
- Advertising
- Shipbuilding
- Coastal/Inland
- Law & Regulations

TransAtlantic Speed Record: Will it Ever be Broken Again?

Posted by Greg Trauthwein June 22, 2015

Will the prestigious TransAtlantic speed and endurance record ever be broken? Should it?
Twenty five years ago headlines around the world announced a new world record, the fastest crossing of the Atlantic Ocean, by a ship built in Australia.
Incat Tasmania reports that June 23, 2015, marks 25 continuous years that Incat built fast ships have held the record for the fastest Transatlantic Crossing.
On 23 June 1990 Hoverspeed Great Britain, a ship (Incat hull 025) built by Incat in Tasmania, for operation between England and France by Sea Containers Ltd, broke the record for the fastest crossing of the Atlantic Ocean by a commercial passenger ship. The crossing from Ambrose Light at New York commenced at 7.30pm on June 19, 1990 ending her 2922 mile trip at Bishop Rock in the UK on the morning of 23 June.
The Hales Trophy is awarded to "The Ship which shall for the time being, have crossed the Atlantic Ocean at the highest average speed".. …So it is not simply reaching the highest speed momentarily, the right to fly the Blue Riband is a test of endurance as well, because the high speed needs to be maintained over the entire crossing (naturally slower at the beginning with a full fuel load and becoming faster at the end of the journey).
The previous record had been held for 38 years by the SS United States (1952 - 1990), prior to the SS United States win, the great liners vied for the honour to fly the Blue Riband. The Incat built high speed catamaran Hoverspeed Great Britain, which broke the record winning the Hales Trophy on 23 June 1990, held the record and the owners held the Trophy, until 1998 when another Incat built ship Catalonia took the record in June 1998, then just a month later in July 1998 yet another ship built by Incat, CatLink V broke the record. It was the first time in the history of the transatlantic records (dating back to the 1860s) that three ships to win the trophy in succession had been built by the same shipyard.
There have been no challenges to the record which was set in July 1998, and none in sight. The current record is 41.284 knots (76.5 km/ per hour) average over two days, 20 hours and 9 minutes. The Hales Trophy is a heavily gilded ornate trophy over one metre in height and is on display in the Fast Ferry Museum located at the Incat shipyard in Hobart. The ship then known as Hoverspeed Great Britain is now operating as Cosmos Jet for Sea Jets in Greece.
Related News
Esl shipping's first plug-in hybrid vessel electramar christened.

Electramar, the first in a series of 12 plug-in hybrid vessels being built by Chowgule and Company shipyard in India for…
No Shortage of Good Ideas to Address the Mariner Shortage

The U.S. mariner shortage continues to be a strategic national security concern for all maritime industry stakeholders. So…
US Says Warship Intercepted Houthi Missile, Merchant Vessel Untouched

The U.S. navy's destroyer the USS Mason intercepted an inbound Houthi anti-ship missile over the Red Sea on Monday, U.S.
Second Generation Intelligent Tugs Delivered to Tianjin Port

Tianjin Port has held a naming ceremony for its two latest RAmparts 3500 ASD tugs, Jingang Lun 36 and Jingang Lun 37, designed…
Sponsored Content
Evaluating marine license insurance providers.

For professional mariners, safeguarding their USCG credentials with marine license insurance is vital. Yet, not all insurers offer the same caliber of service and expertise.
Revolutionized Fleet Management with ABS Wavesight Nautical Systems™ Mobile

As the maritime industry continues to rapidly advance with increasingly stringent regulations and ever-evolving technology, staying ahead of the curve requires embracing innovative technological
GLO Marine: Acting as a Vessel Upgrade Department in the hybridization of the MV Mygan.

In a showcase of expert project management and engineering precision, GLO Marine successfully integrated a mild-hybrid prototype onboard the MV Mygan, a 6000 tonnes deadweight cargo ship.
Chief Steward
Second assistant engineer (d), operations chief, chief radio electronics technician iat - mixed work schedule, chief radio electronics technician (iat).

ABS Wavesight eLog Books for Offshore Drilling

Maritime Employers: Working to Find Workers
Subscribe for Maritime Reporter E-News
Maritime Reporter E-News is the maritime industry's largest circulation and most authoritative ENews Service, delivered to your Email five times per week

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- Boat Pro Home
- Superyacht Insight
- Global Order Book
- Premium Content
- Product Features
- Testimonials
- Pricing Plan
- Tenders & Equipment

Comanche sets new Transatlantic Race record
Related articles, superyacht directory.
The 30.48 metre sailing yacht Comanche has set a new monohull race record after taking Monohull Line Honours in the 2022 RORC Transatlantic Race.
Skippered by Mitch Booth, Comanche and its crew completed the 3,000 nautical mile race from Lanzarote to Grenada in seven days, 22 hours, 1 minute and 4 seconds (that's two days quicker than the previous record holder).
Constructed in carbon fibre by American builder Hodgdon to a design by VPLP/Verdier Maxi, the yacht was delivered in 2014 after being commissioned by software mogul Jim Clark.
This is not the first time Comanche has tasted success – since its launch the yacht has set several speed records, most notably sailing from New York’s Ambrose Lighthouse to the UK’s Lizard Point in five and a half days in 2016.
The sailing yacht also finished in second place during the 2014 Sydney Hobart race and broke a 24-hour record in the 2015 Transatlantic Race after covering 618 nautical miles in one day.
Described as a “Laser dinghy or 49er morphed with rocket ship” by BOAT’ International's own Marilyn Mower , Comanche ’s defining feature is its comparatively wide 7.6 metre beam which helps save weight, in turn increasing its speed.
Other notable features include its rig which rises 47 metres above the water and a solid stainless steel keel.
Comanche is the largest yacht entered in the 2022 RORC Transatlantic Race and the team must now wait until the remaining competitors have crossed the finish line, to see if any of the 21 teams performing can eclipse their corrected time.
More about this yacht
More stories, most popular, from our partners, sponsored listings.
July 1, 2023 - 4 PM CET
Genoa In-Port race starts in
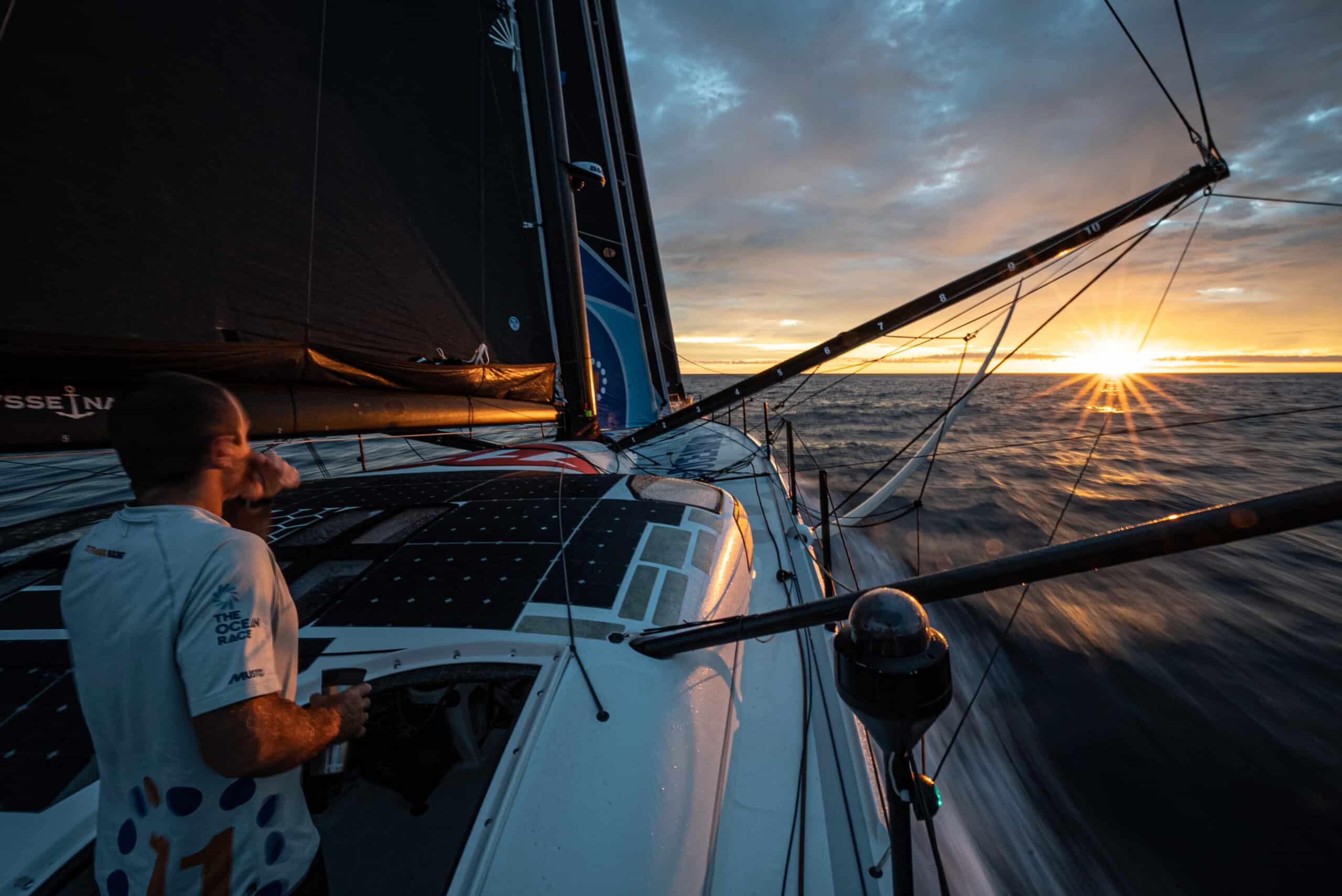

Team completes “fastest” transatlantic to date setting new benchmark for 24-hour distance; Fall plans unveiled
A week has passed since we returned to our French base in Concarneau, Brittany after a 3,050 nautical mile transatlantic training run from our US base in Newport, Rhode Island, and the data sets from onboard shows a new benchmark for distance covered in 24-hours by a yacht 60-foot or under.
Two days after leaving Newport, the crew began the start of a 24-hour stint in fast conditions, sailing 560.54-nautical miles [621 miles or 1,037 kilometers] at an average speed of 23.36 knots [26.88 miles/h or 43.26 kilometers/h], which would be the furthest recorded distance sailed by a boat 60-foot or less, and the first to break the 1,000 kilometer barrier.
This distance would be 20.29 nautical miles* further than the current World Sailing Speed Record Council (WSSRC) record, held by the IMOCA Hugo Boss [which 11th Hour Racing Team went on to own and race as Alaka’i], skippered by Alex Thomson with a crew of four, who covered 539.71 nautical miles**, at an average speed of 22.49 knots*** in 2018.
The Team did submit its data to the WSSRC on arrival in Concarneau, but the Council is unable to ratify the data as the team didn’t notify the Council of a record attempt before setting off from the USA.
Skipper Charlie Enright’s (USA) crew for the crossing on the Team’s sixty foot IMOCA race boat, Mālama , were Simon Fisher (GBR), Francesca Clapcich (ITA), Jack Bouttell (GBR/AUS), and media crew member, Amory Ross (USA). The five-strong crew completed the entire crossing in 7 days, 13 hours and 15 minutes, one of the fastest sailboat crossings of the world’s second largest ocean they’ve experienced. Between them they have 56 transatlantics under their belts.
“That was my sixteenth transatlantic crossing and the fastest one to date,” commented Enright. “We didn’t leave Newport with an eye on the weather systems and weren’t pushing for any kind of record, but the numbers kept on creeping up. We had perfect wind conditions with an average of 20 knots of breeze and a cooperative sea state. Mālama just flew, and although it made living conditions onboard very uncomfortable with the slamming, it was great to see her like this in action. “We weren’t chasing a record, and didn’t set out expecting to achieve one, but I believe this boat is something special. It’s a real testament to everyone’s hard work – the designers, boat builders, and our shore team, and shows that a sustainable approach to the build of a boat can work hand in hand with on-the-water performance. I am sure this distance will be surpassed a number of times during The Ocean Race, but to see what can be achieved with Mālama without chasing a record of any sorts is of course a small boost of confidence five months out from the start of the Race,” Enright concluded.
The sailing team remained in Concarneau for a few days of debrief, data analysis and coaching before Mālama headed into the build shed for a three week refit, ready to sail again in early September. The Team is currently planning on entering the Défi Azimut, a multi-day regatta based out of Lorient, France, from September 15-18, that will pit the four announced entries into The Ocean Race 2022-23 against each other for the first time, and in a fully crewed set-up.
The Défi Azimut has opened its startline to crewed IMOCAs for the first time in the history of the event. The unique mixed-format regatta includes timed speed runs, a 48-hour race and a dash around the Île de Groix – a sprint off the coast of Lorient.
The current plan for the rest of the year will see the Team remain in France, where they will take on new sails and foils, and with blocks of training with Pôle Finisterre, the world renowned training school for offshore sailing.
Mark Towill, CEO of 11th Hour Racing Team commented, “This Transat has been the culmination of two months of activity with our 11th Hour Racing family in Newport, Rhode Island. We celebrated #OceanHourWeek with schools and community groups learning about our impact on ocean health, were joined by over 1,000 people for the global premier of Under the Hull , the feature film focused on the Team in the run up to last year’s Transat Jacques Vabre, and also had an incredible four days sailing in Narragansett Bay joined by young adults from local sailing clubs across the Bay. It’s been great to spend time within the wider organization but for now, it is head-down for the shore crew to get the boat prepared for a busy Fall of training and racing.”
11th Hour Racing Team is one of four IMOCA teams currently announced to take part in The Ocean Race 2022-23, billed as the world’s longest and toughest sporting event. The Race will leave Alicante, Spain on January 15, 2023 and the teams will race West around the world, stopping in seven locations including Newport, Rhode Island, in May 2023, the Race’s only North American stopover.
* 20.29 nautical miles is 23.35 miles or 37.6 kilometers
** 539.71 nautical mile is 621.08 miles or 999.54 kilometers
*** 22.49 knots is 25.88 miles per hour or 41.65 kilometers per hour
Privacy Overview
- https://www.facebook.com/11thHourTeam/
- https://twitter.com/11thhourteam
- https://www.linkedin.com/company/11th-hour-racing/about/
The Geography of Transport Systems
The spatial organization of transportation and mobility
Liner Transatlantic Crossing Times, 1833 – 1952

Note: Liverpool / New York. Source: data from P.J. Hugill (1993) World Trade since 1431, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, p.128. Stopford, M. (2009) Maritime Economics, Third Edition, London: Routledge.
The passenger liner era roughly lasted for about 100 years, from the mid-19th century to the mid-20th century. Its evolution can be divided into four distinct phases:
- Introduction . The steamship Great Western can be considered one of the first liners in 1838, crossing the Atlantic in 15.5 days. Early liners were made of wood and used paddle wheels, often complemented by sails, as the main form of propulsion. Their capacity was limited to less than 200 passengers. This phase demonstrated the possibility and market potential of transatlantic liner services.
- Growth . By the 1860s, the introduction of iron hulls, compound steam engines, and screw propulsion significantly reduced crossing times to about 8-9 days. No longer limited by the technical limits of wood armatures, the size of liners increased substantially, with a tonnage exceeding 5,000 tons and a capacity of 1,500 passengers. The number and frequency of liner services across the Atlantic (and across the world) increased substantially as the market potential was being realized.
- Maturity . The early 20th century represented the Golden Age of the liner, where those ships dominated long-distance passenger movements. In 1907, the liner Mauretania with a capacity of 2,300 passengers, was able to cross the Atlantic in 4.5 days, a record held for 30 years until the liner Queen Mary reduced the crossing time by half a day (4 days). Liners reached their operational capacity of around 1,500 to 2,000 passengers, and Atlantic crossing times stabilized around 5 days. They relied on quadruple screws using turbine steam engines. This also corresponded to the peak American immigration years from European countries, a process to which liners contributed substantially.
- Obsolescence . By the 1950s, the prominence of the liner was challenged by the first regular transatlantic commercial flights. This challenge quickly asserted itself, and in a decade, the liners shifted from being the main support of transatlantic passenger movements to complete obsolescence. One of the last liners, the United States (mainly made of aluminum), held the transatlantic crossing speed record of 3.5 days in 1952. By the 1960s, air transportation had overtaken the supremacy of liners for transatlantic crossings, and reference time became hours instead of days. Liner services disappeared, and the surviving ships became the first cruise ships .
The usage of ships for carrying passengers is now restricted to cruise shipping, ferries, and small-scale passenger crafts in archipelago countries (Indonesia, the Philippines, Greece, the Caribbean) or great river systems in developing economies (Chang Jiang, Huang He, Nile, and Amazon).
Share this:

The Tactical Air Network
Global Military Aviation
The SR-71’s Record-Breaking Transatlantic Crossing
September 1st, 1974, was pretty much just another average day for New Yorkers. It didn’t look like either the Yankees or the Mets would make the playoffs (neither did), and the temperature was in the high-70s (Fahrenheit) at the tail end of yet another long, hot summer. Most were unaware of what was unfolding in the skies above them at altitudes closer to the edge of space than the regular cruising heights of the glistening airliners belonging to Pan Am, TWA and other carriers of the time. Controllers on the ground at LaGuardia Airport and John F. Kennedy International Airport were well-informed ahead of time of what would soon be streaking over their heads, departing just as quickly as it appeared.
Meanwhile, Majors James V. Sullivan and Noel F. Widdifield, the pilot and reconnaissance systems officer (RSO) respectively of the sleek black jet ripping through the airspace over New York, were steeling themselves with mere seconds left on the clock before they began a record-setting flight- the fastest Transatlantic crossing in history. Their chariot was none other than the fastest manned jet in history (at least that we know of), an aircraft that looked more like something out of a science fiction comic book than a conventional design that would come off the drafting tables at one of the most well-established aerospace corporations in the country. Their Lockheed SR-71A Blackbird, serial number 64-17972, was slated to function as a static display showpiece at the Farnborough Air Show for a week- the very first time the top secret spy plane was shown off outside the United States. US Air Force and Lockheed Corp. officials had agreed to and planned the flight over, which would see the the Blackbird cross imaginary gates over New York and speed over to another set of imaginary gates set up over London. At the time, New York City-to-London was arguably one of the most popular Transatlantic routes available to travelers; at least those who could afford it. Airlines regularly strove to decrease the time taken to travel between the two cities, culminating in the introduction of Concorde, the supersonic delta-winged European airliner which was retired just 12 years ago. The Concorde still holds the record for the fastest airliner crossing of the Atlantic Ocean, with a time of 2 hours, 52 minutes, 59 seconds, right from takeoff at London Heathrow International (LHR) to John F. Kennedy (JFK) in February of 1996. However, it still doesn’t come close to what Sullivan and Widdifield were able to pull off that September day, 22 years before Concorde’s record-setting flight.
US Senator Barry Goldwater was responsible for bringing about the Transatlantic crossing, after having flown as a passenger in a Blackbird himself. Having retired from the Air Force Reserves in 1967 as a Major General, and possessing significant political clout due to his lengthy career as a politician in Congress, Goldwater was able to convince then-US President Gerald R. Ford to allow the Air Force to fly a Blackbird to Farnborough for the rest of the world to see, thus demonstrating the power and might of American innovation and engineering. When Ford approved of the trip, the Blackbird’s parent wing’s commanding officer picked out two crews to fly one of his birds to and from the air show. Though the SR-71 wouldn’t be performing its usual reconnaissance overflights, operations personnel planned out the whole event as though it was a regular mission. Air bases for emergency diverts were assigned, radio frequencies for tanker and ground control communications were listed and no detail was left out.

