had written about in “Words Are Also Deeds,” the advent of dissent as a cultural and political fact of life, seemed years off.
Even after Gorbachev took power, in March of 1985, Karpinsky never dreamed that change could happen so quickly. And, at first, it did not. Although the liberals in the Politburo secured the editorship of Moscow News for Karpinsky’s friend Yegor Yakovlev and told him to transform the tourist giveaway sheet into “a tribune of reform,” glasnost was initially a process of hints, insinuations. To read now through a stack of Moscow News issues from 1987 and 1988 is to get lost in a blur of non-language. The barriers were immense at first, the victories almost unbearably difficult. When the editors of Moscow News wanted to print a simple obituary of the writer Viktor Nekrasov, the Politburo itself had to give permission, and did so only after long debate.
“But still the change was tremendous,” Karpinsky said. “The difference between the thaw and glasnost was a difference in temperature. If the temperature under Khrushchev was two degrees above zero Celsius, then glasnost pushed it to twenty above. Huge chunks of ice just melted away, and now we were talking not only about Stalin’s personality cult but also about Leninism, Marxism, the essence of the system. There had been nothing like that under Khrushchev. It had been just a narrow opening, through which only Stalin’s cult could be seen. There had been no real changes. And, as we saw, it could all be reversed. The bureaucracy, the Party, the K.G.B.—all the repressive apparatus in charge of the intelligentsia and the press—were in place.”
For Karpinsky, Moscow News provided the opening to a public hearing and also to a rehabilitation. In March of 1987, he published a long article entitled “It’s Absurd to Hesitate Before an Open Door.” Like his liberal pieces of the past, it was a mixed performance. He made sure to blast the West for what he thought was its phony concern for the Soviet dissidents, but he also made a crucial point that was then getting close consideration within the government: the critique of Stalin begun in 1956 would have to go deeper. Reform without a thorough assessment of the country’s “core” problems, the rottenness of its history and foundations, would be meaningless.
Karpinsky wanted to rejoin the Party, not only as personal vindication but also in order to play a role in what was still the central institution of political power. At a meeting with the chairman of the Party’s Control Committee, however, the hard-liner Mikhail Solomentsev mocked Karpinsky. From a thick stack of papers that had obviously been compiled by the Party and the K.G.B., Solomentsev pulled out a copy of “Words Are Also Deeds,” and, holding it up, he shouted, “You still have not disarmed ideologically! Nothing has changed in our party!” But things had changed. The sharp ideological divisions within the Party had become an open secret, an open struggle, and the trick was to get the support of powerful liberals within the structure. Three old friends of Karpinsky’s—Yuri Afanasyev, Nikolai Shmelyov, and Yuri Karyakin—brought to the Nineteenth Special Party Conference, in June of 1988, a petition demanding his rehabilitation. With the help of his old acquaintances Aleksandr Yakovlev and, amazingly, Boris Pugo, the gambit worked. By the next year, Karpinsky was in the regular rotation as a columnist at Moscow News —a golden boy, he says, “of a certain age.”
In the past few years, Moscow has been a newspaper fanatic’s dream. Karpinsky’s columns and Moscow News are only a part of the morning haul. Having started from nothing, from the jargon of the Communist Party press, Moscow has become the most exciting newspaper city since New York after the Second World War. The thaw was a liberalization dominated by a few works of real literature, but glasnost has been a period of journalism—of investigation, history, sensation, commentary, and scoop. At first, the most obvious mainstays of glasnost were Moscow News and the weekly magazine Ogonyok. But, as glasnost evolved into more genuine freedom for the press, the democratic vista widened. Today, there are the breathless papers that rush to the aid of the Yeltsin cause: the semi-official daily, Rossiiskaya Gazeta , and, with a circulation of twenty million, Komsomolskaya Pravda . Literaturnaya Gazeta prints a blend of high-minded cultural criticism, political analysis, and Yuri Shchekochikhin’s investigative work on the K.G.B. Argumenty i Fakty , with a circulation of more than twenty-five million, is a kind of weekly bulletin board of two-hundred-word articles and factoids. When it ran a poll a couple of years ago revealing Andrei Sakharov’s enormous popularity and Gorbachev’s slump, Gorbachev had a public fit and threatened to fire the editor. (Instead, he fired the hawkish editor of Pravda , Viktor Afanasyev.)