The Blackbird, belonging to a reconnaissance squadron in California on the west coast of the United States, was slated to link up with a KC-135Q Stratotanker, one of a specially-modified fleet available exclusively to support the Blackbird program. Being that the Blackbird was already at approximately 2000 miles per hour when crossing the New York gates, it needed a minimum of one in-flight refueling, thanks to the astonishing amount of fuel it consumed while in afterburner. The route was calculated at around 3461.53 miles, and radio coordination between controllers in New York and London would ensure the highest degree of accuracy in timing the Blackbird’s flight across. Having already surged across the Atlantic in a sustained supersonic cruise at speeds in excess of Mach 2.5-2.6 (the Blackbird was actually capable of hitting Mach 3.5, and cruising at around Mach 3.2-3.3), Sullivan began a descent that would bring him to the only refueling point of their mission. After tanking up, the duo climbed away and once again nudged the throttles ahead. The time taken up by the in-flight refueling was deemed virtually negligible when the Blackbird flew through the London gates. Overall, the flight had taken 1 hour, 54 minutes and 56.4 seconds, and maintained an average speed of about 1807 miles per hour. Just about an hour less than what the Concorde would accomplish 22 years later. Upon observing his brainchild set the Transatlantic speed record (which still remains today), Clarence “Kelly” Johnson, who was flown over to Farnborough to receive the aircraft upon its arrival, proudly remarked, “It has exceeded all my expectations.”

The exact same Blackbird, flown by a different aircrew (Captain “Buck” Adams and Major William Machorek (pilot/RSO)) for the return flight to the US, set yet another speed record by flying from London to Los Angeles (5447 miles) in 3 hours, 47 minutes and 39 seconds at an average speed of 1435 miles per hour. If the Federal Aviation Authority and the Air Force hadn’t imposed speed restrictions on the aircraft, especially over a number of US cities it flew over on its run, the time it took would have probably cut down even further. Even with the restrictions put in place, local police departments and military switchboards were lit up with reports of sonic booms and resultant shattered windows. Years later, the very same Blackbird would once again set a number of records including the fastest time for a Los Angeles-to-Washington, DC cross-country route on its very last flight to its current resting place, the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum. On March 6th, 1990, Lieutenant Colonels Ed Yeilding and Joseph Vida (pilot and RSO respectively) flew Blackbird 64-17972 from Palmdale, California to Dulles International Airport, just outside of DC, averaging 2124 miles per hour and finishing the flight within 1 hour, 4 minutes and 20 seconds; another record that hasn’t been broken and likely will remain in place for years and years to come. This also happened to be the last SENIOR CROWN (the USAF’s official name for the Blackbird program) flight in history. Today, 64-17972 sits on permanent display at the Smithsonian’s Udvar-Hazy annex to the National Air and Space Museum.

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Published by
Ian d'costa.
Ian is the managing editor of TACAIRNET. You can find his work on Military Times, Business Insider, We Are The Mighty, Real Clear Defense, and more. View all posts by Ian D'Costa
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

How To Cross the Atlantic, Routes and Timelines
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
Before the time of ocean liners and airplanes, crossing the Atlantic used to be a great adventure that took a long time to complete. Nowadays, it’s very different; it’s still a great adventure, but the time it takes to complete has changed.
Here’s how long it takes to cross the Atlantic on various types of boats.
Looking at this table we can clearly see that the time it takes to cross the Atlantic has decreased exponentially. Some big developments were of course the steam engine that allowed for bigger and much faster ships to travel the Atlantic while also bringing a lot more cargo.
If we look at the Sailboats in this list, we can see that the more hulls you have the faster it goes (if you want to know more about how that works, check out this article)
There is not a significant difference in time to complete between the catamarans and the trimarans in the short run, but in a circumnavigation of the world, the difference can be huge.
A monohull on the other hand is slower, this is mainly due to the amount of drag this type of hull has.
This table compares different types of boats under the same conditions and adds an airplane as a point of reference.
Transatlantic Crossing in Record Time
Here are the records for the fastest crossings of the Atlantic in a Sailboat.
The 2880 Nautical miles(5330 Km) long route starts at Ambrose Light in New York and finishes on an imaginary line between Lizard Point and Ushant of the coast of England
As you might have noticed, there aren’t any numbers for catamarans since the classes are divided between monohulls and multihulls. Since trimarans (three hulls) are faster than catamarans (two hulls), there is no real point in racing a cat.
What you also may have noticed are the ridiculously high speeds these boats are doing. Bear in mind that these are racing boats optimized for speed and made to smash world records.
There’s a big difference between the 28 knots a racing trimaran will make and the 9 knots a cruising catamaran will.
What Type of Sailboat Do You Need To Cross The Atlantic?
Crossing the Atlantic can be done in almost any sailboat or ship. As a matter of fact, it has already been done in small rowboats and open catamarans, so everything is possible.
If your question is what boat should I use to get a somewhat comfortable and safe trip, well, then we have something to talk about.
Choosing between a monohull or a multihull has more to do with personal preferences. Some people really like the stable platform of a catamaran, and others dont think it’s a real way of sailing and wants to be heeling over to its side to fully get that true sailing experience.
For me? Catamaran every day, speed, and comfort, but I’m also not a purist sailor in any way. I’m an adventurist, and the boat is merely a way to experience adventures.
The size I would say matters, bigger usually means it’s safer and can handle bigger waves, although it might be harder to handle on your own I something happens to you or your crew mid-sea.
Most people seem to cross the Atlantic with a boat in the 35 -45 ft spectrum, which fulfills both requirements!
If you are interested in digging deeper into what sized boat you should get, check out my article on Best Sized Catamaran for Ocean Sailin g
Other aspects you might consider are the size in terms of space onboard , how many people are you doing the passage with, the more people, the easier operating the boat will be. This assumes you have a well-trained crew that you know well.
And what are you going to do once you get there, is it the end of your trip or is the beginning. If you’re doing everything just to cross the ocean and then get someone else to bring it back, that’s one thing. But if its the start of a long adventure, the requirements are different. You are going to want more space for scuba gear, and other toys.
I do think the most important aspect is that you have a seaworthy boat that it’s capable of withstanding weeks on end with sailing in many times rough conditions.
This means that your equipment spent has to be the most expensive and handy, but it needs to be in good condition, and you need to be able to handle your great in every weather.
What Gear Do You Need to Cross the Atlantic?
Not including your average stuff when sailing, such as life vests, etc. There are some great that you might not be on your everyday say m still that could be of high importance during such a formidable sail as this.
- Emergency food
- Satellite coms
- Storm drogue (want to know what it is and how it works, read this)
- Spare parts(tiller, sails, etc.)
- Entertainment
Different Routes to Cross the Atlantic
Westward route: europe to the caribbean.
According to Jimmy Cornell, a well-known sailor and circumnavigator that has made his own research on the subject, Las Palmas is one of the biggest ports of departure for sailboats crossing the Atlantic.
Around 75’% of the sailboats that arrive in Las Palmas on the Canary Islands will depart for an Ocean crossing.
Getting to The Canary Islands, you should not be in a hurry; there are many very beautiful places en route. No matter where you are coming from this is a good stop well worth a visit.
Coming from the north of Europe, you have France, Spain, and Portugal. Entering from the Mediterranean, you have Italy, Croatia, Greece, and so many other interesting places that you shouldn’t miss unless you’re on a very tight schedule.
Once you reach Las Palmas, you can either go straight towards the Caribbean island of Barbados, or you can do a stop along the way at Cap Verde.
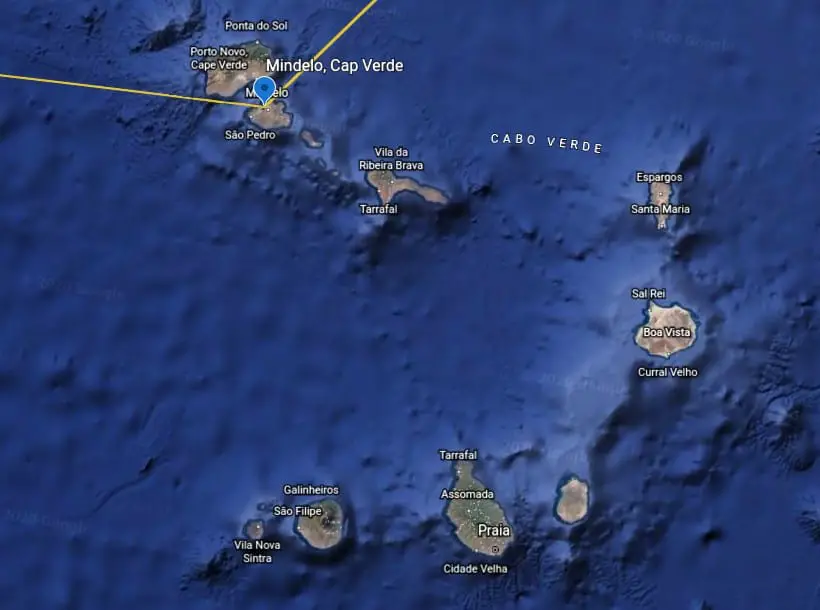
Planing a Stop on Cape Verde
A stop at cap Verde makes sense in many ways; for one, it makes the transatlantic trip more manageable by dividing it into two sections.
The second reason is that it gives you the possibility to stock up on fuel and water that you might have used more than you thought. Since Cap Verde is well developed when it comes to receiving boats doing this type of passage, there is no technical expertise on the island.
From Cap Verde, you can also take a direct flight to Portugal and onwards if the need arises.
Even though you might not plan to stop here, the recommendation is to at least plan your sailing, so you pass close to the islands, so if something happens, you can head to Mindelo port and fix it.
Another good reason why you would go close is that the further south you go, the better chance you will have of catching those sweet tradewinds that will take you safely and enjoyably to the warm waters of the Caribbean.
Westbound Route On a Catamaran
Sailing west is the preferred option for any sailor and especially if you are on a boat that doesn’t sail perfectly upwind, such as a catamaran.
Sailin g west and using the tradewinds is perfect on a catamaran, the sail will be faster and more comfortable than a monohull of the same size.
Looking at the 2019 ARC (Atlantic Rally for Cruisers), a 55ft french catamaran outclassed the 65 ft professionally sailed monohull with a 10-hour lead. All this while doing yoga on board, something that I can promise was not happening on the monohull.
The stable platform of a catamaran with the wind on your stern makes sailing west on a transatlantic passage perfect for Catamaran.
Eastbound Route: The Caribbean to Europe
Coming back to Europe, I would argue that the same principles are still valid: to stop at or pass by islands close enough to have the option of going into port if need, and using the tradewinds to your advantage.
Considering this, most people leave the Caribbean from Tortola, Britsh virgin islands, or St Marteen. These make great starting points for the eastward journey since they are the last point where there is plenty of fuel, spare parts, and food for the long and sometimes arduous trip back to Europe.
Though it is not necessary, many sailors make a halt at Bermuda; this is a good start to fix anything broken or wait for the right weather before your head on to the next part of your trip.
The Azores, the same goes here, you can skip it, but staying close to it adds safety and comfort if needed, and I would also stop by just to enjoy the islands. It’s a beautiful place and good for a few days of low-intensity cruising.
If you still have some energy left after the trip from Bermuda, one option is to head for a place called Horta. The place is well remembered for its hospitality towards sailors heading towards Europe.
Once you have refueled on diesel and energy, it is time to head for northern Europe. This is usually done by sailing north until the 45th latitude and then heading east.
When is The Best Time to Cross The Atlantic
Choosing a route has a lot to do with your intended purpose of the trip, are you going for a speed record, then going more north might be an option, and accepting the risk might be ok for you and your crew.
If you are going west but more interested in doing it safely and are able to spend a little more time out at sea, then the southern routes mentioned above with a departure date around November and December.
Going west on your way to the Caribbean, you’ll notice the days are getting warmer and longer; this is because going west, you also travel south towards the equator where the days and nights are equally as long be it summer or winter.
This weather window is to avoid the hurricane season in the Caribbean that ends in late November, these are the main risk and must be considered in your plan.
What Is The Best Route For an Atlantic Crossing
Taking into consideration the information above with trade winds, the possibility of breakdowns, and the collective knowledge of the area.
The best route for a westbound Atlantic crossing is from Las Palmas (on the Island of Gran Canarias) to Barbados Via Cap Verde. The best route going east is from St Marteen to the Azores Via Bermuda.
This is, of course, based on the assumptions we have discussed above, and it might not apply to your skillset or aim of the crossing.
Can You Cross the Atlantic Single Handed?
You can definitely cross the Atlantic on your own (short-handed). As a matter of fact, many do every year. Of course, this demands more of the sailor since there is nobody to ask for advice or to help while underway.
Neither is there anyone that will help you with handling sails or maintenance while underway; because of this, it is more dangerous and more difficult to solo sailor sail short-handed as it is also called.
The usual way is to either bring a crew of your own, recruit a crew from the port of exit, or find one online via crewseeker.net.
Is Transatlantic Passages Dangerous?
Sailing in big oceans is never a hundred percent safe. This is why it is an adventure if it was absolutely safe, where would the attractiveness and the excitement lie?
Looking at the data, there aren’t many accidents happening, and of those, there are even fewer that are deadly or leave the crew injured for life.
There are also ways to make it safer; we have discussed boat size and crew skills; other route selection factors are vital. It might not be the quickest to cross the Atlantic, but the southern route seems to be a safer bet.
Prepare yourself, your crew, and the boat, and the chances for accidents will still be there, but they will be small and manageable.
How Lonely Is Crossing The Atlantic?
Spending two to three weeks in the middle of the ocean can definitely be lonely, but it can also be the absolute opposite. If you’re sailing with a crew, you will share the same small space with everyone else, always bumping your elbow. If the weather is rough, you may all be a little tired, which also adds to the group dynamics.
But even if you would get sick and tired of your crew, there are ways to call back home. You might have a Satellite phone, which is expensive by the minute but a lovely way to hear the voice of a loved one back at land. Much better than a text message through Email.
Sending emails has been a pretty straightforward process since the SSB radio started to be utilized. This type of radio is very simplistic and has good reception up to thousands of miles .
The nice thing with this radio is that it allows for data traffic, which means not only are you able to receive weather updates, but you can also contact your family through Email.
Can You Get Rescued If Something Goes Wrong?
Yes, there might not be a coast guard or anything nearby, and you might be way out to sea, but there is help to get. Since every ship is listening to some set of frequencies, usually, the first step is to call for a Mayday on that channel.
If you’re not getting anyone’s attention, then they might still see you on the AIS, Automatic Identification System, which makes anyone around you know where you are.
Many times the crossing is done together with a lot of other vessels; this gives comfort as they might also be able to help in case of emergency.
If all this fails, you probably also will have your EPIRB, Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon , which is a gadget that can be activated through certain triggers such as water, tilt angle, or manually activated.
Once activated, it sends an emergency signal at different frequencies and relays the information back to shore for someone to come help you.
Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...


Time to Cross the Atlantic by Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide
Alex Morgan