The former government organ Izvestia held a putsch of its own in August, tossing out its apparatchik editor, Nikolai Yefimov, and replacing him with a team that has made Izvestia the daily paper of record: stolid, wealthy, rich with foreign news, humorless. Izvestia ’s series on Moscow’s destruction of Korean Airlines Flight 007 was at least as good as anything on that subject published in the West. For tabloid sensation, there are Top Secret ’s true-crime stories (“Murder on Kutuzovsky Street!”) and Megapolis-Express ’s local muckraking. The puckish Kommersant , edited by Yegor Yakovlev’s son Vladimir, covers the emerging business world, letting young entrepreneurs know which clan rules which district and how to find cheap computers on the black market. In train stations and on street corners, hawkers do a brisk business in Baltic sex papers, mimeographed neo-Bolshevik sheets, and pirated copies of a booklet called “How to Find a Job in America and Europe.” For nostalgia’s sake, it’s still worth reading Pravda as it tries desperately to prove, out of the side of its mouth, that it never really meant what it had been saying for almost a century. Lately, Pravda has become the mouthpiece of a neo-Bolshevik movement, but, like Bolshevism, it may soon go out of business. And for the hard-liners there is Sovietskaya Rossiya , which published the key manifestos leading up to the coup, and Dyen (“The Newspaper of the Spiritual Opposition”), edited by Aleksandr Prokhanov, a theocratic militarist known affectionately as the Nightingale of the General Staff. Among the wire services, the old Big Brother of the ticker, TASS, which is now known as ITAR-TASS, has been neutered and taken over by the Russian government, while Interfax and a few agencies in the other republics have the manic intensity of the Associated Press on a good day. Interfax’s leading reporter, Vyacheslav Terekhov, is a bulldog in a brown suit, pestering politicians and filing dispatches from breakfast until midnight. He scooped the world by several hours last August when he reported that Gorbachev would dissolve the Communist Party.
Until 1988, or 1989 at the latest, Moscow News remained the country’s singular iconoclast, always smashing idols just before the reformers in the leadership did. In any given week, a foreign reporter in the Soviet Union could sit down with a copy of Moscow News and simply rewrite two or three of its revelations to make news at home. The hard-liner Yegor Ligachev called Moscow News an “ersatz” paper, but Gorbachev, Shevardnadze, and Aleksandr Yakovlev obviously felt otherwise. Moscow News was clearly the voice of the liberals in the Politburo. But the lack of real independence at Moscow News , its link to Gorbachev himself, began to work against it in 1990 and 1991. As the country became more diverse, as the liberal intelligentsia’s ideas about the future of society and politics grew far more radical than Gorbachev’s own, Moscow News , under Yegor Yakovlev, began to look a bit timid and almost comically protective of its original patron.
“Without realizing it, Yegor was turning Moscow News into Pravda ,” I was told by Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s editor, Vitaly Tretyakov, who was Yakovlev’s deputy at the time. “Just as Pravda was the tribune of the old powers, he wanted Moscow News to be the tribune of the new power, the left-of-center position, the Gorbachev position in the Politburo. When I became Yegor’s deputy, I began to see how many visitors and calls there were from the Central Committee, and it was obvious that the paper was not operating independently. Len Karpinsky was much more radical than Yegor, but Moscow News could be only as radical as Yegor would allow it to be. Yegor has the personality of a dictator, and that may be necessary, but he always wanted to be in possession of ultimate truth—he claimed to know all the answers. None of us at Moscow News could take a step without Yegor’s say-so. You couldn’t mention Lenin, for instance, because Yegor thought he knew all there was to know about him. And then there was Gorbachev: we could not criticize him directly. And what could someone like Len do? After all, it was Yegor who pulled Len out of obscurity and got him a job.”
By the summer of 1990, millions of people were quitting the Communist Party. The party that called itself “the initiator of perestroika ”—an appalling bit of self-congratulation, considering the blood on its hands—had lost the power to convince many of its own members that it supported radical change. At Moscow News , Tretyakov proposed that the members of the paper’s Party committee all resign as one. But Yakovlev said no, they should “stay the course.” As usual, Yakovlev had the votes, Karpinsky’s included.
Tretyakov was feeling more alienated by the day from his colleagues at the paper. He was not a man of the Gorbachev generation, and he did not have the Old Bolshevik background and Party connections of so many of the shestidesyatniki . His parents were laborers. Tretyakov had worked for years on some of the glossy propaganda magazines that the government printing organs ground out like sausage meat: Soviet Life , Études Soviétiques , Soviet Woman , and the rest. His time at Moscow News was “a gift,” but, he decided, the time had come to leave. “My idea was to start something new, a better Moscow News ,” Tretyakov said.
After spending a couple of weeks recently at Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s offices and sitting in on editorial meetings, I realized that Tretyakov had had very little idea of what he wanted when he held his first planning sessions, in the summer of 1990. He knew only that he did not want to tie the editorial direction and the tone of the paper to the fate of Mikhail Gorbachev or any other political personality. At first, he tried to induce some of the best-known writers in Moscow to join him. They all turned him down. No one with a family and an established position was prepared to risk them on an experiment, a notion. Tretyakov’s one essential break came with the election of liberal democrats to Moscow City Hall. The new mayor, Gavriil Popov, and his deputy, Sergei Stankevich, were interested in Tretyakov’s idea, and gave him a start-up loan of three hundred thousand rubles. No strings attached, Popov said. Remarkably, the city officials kept their word. They have never considered the paper their own, and have never interfered in editorial or business policy. “It was just a small investment in the transition to a free press,” Stankevich said.