Crossing the Atlantic by sailboat is a thrilling and challenging adventure that requires careful planning and preparation. The duration of the crossing can vary depending on several factors. To provide you with a better understanding, let’s delve into the details.
The Atlantic crossing refers to the journey of sailing across the Atlantic Ocean from one continent to another. It is a significant achievement for sailors and offers a unique experience of being surrounded by vast open waters for an extended period.
Several factors come into play when determining the duration of an Atlantic crossing. These factors include:
The chosen route significantly impacts the duration of the journey. Sailors can opt for the trade wind route, northern Atlantic route, or southern Atlantic route, each offering different challenges and opportunities.
The type and size of the sailboat also affect the duration. Factors such as speed, stability, and design of the sailboat contribute to the overall performance during the crossing.
Weather conditions, including wind patterns, currents, storms, and calms, play a crucial role in determining the speed and progress of the sailboat. Unpredictable weather can lengthen the crossing.
The skill and experience of the crew members onboard influence the efficiency of sailing maneuvers, navigation, and decision-making. A well-prepared and experienced crew can optimize the sailing process.
There are three main routes commonly used for crossing the Atlantic by sailboat:
The trade wind route follows the prevailing easterly winds, known as the trade winds. This route takes advantage of consistent winds and is the most popular and direct route for sailors.
The northern Atlantic route involves sailing closer to the polar regions, taking advantage of the prevailing westerly winds. This route allows for unique experiences and challenges due to colder temperatures and potentially hazardous weather conditions.
The southern Atlantic route involves sailing closer to the equator, where winds are often weaker and the crossing requires careful navigation. This route offers opportunities for exploring tropical areas but can be challenging due to unpredictable weather patterns.
The duration of an Atlantic crossing varies depending on the chosen route, weather conditions, and sailboat performance. On average:
The trade wind route typically takes around 18 to 21 days to complete.
The northern Atlantic route can vary from 15 to 30 days , depending on weather conditions and specific route choices.
The southern Atlantic route can take anywhere from 20 to 40 days due to weaker winds and potentially longer distances.
To ensure a successful and safe Atlantic crossing, consider the following tips:
Thoroughly plan the route, provisions, fuel, and necessary equipment. Adequate preparation is key to a smooth voyage.
Stay updated on weather forecasts and make informed decisions based on the expected conditions. Anticipating and avoiding adverse weather can contribute to a safer crossing.
Establish reliable means of communication with shore and other vessels. Regular contact can provide essential support and updates during the journey.
Check and maintain all safety equipment, including life jackets, life rafts, EPIRBs, and fire extinguishers. Safety should always be the top priority.
By understanding the factors influencing the duration, choosing the right route, and following safety guidelines, sailors can embark on a remarkable Atlantic crossing experience.
##Key takeaways:
Key takeaway:
- The duration of crossing the Atlantic by sailboat depends on various factors including the route chosen, type of sailboat, weather conditions, and skill of the crew.
- There are three main routes for crossing the Atlantic by sailboat: the Trade Wind Route, the Northern Atlantic Route, and the Southern Atlantic Route.
- The average duration of crossing the Atlantic varies according to the chosen route, with the Trade Wind Route being the fastest.
- Tips for a successful and safe Atlantic crossing include proper planning and preparation, monitoring weather conditions, maintaining good communication, and ensuring the availability of safety equipment.
What Is the Atlantic Crossing?
The Atlantic Crossing , also known as sailing across the Atlantic Ocean , is a challenging voyage that requires careful planning and preparation. Factors such as the route chosen , the type of sailboat used , weather conditions , and crew experience all play a role in this adventure.
The route for the Atlantic Crossing depends on the time of year and weather patterns. There are various popular routes to choose from, including the Trade Wind Route , the Northern Atlantic Route , and the Southern Atlantic Route . Each route presents its own set of challenges and advantages.
The choice of sailboat impacts the duration of the journey. It’s important to consider factors such as the size, stability, and performance capabilities of the sailboat . As weather conditions along the route can change rapidly, the type of sailboat can affect crossing speed and overall safety.
Having a skilled and experienced crew is crucial for a successful Atlantic Crossing . They must possess essential skills including navigation , sailing techniques , safety procedures , and emergency preparedness . With a knowledgeable and experienced crew , the journey can be made smoother and safer.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Atlantic Crossing
Planning an Atlantic crossing by sailboat? Get ready to explore the factors that impact the duration of this incredible journey. From the chosen route and type of sailboat, to the ever-changing weather conditions and the skill of the crew, each variable plays a crucial role in the time it takes to traverse the vastness of the Atlantic. So, grab your compass and chart, as we dive into the elements that shape the ultimate adventure across the open seas.
When planning an Atlantic crossing by sailboat, choosing the right route is crucial in determining the duration of your journey. Here are the steps to consider when deciding on the best route:
1. Research the Trade Wind This is the most popular and direct route across the Atlantic. It takes advantage of the steady easterly winds, also known as the trade winds.
2. Explore the Northern Atlantic Set sail north towards Iceland and then turn east to avoid the doldrums and harness the powerful westerly winds.
3. Consider the Southern Atlantic Head south towards the Canary Islands and then catch the trade winds to cross the Atlantic. While this route is longer, it offers a more enjoyable downwind passage.
4. Assess the weather conditions: Examine weather patterns and forecasts to determine which route will have the most favorable conditions during your planned crossing.
5. Evaluate the sailboat’s capabilities and speed: Take into account factors such as size, design, equipment, and performance under different wind conditions.
6. Factor in the crew’s skill and experience: Their ability to handle various sailing conditions and make strategic decisions will influence the choice of route and overall duration.
7. Choose the route that aligns with your goals and preferences: Consider the desired level of challenge, the sights along the way, and any specific destinations you want to reach.
By carefully considering these factors, you can determine the optimal route for your Atlantic crossing, ensuring a safe and successful journey.
Type of Sailboat
The type of sailboat is crucial when planning an Atlantic crossing. Various sailboats have different capabilities and features that impact the duration of the journey. Factors to take into account when selecting a sailboat for an Atlantic crossing include:
- Size: Larger sailboats offer more comfort and stability, but may require a larger crew and more resources. The size also affects the boat’s ability to handle harsh weather conditions.
- Design: The design of the sailboat influences its speed, maneuverability, and stability. Some sailboats are specifically designed for long-distance voyages and ocean crossings, featuring a full keel for stability and a cutter rig for versatility.
- Sail Configuration: The configuration of the sails, including the number and type, affects performance in different wind conditions. Certain sailboats have a single mast with a mainsail and jib, while others have multiple masts and various sail combinations.
- Equipment: On-board equipment, such as navigation systems, autopilot, and safety gear, enhances crew safety and efficiency during the crossing. It is vital to choose a sailboat that is equipped with the necessary systems and equipment for a successful journey.
- Construction: The construction materials and methods used for building the sailboat impact its durability and seaworthiness. Common materials include fiberglass, aluminum, and steel, each with their own advantages and considerations.
- Experience: The experience and skill level of the crew are crucial when handling the sailboat during an Atlantic crossing. It is important to choose a sailboat that matches the crew’s level of experience and expertise.
Considering these factors helps in determining the best sailboat for a safe and successful Atlantic crossing.
Weather Conditions
When crossing the Atlantic by sailboat, weather conditions are crucial.
1. Wind: Sailors rely on favorable wind to make progress. Strong and consistent trade winds, blowing from east to west, are ideal.
2. Storms and hurricanes: Weather systems in the Atlantic can be unpredictable and potentially dangerous. Sailors need to be aware of the hurricane season and avoid storm-prone regions. Monitoring forecasts and navigating around adverse weather is essential for safety.
3. Sea states and waves: The Atlantic Ocean can have large swells and waves, especially during storms. Sailors need to be prepared and have a capable boat.
4. Fog and visibility: Fog impairs visibility and makes navigation challenging. Sailors must be cautious and have radar and navigation aids for safe navigation.
5. Ocean currents: The Atlantic has various currents that can help or hinder progress. Knowledge of these currents, like the Gulf Stream, helps sailors plan routes efficiently.
Understanding current and forecasted weather conditions is crucial for a successful and safe Atlantic crossing. Sailors should consult weather charts, use modern forecasting tools, and consider professional meteorologists. By considering weather conditions, sailors can optimize their route, adjust their sail plan, and ensure a smoother crossing.
Skill and Experience of the Crew
The success and safety of an Atlantic crossing by sailboat heavily rely on the skill and experience of the crew. Their expertise can have a significant impact on the duration of the journey, as a well-trained and experienced crew is capable of navigating more efficiently. Let’s explore the various aspects where the crew’s skill and experience come into play.
Firstly, navigation plays a vital role in determining the duration of the crossing. With their expertise and experience, a skilled crew can choose the most efficient routes, avoiding unnecessary detours and delays. By making informed decisions, they can optimize the sailing path, ultimately reducing the overall time taken.
The crew’s sailing techniques are crucial in maximizing speed and efficiency. An experienced crew knows the most effective techniques to employ, allowing them to harness the wind’s power and propel the sailboat forward swiftly. By implementing these proven methods, they can cover more distance in a shorter amount of time.
In the event of emergency situations, the crew’s experience becomes invaluable. With their knowledge and practice, they can quickly and effectively handle unforeseen circumstances, minimizing disruptions and delays. Their ability to remain calm and composed during such situations ensures that the journey remains on track, preventing any unnecessary setbacks.
Effective crew coordination is another key factor in a successful Atlantic crossing. Through clear communication and mutual support, the crew can ensure smooth operations and timely decision-making. This cohesion fosters an environment where everyone understands their roles and responsibilities, enabling efficient teamwork and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
It is important to note that crew members must undergo appropriate training and gain experience in various sailing conditions before attempting an Atlantic crossing. By building their skills and experience through shorter voyages and training programs, they can enhance their confidence and proficiency. This cultivation of competence and capability ensures the crew is well-prepared for the challenges they may face during the journey across the Atlantic.
Routes for Crossing the Atlantic by Sailboat
Looking to set sail across the vast Atlantic by sailboat? Let’s explore the numerous routes available for this incredible adventure. From the renowned Trade Wind Route to the lesser-known Northern and Southern Atlantic Routes, each option offers its own unique challenges and rewards. Whether you seek steady winds or a more adventurous path, these sub-sections will unveil the secrets and possibilities of each route, helping you plan your epic journey across the Atlantic Ocean.
Trade Wind Route
The Trade Wind Route is a popular route for crossing the Atlantic by sailboat. Sailors on this route can take advantage of the consistent easterly trade winds in the subtropical regions. These winds are caused by temperature differences and the Earth’s rotation.
The trade winds on this route typically blow at speeds of 10 to 25 knots , occasionally gusting stronger. Sailors can expect a smooth journey with smaller waves and less challenging weather compared to other routes.
The duration of the Atlantic crossing varies based on factors such as boat size , type, crew experience , and weather conditions. On average, it takes 14 to 21 days to complete this crossing.
To navigate the Trade Wind Route successfully, sailors should plan, prepare, monitor weather conditions, maintain communication, and ensure safety equipment is in place . Following these guidelines ensures a safe and enjoyable crossing.
Northern Atlantic Route
The Northern Atlantic Route is a popular sailboat route between Europe and North America . It offers an adventurous journey across the Atlantic Ocean .
Factors to consider when taking the Northern Atlantic Route include:
– Route Distance: The route covers approximately 2,800 nautical miles .
– Weather Conditions: The Northern Atlantic can have unpredictable weather with variable winds and potential storms. Sailors need to be prepared for adverse conditions and strong currents .
– Strong Currents : The North Atlantic Drift is a strong eastward-flowing current that can affect the progress of sailors. It is important to consider these currents when planning the route and timings.
– Potential Hazards: Icebergs are a potential hazard, especially in the Labrador Sea . It is crucial to be aware of these hazards and navigate safely around them.
– Duration: The duration of the journey can vary depending on factors such as weather conditions, boat size and speed, and crew experience. On average, it takes between 15 to 25 days to complete the journey.
When planning a sailboat journey on the Northern Atlantic Route , sailors should carefully consider the distance, weather conditions, strong currents, potential hazards, and expected duration. Adequate preparation, monitoring of weather conditions, and good communication are essential for a safe and successful crossing.
Southern Atlantic Route
The Southern Atlantic Route is a popular choice for sailors crossing the Atlantic. It offers a unique experience compared to other routes.
1. Strong Trade Winds: The route experiences strong and consistent trade winds blowing from the southeast. These winds provide favorable conditions for sailing and can increase speed.
2. Great Circle Route: The Southern Atlantic Route follows the shortest distance between two points on a globe. This allows for a more direct and efficient path, reducing the duration of the crossing.
3. Warmer Climate: Sailing along this route means encountering a warmer climate compared to northern routes. The waters are generally calmer, making it a more comfortable journey.
4. Wildlife and Scenic Views: Sailors have the opportunity to witness diverse marine life and enjoy picturesque views. Dolphins, whales, and other marine creatures are often spotted along the way.
5. Possible Stopover: Some sailors choose to make a stopover in Cape Verde , an archipelago off the coast of West Africa. This allows for a break in the journey and an opportunity to restock supplies.
The Southern Atlantic Route provides an exciting and challenging adventure for sailors. With its strong trade winds, shorter distance, and beautiful scenery, it is a popular choice for those seeking a memorable journey.
Average Duration of Atlantic Crossing
Ready to embark on a journey across the vast Atlantic? In this section, we’ll explore the average duration of an Atlantic crossing, providing insights into various routes such as the Trade Wind Route , Northern Atlantic Route , and Southern Atlantic Route . Discover the importance of proper planning, vigilant monitoring of weather conditions, effective communication, and ensuring essential safety equipment is in place. Get ready to set sail and unlock the secrets of crossing the Atlantic like a seasoned sailor.
The Trade Wind Route is a popular route for sailing across the Atlantic due to its favorable wind patterns. These winds, known as trade winds, blow from east to west in the tropics. The route starts from the Canary Islands and heads west towards the Caribbean or South America .
Sailing along the Trade Wind Route offers advantages. The trade winds provide consistent and steady winds, making it easier to maintain a good sailing speed. The route offers a smooth and comfortable passage with less rough seas compared to other routes. The Trade Wind Route allows sailors to take advantage of warm and pleasant weather conditions in the trade wind belt.
The time it takes to cross the Atlantic via the Trade Wind Route varies depending on factors such as sailboat size, speed, weather conditions, and crew experience. On average, it takes around 15 to 21 days to complete the crossing using this route. It’s important to note that these are rough estimates and actual crossing times can vary.
Fact: Some sailors have reported completing the Atlantic crossing via the Trade Wind Route in under two weeks, while others have taken over a month. The duration largely depends on the specific conditions encountered during the voyage.
The Northern Atlantic Route is an important consideration for sailors planning to cross the Atlantic by sailboat. The duration of the crossing via this route is influenced by various factors. The route itself, sailing from Europe to North America, can be longer due to distance and prevailing wind and current patterns. The type of sailboat used also impacts the duration, as different boats have different speeds and capabilities. Weather conditions along the route, including storms, wind patterns, and currents, can significantly affect the crossing time. The skill and experience of the crew onboard also play a role in navigating the route efficiently. Sailors should carefully consider these factors for a safe and successful journey.
The Southern Atlantic Route is popular for sailboat crossings due to favorable weather conditions and reliable wind patterns. This route, also known as the Cape Town Route , starts from Europe or the Americas and heads south towards the Canary Islands . Sailors then continue southwest across the Atlantic Ocean towards their final destination in South America or South Africa .
The Southern Atlantic Route offers consistent trade winds and mild weather compared to other routes. The prevailing winds blow from the southeast, providing a steady breeze that helps propel the sailboat forward. This makes it easier to maintain a good average speed and complete the crossing efficiently.
The duration of the Southern Atlantic Route can vary depending on factors such as sailboat type, crew skill and experience, and specific weather conditions encountered. On average, the crossing from Europe to South America takes around 20 to 30 days, while the journey from Europe to South Africa typically takes around 25 to 35 days.
Sailors navigating the Southern Atlantic Route should be prepared for challenges posed by the open ocean, including unpredictable weather patterns, potential storms, and the need for self-sufficiency. It is crucial to plan and prepare adequately, monitor weather conditions constantly, maintain good communication, and ensure all safety equipment is in place for a successful and safe crossing.
The Southern Atlantic Route has been a preferred route for sailors for centuries, connecting Europe with Africa and South America . The route played a significant role in the Age of Discovery , facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between continents. Today, it continues to be a popular route for adventurous sailors seeking to experience the thrill and challenge of crossing the Atlantic Ocean by sailboat.
Tips for a Successful and Safe Atlantic Crossing
Add tips for a Successful and Safe Atlantic Crossing
Here are some tips for a successful and safe Atlantic crossing:
1. Plan your route carefully, considering weather patterns, currents, and potential hazards. Have charts, navigation equipment, and a reliable GPS system.
2. Prepare your boat by inspecting for wear or damage. Ensure all safety equipment, including life jackets, flares, and a well-maintained life raft, is in good working condition.
3. Stock up on essential supplies like non-perishable food, water, and fuel. Have enough provisions for the entire journey and extra reserves for emergencies or delays.
4. Stay informed about potential hazards or changes in weather conditions by communicating with other sailors and maritime authorities.
5. Develop a detailed sailing plan that includes rest cycles for the crew and potential stops for restocking supplies or refueling.
6. Ensure all crew members are experienced and prepared for the challenges. Conduct regular safety drills and assign specific roles and responsibilities.
7. Monitor weather conditions closely and be ready to alter course or adjust schedule if needed. Prioritize safety above all else.
By following these tips, you can increase your chances of a successful and safe Atlantic crossing.
Plan and Prepare Adequately
When planning and preparing for an Atlantic crossing by sailboat, it is important to plan and prepare adequately to ensure a successful and safe journey. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Research the route: It is crucial to thoroughly research the different routes available for crossing the Atlantic, such as the Trade Wind Route, the Northern Atlantic Route, and the Southern Atlantic Route.
- Check weather conditions: Monitor weather forecasts and have a clear understanding of the typical weather patterns along your chosen route. Take note of any potential storms or unfavorable conditions that may arise.
- Prepare the sailboat: Before setting off, ensure that the sailboat is in good condition and equipped with all the necessary safety equipment. This includes life jackets, flares, a first aid kit, and emergency communication devices.
- Stock up on supplies: Make a comprehensive list of essential provisions needed for the journey, including an ample supply of food, water, fuel, and spare parts. Calculate the amount needed based on the estimated duration of the crossing.
- Create a navigation plan: Develop a detailed navigation plan that includes waypoints, potential stops, and alternative routes. Familiarize yourself with navigational charts and instruments to aid in navigation throughout the journey.
By following these steps and planning and preparing adequately , you can embark on your Atlantic crossing with confidence and peace of mind . Just like Christopher Columbus , who meticulously planned and prepared for his transatlantic voyage , you too can open up new horizons for exploration and have a smooth and safe journey.
Monitor Weather Conditions
When crossing the Atlantic by sailboat, it is crucial to monitor weather conditions for a safe and successful journey. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Check weather forecasts: Stay updated with the latest forecasts for your entire journey. Pay attention to wind patterns, storm systems, and potential hazards.
2. Use weather routing services: Subscribe to a specialized routing service tailored to your specific route. These services can help you navigate around unfavorable weather conditions.
3. Monitor weather systems: Keep a constant eye on changing weather systems, especially tropical storms or hurricanes that can pose a significant threat. Take appropriate measures to avoid these dangerous conditions.
4. Be aware of wind patterns: Understand the prevailing winds along your route for planning and optimizing your sailing strategy. Trade wind routes offer consistent winds for a faster crossing.
5. Consider swell and sea state: Besides wind conditions, pay attention to the sea state. Large swells and rough seas can affect your comfort and safety at sea.
By actively monitoring weather conditions during your Atlantic crossing, you can make informed decisions and adjust your plans accordingly. Remember, safety should always be the top priority.
Maintain Good Communication
Maintaining good communication is absolutely crucial during an Atlantic crossing by sailboat. It is of utmost importance as it guarantees the safety and seamless operation of the voyage.
To ensure effective communication, there are several key steps that need to be taken:
1. Establish clear communication protocols: It is essential to set up a system that allows crew members and the skipper to effectively communicate with each other. This can be achieved by using designated channels such as radios or walkie-talkies for conveying important messages.
2. Implement regular check-ins: Designate specific times for crew check-ins. This enables everyone to report their status, share vital information, and address any concerns that may arise.
3. Create a comprehensive communication plan: Develop a plan that outlines how to communicate with land-based support teams or coastguard services in case of emergencies. This plan should include contact information and the correct procedures to be followed.
4. Maintain good radio etiquette: It is crucial to adhere to proper radio protocols in order to ensure clear and concise communication. Utilize standard phrases and refrain from engaging in unnecessary chatter to prevent any confusion.
5. Utilize technology: Take advantage of modern communication devices, such as satellite phones, that provide reliable coverage even in remote areas. This will enable seamless communication throughout the entire journey.
It is important to remember that maintaining good communication is not solely about accurately conveying information. It also plays a vital role in fostering teamwork and creating a sense of security among the crew members. By communicating effectively, the crew can promptly respond to any changing conditions and thus ensure a safe and successful Atlantic crossing.
Ensure Safety Equipment is in Place
Ensuring safety equipment is crucial for a successful and safe Atlantic crossing by sailboat. Follow these steps:
- Inspect and test all safety equipment before departure, including life jackets, harnesses, tethers, and personal locator beacons, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Ensure the boat has proper navigation equipment, such as GPS, charts, and radar, for accurate navigation and to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Install and regularly check the functioning of essential safety devices like EPIRBs and SARTs, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Equip the boat with a well-stocked first aid kit, including necessary medications, bandages, and disinfectants, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Have a reliable communication system, such as a VHF radio or satellite phone, to stay in contact with other vessels and emergency services and to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Ensure the boat has proper fire extinguishers, smoke detectors, and carbon monoxide detectors, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Install and regularly test the boat’s bilge pumps to handle water ingress and to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Keep all essential safety equipment easily accessible and in good working condition, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Train the crew on how to use and deploy safety equipment properly, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
- Regularly review and update the safety plan, considering the specific challenges and risks of the Atlantic crossing, to ensure safety equipment is in place.
By following these steps and ensuring safety equipment is in place, sailors can improve their preparedness and enhance the overall safety of the Atlantic crossing.
Some Facts About How Long To Cross The Atlantic By Sailboat:
- ✅ An Atlantic crossing on a sailboat takes an average of 20 to 25 days.
- ✅ It is important to know the shortcuts, maximize speed, and have experience to cross the Atlantic.
- ✅ The best time to cross the Atlantic is between November and February.
- ✅ The total distance of the trip can be as much as 4,000 nautical miles.
- ✅ The trade winds blow from east to west and are predictable due to the rotation of the earth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to cross the atlantic by sailboat.
An Atlantic crossing on a sailboat takes an average of 20 to 25 days, but can be completed in two weeks if lucky, take shortcuts, and have a fast sailboat. The time it takes to cross depends on the route, type of ship, size, skills, and speed.
What are the best routes for crossing the Atlantic by sailboat?
There are two main routes for crossing the Atlantic by sailboat: the Southern passage (east to west) and the Northern passage (west to east). The Southern passage starts from Europe and goes to the Canary Islands, Cape Verde, or the Windward Islands. The Northern passage starts from the Caribbean and goes to Bermuda, the Azores, and then the Portuguese coast.
When is the best time to cross the Atlantic by sailboat?
The best time to cross the Atlantic by sailboat is between late November and February, as there is less chance of hurricanes and the water is warmer. Timing is important to avoid the hurricane season, which lasts from June to November.
What are the challenges of crossing the Atlantic by sailboat?
Sailing across the Atlantic can be challenging mentally and physically. It requires sailing expertise, familiarity with weather forecasting and navigation, and the ability to quickly adjust to sudden changes in weather. The trip can also involve long travel, large waves, severe weather, collisions, encounters with whales, and epic proportions of wear and tear on the boat.
What type of sailboat is suitable for crossing the Atlantic?
The best sailboat for crossing the Atlantic should be at least 30 feet long, have a fixed keel, and be sturdy with durable sails. A monohull sailboat is recommended over a sailboat with multiple hulls. The type of boat used affects the speed of travel, and the location can also be a factor.
Can I hire a skipper for the Atlantic crossing if I lack experience?
Yes, hiring an experienced skipper is an option for those without the necessary skills and experience to safely make the journey. A skipper can provide guidance, navigation expertise, and help ensure a successful crossing.
About the author
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

The history of sailing – from ancient times to modern adventures
History of Sailing Sailing is a time-honored tradition that has evolved over millennia, from its humble beginnings as a means of transportation to a beloved modern-day recreational activity. The history of sailing is a fascinating journey that spans cultures and centuries, rich in innovation and adventure. In this article, we’ll explore the remarkable evolution of…

Sailing Solo: Adventures and Challenges of Single-Handed Sailing
Solo Sailing Sailing has always been a pursuit of freedom, adventure, and self-discovery. While sailing with a crew is a fantastic experience, there’s a unique allure to sailing solo – just you, the wind, and the open sea. Single-handed sailing, as it’s often called, is a journey of self-reliance, resilience, and the ultimate test of…

Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Practices on the boat
Eco Friendly Sailing Sailing is an exhilarating and timeless way to explore the beauty of the open water, but it’s important to remember that our oceans and environment need our protection. Sustainable sailing, which involves eco-friendly practices and mindful decision-making, allows sailors to enjoy their adventures while minimizing their impact on the environment. In this…

The Man in Seat 61
The transatlantic ferry
Cunard's queen mary 2.
- Buy train tickets
- Buy ferry tickets
- Book a hotel
- Privacy & cookies
- Home
Train travel UK & Ireland...
Train travel in europe..., train travel in asia..., train travel in africa..., train travel in america..., train travel in australasia, london to new york without flying.
This is a guide to travel between Europe & the United States using Cunard's Queen Mary 2.
Cunard maintain a scheduled transatlantic passenger service between Europe and the United States, usually one sailing a month in each direction between Southampton & New York from April to December taking 7 nights.
You travel aboard the greatest ocean liner in the world, Cunard's Queen Mary 2 (QM2). It's a crossing , not a cruise , and many people use the QM2 as their preferred mode of transport between Europe & the United States. The Queen Mary 2 is a proper ocean liner, built with the extra structural strength & power to withstand the rigours of the North Atlantic in all weathers. The QM2 took over the transatlantic service from Cunard's 1967-built QE2 in 2004.
You can forget being bored, it's a week of relaxation, with cinema, theatre, interesting lectures, spa treatments, swimming pools, cocktail bars, restaurants, an excellent library, shops and even the world's only sea-going planetarium. Plus the cold grey Atlantic which I never tire of watching. You can also forget seasickness, the 150,000 ton QM2 is rock-steady in most weather amidships, you'll need to walk forward towards the bows to feel any up and down movement. Westbound, the crossing is rounded off by an awe-inspiring early-morning arrival into New York City, in my opinion the best way to arrive in the Big Apple.
Crossing the Atlantic by ocean liner needn't cost much more than a business-class flight, fares for two people sharing the cheapest Britannia stateroom start from £1,099 per person each way, for 7 nights accommodation, all meals & entertainment.
The Man in Seat Sixty-One says: "From personal experience, staggering round a transatlantic liner in a dinner jacket with a martini is the normal, rational, reasonable way to cross the Atlantic. Heading for an airport and strapping yourself to a flimsy aluminium tube is an unfortunate and eccentric aberration."
Transatlantic sailing dates
Southampton ► new york.
2024 transatlantic sailings: 28 April, 16 May, 9 June (6 night), 23 June (6 night), 21 July (6 night), 16 August, 15 September, 17 October (8 night), 13 November, 14 December.
2025 transatlantic sailings: 9 January (9 nights, Queen Anne), 8 March, 27 April (8 nights), 16 May, 6 June, 24 June, 27 August, 26 September, 24 October, 19 November, 15 December.
All crossings are now 7 nights except where shown. The Queen Mary 2 usually sails from Southampton at 17:00, arriving in New York 7 nights later at 06:30-07:00. The terminal she uses in Southampton varies. In New York she arrives at the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal.
New York ► Southampton
2024 transatlantic sailings: 3 January (8 nights), 5 May, 23 May, 15 June (8 nights), 6 July (8 nights), 27 July (8 nights), 23 August, 4 October (9 nights), 25 October, 3 December.
2025 transatlantic sailings: 3 January (8 nights), 6 April (8 nights), 5 may, 23 may, 13 June, 8 July, 8 august, 3 September, 17 October, 31 October, 8 December then 3 January 2026 (8 nights).
The QM2 usually sails from New York Brooklyn Cruise Terminal at 17:00, with check-in opening at 13:00 and closing at 15:45. She arrives in Southampton at 06:30 seven nights later.
How to check sailing dates, times, prices & availability
Back to top
How much does it cost?
Typical Cunard one-way fares for transatlantic crossings. Late bookings in late season can often be cheaper than this!
Inside = without window, oceanview = with porthole, see the cabin accommodation guide . All other staterooms & suites have a balcony, except the two Q3 Royal Suites.
Britannia = allocated to the Britannia restaurant for meals. Princess or Queen's Grill = allocated to the superior Princess or Queen's Grill restaurants for meals.
How to find cheaper tickets: You'll often find cheaper fares if you buy your tickets from a cruise specialist such as www.cruisenation.com (UK-based) or www.cruisedirect.com (in the USA or Canada), both of which have online booking for transatlantic crossings and cruises. Agencies like these can save perhaps £100 per person or more off the official Cunard price, and you'll also find cheaper fares if you shop for last minute deals and late-season crossings, as low as £799 or better, for example. However, be aware that in high summer transatlantic sailings can get full many months in advance.
Round trip fares: There are special round trip fares covering two back-to-back crossings with just 1 day in New York, but if you plan to spend more than a day at your destination you'll need to pay one-way fares each way. In other words, for all practical purposes a round trip on the QM2 means buying two one-way tickets.
Cunard Fare & Saver fare: The Cunard fare lets you choose a specific cabin & dinner sitting up front. The Saver fares are several hundred pounds or dollars cheaper and guarantee a cabin in the booked grade or higher, but the cabin and dinner sitting time are allocated for you. You can log in to Cunard's voyage personaliser at my.cunard.com/en-gb/mycruise/login a couple of weeks before departure to see what cabin & sitting you have been allocated.
Child fares: See here .
What does the fare include? All Queen Mary 2 transatlantic fares include your cabin accommodation, all meals & afternoon tea, on-board entertainment such as shows, lectures, films, access to the swimming pools & library, plus the tea, coffee & juices available in the Kings Court self-service. The fare does not include alcoholic & non-alcoholic drinks served in bars or at meals, Canyon Ranch Spa access & treatments, or internet access . Also, a 'discretionary' fee of around $11-$14 per person per day will be added to your on board account each day as a gratuity for staff.
How to buy tickets
if you live in uk & europe, if you live in the usa or canada, how does the ticketing work , westbound transatlantic guide.
Here is a typical transatlantic timetable, port transfer, embarkation arrangements & journey information for a typical westbound transatlantic sailing on the QM2. Although they normally follow this same pattern, always check the sailing time & check-in times for your specific date. If you find that something has changed, please let me know . If you're sailing eastbound, see the eastbound information . Are westbound or eastbound crossings better?
Take the train from London Waterloo
Fast air-conditioned trains run from London Waterloo to Southampton Central every 30 minutes taking around 1h17. No reservation is necessary, just turn up, buy a ticket and hop on the next train.
London to Southampton costs £43.10 adult one-way Super Off-Peak in standard class or £86.80 one-way Off-Peak in 1st class.
These tickets have unlimited availability, you can buy them on the day, the price doesn't change. Children under 16 half price, children under 5 free.
If you book in advance and commit to a specific train, cheaper Advance fares are available from around £10 in standard class or £16 in 1st class. These tickets have limited availability at each price level.
Check train times & fares from London Waterloo or anywhere in Britain to Southampton at www.thetrainline.com . Direct trains run from Manchester, Birmingham, Oxford, Reading, Bristol & Cardiff to Southampton, so you won't have to cross London. See a beginner's guide to UK train travel .
For train connections from Paris or any other European city to London, see here . I'd recommend a night in London before taking the train to Southampton on sailing day.
Transfer by taxi in Southampton
Make sure you know which of the four possible terminals the QM2 is sailing from, the QEII terminal (dock gate 4), City Cruise Terminal (dock gate 10), Mayflower Cruise Terminal (dock gate 10), or the new Ocean Terminal (dock gate 4). Map of Southampton, showing all cruise terminals, Southampton Central Station & the historic Ocean Terminal .
A taxi from Southampton Central station takes 10 minutes and costs around £10 to the Mayflower or City cruise terminals, around £13 to the QEII terminal or Ocean Terminal. You'll find plenty of taxis waiting at the station, the taxi rank is on the same side of the station where most trains from London arrive, so no bridges or subways to negotiate., level access from platform to booking hall to forecourt.
QM2 check-in procedures
Check-in typically opens at 13:00 and closes around 15:45. Cunard will give you a specific check-in time on your e-ticket to stagger people arriving, but you can arrive earlier if you like, it's not a problem.
Visitors are not allowed on board, so anyone seeing you off will have to leave you at the terminal. Cunard either send you or allow you to download labels showing your departure date & cabin number, remember to put one on each bag before arriving at the terminal.
When you get out of the taxi at the terminal drop-off point your large bags are immediately taken from you and whisked away, they will magically reappear later in your stateroom. No bag should exceed 23Kg (50lb) but you can take as many bags as you like as long as they will all fit into your stateroom.
You then walk into the check-in hall and go to the first available check-in desk, this usually doesn't take long. At the check-in desk, you show your e-ticket, your passport & your credit card for on-board purchases, and a webcam photo is taken of each passenger for security purposes. You may be asked to fill out a brief health form to notify the ship of any fever you have or any diarrhoea you've had in the last 48 hours. Each passenger is given a credit-card sized plastic card which is your embarkation card, your cabin key and your charge card for buying drinks & souvenirs on board.
After check-in there's an airline-style X-ray & metal detector security check, then straight onto the gangway onto the QM2, entering the Grand Lobby on deck 3. It's a painless process compared to airports. If you feel like a late lunch, or just a tea, coffee or juice when you board, you'll find the King's Court self-service restaurant on deck 7 open for business and offering all of these.
What's an Atlantic crossing like?
The Queen Mary 2 is usually due to sail from Southampton at 17:00. This is the most usual time, but please check for your sailing date. Once on board and settled into your stateroom, listen for announcements about emergency drill. This is held at 16:00 and takes about 20 minutes. You listen for the alarm bells, fetch your lifejackets from your stateroom and go to your allocated muster station where staff will brief you on emergency procedures and you'll listen to an announcement by the captain. When it's over, return your lifejackets to your stateroom and head up on deck for departure...
Soon after 17:00 the QM2 sails, with a band playing on her aft decks and glasses of champagne available (around $17). She is sometimes moored facing upstream, sometimes downstream, and if she's moored facing upstream at the City or Mayflower terminals, she'll first head further upstream before turning around, somehow managing to turn her 1,130 foot length without hitting the far bank of the river or the small boats moored there.
Southampton's historic Ocean Terminal: Cunard no longer use the traditional and historic Ocean Terminal dock, from which the original Queen Mary, Queen Elizabeth and even Titanic would have sailed. Indeed, the old 1950 terminal building was demolished in 1983 and this hugely historic location now looks totally unremarkable, a freight dock with a couple of multi-storey car parks next to it for vehicle exports. You won't know that you're looking at it unless you know where it is, so see this map . It's just north of the QEII terminal, just south of the City & Mayflower terminals. About the old Ocean Terminal .
The Queen Mary 2 heads downstream into the Solent, heading directly towards Cowes on the Isle of Wight before making a tight turn to port (left) in the deep water channel, passing Ryde to starboard (right) and Portsmouth to port. The QM2 rounds the Isle of Wight using the deep water route to the east (although this looks like the long way round on a map) and heads out into the English Channel. By breakfast next morning, you're well past Bishop Rock lighthouse and out in the Atlantic...
Seven nights at sea on the Atlantic. Cunard slowed down their crossings from 6 nights to 7 nights from 2011 onwards, although an occasional crossing may take 6 or 8 nights. This is two days slower than it used to be, as the weekly service operated from 1946 to 1967 by the original Queen Mary and her consort Queen Elizabeth took just 5 nights for the 3,150 nautical miles (3,625 miles).
There may be no coastline or islands to see in mid-Atlantic (or even other ships, usually), but I never tire of gazing at the brooding waters of the North Atlantic. It changes from day to day, sometimes smooth and glassy, sometimes choppy and sombre, sometimes sunny, sometimes foggy with the Queen Mary 2's fog horn blaring at regular intervals.
You may get rough crossings especially in October, November or December, but my summer crossings on the 150,000 ton Queen Mary 2 or 70,000 ton QE2 have been rock steady all the way. You could be in a 5 star hotel rather than on board a ship!
The QM2's clocks are put back an hour at 2am on 5 of the 7 nights because of the time difference, giving you a welcome extra hour's sleep in this direction. You will pass within a few miles of the resting place of the Titanic (within 38 nautical miles on one of my westbound crossings) and an announcement may well be made on board. Naturally, you'll find a whole programme of entertainment & activities on board every day, and if you really want to be bored you'll have to work hard at it.
The QM2 arrives in New York at the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal at 06:30. This is the highlight! Whether you're a natural early riser or not, make sure you're up and on deck by 04:45 on the morning of arrival in New York, as the arrival into New York by ocean liner is something you will remember all you life. There's a forward-facing observation deck on deck 11, immediately below the bridge, accessed from 'A' stairway. You'll see the lights of Long Island to starboard (the right-hand side), Staten Island to port, and the Verrazano suspension bridge dead ahead at the entrance to New York harbour. The Queen Mary 2 passes under the bridge with just a few precious feet of clearance above her funnel, and as she does so the fabulous Manhattan skyline comes into view. The QM2 no longer uses Cunard's traditional terminal at Pier 90 on Manhattan itself, so she no longer steams right past the Statue of Liberty, but instead she turns to starboard (to the right) opposite the statue and heads into the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal, berthing within sight of the famous Statue and Manhattan skyline.
QM2 disembarkation in New York
A note explaining QM2 disembarkation procedures appears outside your stateroom a day or two before arrival, and each deck is allocated a disembarkation time. Disembarkation takes place between 08:00 & 11:00. The upper decks with the more expensive cabins disembark first (e.g. decks 9, 10, 11, 12), other decks such as 4, 5 or 6 later.
Labels for your bags appear outside your stateroom the day before arrival. You put a label on each of your bags and place them in the corridor outside your stateroom between 20:00 & midnight before arrival. Your bags will disappear and will be waiting for you in the terminal hall next morning, in an area marked with the same colour as your labels.
It's then just a matter of going through the U.S. immigration check, a slowish process but no worse than any airport. They you walk out of the terminal.
Express disembarkation: If you want to get off sooner and are happy managing all your own bags, you can register for Express disembarkation at the purser's desk on deck 2 the day before arrival. You are given an express disembarkation card. Express disembarkation passengers gather in the Queens Room from 06:45 onwards with all their luggage, and at around 07:00 when the gangway opens you simply walk off the ship with your bags, straight into the terminal. With a Deck 4 cabin we were allocated an 11:00 disembarkation time, which would have meant half a day in New York wasted, so I'd go for express disembarkation every time!
Transfer by taxi to Manhattan
The Tour Office on deck 2 offers private transfers by minivan from Brooklyn Cruise Terminal to any Manhattan hotel for a ridiculous $429, or they can sell you tickets for a transfer bus for $59 per person.
However, both options are crazy, because a normal yellow cab from the terminal taxi rank to anywhere in Manhattan costs only $40 for up to 4 people and all your bags, and you'll find plenty of taxis waiting right outside the terminal building. Enjoy the drive across the famous Brooklyn Bridge in a New York Yellow Cab!
You'll also find plenty of black private hire vehicles outside the terminal with a fixed price of around $55 to a Manhattan hotel, also a good relaxed option. The ride takes 20 minutes.
Alternatively, the cheapest option (just $4) is to take the frequent ferry from Brooklyn's Red Hook ferry terminal to Pier 11 on Wall Street at the southern end of Manhattan. Red Hook ferry quay is only 100m from the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal, and it'll take you to Manhattan in a matter of minutes, see www.ferry.nyc . It's aimed at locals, but taking a suitcase isn't usually a problem. See walking map cruise terminal to Red Hook ferry .
By train from New York to other U.S. cities
You can be at Penn Station by 11:30 or earlier, for onward train connections. Washington DC is only 3 hours away by train, Boston 4 hours or less. The Lake Shore Limited train to Chicago leaves Penn Station around 15:45 arriving in Chicago next morning, with connections for all points west including Los Angeles, San Francisco, Denver, Dallas, Seattle. You'll also make the afternoon Crescent overnight train to Atlanta & New Orleans, or the afternoon Silver Meteor overnight to Florida.
You can book any of these trains online in advance at www.amtrak.com , collecting your ticket from the self-service machines at Penn Station. Note that between New York & Washington or New York & Boston you'll be offered two different types of train: The premium-fare Acela Express 150mph high-speed train with business class and first class, but no coach class, and the slower but cheaper Northeast Regional trains with coach class and business class.
You can book Amtrak trains yourself, but if you want an agency to sort a package of train connections and hotels from New York to other US cities, call Railbookers on 0207 864 4600 (UK office) or 1-888-829-4775 (US office). Beginner's guide to train travel in the USA .
By train from New York to Toronto, Montreal & Canada
Two daily trains link New York with Canada, the Maple Leaf to Toronto and the Adirondack to Montreal. Both trains leave New York in the morning, so you'll need to spend the night in New York. It's a very scenic run along the Hudson River valley, past West Point Military Academy, Storm King Mountain and Bannerman's Island. As it's name suggests, the train to Montreal also passes through the scenic Adirondack Mountains and past Lake Champlain. Information on trains from New York to Canada . Change in Toronto for the famous Canadian trans-continental train 2-3 times a week to Winnipeg, Edmonton, Jasper & Vancouver.
You can book Amtrak & VIA Rail trains yourself, but if you want an agency to sort a package of train connections and hotels from New York to major Canadian cities, call Railbookers on 0207 864 4600 (UK office), 1-888-829-4775 (US office, toll-free) or 1-855-882-2910 (Canada, toll-free). Beginner's guide to train travel in Canada .
Eastbound transatlantic guide
Here is a typical timetable, transfer & journey information for most eastbound trans-Atlantic crossings. Although they usually follow this pattern, please check sailing & check-in times for your specific date when you book in case they are different. If you find that anything has changed, do let me know . If you plan to travel westbound, click here . Are westbound or eastbound crossings better?
By train from Washington DC & other US cities to New York
Amtrak trains link Washington DC & New York in less than 3 hours, Boston to New York in under 4 hours. The daily Lake Shore Limited links Chicago & New York overnight, with connections in Chicago from LA, San Francisco, Seattle, etc. However, the Lake Shore arrives at New York's Penn station in the early evening, too late for same-day connections with the 'Mary, so you'll need to leave Chicago two nights before the 'Mary sails and spend a night in New York before sailing day. You can check schedules and fares and buy tickets for any of these trains online at www.amtrak.com . Note that between New York & Washington or New York & Boston you'll be offered two different types of train: The premium-fare Acela Express 150mph high-speed train with business class and first class, but no coach class, and the slower but cheaper Northeast Regional trains with coach class and business class. You can book Amtrak trains yourself, but if you want an agency to sort a package of train connections and hotels from other US cities to New York for you, call Railbookers on 0207 864 4600 (UK office) or 1-888-829-4775 (US office. Beginner's guide to train travel in the USA .
By train from Toronto, Montreal & Canada to New York
Two daily trains link Canada with New York, the Maple Leaf from Toronto and Adirondack from Montreal. Both trains arrive in New York in the evening, so you'll need to spend a night in New York before sailing day - Check hotels in New York . It's a very scenic run down the Hudson River valley, past West Point Military Academy, Storm King Mountain and Bannerman's Island. As it's name suggests, the train from Montreal also passes through the scenic Adirondack Mountains and past Lake Champlain. Information on trains between Canada & New York . The famous Canadian trans-continental train links Vancouver & Toronto three times a week, via Jasper, Edmonton & Winnipeg. You can book Amtrak & VIA Rail trains yourself, but if you want an agency to sort a package of train connections and hotels from a Canadian city to New York for you, call Railbookers on 0207 864 4600 (UK office) or 1-888-829-4775 (US office, toll-free) or 1-855-882-2910 (Canada, toll-free). Beginner's guide to train travel in Canada .
By taxi from Manhattan to Brooklyn Cruise Terminal
A normal yellow cab from New York Penn Station or any hotel in Manhattan to the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal costs around $40 for up to 4 people and all your bags. Enjoy the drive across the famous Brooklyn Bridge in a traditional New York Yellow Cab! The taxi ride takes 20 minutes.
Alternatively, a frequent ferry operates from Pier 11 at the end of Wall Street in Manhattan to Red Hook ferry terminal in Brooklyn, this is just 100m from the Brooklyn Cruise Terminal, fare $4, see www.ferry.nyc . See walking map from Red Hook ferry terminal to Brooklyn Cruise Terminal .
QM2 check-in procedures in New York
Check-in usually opens around 13:00 and closes around 15:45. Cunard will give you a specific check-in time on your e-ticket to try and stagger people arriving, but you can arrive earlier if you like. Visitors are not allowed on board, so anyone seeing you off will have to leave you at the terminal then wave from the shore.
Cunard will have sent you adhesive labels showing your departure date & cabin number, remember to put one on each bag before arriving at the terminal, as when you get there your larger bags are immediately taken from you. They will magically reappear later in your stateroom. No one bag should exceed 23Kg (50lb) but you can take as many bags as you like as long as they will all fit into your stateroom.
You then walk into the terminal and join the short queue for a ticket check, then another short queue for the X-ray and metal detector security check, then you join a long zig-zag queue for check-in proper.
At the check-in desk, you show your e-ticket, your passport & your credit card for on-board purchases, and a webcam photo is taken of each passenger for security purposes. You also hand in a brief health form notifying the ship of any fever you have or any diarrhoea you've had in the last 48 hours. Each passenger is given a credit-card sized plastic card which acts as your embarkation card, cabin key and charge card for buying drinks & souvenirs on board. You then go up the gangway onto the QM2, entering the Grand Lobby on deck 3.
Apart from the time spent in the main queue (have a reading book and some refreshments to hand), it's a painless process compared to airports. If you feel like a late lunch, or just a tea, coffee or juice when you board, you'll find the King's Court self-service restaurant on deck 7 open for business and offering all of these.
What's an eastbound Atlantic crossing like?
The ship normally sails from New York at 17:00. This is the usual time, but please check for your specific departure date. Once on board and settled into your stateroom, listen for announcements about emergency drill. This is held at 16:00 and takes about 20 minutes. You listen for the alarm bells, fetch your lifejackets from your stateroom and go to your allocated muster station where staff will brief you on emergency procedures and you'll listen to an announcement by the captain. After this you're free to go up on deck and admire the Manhattan skyline astern and the Statue of Liberty to starboard (right-hand side). At 17:00 she casts off, and with a band playing on her aft decks and glasses of champagne available (around $17) she heads out to sea. Manhattan and the Statue of Liberty slowly disappear astern, and the QM2 heads toward and then underneath the huge Verrazano suspension bridge out into the Atlantic. There is just a few precious feet of clearance above her red funnel! An NYPD police boat follows behind (seeing you off the premises?), and a police helicopter buzzes overhead.
Seven nights at sea on the Atlantic. Cunard slowed down their crossings to from 6 to 7 nights from 2011 onwards, although an occasional crossing still takes 6 nights. Naturally, you'll find a whole programme of entertainment & activities on board every day, and if you really want to be bored you'll have to work hard at it! There are no islands or coastline to see in mid-Atlantic (or even other ships, usually), but personally I never tire of gazing at the brooding waters of the North Atlantic. It changes from day to day, sometimes smooth and glassy, sometimes choppy and sombre, sometimes foggy, sometimes sunny. You may get rough crossings especially in October, November or December, but my own transatlantic crossings on the 150,000 ton Queen Mary 2 or 70,000 ton QE2 have been rock steady all the way. You could be in a 5 star hotel rather than on board a ship! The QM2's clocks are put forward an hour at 2am on five of the seven eastbound nights because of the time difference, giving you an hour's less sleep in this direction - if there's one reason why a westbound crossing can be nicer than an eastbound one, this is it! (update 2013: Cunard has tried the crazy idea of putting the clocks forward at midday on recent crossings, much to passengers dismay, as it can be confusing and means dinner is too soon after lunch!) You will pass within a few miles of the resting place of the Titanic and an announcement may well be made on board. On the last evening at dinner you may catch site of the Isles of Scilly in the distance (about 35 miles west of Land's End), and later the lights of Cornwall twinkling to port. A first view of Great Britain! You're now past the Bishop Rock lighthouse an in the English Channel. Incidentally, a modern transatlantic crossing is now two days slower than it used to be, as the weekly service operated by the first Queen Mary and her consort Queen Elizabeth from 1946 to 1967 took just 5 nights.
The ship arrives in Southampton at 06:30. You'll need to be up early, at around 04:30, if you want to see the ship round the Isle of Wight and head past Portsmouth & Ryde and into Southampton Water, although this hardly lives up to the spectacular arrival in New York on a westbound transatlantic. There's a forward-facing observation deck on deck 10, immediately below the bridge, accessed from 'A' stairway. Otherwise, you'll find the ship docked at the Southampton Terminal when you awake, and the Kings Court & Britannia restaurants serving a welcome cooked breakfast to send you on your way.
QM2 disembarkation in Southampton
It's then just a matter of going through the UK immigration check. They you walk out of the terminal.
Express disembarkation: If you want to get off sooner and are happy managing all your own bags, you can register for Express disembarkation at the purser's desk on deck 2 the day before arrival. You are given an express disembarkation card. Express disembarkation passengers gather in the Queens Room from 06:45 onwards with all their luggage, and at around 07:00 when the gangway opens you simply walk off the ship with your bags, straight into the terminal.