I had heard about the paper long before its first issue appeared. One summer afternoon two years ago, I drove to the country town of Peredelkino to visit Andrei Karaulov, a young theatre critic, and his wife, Natasha, who is the daughter of the playwright Mikhail Shatrov. Karaulov was a journalist-hustler the like of which I have never seen—at least, not in Moscow. Even in the early days of perestroika , he managed to get interviews with one Politburo member and spymaster after another. He somehow made patently evil and slimy men feel comfortable, then tortured them with a combination of unctuous charm and barbed questions. He even managed to get me in to see Gaidar Aliyev, a member of the Brezhnev circle, who has been described by the Moscow jurist and writer Arkady Vaksberg as “the living definition of the Mafia man.” Karaulov’s knack was so uncanny that some of his rivals moaned that he must have “dark connections.” Another guest at the Peredelkino dacha that afternoon was a man in his early forties named Igor Zakharov. Zakharov turned out to be just about the most cynical man I have ever known, and he seemed to scorn himself most of all. He had worked for years at the Novosti Press agency, editing propaganda magazines with Tretyakov. “I am a born functionary,” he said. “I never believed in anything official—not in Communism and not in the possibility of perestroika . I may have published all that shit, but I never believed it. You know that expression ‘Life is elsewhere’?” But this willingness to work with odious bureaucrats while holding opposing beliefs seemed to arouse less sympathy for him than it did for Karpinsky. It was somehow touching that Karpinsky actually did believe in something when he was young and then believed in something else later on. Zakharov believed in nothing but the hopelessness of almost everything, and the sudden advent of radical changes in the country made his cynicism seem worthless. So when he and Karaulov began telling me about their work with Vitaly Tretyakov on a new newspaper, to be called Nezavisimaya Gazeta , not only did I think it would fail—I also hoped that it would.
I forgot about that discussion and Nezavisimaya Gazeta until six months later, when, in December of 1990, I was on a plane from Riga to Moscow. Eduard Shevardnadze had just resigned, and the Balts suspected that they were about to become the targets of the crackdown that Shevardnadze had been warning about; they were proved tragically correct the following month. On the plane, I borrowed two issues of an unfamiliar broadsheet—the first and second issues of Nezavisimaya Gazeta —and I was startled. The front page of the first issue featured little mug shots of the country’s political leaders, and above the pictures was the headline “They Rule Us: But What Do We Know About Them, the Most Powerful People in Our Country? Almost Nothing.” On page 5 (“Ideas and People”) the historian Yuri Afanasyev published what was surely the year’s most incisive piece of political commentary: “We Are Moving to the Side of Dictatorship.” In details that proved absolutely accurate, Afanasyev described Gorbachev’s “tragedy”—how his own internal and political limitations left him open to the pressures of the hard-line Communists in the regime. It was just the sort of political critique of Gorbachev that Moscow News could not bring itself to publish. Then, on page 8 of the first issue—the back page—was a manifesto by Tretyakov declaring that there had never been “in the history of the Soviet Union” a paper independent of political interests. He would publish one. The second issue led with the headline “Eduard Shevardnadze Leaves. The Military-Industrial Complex Stays. What Choice Will Gorbachev Make?” A few pages later, Karaulov weighed in with a fascinating interview with the No. 2 man at that time in the K.G.B., Filipp Bobkov—the man who had interrogated Len Karpinsky fifteen years earlier.
One day during those first weeks of Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s life, I went to the paper’s offices with Karaulov. As we walked along the muddy streets near the K.G.B. buildings, he was trying to sell me—literally—some crackpot spy-story documents involving the Bolshoi Theatre. Information is constantly for sale now in Moscow. The Russian prosecutor assigned to investigate the August coup charges at least five hundred dollars for interviews about his work. “Interviews are creative works,” he says. When I refused Karaulov’s “tip” on the Bolshoi and explained Western rules about not paying for information, he seemed alternately bemused and hurt. “Besides, you’d never find the place without me,” he said. “You owe me for that, at least.” He had a point. Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s offices are tucked away in an obscure courtyard building not far from Lubyanka Square. At the time, the paper shared the building with the Voskhod (Sunrise) printing company. Expansion eventually eased the printers out. The paper originally had twenty people on its staff and appeared three days a week; now it has two hundred and appears five days a week. When I first visited the office, the place was a sea of paper and ironic memorabilia—faded portraits of old Politburo members a specialty. No one looked as if he had slept, showered, or shaved in days.
Rejected by the older newspaper stars, Tretyakov got his journalists wherever he could find them. Most of them had worked at second- or third-tier publications—at movie and theatrical quarterlies, Baltic underground sheets, Komsomol dailies. Some had no journalistic experience at all. They were biologists, secretaries, manual workers, students, diplomats—anything. Whatever skills they did or did not have, they had a unanimous contempt for all things sovok —a slang term for “Soviet.” (The staff’s favorite early fan letter read “Congratulations: You are neither pro-Soviet nor anti-Soviet. You are simply non-Soviet.”) All were young, and they did not bother to struggle with the questions of their elders. The ideological ruminations of a man like Len Karpinsky were for these people irrelevant and just a little bit sad.
Mikhail Leontiev, the paper’s economics editor, who was thirty-three years old, was a typical new employee. He had studied economics at the Plekhanov Institute, in Moscow, but to avoid doing “idiot work for the regime” he quit the academic world and worked for years restoring old furniture. He hardly ever wrote then, he told me. “Why bother?” He did write one prescient essay for a Latvian paper in 1989; called “The New Consensus,” it dealt with the growing front of Fascists, nationalists, and military leaders. “That was about all I could do,” Leontiev later told me between meetings at Nezavisimaya Gazeta . “I just couldn’t work for any of the old papers. Coming here, discovering Nezavisimaya Gazeta , was a revelation—the revelation we were all waiting for. The coverage of economics in our paper starts from the principle that we don’t need to tear our hair out about whether Marxism-Leninism or capitalism is the right way to go. That debate is as dead as can be. Do we really have to go crazy over whether it is good to find a healthy balance between efficiency and social welfare? About whether the rules of the market are ultimately correct? I don’t think so. I don’t cover Communism or any other religion in these pages. That’s not my business.”
The darkening political mood in the winter of 1990-91, the ominous sense that the Army, the K.G.B., and the Communist Party were now forming an open alliance against a radical reform of the country, gave the paper a clear sense of purpose. To Muscovites reading Nezavisimaya Gazeta in its first month of publication the new paper conveyed an understanding of and a foreboding about the political earthquake to come. Not so Moscow News , which still kept its reports within certain bounds. Moscow News was now responding not to censors—they had been either removed or rendered completely benign—but, rather, to an internal sense of propriety and caution, a lingering reverence for Gorbachev and the old hopes of the thaw generation.
All this changed on the streets of Vilnius. The bloody, and failed, coup attempt in Lithuania in January of 1991 changed everything for nearly all the middle-aged and older intellectuals who had remained loyal to the idea of a reformed Communist Party. While Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s staff was reporting the story of the Lithuanian coup attempt as if it were the logical extension of the events of the months before, Moscow News suddenly went through an ideological conversion. It lost all faith in Gorbachev. Karpinsky, Yegor Yakovlev, and a long list of shestidesyatniki signed a front-page editorial expressing outrage at the assault and declaring that the regime was “criminal” and was well into its “death throes.” For so long, most of these men and women had thought in terms of a socialism made somehow humane, of a steady pace of reform. Yakovlev, especially, had never liked Boris Yeltsin—never liked the way he attacked Gorbachev or conducted himself. Now this generation had nowhere to go but to Yeltsin and to the people Gorbachev had venomously referred to as “the so-called democrats.”
The staff at Nezavisimaya Gazeta viewed the conversion of Moscow News as pathetic. “The truth is, I could never understand why those people decided to make their split only when the tanks rolled into Vilnius,” Igor Zakharov said later. “It’s like trying to figure out why a woman who hates her husband for twenty years finally decides one day, after one little incident, to get up, walk out, and never come back.”
The dreams and the delusions of the editors at Moscow News died slowly. In March, Yakovlev invited Karpinsky and a few other friends to his apartment for a sixtieth-birthday party. “It was a meeting of people who didn’t know what to say to one another,” Yakovlev’s son Vladimir said. “The energy they used to have was gone, and the world around them was no longer their world. And, most important, they didn’t know how to relate to this new world. It was the feeling you get at the gatherings in Russia forty days after someone dies. No one is crying anymore, but no one knows quite what to say. These birthday gatherings had always been such celebrations. Now it was just all silence, a complete breakdown.”
Week after week, Nezavisimaya Gazeta was reinventing the newspaper in Moscow, and a twenty-seven-year-old reporter named Sergei Parkhomenko was consistently the paper’s most incisive political commentator. The son and grandson of journalists, Parkhomenko first won a name for himself at the monthly Teatr when he covered the first session of the Congress of People’s Deputies, in May of 1989—a job he called “the ultimate in theatre criticism.” He told me, “Imagine if you in America had held the Constitutional Convention live on television. The old order died a little every day. No play ever changed an audience more thoroughly.”
One night, I went with Parkhomenko to the printing presses at Izvestia , where Nezavisimaya Gazeta is published. He was the night-duty editor, acting as a liaison between the printers and the editors back at the Gazeta office, who are constantly trying to shove late items into the paper. He had already written a column in the morning and had called in a few items for his after-hours job as a stringer. Like many good young reporters in Moscow, Parkhomenko had discovered that he could make some hard currency on the side by working for a foreign news organization—in his case, Agence France-Presse, the official French wire service. As it turned out, the experience expanded his feeling for journalism. “With the French, I got a taste of real reporting,” he said. “It was a new sort of game. Who can be the first to get the information? Who can get sources? Before, it was all ‘I think this, I think that.’ Now the game had changed, and I loved it, and the skills were just what I needed. You see, I somehow always knew I would work at a place like Nezavisimaya Gazeta . I knew it instinctively. I wanted a place that was born without any complexes. There are more radical publications, but I’m not interested in the contest for who can be the most radical or liberal. I can’t stand unity and consensus.”
Parkhomenko is best known in Moscow for his commentaries—mainly because he refuses to shill for any one politician or party line—but he is also an instinctive investigative reporter. Last year, he caused a terrific scandal when he discovered that the Central Committee had for years been running a huge, fourteen-room workshop for manufacturing fake Western passports. He reported that there were fake stamps, blank passports for dozens of foreign countries, and even false mustaches and beards for the passport photographs.