Transfer by taxi to Southampton Central station
The Queen Mary 2 can use any one of four different terminals in Southampton, either the QEII terminal (dock gate 4), City Cruise Terminal (dock gate 10), Mayflower Cruise Terminal (dock gate 10), or the new Ocean Terminal (dock gate 4). Map of Southampton, showing all cruise terminals, Southampton Central Station & the original historic Ocean Terminal . A taxi to Southampton Central station costs around £10 from the Mayflower or City cruise terminals, or around £13 from the QEII terminal or Ocean Terminal. You'll find plenty of taxis waiting at the terminal, although there can be a long wait as there are so many other passengers. The taxi ride takes just 10 minutes.
Take the train to London Waterloo
Cunard no longer organise a special 'boat train' in connection with QM2 sailings. However, fast air-conditioned trains link Southampton Central with London Waterloo every 30 minutes taking around 1h17. No reservation is necessary or even possible for Southampton-London trains, you just turn up, buy a ticket and hop on the next train.
Southampton to London costs £43.10 adult one-way Super Off-Peak in standard class or £86.80 one-way Off-Peak in 1st class.
I would not buy a cheaper advance-purchase Advance fare because this commits you to a specific train and you are not in control of exactly when you arrive and disembark. Super Off-Peak, Off-Peak and Anytime fares can be bought on the day and used flexibly, so you can catch the next train.
You can check train times & fares from Southampton to London Waterloo or anywhere in Britain using www.thetrainline.com . Direct trains run from Southampton to Reading, Oxford, Birmingham, Manchester, Bristol & Cardiff, so you won't have to cross London. Beginner's guide to UK train travel . Find a hotel in London .
Onward trains from London to Paris & beyond
Onwards to Paris: Allow plenty of time for onward connections, certainly several hours, and maybe stay in London overnight. For Paris, take a UK domestic train from Southampton central to London Waterloo (no reservation necessary, see the section above), then take a taxi or Underground across London to St Pancras Station. Eurostar runs every hour or so from London St Pancras to Paris Gare du Nord in central Paris, journey time 2 hours 20 minutes. For a beginner's guide to Eurostar travel, see the London to Paris by Eurostar page . You can book tickets online in advance at www.eurostar.com , and you should indeed pre-book, as London-Paris prices start from £52 in advance but up to £200+ if you wait and buy on the day of travel.
Onwards to other countries: See this page for information on getting from London to any country in Europe . Having crossed the Atlantic on the luxurious Queen Mary 2, how about taking the Venice Simplon Orient Express vintage luxury train to Italy ? This runs on most Thursdays from April to October, and takes 24 hours from London to Venice, a real treat. You can book European trains yourself, but if you want an agency to put together a package of train connections and hotels from anywhere in Europe to Southampton for you, call Railbookers on 0207 864 4600 (UK) or 1-888-829-4775 (US office).
Which cabin to choose?
There are a bewildering range of staterooms on the Queen Mary 2 at varying prices, but they basically fall into these categories, in ascending order of cost:
Britannia Inside: An Inside cabin means it has no window, but even though this is the cheapest option, these staterooms are spacious, beautifully designed and have all the facilities mentioned above. They have double or twin beds for 2 people, although some rooms are fitted with an additional two drop-down upper berths making a 3 or 4-berth room. Some cabins are wheelchair-accessible. Allocated to the Britannia restaurant. Typically 155 sq ft.
Britannia Atrium View: There are a handful of standard inside cabins on decks 4, 5 & 6 which have a small window opening onto the atrium above the Grand Lobby. They have double or twin beds for 2 people, but none of these rooms are fitted with additional berths. Also allocated to the Britannia restaurant. Typically 161 sq ft.
Britannia Oceanview: These are outside cabins meaning they have a small non-opening porthole for sea views. Some seasoned travellers will tell you that with no coastline or islands to see on a 6 day transatlantic crossing, a window is unnecessary. However, I enjoy seeing where I am and love gazing at the vast and always-changing waters of the North Atlantic. Paying the extra for a Standard Oceanview is well worth it, both for the views and the natural light. These staterooms have double or twin beds for two people, but some rooms are fitted with an additional two drop-down upper berths making a 3- or 4-berth room. Some are wheelchair-accessible. Also allocated to the Britannia restaurant. Typically 194 sq ft.
I've crossed with an inside cabin and with an outside cabin, and I think it's well worth the extra for a porthole. It lets natural light into the cabin and it gives you a much greater sense of place - not to mention sunsets over the Isle of Wight and views of the Statue of Liberty as you pack up on arrival!
Britannia Balcony (Obstructed View) : The cheapest cabin type to have its own balcony, allocated to the Britannia restaurant. These are all on Deck 8 above the promenade deck, but with their view heavily obstructed by the ship's lifeboats. They have a double or twin beds for 2 people, and a few cabins have a 3rd berth in the form of a pull-out sofa bed.
I'd definitely pay a little more for an sheltered balcony, without any obstruction.
Britannia Sheltered Balcony: The next cheapest cabin type to have its own balcony, allocated to the Britannia restaurant, also with a double or twin beds for 2 people, a few cabins have a pull-out sofa bed as well. Sheltered balcony cabins are on decks 4, 5 & 6 below the promenade deck with a small balcony cut into the hull. Typically 269 sq ft, including balcony.
This is my own first choice (unless you can afford a megabucks suite, of course), arguably a better choice for a transatlantic crossing than a more expensive cabin with a more windswept balcony in the ship's superstructure. See the photos below.
Britannia Balcony: Also allocated to the Britannia restaurant, these are slightly smaller than the Sheltered Balcony rooms, but have a glass-fronted balcony higher up in the ship's superstructure, on deck 8 and above.
The open glass-fronted balcony lets even more natural light into the cabin than a sheltered balcony, but it'll be more windswept than a sheltered balcony on a transatlantic crossing! Typically 248 sq ft, including balcony.
Britannia Club Balcony: Similar to a Britannia Balcony, but allocated to the single-sitting 'Britannia Club' restaurant, a separate off-shoot of the main Britannia restaurant. Typically 248 sq ft, including balcony.
Princess Balcony Suites: Suites with balcony, all allocated to the Princess Grill restaurant. Typically 381 sq ft, including balcony.
Queens Balcony Suites: Various types of suite, up to and including the extravagant Grand Duplex suites, all allocated to the Queen's Grill restaurant. All have balconies, except the two Q3 grade Royal Suites. Size varies from 506 sq ft to 2,249 sq ft.
QM2 deck plans in PDF format
If you pay the more expensive Cunard fare so you can choose a specific cabin, here are some things to consider.
You can feel a slight up & down movement of the ship towards at the bows, but will feel hardly any movement at all amidships. For this reason mid-ships cabins are higher-graded and cost more (Even if you pay the cheaper Saver fare, you can select a higher grade to ensure a mid-ships cabin).
Some people have reported noise from below when occupying sheltered balcony cabins on 4 deck directly above the Illuminations or Royal Court Theatre, so 5 or 6 Deck may be preferable. However, we had 4101 & 4105 over the Chart Room bar and these were perfect.
Adjacent cabins with connecting doors are marked on the QM2 deck plan . Choose these if four of you are going to book two cabins. But don't choose these if you're only booking one cabin, as a wall with connecting door is never as totally soundproofed as a wall without.
Facilities in all cabins
Even the cheapest QM2 cabin (or stateroom as Cunard calls them) features comfortable beds, a private bathroom with shower, sink & toilet, a dressing table, flatscreen TV, a small coffee table & chair, 240v UK & 110v US style power sockets, pay-per-minute internet access , soap, shower gel, shampoo & conditioner, bathrobes, hairdryer, plenty of wardrobe space, room service menu and a solid electronic safe for your valuables that's large enough for a 14" laptop. A bedtime chocolate is delivered to your stateroom when the steward turns down your bed.
Where cabins can be configured with either twin beds or a double, you can select your preference in advance using the online voyage personaliser at my.cunard.com/en-gb/mycruise/login the same online system where you download and print your luggage labels and e-ticket. You log on with your Cunard booking reference and personal details.
Britannia sheltered balcony See 360º image
This is cabin 4101 on 4 Deck. The Man in Seat 61 says , "This is my own preferred cabin for a transatlantic crossing. Even at 20 knots in mid-Atlantic the balcony remains wind-free just as the word sheltered suggests. Some people say you won't get much use out of a balcony on the Atlantic, but I loved being able to stroll outside at any time and stand at the rail watching the Atlantic drift past. On a sunny summer crossing off Newfoundland we did indeed sit outside, and even when inside, the French windows let in lots of natural light, making it a far nicer room than an inside or outside cabin, so upgrade if you can. I have yet to travel with a more expensive full-balcony cabin, but I expect those are a lot more windswept!". Click the photos for larger images.
Britannia inside & oceanview
Qm2 restaurants, which restaurant.
The fare includes breakfast, lunch and dinner, as well as afternoon tea in the Queen's Room or King's Court. It does not include drinks, other than the basic water, tea, coffee & juice available at the drink stations in the Kings Court buffet restaurant. Bottles of wine start at around $30 and real ale lovers can choose Old Speckled Hen or Spitfire for around $6 a bottle.
Your allocated restaurant: Each stateroom is allocated a restaurant. Most cabins, including the Inside, Oceanview & Sheltered Balcony, are allocated to the Britannia restaurant on decks 2 & 3. The more expensive staterooms are allocated to the more intimate Princess Grill on deck 7, and the very best staterooms to the Queen's Grill , also on deck 7. The food is excellent, and you choose from a menu of half a dozen different starters, main courses and desserts, which changes every day.
Optional dining venues: You can also choose to eat any given meal in the informal King's Court buffet on deck 7, or pub grub in the Golden Lion pub on deck 2, instead of your allocated restaurant. It's entirely up to you, you can decide on a day by day basis.
There is also the Veranda Restaurant aft on deck 8. This does seafood and steaks, and is an extra-cost option - you reserve a table and pay extra to dine there instead of your allocated restaurant.
Room service: If you'd rather eat in your cabin, every cabin has free room service from a simple menu including burgers, pasta, cheese & crackers. You can order by phone at any time, it's all included in your fare. However, if you order any drinks from room service, including soft drinks, these are charged at bar prices. You can also choose to have breakfast delivered to your stateroom, except on the morning of arrival. Just hang the breakfast order form on your cabin door before retiring.
Britannia restaurant
Most staterooms are allocated to the Britannia restaurant , a magnificent two-storey 1,300 seat restaurant spanning decks 2 & 3 and reminiscent of the grand dining saloons of the great ocean liners of the past. There are two sittings for dinner, 6pm & 8.30pm. If you pay the Cunard fare you can choose a sitting when you book, if you pay the cheaper Saver fare you will be allocated a sitting, perhaps the less popular 8.30pm one. If you log onto your online voyage personaliser at my.cunard.com/en-gb/mycruise/login with your booking reference and personal details it will confirm your sitting before you travel. Evening entertainment is arranged so that both sittings can enjoy it, although the 6pm sitting gives you the rest of the evening free, and is arguably more relaxed than the later one. If you've young children, see the section below . There are no specific sittings or allocated tables for lunch or breakfast, you are allocated a table when you walk in, choosing your own table for 2, table for 4 or if you prefer, seats at a shared table so you get to meet other passengers.
Princess Grill & Queen's Grill
More expensive staterooms are allocated to the Princess Grill , the most expensive suites to the Queens Grill . Both are aft on deck 7, served by the same galley. There are no sittings, you can dine any time you choose when the restaurant is open. If you want a drink before dinner, the Grill Lounge is a lounge and bar exclusively for Princess & Queens Grill passengers, on 7 deck aft, directly opposite the entrance to the Queens Grill.
Kings Court
The Kings Court buffet restaurant takes up most of the centre section of deck 7, and it's open almost continuously from early until late, with only half an hour here and there were breakfast dishes are swapped for lunch or lunch for dinner. There's a wide variety of food, all good quality, including a carvery. The window tables with sea views cross the promenade deck are the nicest. Tea, coffee, hot chocolate, water & juices can be had for free from the drinks stations in several locations around the Kings Court area. Stewards will take your order for wine, beer, cocktails, mocktails or fizzy soft drinks and deliver them to your table, these drinks must be paid for, added to your on board account.
The Man in Seat 61 says , "If you fancy a first breakfast in the Britannia restaurant then a second breakfast in the Kings Court, why not? After all, Second Breakfast is the most important meal of the day..."
The Verandah restaurant
The Verandah restaurant aft on deck 8 is an extra-cost option, specialising in steaks and seafood. You can make a reservation at the Verandah restaurant whilst you are on board, or you can book a table for one or more nights at your desired time before you travel, by logging into your voyage personaliser at my.cunard.com/en-gb/mycruise/login booking the table and paying the extra.
The Man in Seat 61 says , "With our normal Britannia sitting not until 8.30pm, we booked a table at the Verandah for 6pm on our last evening before getting up early to see the arrival into New York. I wished we'd dined there on more than just one occasion, the steaks were top class."
QM2 bars & lounges
There is no shortage of watering holes on the Queen Mary 2. Personally, the Chart Room works for cocktails before or after dinner as it's near the social centre of the ship on deck 3, but for quiet reading, working on a laptop and generally getting away from it all, the Commodore Club with its forward view over the bows is my top choice. Drinks are not too expensive: A tea is $2, a glass of wine perhaps $6, a cocktail $10. Although I'm a non-smoker 99.9% of the time, one of Havana's Montecristo number 2 cigars and a 1979 Armagnac were sound recommendations from the barman on the last night of a return crossing from New York.
Champagne bar
Sponsored by Veuve Cliquot, the Champagne Bar is on 3 Deck, on the upper level of the Grand Lobby in the centre of the ship.
Commodore Club
Located on deck 9 on 'A' stairway at the forward end of the superstructure. It's away from the hustle and bustle, a quiet and relaxing place for a cocktail and a read or chat. You get a great forward view over the bows, although blinds are drawn at dusk so the light does not interfere with the view from the bridge above. This is my favourite place on QM2 - it does a great range of cocktails and other drinks, the Churchill Cigar Lounge opens off the Commodore Club, the library is one deck down also on 'A' stairway, and the open-air observation deck below the bridge is two decks up on 'A' stairway. There's a huge illuminated model of the QM2 behind the bar.
Chart room bar
Located on deck 3 near the Britannia restaurant, this is the largest and busiest of the QM2's bars. Click the photo for larger image.
Golden Lion Pub
Located on deck 2 near the Britannia restaurant, this is not only a good place for a pint of London Pride, you can take meals here too, with pub-style food such as fish and chips or sausages and mash. Click the photo for larger image.
Carinthia Lounge
Located on deck 7 next to the Kings Court buffet with doors opening onto the promenade deck. This is a good place to sit, read, and have a tea or coffee. You may also find some complimentary snacks or soup here too, at the kitchen counter. Click the photo for larger image.
Afternoon tea in the Queen's Room
Every day at around 3.30pm, afternoon tea is served in the Queen's Room, on 2 Deck aft. A choice of teas comes with daintily-cut sandwiches, scones and cakes, served by stewards in white gloves. Afternoon tea is included in the fare, but a glass of champagne is extra.
Grill Lounge
The Grill Lounge is a lounge and bar exclusively for passengers travelling in the upmarket staterooms and suites allocated to the Princess and Queen's Grill restaurants. It's located on 7 Deck aft, directly opposite the entrance to the Queen's Grill and the ship's width away from the entrance to the Princess Grill. It seemed to be empty most of the time even with the ship sailing full, it's main purpose seems to be drinks before dinner.
Churchill's Cigar Lounge
This is a sealed and specially-ventilated room opening off the starboard side of the Commodore Club. Here you can order a whisky or cognac and choose from a cigar menu. The rest of the ship's accommodation is of course non-smoking!
QM2 activities & entertainment
A daily programme for the following day is delivered to your stateroom each evening. It shows details of the entertainment and activities on board, along with navigational & itinerary information and the opening and closing times of all restaurants, bars and other facilities. There's an ongoing programme of shows, plays & lectures. For example, recent crossings featured talks by John Cleese about his work on Monty Python & Fawlty Towers, excellent lectures by an expert on New York skyscrapers, an edited version of Shakespeare's 'Taming of the Shrew' and Oscar Wilde's 'The Importance of being Earnest'. The QM2 also features the world's only sea-going planetarium, called the 'Illuminations'. And of course there are several live bands on board, with dancing every evening, sometimes themed such as the 'Black & White Ball' and 'Ascot Ball'. If it's disco you prefer, you'll find that in the G32 nightclub. You'll also find the Canyon Ranch spa on deck 7, offering a wide range of treatments from manicures to massages, Jacuzzis to saunas. If you want to be bored, you'll have to really work at it.
Library & bookshop
The QM2 has an excellent library - for me, one of its best features - located on 8 deck forward on 'A' stairway directly below the Commodore Club. You can take out books using your cabin key, or read them in the library, with comfy seats, some with a forward-facing view over the QM2's bows. The library is open during office hours every day, outside these times the bookshelves are locked but the library itself remains accessible. As you'd expect, the QM2's library has a particularly good section of books about ocean liners. Next to the library is a bookshop selling travel guides, QM2 souvenirs & ocean liner/QM2 books. Click the left-hand photo for larger image .
Swimming pools
The QM2 has several swimming pools. The most popular (certainly on a transatlantic crossing) is the Pavilion Pool on 12 deck, with sun loungers, two hot tubs, see the photo below. The roof can slide away when the QM2 visits warmer climates, but it remains closed on the Atlantic. Towels are provided, there are toilets (visible below behind the two hot tubs) which you can use as changing rooms, or you can change in your cabin and use your bathrobe. You can see the funnel from the pool through the glass roof, towering above you. Don't jump when the ship's horns are tested at midday! There's also a bar here, open at certain times of day. In addition to this indoor pool there are two outdoor pools on the open decks aft (7 & 8 Deck), one of which is only shallow for kids, the other designated as adults-only. Click the photo for larger image .
Illuminations
The QM2's Illuminations towards the forward end of Deck 2 can be used as a lecture theatre, cinema or (with an ingenious dome lowered from the ceiling) the world's only ocean-going planetarium. You'll usually find varying recently-released films shown most evenings, and planetarium sessions at various times on most days. There's also usually a lecture series or two during each crossing with subjects varying from New York Skyscrapers to pirates on the high seas to the design and build of the QM2. Click the photo for larger image .
Royal Court Theatre
The QM2's Royal Court Theatre is used for various shows and performances, for example I have seen an interview with John Cleese here, and some stand-up comedy. Click the photo for larger image .
Spa & gymnasium
The QM2's Canyon Ranch Spa is at the forward end of Deck 7, with with treatment rooms and pool, plus a small beauty salon above on Deck 8. You can make appointments at the reception desk, treatments & massages are billed to your on-board account. There's a free-to-use gymnasium at the forward end of Deck 7, pictured below right.
The Cunard heritage trail
The Queen Mary 2 is filled with paintings, information panels and even interactive screens telling the history of Cunard Line, its ships, and the famous people who crossed the Atlantic aboard them.
Travelling with children
You won't be the only family on the QM2, especially on a transatlantic run! You'll find plenty of entertainment for children in the Play Zone at the aft end of 6 deck.
Arrangements for children & pregnant women on the Queen Mary 2
The play zone & child care.
The Zone is aft on deck 6, staffed by a team of friendly young British-trained nannies. It has a toddler zone for ages 1-3, a Play Zone for ages 4-6 and The Zone with various computer games and other activities for older kids up to 17. There's plenty to do, and activities such as treasure hunts or ship tours are organised by the Play Zone team.
Children from 2 to 7 inclusive can be left free of charge with the nannies in the Play Zone during its opening hours, 09:00-12:00, 14:00-17:00, 18:00-24:00 (shorter hours apply on the first and last nights). In other words, you can sign them into the Play Zone at 9am, pick them up at noon and take them to lunch, sign them back in at 2pm and enjoy an afternoon show, pick them up at 5pm and take them to the children's tea provided in the King's Court 'Chef's Galley' area between 16:30 & 17:30. Then you can check them back into the Zone at 6pm until midnight, leaving you free to enjoy a formal dinner and evening entertainment while the kids play happily in the Zone and later settle down and fall asleep in front of some cartoons. Outside the Play Zone, children 1 to 7 must always be accompanied by an adult around the ship.
Children 8 and up to 17 can also use the Zone, signing themselves in and out. They are free to wander the ship solo.
I suggest calling Cunard to check current childcare arrangements as they tweak them from time to time, but they don't properly explain them on their website - indeed, we didn't know how extensive their childcare facilities were until we we actually on board!
Cabins & dinner sittings
If you have young children, it's worth asking for a cabin towards the stern of the ship. We were given a stateroom at the extreme forward end of deck 6, whereas the Play Zone is at the extreme aft end of deck 6. That meant we had to walk a sixth of a mile from cabin to Play Zone to sign the kids in, then a sixth of a mile back again to get changed. It proved impossible sign the kids in at 6pm when the Zone opens, walk all the way back to the cabin, get changed into formal dress, then walk forward again to the Britannia restaurant for a 6pm sitting.
From this experience on our outward crossing, we changed our sitting for the return crossing to 8.30pm. The evening then worked better, although some after-dinner films or shows finished after midnight so could not be attended without leaving early to collect the kids. The dinner tended to take up much of the evening. A stateroom near the Zone, and dressing for the 6pm dinner sitting before taking the kids to the Zone, might be the ideal solution, but my wife's and my opinion is divided!
If you've small children, remember to take your folding buggy (stroller). It's a big ship!
Other useful information
There is no baggage limit on the Queen Mary 2, either in terms of total weight or the number of bags. You can bring what you like, as long as it all fits in your stateroom. However, for safe lifting by staff, no one item may exceed 23Kg (50lb). Bags are taken from you on arrival at the terminal and they reappear in your stateroom on board. At the end of the crossing, they are transported ashore for you. See the embarkation & disembarkation arrangements above. If you plan to go one way by ship, the other by air, one advantage of taking the ship on the return leg is that you can take as much shopping as you like!
Cunard sometimes have to fight off a stuffy image, and it didn't help that until 2013 they had a three-tier dress code as complicated as a Virgin Trains Saver Ticket restriction. However, they now have just two codes, formal and informal. One of two dress codes will apply each evening after 6pm in all the main restaurants and bars, although not in the Kings Court buffet restaurant. You'll be told which dress code applies on which night in if you log on to your voyage personaliser and it's also stated in the daily programme delivered to your stateroom.
Payment on board
Everything on board, including drinks in the bar, books from the bookshop, massages in the spa, purchases in the shops or internet access, is billed to your on board account. You simply show your cabin card and sign for the payment. At the end of the crossing, the total is automatically deducted from the credit card you gave them at check-in and you'll get a summary of your account delivered to your stateroom half-way across and at the end of the voyage. Just be aware that Cunard follow the American practice of quoting you one price but charging you a slightly higher price, as all bar prices shown on the drinks menu have 15% service fee added to them automatically. As service is then included, there is no need to add a gratuity unless the service has been particularly special.
Internet & mobile phone access
Internet access is available for a fee throughout the QM2, both in your cabin and in all the public areas including bars but excluding the theatres & restaurants. It generally works well with good download speeds. You pre-pay for a bundle of minutes and this is added to your normal on-board account.
2019 prices: $15 for 30 minutes (= $0.50 per minute), $45 for 120 minutes (= $0.38 per minute) or $80 for 240 minutes (= $0.33 per minute).
You can spend these minutes individually, so for example you can buy 120 minutes and spend them over the course of the whole voyage, logging on to download emails, logging off again to compose replies offline, then logging on again to send, and so only using a few minutes at a time.
To use your own laptop, simply click on the 'Qm2_Guest_internet' internet connection and open a web browser to see the log-in screen. Register with your name & cabin number on this log-in page and the cost will be billed to your QM2 stateroom account. If you don't have your own laptop, the Cunard Connexions rooms on deck 2 or the library on deck 8 have self-service internet PCs which you can use for the same rates. You'll find power sockets for laptops (both British 3-pin and US 110v) in your cabin, and (if you hunt for them) British 3-pin sockets in certain areas of most bars including the Commodore Club on deck 9 forward and the Chart Room on deck 3. Tip: I found that the Commodore Lounge on 9 deck was the quietest and nicest place to work, there's a 3-pin power socket near the skirting in the 'bridge wing' far side of the lounge. Mobile phone access is available on board throughout the crossing, although it isn't cheap, you'll need to ask your phone network for their rates.
The QM2 is entirely non-smoking apart from the open decks and the Churchill Cigar Lounge forward on deck 9 next to the Commodore Club.
As well as a hotel-style pay-per-item laundry service for laundry collected from your stateroom, you'll find a small free-of-charge self-service laundrette on cabin decks 4, 5, 6 & 8, see the photo below. These have washers, driers, free detergent sachets, iron & ironing board. This came in very handy on both our outward and return crossings on a 7-week trip to the States, as we arrived in the US with bags full of clean clothes and arrived back in Blighty without a huge laundry backlog. Also useful for ironing dress shirts that have become creased in the baggage.
Taking your dog
Yes, you can take your dog across the Atlantic on the Queen Mary 2, but they will be kept in the ship's kennels on 12 Deck during the crossing and (except for guide dogs) are not allowed in the public areas. Contact Cunard for details. There's an exercise area next to the kennels.
Visiting the QM2's bridge
There are no official bridge visits, but there is a viewing room behind the bridge with two large soundproofed windows so you can see what's going on. It's normally open 09:00-16:00 on sea days, although it's closed in bad weather. The entrance is on the port (left-hand) side of the ship on deck 12, accessed via 'A' stairway. No photography is allowed now - the photos below were taken in 2010 although little has changed here.
Which is better, a westbound or an eastbound transatlantic crossing ?
If you really haven't got the time or money to go both ways by sea, you might want to go one-way by sea and the other by air. You can often find one-way QM2 fares with a 'free' air fare in the other direction. If you're British and a shopaholic, the obvious advantage of going out westbound by air and back eastbound by sea is that you can shop in New York and bring back as much as you like, as there are no baggage limits on the Queen Mary 2. And you'll have the leisurely voyage back home to look forward to at the end of your trip. However, for my money (not being a great shopper), westbound is much better. There's the growing anticipation as you near America at the end of an outward westbound crossing, there's the significant advantage of 25-hour days as the clocks are put back on 5 of the 7 nights due to the time difference, and best of all the spectacular arrival into New York harbour in the early morning, with that Manhattan skyline lit by the rising sun. When you're enjoying your evenings on the town (or rather, the ship) until late at night, the 23-hour days on an eastbound crossing as the clocks are put forward can be a killer! On the other hand, if I were an American heading for Europe, I might well be tempted to head out by sea eastbound, returning west by air.
Forum for cruise reviews, questions & the latest advice
A good place to find advice & reviews about the Queen Mary 2 and other ships, and to post your own questions and reviews of your trip, is the online cruise forum at www.cruise.co.uk .
About Queen Mary 2
The QM2 was built in 2003 at St Nazaire in France, by Chantiers de l'Atlantique, the same shipyard that built the famous French Line ships Ile de France , Normandie and France . The Queen Mary 2 is no longer the biggest passenger ship in the world in terms of Gross Tonnage, as the Queen Mary 2's 148,528 tons have now been exceeded, first by Royal Caribbean's 154,000-ton Freedom of the Seas in 2006, and then by the 225,000-ton Oasis of the Seas in 2009. However, the QM2 remains the tallest, longest and widest ship ever built, at 1,132 feet long and 148 feet wide. For comparison, the original Queen Mary is just 81,237 tons, 1019 feet long, 118 feet wide, and the Titanic was only 46,000 tons, 883 feet long, 93 feet wide. Queen Mary 2 uses an unconventional propulsion system: Four large diesel engines and two gas turbines generate electricity, and this powers four electrically-powered propellers each housed in a 'pod' attached under her stern. The rear two pods swivel to steer the ship, so the QM2 does not have a conventional rudder. The propellers face forwards rather than backwards, and give her a top speed of around 30 knots (1 knot = 1.1 mph), although she normally crosses the Atlantic at 20 to 25 knots. See Queen Mary 2 Wikipedia entry .
Souvenirs & books about the QM2
Buy a superb model of the Queen Mary 2: The souvenir shop on board QM2 on deck 3 has a couple of models of the Queen Mary 2, but neither (in my opinion) are particularly well detailed, and yet they aren't cheap, either. If you become a QM2 aficionado during your crossing (highly likely!) and want a top-quality model of the QM2 to sit on your shelves or desk, I highly recommend the 1:1250 Queen Mary 2 model at www.galerie-maritim.de . It is hand painted in die-cast metal. You can buy either a full hull version in a glass case, or a waterline model without a case. The models are small enough not to take up too much room, yet are superbly detailed. They are very expensive, but you won't be disappointed!
Books about the Queen Mary 2:
The book by John Maxtone-Graham is beautifully written and illustrated, a great souvenir, search for it at Amazon.com (USA) or Amazon.co.uk (UK). It's also available in the bookshop on board the QM2.
But by far the best book about the design, construction and operation of the QM2 is written by its designer, Stephen Payne, "RMS Queen Mary 2 Manual: An Insight into the Design, Construction and Operation of the World's Largest Ocean Liner", buy it at www.amazon.co.uk (UK) or www.amazon.com (USA). Highly recommended!
QM2 video guide
Alternatives to the queen mary 2, passenger-carrying freighters, hotels & accommodation, hotels in new york.
New York has hundreds of hotels, the two most famous being the New York Plaza Hotel opposite Central Park and the Waldorf-Astoria on 4th Avenue. I've never stayed at the Plaza, but have to say I was not impressed by the rooms at the Waldorf, on either occasion I stayed there. Here's my top tip for New York:
The Algonquin Hotel
The Algonquin is New York's oldest operating hotel, opened in 1902, and a designated New York City Historic Landmark. Perfectly located in mid-town Manhattan, a block or two from Times Square one way and Grand Central the other, with a lovely wood-panelled lobby and even its own hotel cat, which you may find wandering the corridors or sitting on the reception desk. To check prices & book, click here . For the Algonquin's history see en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algonquin_Hotel .
In Los Angeles: Hotel Queen Mary, Long Beach
If you get as far as Los Angeles after your transatlantic crossing, it has to be the Hotel Queen Mary , doesn't it? She makes a good base to explore the Los Angeles - Hollywood - Disneyland area. The original Queen Mary of 1936 has been permanently moored at Long Beach in California since the late 1960s, some 25 miles from Los Angeles Union Station (about a $90 taxi ride), and it's undoubtedly the most fascinating place to stay in LA. The hotel consists of most of the Queen Mary's original first class cabins, and there are plenty of restaurants and bars available on board, too. Hotel guests can more or less wander the ship at will, and even sign up for ghost hunts at night on board (and yes, from my own experience there is definitely something going on aboard that beautiful but ageing ship!). Wood panelled art deco interiors have been preserved, although a few modern items have been installed such as televisions, and (as we worked out from a historic deck plan) in some cases two of the Queen Mary's original cabins have been knocked into one hotel suite by turning one of the en suite bathrooms into a connecting corridor. She is one of the most atmospheric places I have ever stayed.
Back to home page
Yachting World
- Digital Edition