Investigative work has been a signature of the front page of Nezavisimaya Gazeta . A married couple in their twenties at the paper, Anna Ostapchuk and Yevgeny Krasnikov, enraged the Party last summer when they scooped everyone by printing a copy of the Communist Party’s proposed new platform, endorsing a “democratic, humane socialism.” Ostapchuk’s methods were “quite simple and un-Soviet,” she told me. She had gone to the apartment of a Central Committee member, Vasily Lipitsky, and began asking about the platform. He gave her the document, which was twenty-three pages long and had been written by Gorbachev’s aide Georgi Shakhnazarov, and said she could read it, “but no notes and no tape recorders.”
“Then something odd happened,” Ostapchuk said. “Lipitsky said he had to take a phone call in the next room. As soon as he left, I got out my tape recorder and read the thing as fast as I could. He didn’t come back in time. I finished. But I’m sure he wanted me to do just that. It was terrific fun.”
Presented with the scoop, Tretyakov was stunned. At Moscow News , his bosses would never have permitted such a thing—too dangerous, a distinct lack of respect. But Tretyakov immediately published the piece. In a wry note to the readers, he wrote that ordinarily Nezavisimaya Gazeta did not print party manifestos and platforms, “because that would be a form of advertising,” and added, “But from such a party we would rather not take any money.”
The next day, as every newspaper in Moscow scurried to catch up with the story in Nezavisimaya Gazeta , Parkhomenko got a swift lesson in the sensibilities of the powerful. At a small, late-night press conference in the Moscow suburb of Novo-Ogarevo, Gorbachev looked at the reporters and said, “O.K., so who here is from Nezavisimaya Gazeta ?”
The reporter from state television, a whinnying timeserver, blanched and panicked. “No, no, it’s him,” he said, pointing at Parkhomenko.
“Where did you steal it from?” Gorbachev said.
“I can’t say,” Parkhomenko said.
“And why not?”
“Because that’s the way we work.”
After the press conference, two of Gorbachev’s aides tried to weasel the information out of Parkhomenko.
“Oh, come on,” one of them said. “You can tell me. I won’t tell another soul!”
Shakhnazarov, for his part, told me that he was shocked to see his work in the paper. “Woodward and Bernstein—that is not exactly something we’re used to,” he said.
Sometimes Tretyakov and Zakharov, the village elders at the paper, are scared by their own reporters—by the reporters’ relentlessness and giddy fearlessness. They are well aware of how inexperienced the reporters are, how little they know about degrees of reliability and balance. Often, reporters will turn in stories that are little more than rumors that seem too good to check. But, while the top editors often demand more reporting and numerous rewrites, they have seldom killed stories. According to everyone at the paper, the only story that Tretyakov refused to run without further questioning was the stuff about the K.G.B. and the Bolshoi Theatre that Karaulov had been trying to peddle to me.
“The reason these kids do things like investigative work is that they not only don’t fear the system—they don’t even respect it,” Zakharov said. “These kids are arrogant, silly, uneducated, and undisciplined, and they live only in the present. They don’t care about yesterday and have no idea that there is nothing new under the sun. But they have no prejudices. They don’t think ahead and wonder if someone at the Kremlin will think this or that about what they do. They just go ahead and do it.”
The young reporters have also changed the language of newspapers. They have dispensed with the wooden bureaucratese and fanatic sloganeering of the Soviet period. “We don’t talk Pravda language,” Parkhomenko said at the printshop.
Before I moved to Russia, I took a course at George Washington University in something my classmates and I called “newspaper Russian.” For weeks, we memorized endless lists of political clichés: “The talks were held in a warm and friendly atmosphere”; “The peace-loving comrade-nations of the world will face the imperialists in a round of negotiations next week”; and so on. It was the language of Novoyaz , or Newspeak, and nowhere had it reached such a level of absurdity as in the Soviet Union. But Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s younger reporters had never had to write that way—or, at least, not for long. While someone like Len Karpinsky still has trouble removing the Novoyaz sludge from his prose—“I try, but I can’t always get it clear”—the Nezavisimaya Gazeta writers work under no such handicap.
“Right away, we tried to imitate Western language,” Parkhomenko said. “In Russian, there had never been the political language of a civilized country. So we adopted phrases like ‘the Yeltsin administration’—how could you talk about ‘the Brezhnev administration,’ or even ‘the Gorbachev administration’? At a certain point, we had to use Western terms for what had become, essentially, Western politics. All the old phrases of Pravda went out the window. The same was true of economics—we had to accommodate ‘investment,’ ‘entrepreneurship,’ and all the rest. Where we don’t imitate the Americans is in the question of point of view. We make no bones about the fact that the reporter is making some evaluation of what has happened. For us, the guarantee of fairness or objectivity is not that the reporter has no opinion but, rather, that the paper as a whole will hold a wide range of opinions.”
Tretyakov likes nothing better than to keep all political sides slightly angry with him. Yeltsin’s former press secretary, Pavel Voshchanov, wrote letters of complaint, expressing incredulity at how an independent newspaper could be so critical of a democratic leader. When Gorbachev’s popularity was at its lowest, last spring, Tretyakov wrote a piece called “Apologia for Gorbachev,” which did not dispute the attacks on Gorbachev but did remind readers of the Soviet President’s accomplishments since he came to power. In the West, the piece might have seemed self-evident, even a last roar of Gorbymania. But in Moscow, where Gorbachev was alone in a political “center” that existed nowhere except in his mind, Tretyakov’s piece, with its insistence on Gorbachev’s extraordinary achievements of ending the Cold War and the arms race, and creating democratic parliaments and a free press, was a contrarian bombshell. The Yeltsin forces wondered just what this new paper was up to. “And that is just the way I like it,” Tretyakov said.