The best route for an Atlantic crossing? It depends when you go
- Belinda Bird
- May 29, 2015
Sailor and meteorologist Chris Tibbs advises go south for comfort and safety; go north for speed

Weather is a large part of any Atlantic crossing: deciding when to go, which route to follow and the sails to carry. The main consideration is to avoid the hurricane season from June to November, so most yachts leave in late November to arrive in time for Christmas, although the tradewinds in January are often stronger.
However, it is human nature to push boundaries and some crews always leave early to get a longer season. The earlier you leave, though, the more important it is to stay east before committing to a westerly course. Late hurricanes generally develop to the west, making a passage via the Cape Verde islands more attractive. It shortens the time in potential hurricane areas and offers an escape route south as hurricanes rarely track south of 10°N.
Flexible sailplan
During a typical crossing, the tradewinds will be Force 4 or 5, with some lighter periods and a few days of winds of 25-plus knots. A flexible sailplan is necessary to take account of the changing wind strengths – there is no one-size-fits-all answer. The most common sailplan is goosewinged, with most skippers carrying a specialist downwind sail for when the wind goes light.

Because squalls are common and can have gale-force gusts on the leading edge, it is important to be able to reduce sail quickly. Boats with only asymmetric spinnakers tend to struggle in strong downwind conditions and I would always carry a whisker pole to pole out a headsail as well.
Sailing hot angles may work for a lightweight flyer, but it adds a lot of distance. For a heavier cruising boat it is hard to gain the increase in speed to compensate for the extra distance. Once hull speed is reached, shorter will always be faster. ( See our feature on the best yacht for an Atlantic crossing )
North is fastest
With well-established high pressure, a direct (that is, northerly) route is usually fastest, staying far enough away from the high to keep the wind, but minimising distance. However, the less established the high is, the greater the chance of a mid-Atlantic trough or low developing, giving adverse winds. In this case a more southerly route is better.
Racing boats often take the northerly route and the faster the boat, the more likely this will pay off. However, it runs the risk of meeting depressions which develop mid-Atlantic.
These should not be underestimated and the potential gain of passing north of a depression must be balanced against the risk that it could deepen and track across the route. The route is also more prone to a northerly swell.
The southerly route, on the other hand, offers lower risk, with steadier tradewinds and less chance of an uncomfortable northerly swell.
When does the engine go on?
I like to arrive with at least one-third of my fuel left for safety. Others will put on the engine when the wind drops and call in at Cape Verde to refuel if necessary. The choice of route may also depend on fuel capacity and a crew’s willingness to use the engine.
A mid-Atlantic trough giving 24-48 hours of light wind is not unusual and can be motored through to keep on schedule. Yet for some crews, the engine is only for emergencies and a more southerly route will reduce the risk of light winds. Neither route is right or wrong. They are just different ways of sailing in what may be very different boats.
I have sailed across the Atlantic over 20 times and no two times have been the same. There can be a great deal of variation and weather forecasts are important. There needs to be some flexibility in the route to take account of forecasts and how they change over time. I like to pick up weather charts from NOAA and also GRIB files.
So, the default options are: go south for comfort and safety; go north for speed. Most boats take a more middle route, depending on the forecast.

Chris Tibbs is a meteorologist and sailor with over 250,000 miles at sea, including three circumnavigations and six speed records. He is a lecturer to ARC crews and provides routeing services.
See also: 15 things you need to know when planning an Atlantic crossing
This is an extract from a feature in the November 2014 issue of Yachting World
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the foremost international magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have practical features to help you plan and prepare to realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge month by month with a subscription delivered to your door – and at a discount to the cover price. S ee our latest offers now.
- Yachts for Sale
- Sales Report 2024
- FAQ – Luxury Crewed Yacht Charters
- FAQ – Bareboat charters
- FAQ – Sell your Boat
- FAQ – Buying a Yacht
- How Much does it Cost to Charter a Luxury Yacht?
- All Blog Posts and News
- Yachting for beginners
- Indian Ocean
- Mediterranean
- Sales & New build
- Motor Yacht
- Event & News

Best Yachts for Transatlantic Crossing: Our Selection and Advice for 2023

Sailing across the Atlantic is more than just an item on a bucket list for sailors. It’s how you get your boat to new horizons, whether to cruise the Caribbean islands or explore the waters around Europe. It’s a big undertaking and requires serious planning and a solid sailing vessel. You can cross the Atlantic by yourself, with a rally of like-minded racers and cruisers, or as part of a highly competitive race. But no matter how you go, the choice of a good sailing yacht lies at the foundation of a safe and enjoyable crossing.
What does a boat need for a transatlantic crossing?

If you choose to do your transatlantic crossing with a rally or race, you’ll have to meet a stringent list of required equipment and safety checks. That’s easier because you have the lists right in front of you, and a team of inspectors to check your work. Preparing for a crossing with just one boat, the captain has to take all the responsibility and know what to check.
Sailing across the Atlantic is a serious undertaking, and you will sail out of range of shore-based rescue and into rapidly changing and possibly severe weather systems. You will have several thousand miles of nonstop sailing and may be at sea for several weeks.
What you must have
Any boat sailing across the Atlantic needs solid construction and a sound rig, a reliable auxiliary engine, and enough stores for food and water for the crew. That’s a bare minimum. Every boat needs to be checked from stem to stern to make sure systems are reliable, many older boats can certainly make this trip, and not every new boat is suitable.
Some tiny boats have crossed the Atlantic, so minimum size isn’t a requirement. What successful boats have in common is a solid hull and rig, with reliable sails and systems.
Most transatlantic yachts have a lot more
You can cross the oceans with a lightly equipped boat with few conveniences or extra safety gear, but most do not. A few things to look for on your boat include:
- An EPIRB satellite rescue beacon .
- Long range communication devices, such as satellite phones and single sideband radios.
- Certified life raft with space for all crew on board.
- Storm sails
- Storm safety gear such as drogues or sea anchors.
- Access to up-to-date weather forecasts and reports.
Do not head offshore without these
The list of required equipment for races and rallies is exhaustive, and many of the requirements are exacting and expensive. No one is enforcing compliance when you sail on your own. But there are a few things you should not head offshore without.
- A reliable auxiliary engine. If the wind dies and you need to dodge bad weather, this can be a lifesaver.
- Access to good, current weather information.
- Reliable sails. Have all sails inspected by a sailmaker for wear and damage before setting out.
- A life raft. If you run into serious problems and lose your boat, this is your last hope for rescue.
- Spare parts and tools for common repairs.
Read also: 10 Sailing Myths And Bad Advice You Shouldn’t Listen To
What experience do you need to do a transatlantic?
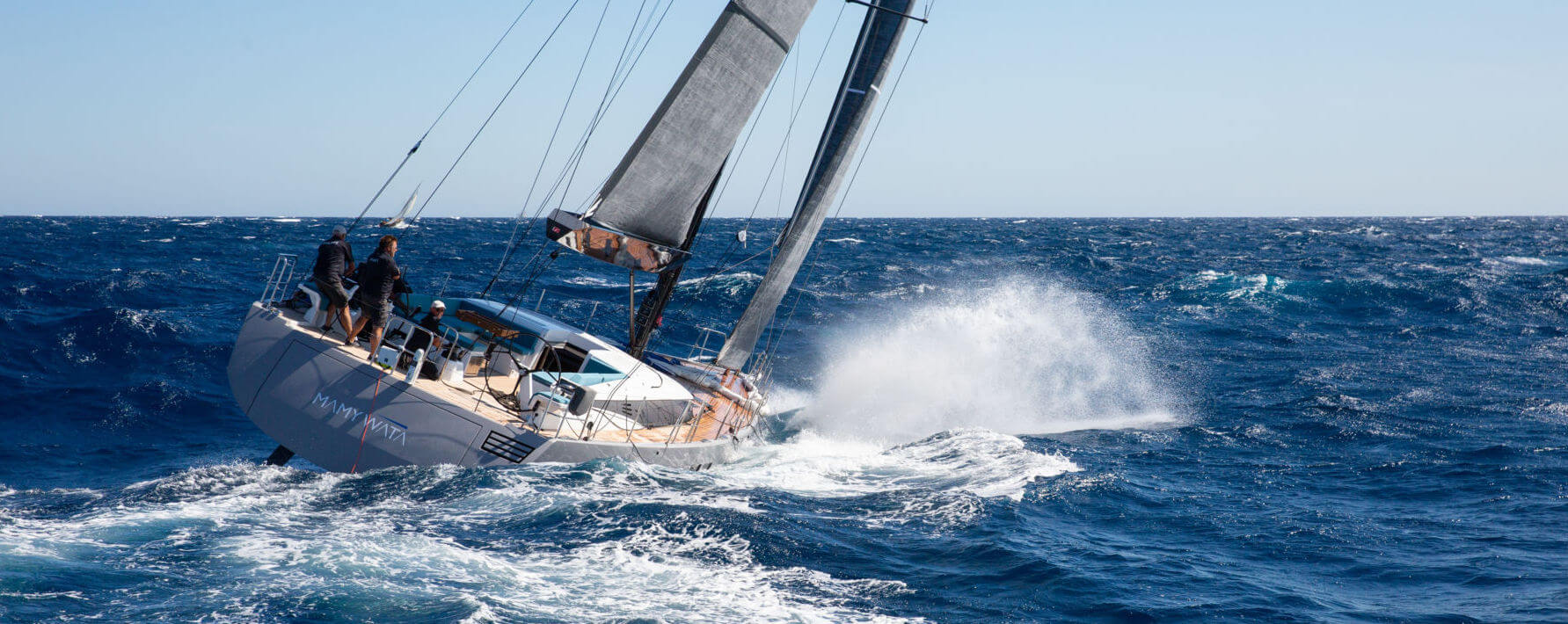

A transatlantic crossing is a major sailing milestone for experienced sailors. The north Atlantic is no place for new sailors and beginners, unless they’re with competent and experienced crew or a qualified captain.
If you’re thinking of a transatlantic crossing on your own, you’ll need experience with multi-day, nonstop passages. Sailing offshore is twenty-four hours a day and nonstop, there’s no place to park. Experience with night sailing, standing watches, navigation, provisioning, and basic engine and system troubleshooting are all a must.
Read also: Five Easy Beginners-Friendly Sailing Trips And Destinations
Chartering a yacht – a great option for less experienced sailors.
Charter fleets make seasonal moves from Europe to the Caribbean are an excellent way to get offshore sailing experience. Charter companies provide a captain and first mate, but you can reserve a spot and fill the roles of a full crew member, standing watch and sailing far offshore.
Many boats are also available for charter in cruising rallies, races, and deliveries. You’ll need to hire a captain with the needed offshore experience, but you may come away with enough experience to skipper your own yacht the next time.
The best yachts for a transatlantic crossing

There are many yachts which are suitable for a transatlantic passage. Some will be less expensive, some will be more comfortable, faster, or better suited to you, your experience, and your budget.
NEEL 51: Fast and easy to sail trimaran
The NEEL 51 is a fast, comfortable trimaran suited to a smaller crew. It’s spacious, but easy to handle while putting up double digit speeds and 200+ mile days. Trimarans can be a little more sea-kindly in waves and chop than catamarans, and don’t heel hard like monohulls. A protected helm station gives great protection offshore and good visibility, and there space on board for plenty of crew and guests.
The racing version of the NEEL 51 is built with lighter materials, and features a larger rig to project more sail area for more speed, while still affording the same luxury and comfort at anchor.
More info about our Neel 51 available for charter
Outremer 5X: High-speed catamaran sailing
The Outremer 5X offers top tier performance and comfort in a single passage. Sustaining double digit speeds with east, the Outremer 5X is one of the fastest cruising catamarans on the market. Outremer is known for both performance and quality, and your transatlantic trip will be fast and safe.
With four different helm stations, she’s a sailing boat foremost. It’s designed for a small crew, even when tearing up the ocean on a fast passage. With options for three or four cabins and a cockpit that can fit a dozen people, she’ll be as comfortable when you arrive as she is fast on passage.
Hallberg-Rassy 57: Sturdy monohull with elegance and speed
Hallberg-Rassy builds tough cruising yachts, and the 57 is no exception. While monohulls don’t put up the blistering speeds you’ll find in multihulls, the Hallberg-Rassy 57 is no slouch and can log 200 mile days. Most offshore sailing and cruising is done in monohulls, and blue water sailors love their stability and seakindliness across all conditions.
The Hallberg-Rassy 57 has generous accommodations, and loads of capacity for gear supplies. The deck layout is clear, and lines and controls are laid out for easy use with a small crew. With a performance design by German Frers, the 57 sails well on all points of sail.
There are many choices for the best boat for you for a transatlantic crossing. No matter which boat you choose for your transatlantic and how you go – on your own, or on a charter – preparation is key. Your boat needs to be equipped with a full range of safety gear, and checked from top to bottom so you know your sails, hull, and engines will get you where you’re going.
Read also: The Caribbean To Mediterranean Sailing Routes: How To Cross The Atlantic Eastward
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
8 gulets, ketches and schooners to consider for a timeless sail , luxury crewed yacht charters – frequently asked questions, luxury yachts for charter perfectly suited for 10 guests.
- Testimonials
- Privacy Policy

Sailing the Big Blue: How Long It Takes to Sail Across the Atlantic
Sailors, both amateur and professional alike, have always seen a transatlantic crossing as a sort-of rite of passage: it’s what separates the men from the boys, the women from the girls, and the sailors from the land-lubbers (that last one was mine).
But how long does it take to sail across the Atlantic? Short answer: about a month. Long answer, well…
How Long Does It Take to Sail Across the Atlantic?
To answer the question, ‘how long does it take to sail across the Atlantic Ocean?’, one needs to look at two things: the vessel you’re using, the weather, and the route you’re taking. The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest ocean in the world; it’s no spring chicken, many people die trying to pull off a transatlantic crossing. But of course, with the amount of information out there plus the number of experienced people you can get help from, your chances of death are minimal.
In ye olden times, it took Christopher Columbus 5 weeks to get from Spain to the New World, and even now, it still takes around 3 to 4 weeks for a person on a sailboat to cross the great blue Atlantic. Of course, the fastest transatlantic sail record is 3 days, 10 hours, and 4 minutes by the ocean liner the U.S.S United States, while the fastest transatlantic sail by a sailboat (in this case, a competitive trimaran) was by the BanquePopulaire V in 2009 which took 3 days, 15 hours, and 25 minutes.
For normal sailors, however, sailing across the Atlantic will take 3 to 4 weeks.
Why Does Sailing Across the Atlantic Take a Month?
There are several ways to sail across the Atlantic; however, the fastest, most efficient way to do it is two-fold:
- Take advantage of the Trade Winds (more on this later)
- Follow one of two routes: The Northern Passage and the Southern Passage
Because of trade winds, a transatlantic crossing going from East to West (Portugal to the Windward Islands in the Caribbean) will usually take around 3 weeks and 6,800 km. In good weather, that’s about 20 days of solid sailing, and while it’s not the easiest thing in the world, it would be a pleasant experience for both novice and expert sailors alike.
In general, however, sailors measure distance and not time, because distance is constant while time can vary depending on the weather. Sailors will use the Nautical Mile , with 1 NM equal to 1.1508 miles OR 1,852 meters.
Transatlantic Sailing Routes
While a transatlantic crossing is generally reserved for highly-experienced sailors, it doesn’t mean that novice skippers can’t sail with more veteran salts; after all, the best experience is experience itself. Transatlantic crossings can be one of the most challenging things you’ll ever go through, but with the right route, frame of mind, and of course, timing, it’s also the most rewarding.
While crossing the Atlantic Ocean usually takes about 3-4 weeks, it depends on the route you take. In general, there are two main routes that sailors use:
The Northern Passage, which starts from the West
The Southern Passage, which starts from the East.
When you see the routes on the map, it doesn’t look like the shortest route as the crow flies; in fact, it looks like a roundabout way of going to places. However, those routes are there for a reason: they’re the most forgiving sail routes for most ships, and has been in use for more than 500 years. Both routes are governed by the Trade Winds, so it’ll be wise to take that into account. Here are more details about each route:
The Northern passage (Sailing from West to East)
The Northern Passage route starts in the island of Bermuda, some 768 miles off the coast of North Carolina. This is one of the best places to start a transatlantic crossing because of the prevalence of Westward blowing winds. Most sailors from the U.S. will usually start somewhere in Florida, down to the Caribbean, then to Bermuda where the real journey can begin.
From Bermuda, you’ll want to set sail to the Portuguese Azores, a volcanic archipelago and autonomous region of Portugal some 900 miles off the coast of Portugal. From Azores, it’s a hop-and-skip away to Lisbon. These are the distances you need to cover:
From the Caribbean to the island of Bermuda: 850NM (around 5 to 8 days of sailing)
From Bermuda to the Portuguese Azores: 1900NM (around 14 to 17 days of sailing)
From Azores to continental Portugal: 738NM (around 4 to 7 days of sailing)

In general, it’s always best to give yourself and your crew an extra 3 to 10 days of allowance when plotting your journey. This will give you some leeway to account for the weather and mechanical breakdowns in the ship. In general, the Northern Passage will take around 3 to 4 weeks, although it does take a little longer (by a few days) than the East-to-West route.
The Southern passage (east to west)
The more popular of the two sailing routes (because it’s slightly faster), the Southern Passage generally starts in Portugal, where sailors must go southeast to the Canary Islands, some 60 miles off the coast of Western Africa. From there, you’ll set sail making a stop at Cape Verde before heading off to the Windward Islands in the Caribbean. Some sailors, however, go straight to the Windward Islands from the Canary Islands, although this is only recommended for highly seasoned skippers. These are the distance covered by the Southern Passage:
Portugal to the Canary Islands: 750NM (around 5 to 7 days of sailing)
Canary Islands to Cape Verde: 850NM (around 5 to 8 days of sailing)
Cape Verde to the Windward Islands: 2222NM (around 12 to 16 days of sailing)
Canary Islands straight to Windward Islands: 2700NM (around 16 to 21 days of saiing)
In summation, the Southern Passage takes around three to four weeks (give or take a few days) to cross around 4,000 nautical miles.
Beware the Atlantic Hurricane Season
All of these estimates, of course, will mean nothing if you plan your journey during the Atlantic Hurricane Season. According to the National Hurricane Center, the Atlantic Hurricane Season usually starts around June and lasts all the way until mid November.
This is why many competitive sailors will usually cast off around late November to arrive either in the Caribbean or Portugal by mid-December. Some sailors, on the other hand, will cast off in January, when the Trade Winds are at their strongest.
What are Trade Winds?
We’ve been talking about Trade Winds since the beginning of the article, but what are they exactly? Well, the Trade Windsare specific weather phenomena that occur in a predictable pattern all across the Atlantic. It was first described in the 16 th century by European explorers and were initially called ‘wind roads’. Since then, they’ve been used by merchants and explorers to make the perilous journey from the Old world to the New.
Trade Winds come about because of the high atmospheric pressure felt by a sizable portion of the center of the Atlantic Basin. Called the Azores High, this area of high atmospheric pressure stretches from the Portuguese coast all the way to the shores of Bermuda.
The Trade Winds are born from the hot air that rises from the tropical regions that cools down significantly as it reaches higher altitudes. This cooled air is then generally deposited in the poles, with the whole process creating winds. Coupled with the Coriolis Effect (that is, the phenomena of the Earth’s Rotation), and you have winds that are both measurable and predictable.
So How Hard is It to Cross the Atlantic?
Honestly, sailing across the Atlantic is a very challenging experience. It isn’t impossible, but without the right mindset, crew, equipment, boat, and timing, it can be fatal. However, cover all of that, and you’ll be going the adventure of a lifetime.
About The Author
Veronica Harris
Related posts.