But, of course, it was the August coup and Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s coverage of the ensuing collapse of the Soviet Union that insured the paper’s reputation. Even now, months later, there is at the paper a distinct nostalgia for the August events—a longing for the excitement and camaraderie. Small wonder. Vladimir Todres, a twenty-five-year-old political reporter, said that he and his friends at the paper saw the coup as the defining event of their generation—the street-level, media-age equivalent of what the Twentieth Party Congress was for Karpinsky, Gorbachev, and the thaw generation.
“For us, the putsch was not simply a matter of politics,” Todres said. “Usually, we hate politics, to tell you the truth. But this was the Pepsi Generation under threat. Our very existence was in jeopardy. The bikers feared for their motorcycles. The young businessmen worried about their markets. The racketeers even thought about their bottom line and came to defend Yeltsin’s White House. Prostitutes, students, scholars—everybody—had an interest in this new life, and we were just not willing to give it all up to these old men. And, also, it was like being in a great movie. Life and art were all mixed up together. My friends who were abroad were heartbroken, not because they felt fear but because they felt left out. They couldn’t have a part in the movie.”
The journalism part of the movie was splendid. On the first day of the coup, Tretyakov decided not to defy the coup plotters’ press ban. His thinking was that a quick wrong move could endanger the staff and end the paper entirely. Some of the younger reporters were furious, especially after they heard that the printers at Izvestia were willing to defy the ban and work the presses. But Tretyakov insisted. The next day, as it became clearer that the coup leaders had neither the will nor the level of organization to mount a full-scale attack on the press as a whole, Tretyakov and the staff put out a Xeroxed version of Nezavisimaya Gazeta . This “underground” paper carried the lead headline “The Feeble Coup: It Is Still Not Over” and was filled with news about the putsch from Moscow and the provinces. At Moscow News , Karpinsky and editors of some of the other liberal papers published a makeshift Obshchaya Gazeta , or Common Newspaper .
In the meantime, the Nezavisimaya Gazeta reporters were working on the story—especially Parkhomenko and Pavel Felgenhauer, the paper’s defense analyst. Felgenhauer stayed in the White House throughout the three-day siege and was in constant contact with the military leaders planning Yeltsin’s strategy of resistance in their makeshift “war room.” Felgenhauer, a bearlike man who speaks English about as well as the average American college professor, never set out to be a journalist or a military expert. He has a Ph.D. in biology and won what he called “a measure of international fame” with his thesis, “RNA Synthesis During the Maturation of Frog Oocytes.” He told me, “I quit science because you can’t do science anymore in this country. We can’t even afford test tubes, or food for the frogs. So I became a journalist. I always liked to write.”
Felgenhauer had followed military affairs the way some American kids follow baseball. It was all a game, a combination of action and statistics. “Pavel is a kid who likes toy soldiers,” Parkhomenko said. “He’s a gigantic forty-year-old kid who is a genius. He loved the coup, because he got to play soldier and war correspondent all at once.”
Parkhomenko could not believe the look of supreme contentment in his colleague’s eyes as they sat in the White House. “As for me, I was terrified,” he said. “I thought I was a dead man—the romance of the White House is long gone. Now they try to say that it was all nothing, that there was never any danger. But that’s ridiculous. It was all a war of nerves, a dangerous telephone war. There were orders and counter-orders by phone. When the Russian government found out that a contingent of tanks was being sent, its people set up rows of gas cannisters so that there would be a huge explosion. Their strategy all along was to maximize the threat of bloodshed, to scare the shit out of the K.G.B. and the putschists by essentially using unarmed people as a shield. It was not an especially humane strategy, but it worked. The coup guys wanted a surgical operation, and the Russians made that impossible. Thank God, we lived.”
After the coup, the paper no longer seemed very new. What took decades at the New York Times took less than a year at Nezavisimaya Gazeta . Russia has entered the post-Soviet age with Vitaly Tretyakov’s brainchild as the country’s premier newspaper. “We have to face it,” Igor Zakharov said. “We’re the establishment now.” At Moscow News , Karpinsky became editor-in-chief late last August, after Gorbachev and Yeltsin put Yegor Yakovlev in charge of the state television bureaucracy.
The Nezavisimaya Gazeta reporters have discovered that respectability has its advantages. Felgenhauer now says that he gets secret military documents “by the boxful,” simply through the connections he developed while he sat with the Russian generals during the coup. A few months ago, two officers from military intelligence provided him with an exposé of incompetence in the agency. The only details Felgenhauer left out were “about a particularly juicy sex scandal—we have standards, unfortunately.”
Nezavisimaya Gazeta is getting better known all the time. At the moment, “no one exactly owns the paper,” Tretyakov said, but he is in the process of setting up a joint-stock operation, with all the employees investing and holding shares. The paper just made a million rubles from an advertising supplement and is buying I.B.M.-knockoff computers for a newsroom that will no longer resemble the set of “The Front Page.” Nezavisimaya Gazeta ’s reputation has grown so quickly abroad that many émigrés prefer it to New York’s Novoye Russkoye Slovo ( New Russian Word ) or the Paris Russkaya Mysl ( Russian Thought ). You can find the paper in Paris and at a few émigré bookstores in New York. Like Moscow News , Nezavisimaya Gazeta is now published in Russian in Israel, in English in the United States and Britain, and in French in France and other European countries. To get hold of more foreign currency, Tretyakov has started a wire service, called NeGa, so that news bureaus in Moscow can keep up with developments in the Russian provinces and former republics. He is also planning a tabloid (“for the lower-brow reader”), and is thinking about getting into radio and television.
But, while Tretyakov is nearly dizzy with success, he realizes that the euphoria around the paper’s office is long gone. The stretch last year when reporters worked for nothing and with no sleep is a memory. Zakharov is fed up with Tretyakov’s insistence on doing everything himself, and is thinking about quitting. The foreign editor hasn’t been getting along with Tretyakov lately, and he may go, too. Some of the youngest reporters, especially, worry that Tretyakov is becoming as autocratic as his old bosses at Moscow News were.
“In one year, the atmosphere around here has changed completely,” I was told by Yuri Leonov, who is twenty-three and writes about foreign affairs. “In the beginning, we sat together and divided up all the questions and decided things together. Now there is a ruling class. I feel like a rank worker all of a sudden—a peon. No one asks my opinion about anything. When we started out, Vitaly said, ‘Don’t you think we need a union?’ We all laughed, and said, ‘What for? Do you think we need a Communist organization?’ Well, now we have discovered that there is nothing to protect us.”
Tretyakov has listened to these complaints many times. After Tatyana Malkina talked with him for four hours one afternoon, recommending a return to the old, informal ways at the paper, Tretyakov showed up for work wearing a sweater and jeans, and constantly asked for suggestions at the morning editorial meetings. But within a couple of days he was back in his jacket and tie.
“Common sense tells me that two hundred people can’t all be friends,” he said to me. “Those days are over. We can’t continue to work in chaos. We can’t have people drinking in the office or Misha Leontiev coming late to every editorial meeting. I have to keep reminding people that this was my idea—I started this paper. If we run this place like a party, we can come up with a few euphoric issues and can all congratulate one another. But that is no way to run a newspaper month after month after month. We are a business now. That’s the brave new world. It’s time we recognized it.”
Just as Tretyakov finished on that stern note, there was a knock at his door. The entire staff had assembled, bearing gifts: a huge bunch of carnations and an eight-pack of Swedish cheese slices. “Remember,” said Tatyana Malkina, the head of the delegation. “We’ll always love you.” Vitaly Tretyakov blushed. It was his birthday. He had forgotten, but the staff had not. He was forty years old. ♦
New Yorker Favorites
Why facts don’t change our minds .
How an Ivy League school turned against a student .
What was it about Frank Sinatra that no one else could touch ?
The secret formula for resilience .
A young Kennedy, in Kushnerland, turned whistle-blower .
The biggest potential water disaster in the United States.
Fiction by Jhumpa Lahiri: “ Gogol .”
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Benjamin Kunkel

By Adam Gopnik

By Joshua Yaffa


IMAGES
COMMENTS
The FREEDOM is a luxurious motor yacht built by Benetti in 1999 and designed by Stefano Natucci. With her elegant and sleek design, she is a stunning sight to behold on the open seas. Specifications. This impressive yacht is powered by Caterpillar engines, giving her a maximum speed of 14 knots. Her cruising speed is a comfortable 12 knots, and ...
The 70.1m/230' motor yacht 'Freedom' (ex. Reverie) by the Italian shipyard Benetti offers flexible accommodation for up to 12 guests in 8 cabins and features interior styling by John Munford.. Built in 2000, Freedom is custom-built for world-class luxury yacht chartering, offering a wealth of spacious living areas and fabulous amenities, you'll be in for a treat from the moment you step on board.
The FREEDOM yacht is a 229ft / 69.8m luxury yacht built and launched by yacht builder Benetti. Delivered to a proud yacht owner in 2000 and refit in 2015, this luxury yacht sleeps up to 12 guests in 8/10 staterooms and has accommodations for 25 crew. She has a beam of 41ft / 12.5m, a draft of 12ft / 3.7m, and she measures in at 1,975 gross tons.
From the George Town yacht owner to globally recognized billionaires, the allure of owning a private yacht remains unwavering. The Influence of Wealth and Taste. ... Owning a yacht goes beyond flaunting wealth; it represents a love for the ocean and the freedom it offers. The ability to explore the world's waters in absolute luxury is an ...
The interior of the yacht features Roberto Cavalli's signature leopard wild prints, adding a touch of sophistication. Roberto Cavalli, a prominent figure in the fashion industry, is the proud owner of the yacht Freedom. The yacht is valued at $15 million, with annual running costs estimated at $2 million.
Freedom is a motor yacht with an overall length of m. The yacht's builder is Benetti SpA from Italy, who launched Freedom in 1999. The superyacht has a beam of m, a draught of m and a volume of . GT.. Freedom features exterior design by Stefano Natucci and interior design by John Munford Design. Up to 26 guests can be accommodated on board the superyacht, Freedom, and she also has ...