Holiday Rentals in Costa Blanca-Javea

Top Places To Visit In Granada

Reasons Why People Love Food

- Select language
- English (United States)
- español (Estados Unidos)
Log in to MyMAPEI Area
Registered user, log in if you are already registered., with a few simple clicks, the world of mapei is yours. when you register at mymapei, you’ll have the choice to:.
- Access exclusive eblasts.
- Receive Realtà MAPEI North America magazine (a digital or physical copy).
- Create your own video playlist.
- Save favorite articles, projects, products, solutions and calculations.
- Sign up for training.
Ambrogio Beccaria triumphs at The Transat CIC race

After 11 days, 16 hours, 17 minutes and 55 seconds of solo navigation across the Atlantic Ocean with an average actual speed of 11.70 knots, Ambrogio Beccaria landed in New York City. Competing in The Transat CIC transatlantic sailing race, Beccaria crossed the finish line first in the Class40 category with his Alla Grande-Pirelli , of which MAPEI is Global Sponsor.

Since his start from Lorient in western France, Beccaria always maintained the top positions of the fleet and took the lead halfway through the race. Despite a close duel with his opponent Ian Lipinski, Beccaria managed to maintain the lead position, except for a few short stretches, until the end.
Battling adverse weather and rigid temperatures that are typical of the North Atlantic, as well as waves, 40-knot winds and contrary currents, Beccaria proved to be solid from a strategic point of view. The Italian skipper’s boat Alla Grande-Pirelli , a latest-Class40-generation vessel that was designed by Gianluca Guelfi, was fast and high-performing even in extreme challenging conditions.
“I did exactly the regatta I dreamed of. I hoped it would really go like this... I knew it would be full of pitfalls and I wanted to do it in the right spirit. I never lost heart and gave everything I had,” Beccaria said while still aboard Alla Grande-Pirelli . “It was a tough race, the hardest I’ve done, but it’s also the one I perhaps managed best. The Transat was a completely new race for me; sailing outside the trade winds is actually wonderful because the weather changes all the time.”
The finish line of The Transat CIC is located 100 miles from New York City. “Crossing the line in the middle of nowhere was a psychedelic experience; between the fog and the lack of sleep, it was truly strange!” Beccaria said.
Having already won the Transat Jacques Vabre last November, as well as the CIC Normandy Channel Race 2023 and the 40' Malouine LAMOTTE, Beccaria brings home his fourth victory in a row and the first solo aboard Alla Grande-Pirelli . He thus confirms himself as the undisputed champion of Italian ocean sailing and one of the strongest ocean sailors of his generation.
The nominations for two awards testify to Beccaria’s success: “Sailor of the Year,” which will be awarded by Italian sailing magazine Il Giornale della Vela on May 25, 2024, and “FIV Sailor of the Year,” which will be awarded by the Italian Sailing Federation on May 27, 2024, in Genoa, Italy.
Photo credits: polaRYSEÓ
MAPEI Corporation Corporate MAPEI Sport Research Centre Alla Grande Ambrogio Beccaria Ocean Sailing
Keep in touch
Subscribe to our newsletter to get Mapei news
- News & Events
- Event detail


Fastest Atlantic crossing by powerboat

The fastest crossing of the Atlantic is 2 days 10 hr. 34 min. 47 sec. by the 68 m. (222 ft.) luxury yacht Destriero from August 6 to 9, 1992. The gas turbine-propelled vessel maintained an average speed of 45.7 knots (84.6 km./h. or 52.6 m.p.h.) despite weighing nearly 400 tonnes (882,000 lb). The skipper was Cesare Fiorio (Italy). The turbines used to power Destriero are marine versions of those used in the F18 Hornet jet fighter, and generate 13,420 kW (18,000 hp) each. They suck water in beneath the vessel and expelling it from the rear at a rate of 60 cu. m. (13,200 gal.) per second, replacing conventional propellers. Because they burn nearly 10 tonnes (21,700 lb) of fuel per hour, Destriero's maximum speed increases from 36 knots (65 km/h or 40 mph) loaded to 65 knots (120 km/h or 75 mph) unladen.

6 Top Transatlantic Cruises for 2024
T ransatlantic cruises are unique when you compare them to traditional cruises most people book for family trips and romantic getaways. These voyages tend to be longer in general, and they have more built-in days at sea and offer a lot more time on board as a result. Repositioning cruises that include a transatlantic crossing tend to attract more retirees and travelers who just want to relax and enjoy their ships' amenities, especially since fewer days in port means fewer excursions and more time doing nothing at all.
That said, the fact that transatlantic cruises can last as few as seven nights means they may fit in your plans more easily than you may think. There are also some benefits to transatlantic crossings that may not be obvious, including lower nightly rates, more onboard credit, and more time to kick back and relax at a floating luxury resort in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean.
If you're curious which transatlantic cruises are best for 2024, here are six top picks with different cruise lengths, itineraries and unique destinations to explore.
Explore cruises on GoToSea , a service of U.S. News.
Cunard Line
Date: Departs May 5, 2024
Departure port: Brooklyn, New York
Starting price: $2,449 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 7 to 18 nights
In May of 2024, Cunard's Queen Mary 2 vessel will offer three different transatlantic crossings of various lengths. Choose from a seven-night sailing from Brooklyn, New York , to Southampton, England; a nine-night sailing to Hamburg, Germany ; and an 18-night round-trip sailing that departs from Brooklyn and crosses the Atlantic twice on the way back to its starting point. This unique combination of itineraries lets you cross the sea and tailor your trip to how long you want to be away from home.
The 18-night itinerary is especially interesting, since it lets you depart from the United States and arrive back in Brooklyn in the end with stops in both England and Germany, as well as plenty of sea days in between. Luxury cruise line Cunard is known for its elegant design, lush amenities and upscale feel, and the Queen Mary 2 is one of the line's most luxurious ships. Highlights on this exclusive vessel include the Royal Court Theatre, a casino, gala evenings, an onboard spa and a vast library. The Queen Mary 2 holds up to 2,691 guests with 1,173 crew to cater to your every need.
Seabourn Cruise Line
Date: Departs March 24, 2024
Departure port: Miami
Starting price: $5,949 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 21 nights
Seabourn is offering a 21-night transatlantic cruise from Miami on Seabourn Quest in March 2024 that offers a diverse range of ports of call before ending its voyage in Las Palmas in Spain's Canary Islands . Departure from Miami is followed by nine days at sea. Then, you'll enjoy multiple stops in the Canary Islands – including Santa Cruz de La Palma and San Sebastián de La Gomera – as well as stops in Praia and Mindelo the Cape Verde archipelago.
This journey with Seabourn makes it possible for travelers to see some of the most beautiful and remote tropical islands in the world. The Canary Islands are known for their white sand beaches , volcanoes and lush greenery; similar landscapes can also be found in Cape Verde's coastal towns and villages. Seabourn Quest, a smaller ocean vessel, accommodates just 229 guests.
MSC Cruises
Date: Departs Nov. 8, 2024
Departure port: Southampton, England
Starting price: $769 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 16 nights
The MSC Virtuosa from MSC Cruises is repositioning from Europe to the Caribbean in November 2024, which gives travelers the chance to enjoy a lengthy transatlantic crossing with plenty of unique ports. This sailing departs from England with eight sea days plus stops in France, the Azores of Portugal, St. Maarten , Antigua and Barbuda, and Martinique . The ship ends its journey in Pointe-a-Pitre, Guadeloupe.
The MSC Virtuosa is a larger cruise vessel that boasts an impressive grand promenade with a LED dome ceiling, dedicated clubs for children and teens, an onboard spa, a lavish casino and the luxurious MSC Yacht Club section of the ship. This vessel holds a maximum of 6,334 passengers at once.
360 Kiosk Email : Tips on Trips and Expert Picks
Princess Cruises
Date: Departs July 5, 2024
Departure port: New York City (Manhattan or Brooklyn)
Starting price: $4,098 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 31 nights
Princess Cruises also offers its share of transatlantic sailings on various vessels. Its 31-night crossing from New York to Barcelona, Spain , on Island Princess in July 2024 is jam-packed with exciting destinations to explore. This lengthy transatlantic voyage has only 13 sea days with planned stops in Canada's Newfoundland, Greenland, Iceland, Scotland, England, Spain, Portugal and Morocco before the journey ends in Barcelona.
This intriguing sailing experience with Princess takes passengers to eight different countries in the span of a month. Island Princess is a nice ship for a long sailing because of its smaller size, with just 2,200 passengers and 900 crew. But the ship is also large enough to have a huge selection of included and specialty dining options, a Vegas-style casino, a sports court, a large central atrium for gathering, and several pools and hot tubs to enjoy.
Celebrity Cruises
Date: Departs April 11, 2024
Departure port: Fort Lauderdale, Florida
Starting price: $760 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 12 nights
Celebrity Cruises is offering a 12-night sailing on Celebrity Equinox in April 2024 that starts in Fort Lauderdale, Florida , and ends in Lisbon, Portugal – making it possible for travelers to enjoy eight relaxing days at sea. What's interesting about this sailing is its stops along the way, which include the Royal Naval Dockyard in Bermuda; Porta Delgada in Portugal's Azores archipelago; and Porto in mainland Portugal.
The Celebrity Equinox accommodates a maximum of just 2,852 passengers at once, so this Celebrity vessel is a solid choice for travelers who want just the right size ship instead of a smaller vessel or a megaship. There are also plenty of onboard features to keep you happy and entertained as you float across the Atlantic Ocean, including The Casino, The Lawn Club with outdoor games like bocce ball and croquet, The Martini Bar, the adults-only Solarium and more.
Royal Caribbean International
Dates: Departs Oct. 24, 2024
Departure port: Barcelona, Spain
Starting price: $876 per person (plus port taxes and fees)
Cruise length: 14 nights
Royal Caribbean's Oasis of the Seas is hosting a transatlantic voyage in October 2024 that departs from Barcelona, Spain, and ends in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. This vessel will make stops in Palma de Mallorca, Valencia, Cartagena and Málaga in Spain, then spend eight days at sea. After that, enjoy a day in Nassau in the Bahamas before the cruise drops passengers off in sunny Florida.
Interior staterooms on this Royal Caribbean sailing start at just $876 per person (plus port taxes and fees), which works out to around $60 per night, per person. The Oasis of the Seas megaship can hold a total of 6,771 guests and 2,109 crew, so it's an enormous vessel – to put it mildly. This size may not be ideal for travelers who want a more intimate cruising experience, but it's perfect for cruisers who want plenty of space to spread out and endless activities to take part in. Oasis of the Seas boasts 20 different restaurants and cafes, 11 bars and lounges, a variety of pools and whirlpools, a rock climbing wall, the AquaTheater diving and entertainment venue, mini-golf, a casino and plenty more.
Why Trust U.S. News Travel
Holly Johnson is a professional travel writer and cruise expert who has covered family travel and cruises for more than a decade. She has cruised more than 40 times across most of the major cruise lines in destinations throughout the Caribbean, Europe and the Middle East. Johnson used her personal experience and research expertise to curate the itineraries for this article.
You might also be interested in:
- The Top Solo Cruises (With No Supplement Fare)
- Sustainable Cruises: The Top Lines Making Progress
- Bucket List Cruises for Seniors and Retirees
- The Best Cruise Insurance Plans
- Cruise Packing List: Essentials Chosen by Experts
Copyright 2024 U.S. News & World Report
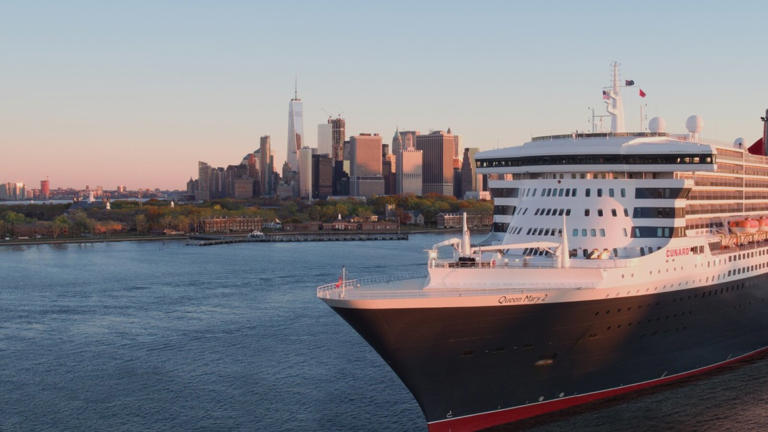


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Transatlantic sailing record. Banque Populaire V, current record holder. Since the five-week voyage of Christopher Columbus in 1492, crossing the Atlantic Ocean, quickly and safely, between Europe and the Americas has always been an important issue. Today, the route has become a classic one among skippers.
Comanche, the 100ft maxi racing yacht built to break records for Jim Clark and Kristy Hinze-Clark, has set an astonishingly fast new transatlantic record. In making the crossing in just 5 days, 14 ...
The crew completed the 2,880-mile course (sailing 2,946 miles, only 66 miles farther than the Great Circle distance) in 5d 14h 21m and, in doing so, Jim Clark's super-machine and her all-star ...
Comanche sets a new 24-hour distance record. The Transatlantic speed record comes 12 months after Comanche set a new 24-hour distance record for monohulls. The record was broken during the 2015 Transatlantic Race after Comanche covered 618.01 nautical miles in 24 hours. Her average speed was recorded as 25.75 knots, on the cusp of some strong ...
At 5 days 14 hours 21 minutes 25 seconds, Comanche holds the Monohull Transatlantic sailing record for the fastest crossing of the Atlantic Ocean, which they achieved on July 28, 2016. [7] In December 2017, Comanche was sold to Australian Jim Cooney, [8] and was renamed to LDV Comanche, as part of a one-time sponsorship from SAIC Maxus ...
The current record is 41.284 knots (76.5 km/ per hour) average over two days, 20 hours and 9 minutes. The Hales Trophy is a heavily gilded ornate trophy over one metre in height and is on display ...
The 30.48 metre sailing yacht Comanche has set a new monohull race record after taking Monohull Line Honours in the 2022 RORC Transatlantic Race.. Skippered by Mitch Booth, Comanche and its crew completed the 3,000 nautical mile race from Lanzarote to Grenada in seven days, 22 hours, 1 minute and 4 seconds (that's two days quicker than the previous record holder).
The Blue Riband (/ ˈ r ɪ b ə n d /) is an unofficial accolade given to the passenger liner crossing the Atlantic Ocean in regular service with the record highest average speed.The term was borrowed from horse racing and was not widely used until after 1910. The record is based on average speed rather than passage time because ships follow different routes. ...
The five-strong crew completed the entire crossing in 7 days, 13 hours and 15 minutes, one of the fastest sailboat crossings of the world's second largest ocean they've experienced. Between them they have 56 transatlantics under their belts. "That was my sixteenth transatlantic crossing and the fastest one to date," commented Enright.
The first officially recognized 24-hour speed run was by the clipper ship Lightning in 1854, when it sailed 436 miles in a day at an average speed of 18.2 knots. Later that year, the American clipper Champion of the Seas logged a day averaging 19.5 knots, a feat that remained the fastest day on record for 130 years.
One of the last liners, the United States (mainly made of aluminum), held the transatlantic crossing speed record of 3.5 days in 1952. By the 1960s, air transportation had overtaken the supremacy of liners for transatlantic crossings, and reference time became hours instead of days. Liner services disappeared, and the surviving ships became the ...
Black Projects Division. The SR-71's Record-Breaking Transatlantic Crossing. September 1st, 1974, was pretty much just another average day for New Yorkers. It didn't look like either the Yankees or the Mets would make the playoffs (neither did), and the temperature was in the high-70s (Fahrenheit) at the tail end of yet another long, hot ...
Here are the records for the fastest crossings of the Atlantic in a Sailboat. Crewed: Time: Boat Name: Hull: Year: Speed: 5d 14h 21min 25s : Comanche : Monohull: 2016: 21.44 knots (39.71 km/h) ... The stable platform of a catamaran with the wind on your stern makes sailing west on a transatlantic passage perfect for Catamaran.
When Cargile left New York, the boat was loaded with nearly 4 tons of fuel. Speed was kept to about 6 knots to minimize consumption. The boat finally arrived at Le Havre, France, having taken 31 days for the crossing and putting into Newfoundland for repairs. The engine had run nonstop for 695 hours, with fuel consumption of 2.13 gallons per hour.
An Atlantic crossing on a sailboat takes an average of 20 to 25 days. It is important to know the shortcuts, maximize speed, and have experience to cross the Atlantic. The best time to cross the Atlantic is between November and February. The total distance of the trip can be as much as 4,000 nautical miles.
The Virgin Atlantic Challenge Trophy is an award for the fastest trans-Atlantic crossing by a surface vessel, one of several such awards that have grown out of the contest for the prestigious Blue Riband of the Atlantic.The trophy was created following Richard Branson's record-breaking Atlantic crossing in 1986 and the refusal by the American Merchant Marine Museum to surrender the Hales ...
2025 transatlantic sailings: 9 January (9 nights, Queen Anne), 8 March, 27 April (8 nights), 16 May, 6 June, 24 June, 27 August, 26 September, 24 October, 19 November, 15 December. All crossings are now 7 nights except where shown. The Queen Mary 2 usually sails from Southampton at 17:00, arriving in New York 7 nights later at 06:30-07:00. The ...
Sailing hot angles may work for a lightweight flyer, but it adds a lot of distance. ... (See our feature on the best yacht for an Atlantic crossing) North is fastest. With well-established high ...
A transatlantic crossing is a major sailing milestone for experienced sailors. The north Atlantic is no place for new sailors and beginners, unless they're with competent and experienced crew or a qualified captain. ... The NEEL 51 is a fast, comfortable trimaran suited to a smaller crew. It's spacious, but easy to handle while putting up ...
Of course, the fastest transatlantic sail record is 3 days, 10 hours, and 4 minutes by the ocean liner the U.S.S United States, while the fastest transatlantic sail by a sailboat (in this case, ... Transatlantic Sailing Routes. While a transatlantic crossing is generally reserved for highly-experienced sailors, it doesn't mean that novice ...
Back. May 15, 2024. After 11 days, 16 hours, 17 minutes and 55 seconds of solo navigation across the Atlantic Ocean with an average actual speed of 11.70 knots, Ambrogio Beccaria landed in New York City. Competing in The Transat CIC transatlantic sailing race, Beccaria crossed the finish line first in the Class40 category with his Alla Grande ...
09 August 1992. The fastest crossing of the Atlantic is 2 days 10 hr. 34 min. 47 sec. by the 68 m. (222 ft.) luxury yacht Destriero from August 6 to 9, 1992. The gas turbine-propelled vessel maintained an average speed of 45.7 knots (84.6 km./h. or 52.6 m.p.h.) despite weighing nearly 400 tonnes (882,000 lb). The skipper was Cesare Fiorio (Italy).
Transatlantic crossings are passages of passengers and cargo across the Atlantic Ocean between Europe or Africa and the Americas.The majority of passenger traffic is across the North Atlantic between Western Europe and North America.Centuries after the dwindling of sporadic Viking trade with Markland, a regular and lasting transatlantic trade route was established in 1566 with the Spanish West ...
Oyster 56. In the ranks of dream bluewater cruisers, Oyster is right up there. The 56 is the British yard's most popular boat; small enough to be handled by two people, big enough to cross an ocean quickly and comfortably, yet not so large or complex as to need a full-time pro crew.
Cruise length: 7 to 18 nights In May of 2024, Cunard's Queen Mary 2 vessel will offer three different transatlantic crossings of various lengths. Choose from a seven-night sailing from Brooklyn ...