He is the owner of the fast motor yacht Freedom. The yacht carries his name on the stern. The Freedom yacht is a luxurious masterpiece owned by fashion designer Roberto Cavalli. Built by Cerri Cantieri Navali in 2018, it showcases exceptional craftsmanship and design. Powered by MAN engines and KAWEMA propulsion jets, the yacht offers ...
48.2m / 158'2 Radez 2019 / 2022. The 48.2m/158'2" motor yacht 'Freedom' by shipyard Radez offers flexible accommodation for up to 22 guests in 11 cabins. Motor yacht Freedom boasts a wealth of convivial spaces, perfect for luxury yacht charters with families of friends, offering ample opportunities to kick back and relax, or enjoy the water on ...
Superyacht Freedom is a rare gem on the high seas and one of only three of its kind in the world. Capable of hosting up to 24 guests across 11 exquisite staterooms, Freedom offers an array of lavish amenities over its four expansive decks, including two master cabins, a cinema, a spa, and a fully-equipped gym.
FREEDOM epitomises the sleek and sexy design of superyachts. Built by Sunseeker in 2017, she is one of the finest examples of the spectacular Sunseeker 116 Yacht series. Her GRP hull and superstructure are carved with striking exterior lines. Powered by Twin MTU 2,640hp diesel engines she can reach speeds of 25 knots and has a range of 1,250 nm ...
FREEDOM is a 41.93 m Motor Yacht, built in Italy by Benetti and delivered in 2018. She is one of 9 Crystal 140 models. Her top speed is 15.5 kn, her cruising speed is 14.0 kn, and she boasts a maximum cruising range of 4400.0 nm at 11.0 kn, with power coming from two MTU diesel engines. She can accommodate up to 10 guests in 5 staterooms, with ...
As Featured In. Interior & exterior photos of FREEDOM, the 70m Benetti Yachts super yacht, designed by Stefano Natucci with an interior by John Munford.
FREEDOM is a 38.1 m Motor Yacht, built in the United States of America by Westport and delivered in 2018. She is one of 9 125 models. Her top speed is 25.0 kn, her cruising speed is 22.0 kn, and she boasts a maximum cruising range of 2500.0 nm at 12.0 kn, with power coming from two MTU diesel engines. She can accommodate up to 10 guests in 5 ...
FREEDOM Yacht Price Summary. Status: This yacht is only on our website as a sold yacht. Learn about the FREEDOM yacht price and specifications below, along with a sampling of similar luxury yachts for sale. The listed luxury yachts for sale on this page range in size from 65m / 213ft to 83m / 271ft , while the median age is 17 years. The sale ...
The Acquisition. Off the Hook Yachts is proud to announce the acquisition of Georgetown Yacht Basin (GYB) now rebranding under Georgetown Yacht Haven - a 300-boat slip full-service marina located on the Sassafras River in Georgetown, MD. Off the Hook plans to restore the yacht basin to its former glory and reconnect with the local community ...
9 January 2012 • Written by Malcolm MacLean. Almost a year to the day since I reported that the 70m motor yacht Reverie had come on the market with Michael White and Peter Thompson at Ocean Independence, comes news of a $10 million price reduction. At the time of her build in 2000 she was the largest superyacht by tonnage built by Benetti and ...
Russia has been subject to major terrorist attacks starting from a series of explosions that hit Moscow apartment blocks in 1999, followed by the Moscow theater hostage crisis in 2002 and the Beslan school siege in 2004. There have been at least a half-dozen attacks in or near Moscow by Muslim terrorists, most of them Chechen militants, over the past 25 years.
Boasting a voluminous 2,562 GT, she proudly holds the distinction of being the inaugural yacht completed at Van Lent's innovative Amsterdam facility. Designed with precision by Feadship's De Voogt studio, Zen's sleek exterior spans five decks, featuring a spacious pool on the main deck, a sun deck Jacuzzi with forward views, and a chic ...
Surprisingly, the luxurious boats are priced rather modestly, and a single ticket goes for $17-$32 (1,100-2,000 rubles); also expect a reasonable restaurant bill on top.
Walking tour around Moscow-City.Thanks for watching!MY GEAR THAT I USEMinimalist Handheld SetupiPhone 11 128GB https://amzn.to/3zfqbboMic for Street https://...
ALASKA OF GEORGETOWN is a 43.89m an exceptional motor yacht build by Shipworks Brisbane in 2004 to the highest standards. She was designed by Bernie Cohen with Burness Corlett developing the naval architecture. With a massive volume of 457GT she offers ample space for Owner and guests, she can accommodate up to 10 people with 9 crew members.
Description: The George Town Yacht Club (GTYC) is located on the waterfront at The Barcadere Marina, Grand Cayman. Conveniently located next to the airport, with a FREE shuttle running every 15 minutes, it is a great place to spend time waiting for a flight. It is accessible by land or sea, with plenty of parking for your car or boat, and is ...
David Remnick meets the city's best-known newspaper editors, including the founder of Nezavisimaya Gazeta—"the closest thing Russia has ever had to a Western daily," he wrote, in 1992.